|
1956 Atlantic Hurricane Season
The 1956 Atlantic hurricane season featured a decent number of tropical cyclones, although most tropical storms and hurricanes affected land. There were twelve tropical storms, a third of which became hurricanes. One of the hurricanes strengthened to the equivalent of a major hurricane, which is a Category 3 or greater on the Saffir–Simpson scale. The strongest hurricane of the season was Betsy, which was also the most damaging storm of the season: it destroyed 15,000 houses and left $40 million in damage in Puerto Rico. Betsy was also the deadliest of the season, having killed 18 people in the French West Indies, two from a shipwreck in the Caribbean Sea, and 16 in Puerto Rico. Tropical Storm Dora struck Mexico in September and killed 27 people. The season officially started on June 15, although an unnamed storm developed about a week prior over the western North Atlantic Ocean. A later storm that formed over the Gulf of Mexico on J ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Hurricane Hunters
Hurricane hunters, typhoon hunters, or cyclone hunters are aircrews that fly into tropical cyclones to gather weather data. In the United States, the organizations that fly these missions are the United States Air Force Reserve's 53rd Weather Reconnaissance Squadron and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's Hurricane Hunters. Such missions have also been flown by Navy units and other Air Force and NOAA units. Other organizations also fly these missions, such as Government Flying Service Hong Kong. The first crewed flight into a hurricane happened in 1943 when a pilot-trainer flew into a Category 1 hurricane near Galveston, Texas on a bet. In the past, before satellites were used to find tropical storms, military aircraft flew routine weather reconnaissance tracks to detect formation of tropical cyclones. While modern satellites have improved the ability of meteorologists to detect cyclones before they form, only aircraft are able to measure the interior ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Subtropical Storm
A subtropical cyclone is a weather system that has some characteristics of both tropical and extratropical cyclones. As early as the 1950s, meteorologists were uncertain whether they should be characterized as tropical or extratropical cyclones. They were officially recognized and titled by the National Hurricane Center in 1972. Beginning in 2002, subtropical cyclones began receiving names from the official tropical cyclone lists in the North Atlantic basin. Subtropical cyclones are also recognized in the South-West Indian Ocean and South Atlantic basins. There are two definitions currently used for subtropical cyclones depending on their location. Across the north Atlantic and southwest Indian Ocean, they require some central convection fairly near the center surrounding a warming core existing in the mid-levels of the troposphere. Across the eastern half of the northern Pacific however, they require a mid-tropospheric cyclone to be cut off from the main belt of the westerlies ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
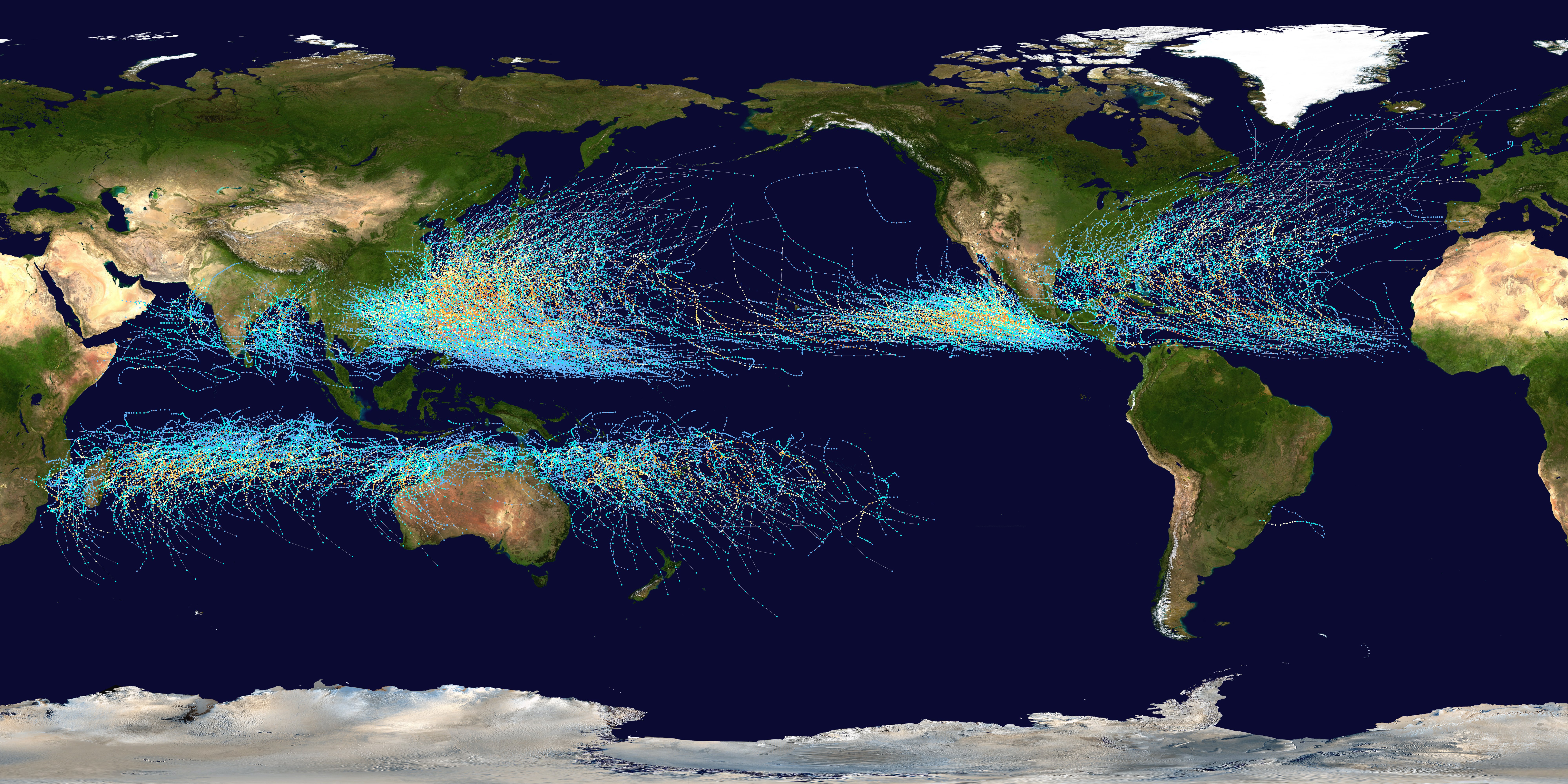
Accumulated Cyclone Energy
Accumulated cyclone energy (ACE) is a metric used to compare overall activity of tropical cyclones, utilizing the available records of windspeeds at six-hour intervals to synthesize storm duration and strength into a single index value. The ACE index may refer to a single storm or to groups of storms such as those within a particular month, a full season or combined seasons. It is calculated by summing the square of tropical cyclones' maximum sustained winds, as recorded every six hours, but only for windspeeds of at least tropical storm strength (≥ 34 kn; 63 km/h; 39 mph); the resulting figure is divided by 10,000 to place it on a more manageable scale. The calculation originated as the Hurricane Destruction Potential (HDP) index, which sums the squares of tropical cyclones' maximum sustained winds while at hurricane strength, at least 64 knots (≥ 119 km/h; 74 mph) at six-hour recorded intervals across an entire season. The HDP index was later modified ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Monthly Weather Review
The ''Monthly Weather Review'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal published by the American Meteorological Society. It covers research related to analysis and prediction of observed and modeled circulations of the atmosphere, including technique development, data assimilation, model validation, and relevant case studies. This includes papers on numerical techniques and data assimilation techniques that apply to the atmosphere and/or ocean environment. The current editor-in-chief is Ron McTaggart-Cowan (Environment and Climate Change Canada). History Source: The journal was first published in January 1873 by the United States Army Signal Corps, but issues were later extended back to the start of the federal government's fiscal year (July 1872). It was issued by the Office of the Chief Signal Officer until 1891. In 1891, the Signal Office's meteorological responsibilities were transferred to the Weather Bureau under the United States Department of Agriculture. The Weather Burea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Trough (meteorology)
A trough is an elongated region of relatively low atmospheric pressure without a closed Isobar (meteorology), isobaric contour that would define it as a Low-pressure area, low pressure area. Since low pressure implies a low Geopotential height, height on a pressure surface, Valley, troughs and Ridge (meteorology), ridges refer to features in an identical sense as those on a topographic map. Troughs may be at the surface, or aloft, at altitude. Near-surface troughs sometimes mark a weather front associated with clouds, showers, and a wind direction shift. Upper-level troughs in the jet stream (as shown in diagram) reflect Cyclonic rotation, cyclonic filaments of vorticity. Their motion induces upper-level wind divergence, lifting and cooling the air ahead (downstream) of the trough and helping to produce cloudy and rain conditions there. Unlike fronts, there is not a universal symbol for a trough on a surface weather analysis chart. The weather charts in some countries or regions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Atmospheric Instability
Atmospheric instability is a condition where the Earth's atmosphere is considered to be unstable and as a result local weather is highly variable through distance and time. Atmospheric instability encourages vertical motion, which is directly correlated to different types of weather systems and their severity. For example, under unstable conditions, a lifted air parcel, parcel of air will find cooler and denser surrounding air, making the parcel prone to further ascent, in a positive feedback loop. In meteorology, instability can be described by various indices such as the Bulk Richardson Number, lifted index, K-index (meteorology), K-index, convective available potential energy, convective available potential energy (CAPE), the Showalter, and the Vertical totals. These indices, as well as atmospheric instability itself, involve temperature changes through the troposphere with height, or lapse rate. Effects of atmospheric instability in moist atmospheres include thunderstorm d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Subtropical Ridge
The horse latitudes are the latitudes about 30 degrees north and south of the Equator. They are characterized by sunny skies, calm winds, and very little precipitation. They are also known as subtropical ridges or highs. It is a high-pressure area at the divergence of trade winds and the westerlies. Etymology A likely and documented explanation is that the term is derived from the "dead horse" ritual of seamen (see Beating a dead horse). In this practice, the seaman paraded a straw-stuffed effigy of a horse around the deck before throwing it overboard. Seamen were paid partly in advance before a long voyage, and they frequently spent their pay all at once, resulting in a period of time without income. This period was called the "dead horse" time, and it usually lasted a month or two. The seaman's ceremony was to celebrate having worked off the "dead horse" debt. As west-bound shipping from Europe usually reached the subtropics at about the time the "dead horse" was worke ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
National Oceanic And Atmospheric Administration
The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA ) is an American scientific and regulatory agency charged with Weather forecasting, forecasting weather, monitoring oceanic and atmospheric conditions, Hydrography, charting the seas, conducting deep-sea exploration, and managing fishing and protection of marine mammals and endangered species in the US exclusive economic zone. The agency is part of the United States Department of Commerce and is headquartered in Silver Spring, Maryland. History NOAA traces its history back to multiple agencies, some of which are among the earliest in the federal government: * United States Coast and Geodetic Survey, formed in 1807 * National Weather Service, Weather Bureau of the United States, formed in 1870 * United States Fish Commission, Bureau of Commercial Fisheries, formed in 1871 (research fleet only) * NOAA Commissioned Corps, Coast and Geodetic Survey Corps, formed in 1917 The most direct predecessor of NOAA was the Enviro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
National Hurricane Center
The National Hurricane Center (NHC) is the division of the United States' NOAA/National Weather Service responsible for tracking and predicting tropical weather systems between the IERS Reference Meridian, Prime Meridian and the 140th meridian west poleward to the 30th parallel north in the northeast Pacific Ocean and the 31st parallel north in the northern Atlantic Ocean. The agency, which is co-located with the National Weather Service Miami, Florida, Miami branch of the National Weather Service, is situated on the campus of Florida International University in University Park, Florida, University Park, Miami, Miami, Florida. The NHC's Tropical Analysis and Forecast Branch (TAFB) routinely issues marine forecasts, in the form of graphics and high seas forecasts year round, with the Ocean Prediction Center having backup responsibility for this unit. The Technology and Science Branch (TSB) provides technical support for the center, which includes new infusions of technology from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Tropical Cyclogenesis
Tropical cyclogenesis is the development and strengthening of a tropical cyclone in the atmosphere. The mechanisms through which tropics, tropical cyclogenesis occur are distinctly different from those through which temperate cyclogenesis occurs. Tropical cyclogenesis involves the development of a warm core, warm-core cyclone, due to significant convection in a favorable atmospheric environment. Tropical cyclogenesis requires six main factors: sufficiently warm sea surface temperatures (at least ), atmospheric instability, high humidity in the lower to middle levels of the troposphere, enough Coriolis force to develop a low-pressure area, low-pressure center, a pre-existing low-level focus or disturbance, and low vertical wind shear. Tropical cyclones tend to develop during the summer, but have been noted in nearly every month in tropical cyclone basins, most basins. Climate cycles such as ENSO and the Madden–Julian oscillation modulate the timing and frequency of tropical c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Low-pressure Area
In meteorology, a low-pressure area (LPA), low area or low is a region where the atmospheric pressure is lower than that of surrounding locations. It is the opposite of a high-pressure area. Low-pressure areas are commonly associated with inclement weather (such as cloudy, windy, with possible rain or storms), while high-pressure areas are associated with lighter winds and clear skies. Winds circle anti-clockwise around lows in the northern hemisphere, and clockwise in the southern hemisphere, due to opposing Coriolis forces. Low-pressure systems form under areas of wind divergence that occur in the upper levels of the atmosphere (aloft). The formation process of a low-pressure area is known as cyclogenesis. In meteorology, atmospheric divergence aloft occurs in two kinds of places: * The first is in the area on the east side of upper troughs, which form half of a Rossby wave within the Westerlies (a trough with large wavelength that extends through the troposphere). * A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |