|
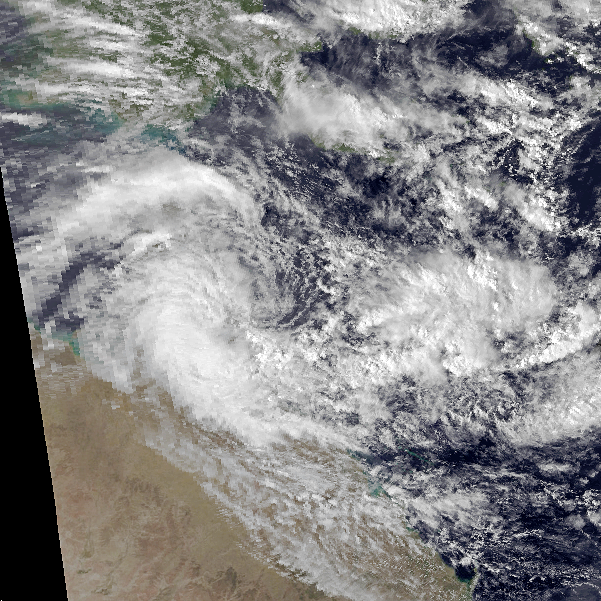
1979 North Indian Ocean Cyclone Season
The 1979 North Indian Ocean cyclone season was part of the annual cycle of tropical cyclone formation. The season has no official bounds but cyclones tend to form between April and December. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the northern Indian Ocean. There are two main seas in the North Indian Ocean—the Bay of Bengal to the east of the Indian subcontinent and the Arabian Sea to the west of India. The official Regional Specialized Meteorological Centre in this basin is the India Meteorological Department (IMD), while the Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC) releases unofficial advisories. An average of five tropical cyclones form in the North Indian Ocean every season with peaks in May and November. Cyclones occurring between the meridians 45°E and 100°E are included in the season by the IMD. Summary ImageSize = width:900 height:200 PlotArea = top:10 bottom:80 right:50 left:20 Legend = columns:3 left:30 top:58 c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
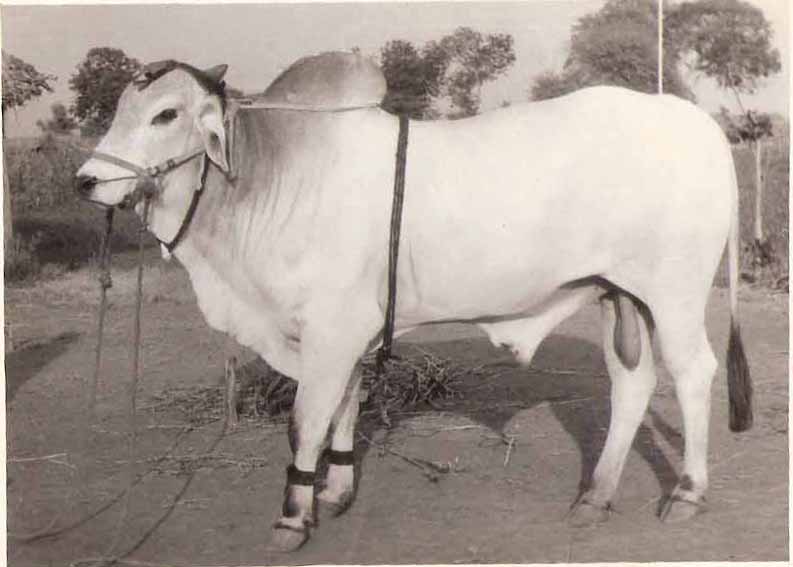
Ongole
Ongole (), natively known as Ongolu, is a city in Prakasam district of the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh. It is the headquarters of Prakasam district. It is known for Ongole cattle, an indigenous breed of oxen. Etymology The name 'Ongole' is believed to be derived from the word 'Vangaprolu' which later had transformed to 'Vangavolu' and then to modern 'Ongolu'. 'Prolu' means Town in ancient Telugu language, Telugu. History The city's history dates from 230 BCE with the era of the Mauryas and Satavahanas who ruled most of what is now Andhra Pradesh. A few inscriptions dating to the Satavahana period have been found in China Ganjam, a village near Ongole. According to the historical inscriptions available at Sri Raja Rajeswara Swami Temple complex, the city was founded by Cholas. Ongole is also mentioned in the inscriptions of the Pallava rulers of the third and fourth century A.D. The city was also ruled by Krishna Deva Raya. This place came into the limelight again during ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1978–79 South-West Indian Ocean Cyclone Season
The 1978–79 South-West Indian Ocean cyclone season was an average cyclone season. The season officially ran from November 1, 1978, to April 30, 1979. Systems ImageSize = width:900 height:190 PlotArea = top:10 bottom:80 right:20 left:20 Legend = columns:3 left:30 top:58 columnwidth:280 AlignBars = early DateFormat = dd/mm/yyyy Period = from:01/12/1978 till:30/04/1979 TimeAxis = orientation:horizontal ScaleMinor = grid:black unit:month increment:1 start:01/12/1978 Colors = id:canvas value:gray(0.88) id:GP value:red id:ZD value:rgb(0,0.52,0.84) legend:Zone_of_Disturbed_Weather_=_≤31_mph_(≤50_km/h) id:TD value:rgb(0.43,0.76,0.92) legend:(Sub)Tropical_Depression_=_32–38_mph_(51–62_km/h) id:TS value:rgb(0.30,1,1) legend:Moderate_Tropical_Storm_=_39–54_mph_(63–88_km/h) id:ST value:rgb(0.75,1,0.75) legend:Severe_Tropical_Storm_=_55–73_mph_(89–118_km/h) id:TC value:rgb(1,0.85,0.55) legend:Tropical_Cyclone_=_74–103_mph_(1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1979–80 South Pacific Cyclone Season
The 1979–80 South Pacific cyclone season saw mostly weak systems. __TOC__ Seasonal summary ImageSize = width:1000 height:200 PlotArea = top:10 bottom:80 right:20 left:20 Legend = columns:3 left:30 top:58 columnwidth:270 AlignBars = early DateFormat = dd/mm/yyyy Period = from:01/12/1979 till:01/05/1980 TimeAxis = orientation:horizontal ScaleMinor = grid:black unit:month increment:1 start:01/12/1979 Colors = id:canvas value:gray(0.88) id:GP value:red id:TDi value:rgb(0,0.52,0.84) legend:Tropical_Disturbance id:TD value:rgb(0.43,0.76,0.92) legend:Tropical_Depression id:C1 value:rgb(0.3,1,1) legend:Category_1_=_63-87_km/h_(39-54_mph) id:C2 value:rgb(0.75,1,0.75) legend:Category_2_=_88-142_km/h_(55-74_mph) id:C3 value:rgb(1,0.85,0.55) legend:Category_3_=_143-158-km/h_(75-98_mph) id:C4 value:rgb(1,0.45,0.54) legend:Category_4_=_159–204_km/h_(99–127_mph) id:C5 value:rgb(0.55,0.46,0.9) legend:Category_5_=_≥2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1978–79 South Pacific Cyclone Season
The 1978–79 South Pacific cyclone season ran year-round from July 1 to June 30. Tropical cyclone activity in the Southern Hemisphere reaches its peak from mid-February to early March. __TOC__ Summary ImageSize = width:1000 height:200 PlotArea = top:10 bottom:80 right:20 left:20 Legend = columns:3 left:30 top:58 columnwidth:270 AlignBars = early DateFormat = dd/mm/yyyy Period = from:01/12/1978 till:01/05/1979 TimeAxis = orientation:horizontal ScaleMinor = grid:black unit:month increment:1 start:01/12/1978 Colors = id:canvas value:gray(0.88) id:GP value:red id:TDi value:rgb(0,0.52,0.84) legend:Tropical_Disturbance id:TD value:rgb(0.43,0.76,0.92) legend:Tropical_Depression id:C1 value:rgb(0.3,1,1) legend:Category_1_=_63-87_km/h_(39-54_mph) id:C2 value:rgb(0.75,1,0.75) legend:Category_2_=_88-142_km/h_(55-74_mph) id:C3 value:rgb(1,0.85,0.55) legend:Category_3_=_143-158-km/h_(75-98_mph) id:C4 value:rgb(1,0.45,0.54) legen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1979–80 Australian Region Cyclone Season
The 1979–80 Australian region cyclone season was an above average tropical cyclone season. The season featured 15 total cyclones, with 9 of them attaining severe tropical cyclone status. The strongest of these was Cyclone Amy, which ended up making landfall in the north-western portion of Western Australia. Seasonal summary ImageSize = width:800 height:200 PlotArea = top:10 bottom:80 right:20 left:20 Legend = columns:3 left:30 top:58 columnwidth:270 AlignBars = early DateFormat = dd/mm/yyyy Period = from:01/08/1979 till:30/04/1980 TimeAxis = orientation:horizontal ScaleMinor = grid:black unit:month increment:1 start:01/08/1979 Colors = id:canvas value:gray(0.88) id:GP value:red id:TL value:rgb(0.43,0.76,0.92) legend:Tropical_Low_=_<63_km/h_(<39_mph) id:C1 value:rgb(0.3,1,1) legend:Category_1_=_63–88_km/h_(39-55_mph) id:C2 value:rgb(0.75,1,0.75) legend:Category_2_=_89–117_km/h_(55-73_mph) id:C3 value:rgb(1,0.85,0.55) legend: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1978–79 Australian Region Cyclone Season
The 1978–79 Australian region cyclone season was the only season in which a reconnaissance aircraft flew into a tropical cyclone. Operationally, Australia's Bureau of Meteorology (BOM) tracked eleven tropical cyclones, while two additional systems were later added to the United States's Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC) best track. Prior to 1985, the Australian region basin was defined as in the southern hemisphere between 90th meridian east, 80°E and 180th meridian east, 160°E, with the modern day season boundaries ranging from 1 November to 30 April of the following year. The first storm, an unnamed system, developed on 19 November 1978. The final cyclone, Kevin, dissipated by 12 May 1979. Tropical cyclones in this area were monitored by three Tropical Cyclone Warning Centres (TCWCs): the BOM in Perth, Darwin, Northern Territory, Darwin, and Brisbane. Tropical cyclogenesis in the season began when an unnamed tropical cyclone developed well west of Australia on 19 Nove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1979 Pacific Typhoon Season
The 1979 Pacific typhoon season featured the largest and most intense tropical cyclone recorded globally, Typhoon Tip. The season also used both male and female names as tropical cyclone names for the first time. Additionally, the season was slightly below-average in terms of tropical cyclone activity, with only 24 storms, 12 typhoons, and 4 super typhoons developing. The season had no official bounds; it ran year-round in 1979, but most tropical cyclones tend to form in the northwestern Pacific Ocean between June and December. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the northwestern Pacific Ocean. The scope of this article is limited to the Pacific Ocean, north of the equator and west of the International Date Line. Storms that form east of the date line and north of the equator are called hurricanes; see 1979 Pacific hurricane season. Tropical storms formed in the entire west Pacific basin were assigned a name by the Joint ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1979 Pacific Hurricane Season
The 1979 Pacific hurricane season was an inactive North Pacific hurricane season, featuring 10 named storms, 6 hurricanes, and 4 major hurricanes. All tropical cyclone activity this season was confined to the Eastern Pacific, east of 140°W. For the first time since 1977, no tropical cyclones formed in, or entered into the Central Pacific, between 140°W and the International Date Line. The season officially started on May 15, 1979 in the Eastern Pacific and on June 1 in the Central Pacific; they both ended on November 30, 1979. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in these basins. The season's first storm, Andres, developed on May 31, while its last, Jimena, dissipated on November 18. In early June, Andres moved onshore Mexico as a minimal hurricane, while in late October, Ignacio struck the coastline as a tropical depression. Impacts from those storms were minimal, as were the effects of the prep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
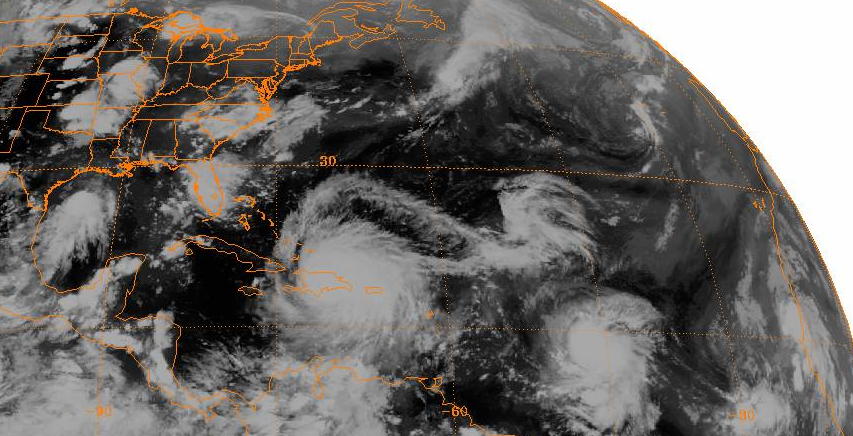
1979 Atlantic Hurricane Season
The 1979 Atlantic hurricane season was the first Atlantic hurricane season to include both male and female names on its list of tropical cyclone names. The season officially began on June 1, and lasted until November 30. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the Atlantic basin. It was slightly below average, with nine systems reaching tropical storm intensity. The first system, an unnumbered tropical depression, developed north of Puerto Rico on June 9. Two days later, Tropical Depression One formed and produced severe flooding in Jamaica, with 41 deaths and about $27 million (1979 USD) in damage. Tropical Storm Ana caused minimal impact in the Lesser Antilles. Hurricane Bob spawned tornadoes and produced minor wind damage along the Gulf Coast of the United States, primarily in Louisiana, while the remnants caused flooding, especially in Indiana. Tropical Storm Claudette caused extensive floo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Indian Ocean Tropical Cyclone
In the Indian Ocean north of the equator, tropical cyclones can form throughout the year on either side of the Indian subcontinent, although most frequently between April and June, and between October and December. The North Indian Ocean is the least active official basin, contributing only seven percent of the world's tropical cyclones. However the basin has produced some of the deadliest cyclones in the world, since they strike over very densely populated areas. The Regional Specialized Meteorological Centre (RSMC) is the India Meteorological Department (IMD) and it is responsible to monitor the basin, issues warning and name the storms. Sub-basins The basin is divided into two sub-basins the Bay of Bengal and the Arabian Sea. The Bay of Bengal, located in the northeast of the Indian Ocean. The basin is abbreviated ''BOB'' by the India Meteorological Department (IMD). The United States's Joint Typhoon Warning Center unofficially designates as ''B'' to classify storms form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coastal Flooding
Coastal flooding occurs when dry and low-lying land is submerged (flooded) by seawater. The range of a coastal Flood, flooding is a result of the elevation of floodwater that penetrates the inland which is controlled by the topography of the coastal land exposed to flooding. The seawater can flood the land via several different paths: direct flooding, overtopping or breaching of a barrier. Coastal flooding is largely a natural event. Due to the effects of climate change (e.g. sea level rise and an increase in extreme weather events) and an increase in the population living in coastal areas, the damage caused by coastal flood events has intensified and more people are being affected. Coastal plain, Coastal areas are sometimes flooded by unusually high tides, such as spring tides, especially when compounded by high winds and storm surges. This was the cause of the North Sea flood of 1953 which flooded large swathes of the Netherlands and the East coast of England. When humans modif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |