|
1972 In France
The following events occurred in France in the year 1972. Incumbents * President: Georges Pompidou * Prime Minister: Jacques Chaban-Delmas (until 5 July), Pierre Messmer (starting 6 July) Events *January – Launch of the Renault 5, one of the world's first small hatchbacks. *23 April – French European Economic Community enlargement referendum, voters approved the accession of the United Kingdom, Denmark, Ireland, and Norway to the EEC. *11 June – Henri Pescarolo (France) with co-driver Graham Hill (UK) win the 24 Hours of Le Mans in the Equipe Matra MS670. *16 June – 108 die as two passenger trains hit debris of a collapsed railway tunnel near Soissons. *1 July – Canadian ketch ''Vega'', flying the Greenpeace III banner, collides with the French naval minesweeper ''La Paimpolaise'' while in international waters to protest French nuclear weapon tests in the South Pacific. *5 July – President Pompidou dismisses prime minister Chaban-Delmas following rumours of financ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlantic, North Atlantic, the French West Indies, and List of islands of France, many islands in Oceania and the Indian Ocean, giving it Exclusive economic zone of France, one of the largest discontiguous exclusive economic zones in the world. Metropolitan France shares borders with Belgium and Luxembourg to the north; Germany to the northeast; Switzerland to the east; Italy and Monaco to the southeast; Andorra and Spain to the south; and a maritime border with the United Kingdom to the northwest. Its metropolitan area extends from the Rhine to the Atlantic Ocean and from the Mediterranean Sea to the English Channel and the North Sea. Its Regions of France, eighteen integral regions—five of which are overseas—span a combined area of and hav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oceania
Oceania ( , ) is a region, geographical region including Australasia, Melanesia, Micronesia, and Polynesia. Outside of the English-speaking world, Oceania is generally considered a continent, while Mainland Australia is regarded as its continental landmass. Spanning the Eastern Hemisphere, Eastern and Western Hemisphere, Western hemispheres, at the centre of the land and water hemispheres, water hemisphere, Oceania is estimated to have a land area of about and a population of around 46.3 million as of 2024. Oceania is the smallest continent in land area and the list of continents and continental subregions by population, second-least populated after Antarctica. Oceania has a diverse mix of economies from the developed country, highly developed and globally competitive market economy, financial markets of Australia, French Polynesia, Hawaii, New Caledonia, and New Zealand, which rank high in quality of life and Human Development Index, to the much least developed countries ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1972 Tour De France
The 1972 Tour de France was the 59th edition of the Tour de France, one of cycling's Grand Tour (cycling), Grand Tours. It took place from 1 to 22 July, with 20 stages covering a distance of . After riding strongly in the first two weeks of the race and being the closest GC contender to Eddy Merckx, Luis Ocaña crashed, in the Pyrenees, leaving Merckx to battle Cyrille Guimard for the win. Guimard, having won four stages, had to leave the race after stage 17 in second place (he already was 7:58 behind at that point), but was given the Combativity award in the Tour de France, combativity award after the race. Teams The 1972 Tour started with 12 teams, each with 11 cyclists, a total of 132. The teams entering the race were: * * * * * Van Cauter–Magniflex–de Gribaldy * * * * * * * Pre-race favourites In the previous year, Luis Ocaña was on his way to beat Eddy Merckx, when he fell as leader and had to give up. Everybody expected Merckx and Ocana to battle fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
André Obrecht
André Albert Obrecht (9 August 1899 – 30 July 1985) was a French executioner who served as the 6th '' Monsieur de Paris'' from 1951 until 1976. He participated in a total of 322 executions. Early life Obrecht was born in the 16th arrondissement of Paris to Jean-Baptiste Léon Obrecht, who worked at La Samaritaine department store and Juliette Rogis, a waistcoat maker descended from a prominent executioner family. Obrecht's mother died of tuberculosis on 29 January 1900, aged 27, when her son was five months old. He was briefly cared for by neighbors, the Durieux couple. In 1903, Obrecht's widowed father later married the couple's daughter, 30-year-old Louise Durieux, subsequently giving birth to Obrecht's four younger siblings. Through his aunt Rosalie, Obrecht was the nephew of the chief executioner Anatole Deibler. He learned of his uncle's job at ten, when a series of postcards, depicting the executions of the Chauffeurs de la Drôme, were published in September 1909. F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
La Santé Prison
La Santé Prison (named after its location on the Rue de la Santé) ( or ) is a prison operated by the French Prison Service of the Ministry of Justice (France), Ministry of Justice located in the east of the Montparnasse district of the 14th arrondissement of Paris, 14th arrondissement in southern Paris, France, at 42 Rue de la Santé. It is one of the most famous prisons in France, with both VIP and maximum security sections. La Santé is one of the three main prisons of the Paris area, along with Fleury-Mérogis Prison, Fleury-Mérogis (Europe's largest prison) and Fresnes Prison, Fresnes, both located in the southern suburbs. History The architect Joseph Auguste Émile Vaudremer built the prison, which was inaugurated on 20 August 1867. The prison is located on the site of a former coal market and replaced the Madelonnettes Convent in the 3rd Arrondissement, which had been used as a prison since the French Revolution. Previously, on the same site, was a ''Maison de la sant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quartier De La Chapelle
The Quartier de La Chapelle () is a neighborhood of Paris, in the eastern part of the 18th arrondissement. It was originally the village of ''La Chapelle'' on the outskirts of Paris and a commune in its own right, separated from the commune of Paris by the wall of the Farmers-General A wall is a structure and a surface that defines an area; carries a load; provides security, Shelter in place, shelter, or soundproofing; or serves a decorative purpose. There are various types of walls, including border barriers between countr .... However, as part of the city's major 19th-century expansion, the former village was absorbed by Paris in 1860. References 18th arrondissement of Paris La Chapelle {{Paris-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protest
A protest (also called a demonstration, remonstration, or remonstrance) is a public act of objection, disapproval or dissent against political advantage. Protests can be thought of as acts of cooperation in which numerous people cooperate by attending, and share the potential costs and risks of doing so. Protests can take many different forms, from individual statements to mass political demonstrations. Protesters may organize a protest as a way of publicly making their opinions heard in an attempt to influence public opinion or government policy, or they may undertake direct action in an attempt to enact desired changes themselves. When protests are part of a systematic and peaceful nonviolent campaign to achieve a particular objective, and involve the use of pressure as well as persuasion, they go beyond mere protest and may be better described as civil resistance or nonviolent resistance. Various forms of self-expression and protest are sometimes restricted by governm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
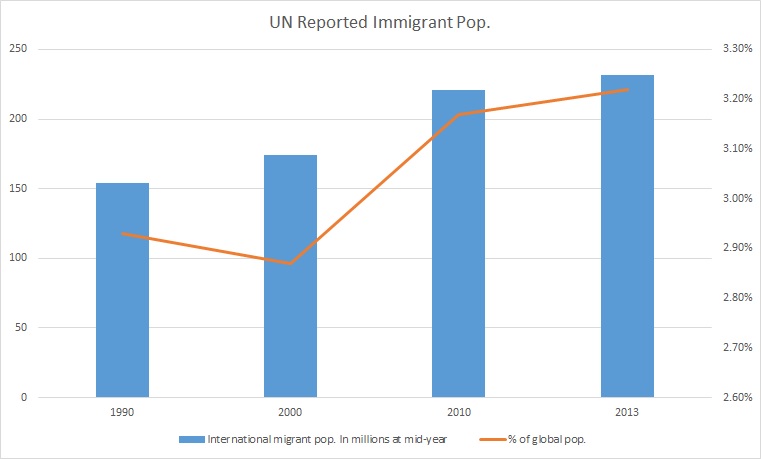
Immigrant Rights
Immigration is the international movement of people to a destination country of which they are not usual residents or where they do not possess nationality in order to settle as permanent residents. Commuters, tourists, and other short-term stays in a destination country do not fall under the definition of immigration or migration; seasonal labour immigration is sometimes included, however. Economically, research suggests that migration can be beneficial both to the receiving and sending countries. The academic literature provides mixed findings for the relationship between immigration and crime worldwide. Research shows that country of origin matters for speed and depth of immigrant assimilation, but that there is considerable assimilation overall for both first- and second-generation immigrants. Discrimination based on nationality is legal in most countries. Extensive evidence of discrimination against foreign-born persons in criminal justice, business, the economy, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Rights Activism
A human rights defender or human rights activist is a person who, individually or with others, acts to promote or protect human rights. They can be journalists, environmentalists, whistleblowers, trade unionists, lawyers, teachers, housing campaigners, participants in direct action, or just individuals acting alone. They can defend rights as part of their jobs or in a voluntary capacity. As a result of their activities, human rights defenders (HRDs) are often subjected to reprisals including smears, surveillance, harassment, false charges, arbitrary detention, restrictions on the right to freedom of association, physical attack, and even murder. In 2020, at least 331 HRDs were murdered in 25 countries. The international community and some national governments have attempted to respond to this violence through various protections, but violence against HRDs continues to rise. Women human rights defenders and environmental human rights defenders (who are very often indigenous) face gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deportation
Deportation is the expulsion of a person or group of people by a state from its sovereign territory. The actual definition changes depending on the place and context, and it also changes over time. A person who has been deported or is under sentence of deportation is called a ''deportee''. Definition Definitions of deportation vary: some include "transfer beyond State borders" (distinguishing it from forcible transfer), others consider it "the actual implementation of n expulsionorder in cases where the person concerned does not follow it voluntarily". Others differentiate removal of legal immigrants (expulsion) from illegal immigrants (deportation). Deportation in the most general sense, in accordance with International Organization for Migration, treats expulsion and deportation as synonyms in the context of migration, adding: "The terminology used at the domestic or international level on expulsion and deportation is not uniform but there is a clear tendency to use th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hunger Strike
A hunger strike is a method of non-violent resistance where participants fasting, fast as an act of political protest, usually with the objective of achieving a specific goal, such as a policy change. Hunger strikers that do not take fluids are named dry hunger strikers. In cases where an entity (usually the State (polity), state) has or is able to obtain custody of the hunger striker (such as a prisoner), the hunger strike is often terminated by the custodial entity through the use of force-feeding. Early history Fasting was used as a method of protesting injustice in pre-Christian Ireland, where it was known as ''Troscadh'' or ''Cealachan''. Detailed in the contemporary Civil code, civic codes, it had specific rules by which it could be used, and the fast was often carried out on the doorstep of the home of the offender. Scholars speculate that this was due to the high importance the culture placed on hospitality. Allowing a person to die at one's doorstep, for a wrong of whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Goutte D'Or
The Goutte d'Or (, ) is a neighbourhood in Paris, located in the 18th arrondissement of Paris. The neighbourhood has large numbers of North African and sub-Saharan residents. It is known for its open-air market, ''le marché Dejean'', which sells goods of African origin.Dyer, Ervin.Little Africa in Paris is a continent within a city" ''Pittsburgh Post-Gazette''. Sunday 27 October 2002. Retrieved on 22 February 2010. Location In common terms, the name 'Goutte d'Or' refers to a loosely defined area around the rue de la Goutte d'Or, to the east of Montmartre and to the west of La Chapelle in the 18th arrondissement of Paris. When used for administrative or statistical purposes, the Goutte d'Or may be defined in at least three different ways: * The "Sensitive Urban Zone" (''ZUS'') of La Goutte d'Or is bounded to the south by Boulevard de la Chapelle, to the west by Boulevard Barbès, to the north by Rue Ordener, and to the east by Rue de Tombouctou and Rue Stephenson. * The neighb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |