|
1 Chronicles 7
1 Chronicles 7 is the seventh chapter of the Books of Chronicles in the Hebrew Bible or the First Book of Chronicles in the Old Testament of the Christian Bible. The book is compiled from older sources by an unknown person or group, designated by modern scholars as "the Chronicler", and had the final shape established in late fifth or fourth century BCE. This chapter contains the genealogies of tribes settled north of Judah: Issachar, Benjamin, Naphtali, Manasseh, Ephraim and Asher. It belongs to the section focusing on the list of genealogies from Adam to the lists of the people returning from exile in Babylon ( 1 Chronicles 1:1 to 9:34). Text This chapter was originally written in the Hebrew language. It is divided into 40 verses. Textual witnesses Some early manuscripts containing the text of this chapter in Hebrew are of the Masoretic Text tradition, which includes the Aleppo Codex (10th century), and Codex Leningradensis (1008). There is also a translation into K ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Books Of Chronicles
The Book of Chronicles ( he, דִּבְרֵי־הַיָּמִים ) is a book in the Hebrew Bible, found as two books (1–2 Chronicles) in the Christian Old Testament. Chronicles is the final book of the Hebrew Bible, concluding the third section of the Jewish Tanakh, the Ketuvim ("Writings"). It contains a genealogy starting with Adam and a history of ancient Judah and Israel up to the Edict of Cyrus in 539 BC. The book was divided into two books in the Septuagint and translated mid 3rd century BC. In Christian contexts Chronicles is referred to in the plural as the Books of Chronicles, after the Latin name given to the text by Jerome, but are also rarely referred to by their Greek name as the Books of Paralipomenon. In Christian Bibles, they usually follow the two Books of Kings and precede Ezra–Nehemiah, the last history-oriented book of the Protestant Old Testament. Summary The Chronicles narrative begins with Adam, Seth and Enosh, and the story is then carrie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
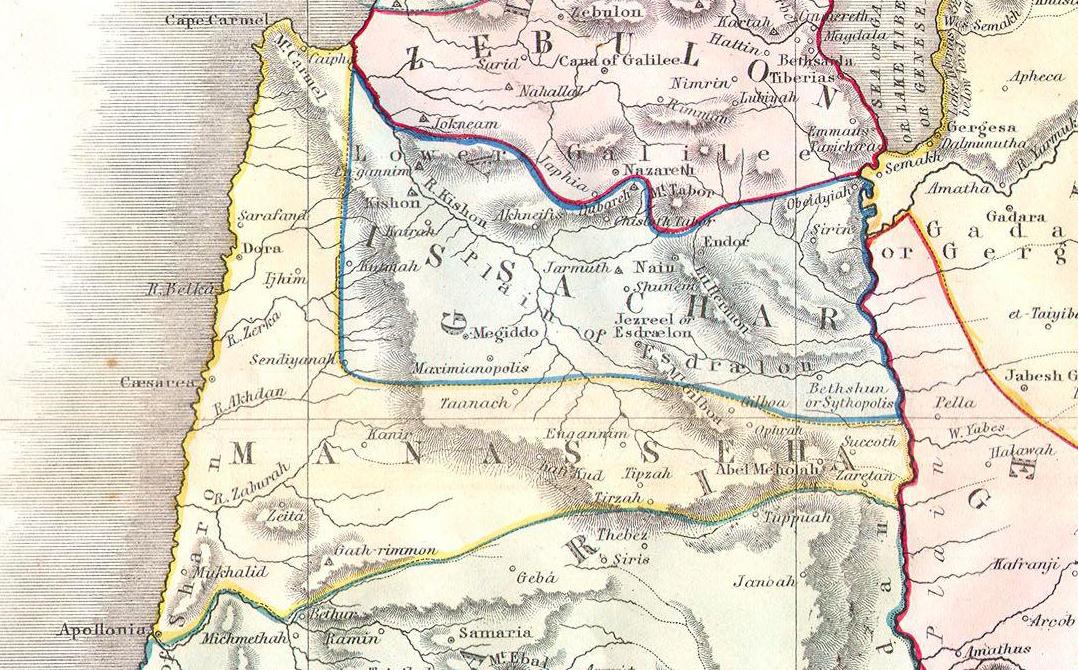
Tribe Of Issachar
According to the Hebrew Bible, the Tribe of Issachar () was one of the twelve tribes of Israel and one of the ten lost tribes. In Jewish tradition, the descendants of Issachar were seen as being dominated by religious scholars and influential in proselytism. The sons of Issachar, ancestors of the tribe, were Tola, Phuvah, Job and Shimron. Biblical narrative In the biblical narrative of the Book of Joshua, following the completion of the conquest of Canaan by the Israelite tribes, Joshua allocated the land among the twelve tribes. The territory allocated to Issachar stretched from the Jordan River in the east to Mount Carmel on the west, near to the Mediterranean coast, including the fertile Esdraelon plain between present-day Lower Galilee and Samaria. It was bounded on the east by East Manasseh, the south by West Manasseh, and the north by Zebulun and Naphtali. There is a consensus among scholars that the accounts in the Book of Judges are not historically reliab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chronology Of The Bible
The chronology of the Bible is an elaborate system of lifespans, 'generations', and other means by which the Masoretic Hebrew Bible (the text of the Bible most commonly in use today) measures the passage of events from the creation to around 164 BCE (the year of the re-dedication of the Second Temple). It was theological in intent, not historical in the modern sense, and functions as an implied prophecy whose key lies in the identification of the final event. The passage of time is measured initially by adding the ages of the Patriarchs at the birth of their firstborn sons, later through express statements, and later still by the synchronised reigns of the kings of Israel and Judah. The chronology is highly schematic, marking out a world cycle of 4,000 years. The Exodus takes place in the year Anno Mundi 2666, exactly two thirds of the way through the four thousand years; the construction of Solomon's Temple is commenced 480 years, or 12 generations of 40 years each, after tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daughters Of Zelophehad
The Daughters of Zelophehad ( he, בְּנוֹת צְלָפְחָד ''Bənōṯ Ṣəlāfəḥāḏ'') were five sisters – Mahlah (מַחְלָה ''Maḥlā''), Noa (נֹעָה ''Nōʿā''), Hoglah (חָגְלָה ''Ḥoglā''), Milcah (מִלְכָּה ''Mīlkā''), and Tirzah (תִרְצָה ''Ṯīrṣā'') – mentioned in the Biblical Book of Numbers. They lived during the Israelites' Exodus from Egypt as they prepared to enter the Promised Land and who raised before the Israelite community the legal case of a woman's right and obligation to inherit property in the absence of a male heir in the family. Zelophehad, a man of the Tribe of Manasseh, had five daughters but no sons, and therefore no male heirs. Biblical account The biblical text tells little of Zelophehad himself, save that he died during the 40 years when the Israelites were wandering in the wilderness, and explicitly that he played no part in Korah's rebellion. does not in any case cite the tribe of Manasseh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New King James Version
The New King James Version (NKJV) is an English translation of the Bible. The complete NKJV Bible was published in 1982 by Thomas Nelson, now HarperCollins. The NKJV is described by Thomas Nelson as being "scrupulously faithful to the original, yet truly updated to enhance its clarity and readability." History The NKJV translation project was conceived by Arthur Farstad. It was inaugurated in 1975 with two meetings (Nashville and Chicago) of 130 biblical scholars, pastors, and theologians. The men who were invited prepared the guidelines for the NKJV. The aim of its translators was to update the vocabulary and grammar of the King James Version, while preserving the classic style and literary beauty of the original 1769 edition of the King James Version. The 130 translators believed in faithfulness to the original Greek, Aramaic, and Hebrew texts including the Dead Sea Scrolls. Also agreed upon for most New King James Bibles were easier event descriptions, a history of ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English Standard Version
The English Standard Version (ESV) is an English translation of the Bible. Published in 2001 by Crossway, the ESV was "created by a team of more than 100 leading evangelical scholars and pastors." The ESV relies on recently published critical editions of the original Hebrew and Greek texts. Crossway claims that the ESV continues a legacy of precision and faithfulness in English translation of the original text. It describes the ESV as a translation that "emphasizes 'word-for-word' accuracy, literary excellence, and depth of meaning." It also describes the ESV as a translation that adheres to an "essentially literal" translation philosophy, taking into account "differences in grammar, syntax, and idiom between current literary English and the original languages." Since publication, the ESV has been endorsed by numerous evangelical pastors and theologians, including John Piper, R. C. Sproul, and Kevin DeYoung. As of July 2015, over 100 million printed copies of the transla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Ellicott
Charles John Ellicott (1819–1905) was a distinguished English Christian theologian, academic and churchman. He briefly served as Dean of Exeter, then Bishop of the united see of Gloucester and Bristol. Early life and family Ellicott was born in Whitwell, Rutland on 25 April 1819. He was educated at Stamford School and St John's College, Cambridge. He married Constantia Ann Becher at St Marylebone Parish Church, London on 31 July 1848. One of their children was the composer Rosalind Ellicott. Ecclesiastical career Following his ordination into the Anglican ministry in 1848, he was Vicar of Pilton, Rutland and then Professor of Divinity at King's College London and ''Hulsean Professor of Divinity'' at Cambridge. The chancel of St Nicholas' Church, Pilton was rebuilt in 1852 in 13th-century style. In 1861, he was appointed Dean of Exeter. Two years later he was nominated the bishop of the See of Gloucester and Bristol on 6 February and consecrated on 25 March 186 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Book Of Nehemiah
The Book of Nehemiah in the Hebrew Bible, largely takes the form of a first-person memoir concerning the rebuilding of the walls of Jerusalem after the Babylonian exile by Nehemiah, a Jew who is a high official at the Persian court, and the dedication of the city and its people to God's laws (Torah). Since the 16th century, it has generally been treated as a separate book within the Bible. Before that date, it had been included in the Book of Ezra; but in Latin Christian Bibles from the 13th century onwards, the Vulgate Book of Ezra was divided into two texts, called respectively the First and Second books of Ezra; a separation which became canonised with the first printed bibles in Hebrew and Latin. Mid 16th century Reformed Protestant Bible translations produced in Geneva were the first to introduce the name 'Book of Nehemiah' for the text formerly called the 'Second Book of Ezra'. Summary The events take place in the second half of the 5th century BC. Listed together with t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Book Of Ezra
The Book of Ezra is a book of the Hebrew Bible; which formerly included the Book of Nehemiah in a single book, commonly distinguished in scholarship as Ezra–Nehemiah. The two became separated with the first printed Mikraot Gedolot, rabbinic bibles of the early 16th century, following late medieval Latin Christian tradition. Composed in Hebrew and Aramaic, its subject is the Return to Zion following the close of the Babylonian captivity, and it is divided into two parts, the first telling the story of the first return of exiles in the first year of Cyrus the Great (538 BC) and the completion and dedication of the new Temple in Jerusalem in the sixth year of Darius I of Persia, Darius I (515 BC), the second telling of the subsequent mission of Ezra to Jerusalem and his struggle to purify the Jews from marriage with non-Jews. Together with the Book of Nehemiah, it represents the final chapter in the historical narrative of the Hebrew Bible. Ezra is written to fit a schem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
King James Version
The King James Version (KJV), also the King James Bible (KJB) and the Authorized Version, is an English translation of the Christian Bible for the Church of England, which was commissioned in 1604 and published in 1611, by sponsorship of King James VI and I. The 80 books of the King James Version include 39 books of the Old Testament, an intertestamental section containing 14 books of what Protestants consider the Apocrypha, and the 27 books of the New Testament. Noted for its "majesty of style", the King James Version has been described as one of the most important books in English culture and a driving force in the shaping of the English-speaking world. The KJV was first printed by John Norton and Robert Barker, who both held the post of the King's Printer, and was the third translation into English language approved by the English Church authorities: The first had been the Great Bible, commissioned in the reign of King Henry VIII (1535), and the second had been th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New American Standard Bible
The New American Standard Bible (NASB) is an English translation of the Bible. Published by the Lockman Foundation, the complete NASB was released in 1971. The NASB relies on recently published critical editions of the original Hebrew and Greek texts. The Lockman Foundation claims that the NASB "has been widely embraced as a literal and accurate English translation because it consistently uses the formal equivalence translation philosophy." Translation philosophy The New American Standard Bible is considered by some sources as the most literally translated of major 20th-century English Bible translations. According to the NASB's preface, the translators had a "Fourfold Aim" in this work: # These publications shall be true to the original Hebrew, Aramaic, and Greek. # They shall be grammatically correct. # They shall be understandable. # They shall give the Lord Jesus Christ His proper place, the place which the Word gives Him; therefore, no work will ever be personaliz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rashi
Shlomo Yitzchaki ( he, רבי שלמה יצחקי; la, Salomon Isaacides; french: Salomon de Troyes, 22 February 1040 – 13 July 1105), today generally known by the acronym Rashi (see below), was a medieval French rabbi and author of a comprehensive commentary on the Talmud and commentary on the Hebrew Bible (the '' Tanakh''). Acclaimed for his ability to present the basic meaning of the text in a concise and lucid fashion, Rashi appeals to learned scholars and beginning students, and his works remain a centerpiece of contemporary Jewish studies. His commentary on the Talmud, which covers nearly all of the Babylonian Talmud (a total of 30 out of 39 tractates, due to his death), has been included in every edition of the Talmud since its first printing by Daniel Bomberg in the 1520s. His commentaries on the Tanakh—especially his commentary on the Chumash (the "Five Books of Moses")—serves as the basis of more than 300 "supercommentaries" which analyze Rashi's choice of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




_Septuagint_(1587).jpg)


.jpg)