|
19th Waffen Grenadier Division Of The SS (2nd Latvian)
__NOTOC__ The 19th Waffen Grenadier Division of the SS (2nd Latvian) (, ) was an infantry division of the Waffen-SS during World War II. It was the second Latvian division formed in January 1944, after its sister unit, the 15th Waffen Grenadier Division of the SS (1st Latvian) with which it formed the Latvian Legion. It was surrounded in the Courland Pocket at the end of the war where it surrendered to the Red Army.Tessin, p. 127 The division was formed in January 1944, from 2 SS Infantry Brigades with the addition of a newly raised third regiment, Waffen Grenadier Regiment 46 (Latvian No. 6). Simultaneously, the designations of the two other grenadier regiments were changed from 39 and 40 to 42 and 43 respectively. The commander of the SS brigade, SS-Oberführer Hinrich Schuldt became the first commander of the division. After Schuldt was killed in action on 15 March 1944, SS-Standartenführer Friedrich-Wilhelm Bock temporarily took command, being replaced on April 13 by S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flag Schutzstaffel
A flag is a piece of fabric (most often rectangular) with distinctive colours and design. It is used as a symbol, a signalling device, or for decoration. The term ''flag'' is also used to refer to the graphic design employed, and flags have evolved into a general tool for rudimentary signalling and identification, especially in environments where communication is challenging (such as the maritime environment, where semaphore is used). Many flags fall into groups of similar designs called flag families. The study of flags is known as " vexillology" from the Latin , meaning "flag" or "banner". National flags are patriotic symbols with widely varied interpretations that often include strong military associations because of their original and ongoing use for that purpose. Flags are also used in messaging, advertising, or for decorative purposes. Some military units are called "flags" after their use of flags. A ''flag'' (Arabic: ) is equivalent to a brigade in Arab countr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Friedrich-Wilhelm Bock
__NOTOC__ Friedrich-Wilhelm Bock (6 May 1897 – 11 March 1978) was a German Waffen-SS commander during World War II who led three SS divisions, the SS Division Hohenstaufen, 4th SS Polizei Division, Waffen Grenadier Division of the SS (2nd Latvian). He was awarded the Knight's Cross of the Iron Cross of Nazi Germany. Awards * Iron Cross (1914) 2nd Class (27 July 1917)Thomas 1997, p. 56. * Honour Cross of the World War 1914/1918 (1934) * Clasp to the Iron Cross (1939) 2nd Class (21 August 1941) * Iron Cross (1939) 1st Class (16 September 1941) * Knight's Cross of the Iron Cross with Oak Leaves ** Knight's Cross on 28 March 1943 as SS-''Obersturmführer'' and ''Oberstleutnant'' of the '' Schupo'' and commander of the II./SS-Polizei-Artillerie-Regiment 4Scherzer 2007, p. 227. ** 570th Oak Leaves on 2 September 1944 as SS-''Oberführer __NOTOC__ ''Oberführer'' (short: ''Oberf'', , ) was an early paramilitary rank of the Nazi Party (NSDAP) dating back to 1921. An ''Oberfüh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Military Units And Formations Disestablished In 1945
A military, also known collectively as armed forces, is a heavily armed, highly organized force primarily intended for warfare. Militaries are typically authorized and maintained by a sovereign state, with their members identifiable by a distinct military uniform. They may consist of one or more military branches such as an army, navy, air force, space force, marines, or coast guard. The main task of a military is usually defined as defence of their state and its interests against external armed threats. In broad usage, the terms "armed forces" and "military" are often synonymous, although in technical usage a distinction is sometimes made in which a country's armed forces may include other paramilitary forces such as armed police. Beyond warfare, the military may be employed in additional sanctioned and non-sanctioned functions within the state, including internal security threats, crowd control, promotion of political agendas, emergency services and reconstruction, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
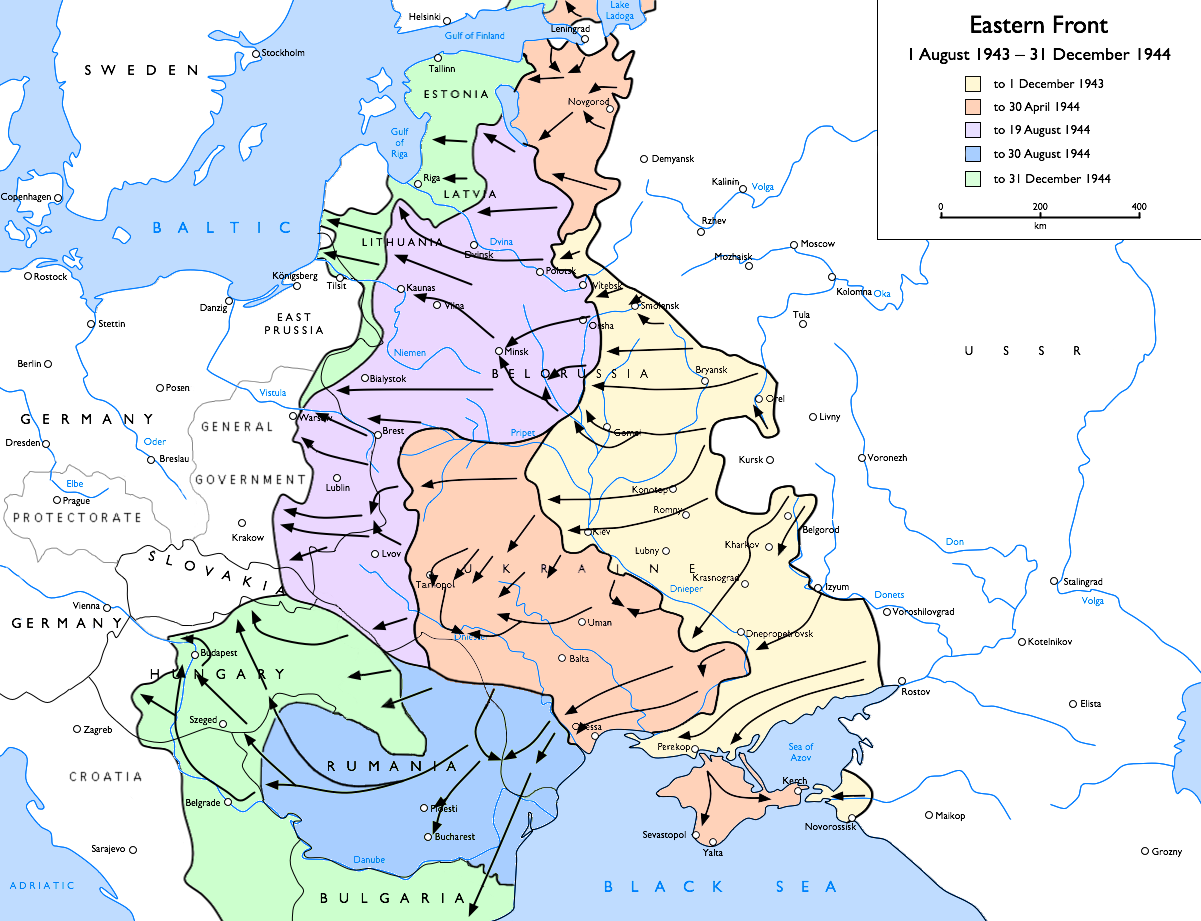
Military History Of Latvia During World War II
After the occupation of Latvia by the USSR in June 1940, much of the previous Latvian army was disbanded and many of its soldiers and officers were arrested and imprisoned or executed. The following year Nazi Germany occupied Latvia during the offensive of Army Group North. The German Einsatzgruppen were aided by a group known as Arajs Kommando in the killing of Latvian Jews as part of the Holocaust. Latvian soldiers fought on both sides of the conflict against their will, and in 1943 180,000 Latvian men were drafted into the Latvian Legion of the Waffen-SS and other German auxiliary forces. In the Baltic Offensive of autumn 1944 the Soviet Union recaptured much of its Baltic coastline, leaving 200,000 troops of Army Group North cut off in the Courland Pocket. Formed into Army Group Courland, this force held out until the end of the war in May 1945, when it surrendered to the Soviet forces and the troops were sent to prison camps. Coup Kārlis Ulmanis staged a bloodless cou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Generalbezirk Lettland
''Generalbezirk Lettland'' (German language, German for "General District Latvia"; ) was an Administrative division, administrative subdivision of the ''Reichskommissariat Ostland'' of Nazi Germany that covered Latvia from 1941 to 1944. It served as the Nazi Civil authority, civilian administration for the German occupation of Latvia during World War II, German occupation of Latvia during World War II, and supervised the collaborationist Latvian Self-Administration of Oskars Dankers. Otto-Heinrich Drechsler was the only ''Reich Ministry for the Occupied Eastern Territories, Generalkommissar'' of Generalbezirk Lettland during its existence. Organization and structure ''Generalbezirk Lettland'' was established in Latvia on 25 July 1941, as one of the administrative districts of ''Reichskommissariat Ostland'' along with ''Generalbezirk Litauen''. It was organized on the territory of the German occupation of Latvia during World War II, German-occupied Latvia, which had until th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waffen-SS Foreign Volunteers And Conscripts
During World War II, the ''Waffen-SS'' recruited or conscripted significant numbers of non-Germans. Of a peak strength of 950,000 in 1944, the ''Waffen-SS'' consisted of some 400,000 “Reich Germans” and 310,000 ethnic Germans from outside Germany’s pre-1939 borders (mostly from German-occupied Europe), the remaining 240,000 being non-Germans. Thus, at their numerical peak, non-Germans comprised 25% of all ''Waffen-SS'' troops. The units were under the control of the '' SS Führungshauptamt'' (SS Command Main Office) led by ''Reichsführer-SS'' Heinrich Himmler. Upon mobilisation, the units' tactical control was given to the '' Oberkommando der Wehrmacht'' (High Command of the Armed Forces). History of the ''Waffen-SS'' The ''Waffen-SS'' (Armed SS) was created as the militarised wing of the ''Schutzstaffel'' (SS; "Protective Squadron") of the Nazi Party. Its origins can be traced back to the selection of a group of 120 SS men in 1933 by Sepp Dietrich to form the ''Sonder ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ranks And Insignia Of The Waffen-SS
This table contains the final ranks and insignia of the ''Waffen-SS'', which were in use from April 1942 to May 1945, in comparison to the ''Wehrmacht''. The highest ranks of the combined SS () was that of ''Reichsführer-SS'' and ; however, there was no ''Waffen-SS'' equivalent to these positions. __NOTOC__ Table Remarks * (SS-applicant) and (SS-aspirant) were both removed as ''Waffen-SS'' ranks before 1941. See also * Comparative military ranks of World War II * Corps colours (Waffen-SS) * Glossary of Nazi Germany * List of SS personnel * Ranks and Insignia of the German Army in World War II * ''SS-Degen'' * Uniforms and insignia of the Schutzstaffel The uniforms and insignia of the ''Schutzstaffel'' (SS) served to distinguish its Nazi Germany paramilitary ranks, Nazi paramilitary ranks between 1925 and 1945 from the ranks of the ''Wehrmacht'' (the German armed forces from 1935), the Nazi Ger ... Notes Citations Bibliography * * * * * * External links Germa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Waffen-SS Units
This is an incomplete list of ''Waffen-SS'' units. ''Waffen-SS'' armies ''Waffen-SS'' corps * I SS Panzer Corps * II SS Panzer Corps * III (Germanic) SS Panzer Corps * IV SS Panzer Corps (formerly VII SS Panzer Corps) * V SS Mountain Corps * VI SS Army Corps (Latvian) * IV SS Panzer Corps, VII SS Panzer Corps (see above ↑ IV SS Panzer Corps) * VIII SS Cavalry Corps (planned in 1945 but not formed) * IX SS Mountain Corps, IX Waffen Mountain Corps of the SS (Croatian) * X SS Corps (made up of disbanded XIV SS Corps headquarters) * XI SS Panzer Corps * XII SS Corps * XIII SS Army Corps * XIV SS Corps – (see above ↑ X SS Corps) * XV SS Cossack Cavalry Corps * XVI SS Corps * XVII Waffen Corps of the SS (Hungarian) * XVIII SS Corps * SS Medical Corps * Serbian Volunteer Corps (World War II), Serbian Volunteer Corps (classified SS by 1944) * British Free Corps * Free Corps Denmark ''Waffen-SS'' divisions * 1st SS Panzer Division Leibstandarte SS Adolf Hitler, 1st SS Panzer Divisi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bruno Streckenbach
Bruno Streckenbach (7 February 1902 – 28 October 1977) was a German SS functionary during the Nazi era. He was the head of Administration and Personnel Department of the Reich Security Main Office (RSHA). Streckenbach was responsible for many thousands of murders committed by Nazi mobile killing squads known as ''Einsatzgruppen''. Early years Bruno Streckenbach was born in Hamburg, Germany on 7 February 1902. His highest education was Gymnasium, which he left in April 1918 to voluntarily report to the German Army during World War I. Just like his close colleagues Erwin Schulz and Heinrich Himmler, he never served on the front lines of the battlefield due to the ceasefire that took place in November 1918. After the end of the First World War, he was an active member of the Freikorps Bahrenfeld, which took part in the 1920 Kapp-Putsch. He was employed as a wholesale merchant, tried his hand at advertising, being a radio editor and also trying to establish himself as the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Red Army
The Workers' and Peasants' Red Army, often shortened to the Red Army, was the army and air force of the Russian Soviet Republic and, from 1922, the Soviet Union. The army was established in January 1918 by a decree of the Council of People's Commissars to oppose the military forces of the new nation's adversaries during the Russian Civil War, especially the various groups collectively known as the White Army. In February 1946, the Red Army (which embodied the main component of the Soviet Armed Forces alongside the Soviet Navy) was renamed the "Soviet Army". Following the dissolution of the Soviet Union it was split between the post-Soviet states, with its bulk becoming the Russian Ground Forces, commonly considered to be the successor of the Soviet Army. The Red Army provided the largest land warfare, ground force in the Allies of World War II, Allied victory in the European theatre of World War II, and its Soviet invasion of Manchuria, invasion of Manchuria assisted the un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waffen-SS
The (; ) was the military branch, combat branch of the Nazi Party's paramilitary ''Schutzstaffel'' (SS) organisation. Its formations included men from Nazi Germany, along with Waffen-SS foreign volunteers and conscripts, volunteers and conscripts from both German-occupied Europe and unoccupied lands. With the start of World War II, tactical control was exercised by the (OKW, "High Command of the Armed Forces"), with some units being subordinated to the (Command Staff ''Reichsführer-SS'') directly under Himmler's control. It was disbanded in May 1945. The grew from three regiments to over 38 division (military), divisions during World War II. Combining combat and police functions, it served alongside the German Army (1935–1945), German Army (''Heer''), ''Ordnungspolizei'' (Order Police), and other security units. Originally, it was under the control of the (SS operational command office) beneath Heinrich Himmler, the head of the SS. Initially, in keeping with the raci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |