|
1950 Assam–Tibet Earthquake
The 1950 Assam–Tibet earthquake, also known as the Assam earthquake, occurred on 15 August and had a moment magnitude of 8.7. The epicentre was located in the Mishmi Hills. It is one of the strongest earthquakes ever recorded on land. Occurring on a Tuesday evening at 7:39 PM Indian Standard Time, the earthquake was destructive in both Assam (India) and Tibet (China), and approximately 4,800 people were killed. The earthquake is notable as being the largest recorded quake caused by continental collision rather than subduction, and is also notable for the loud noises produced by the quake and reported throughout the region. Tectonic setting Northeastern India and southern Tibet lie in the frontal part of the zone of collision between the northward moving Indian plate and Eurasia. The thrust belt that marks this plate boundary zone is formed of a series of sub-parallel thrust faults. The thrust faults in this part of the Himalayas show a rapid lateral change in orientation fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fault (geology)
In geology, a fault is a Fracture (geology), planar fracture or discontinuity in a volume of Rock (geology), rock across which there has been significant displacement as a result of rock-mass movements. Large faults within Earth's crust (geology), crust result from the action of Plate tectonics, plate tectonic forces, with the largest forming the boundaries between the plates, such as the megathrust faults of subduction, subduction zones or transform faults. Energy release associated with rapid movement on active faults is the cause of most earthquakes. Faults may also displace slowly, by aseismic creep. A ''fault plane'' is the Plane (geometry), plane that represents the fracture surface of a fault. A ''fault trace'' or ''fault line'' is a place where the fault can be seen or mapped on the surface. A fault trace is also the line commonly plotted on geological maps to represent a fault. A ''fault zone'' is a cluster of parallel faults. However, the term is also used for the zone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Main Frontal Thrust
The Main Frontal Thrust (MFT), also known as the Himalayan Frontal Thrust (HFT), is a geological fault in the Himalayas that defines the boundary between the Himalayan foothills and Indo-Gangetic Plain. The fault is well expressed on the surface thus could be seen via satellite imagery. It is the youngest and southernmost thrust structure in the Himalaya deformation front. It is a splay branch of the Main Himalayan Thrust (MHT) as the root décollement. Background It runs parallel to other major splays of the MHT, the Main Boundary Thrust (MBT) and Main Central Thrust (MCT). The Sunda Megathrust, which extends from the Banda Islands to Myanmar, is joined with the MFT. The fault strikes in a northwest-southeast direction and dips at an angle of 20° to 30° in the north. The Main Boundary Thrust is another major thrust fault in the Himalaya orogenic wedge that was active in the Cenozoic. It runs parallel to the MFT with a spacing distance of about 20 km. Shortening ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alluvial Fan
An alluvial fan is an accumulation of sediments that fans outwards from a concentrated source of sediments, such as a narrow canyon emerging from an escarpment. They are characteristic of mountainous terrain in arid to Semi-arid climate, semiarid climates, but are also found in more humid environments subject to intense rainfall and in areas of modern glaciation. They range in area from less than to almost . Alluvial fans typically form where a flow of sediment or rocks emerge from a confined channel and are suddenly free to spread out in many directions. For example, many alluvial fans form when steep mountain valleys meet a flat plain. The transition from a narrow channel to a wide open area reduces the carrying capacity of flow and results in Deposition (geology), deposition of sediments. The flow can take the form of infrequent debris flows like in a landslide, or can be carried by an intermittent stream or creek. The reduction of flow is key to the formation of alluvial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trench
A trench is a type of digging, excavation or depression in the ground that is generally deeper than it is wide (as opposed to a swale (landform), swale or a bar ditch), and narrow compared with its length (as opposed to a simple hole or trapping pit, pit). In geology, trenches result from erosion by rivers or by geological movement of tectonic plates. In civil engineering, trenches are often created to install underground utilities such as Pipeline transport, gas, Water distribution system, water, Underground power lines, power and Undergrounding, communication lines. In construction, trenches are dug for foundations of buildings, retaining walls and dams, and for Tunnel construction#Cut-and-cover, cut-and-cover construction of tunnels. In archaeology, the "trench method" is used for searching and Excavation (archaeology), excavating ancient ruins or to dig into stratum, strata of sedimented material. In geotechnical engineering, trench investigations locate faults and investigat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sand Volcano
Sand boils, sand volcanoes, or sand blows occur when water under pressure wells up through a bed of sand. The water looks like it is boiling up from the bed of sand, hence the name. Sand volcano A sand volcano or sand blow is a cone of sand formed by the ejection of sand onto a surface from a central point. The sand builds up as a cone (geometry), cone with slopes at the sand's angle of repose. A volcanic crater, crater is commonly seen at the summit (topography), summit. The cone looks like a small volcanic cone and can range in size from millimetres to metres in diameter. The process is often associated with soil liquefaction and the ejection of fluidized sand that can occur in water-saturated sediments during an earthquake. The New Madrid seismic zone exhibited many such features during the 1811–1812 New Madrid earthquakes. Adjacent sand blows aligned in a row along a linear fracture within fine-grained surface sediments are just as common, and can still be seen in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
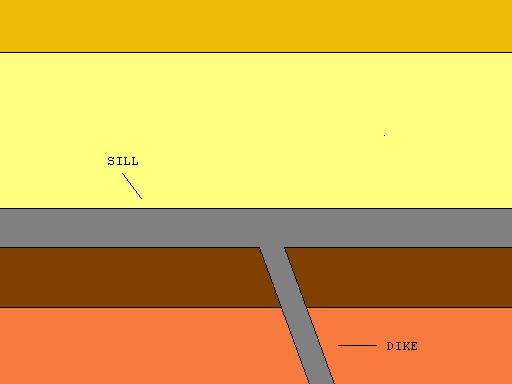
Sill (geology)
In geology, a sill is a tabular sheet intrusion that has intruded between older layers of sedimentary rock, beds of volcanic lava or tuff, or along the direction of foliation in metamorphic rock. A sill is a ''concordant intrusive sheet'', meaning that it does not cut across preexisting rock beds. Stacking of sills builds a sill complex. and a large magma chamber at high magma flux. In contrast, a dike is a discordant intrusive sheet, which does cut across older rocks. Formation Sills are fed by dikes, except in unusual locations where they form in nearly vertical beds attached directly to a magma source. The rocks must be brittle and fracture to create the planes along which the magma intrudes the parent rock bodies, whether this occurs along preexisting planes between sedimentary or volcanic beds or weakened planes related to foliation in metamorphic rock. These planes or weakened areas allow the intrusion of a thin sheet-like body of magma paralleling the existi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soil Liquefaction
Soil liquefaction occurs when a cohesionless saturated or partially saturated soil substantially loses Shear strength (soil), strength and stiffness in response to an applied Shear stress, stress such as shaking during an earthquake or other sudden change in stress condition, in which material that is ordinarily a solid behaves like a liquid. In soil mechanics, the term "liquefied" was first used by Allen Hazen in reference to the 1918 failure of the Calaveras Dam in California. He described the mechanism of flow liquefaction of the embankment dam as: The phenomenon is most often observed in saturated, loose (low density or uncompacted), sandy soils. This is because a loose sand has a tendency to Compressibility, compress when a force, load is applied. Dense sands, by contrast, tend to expand in volume or 'Reynolds' dilatancy, dilate'. If the soil is saturated by water, a condition that often exists when the soil is below the water table or sea level, then water fills the gap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Institute Of Physics, Bhubaneswar
Institute of Physics, Bhubaneswar is an autonomous research institution of the Department of Atomic Energy (India), Department of Atomic Energy (DAE), Government of India. The institute was founded by Professor Bidhu Bhusan Das, who was Director of Public Instruction, Odisha, at that time. Das set up the institute in 1972, supported by the Government of Odisha under the patronage of Odisha's education minister Banamali Patnaik, and chose Dr. Trilochan Pradhan as its first director, when the Institute started theoretical research programs in the various branches of physics. Other notable physicists in the institute's early days included Prof. T. P. Das, of SUNY, Albany, New York, USA and Prof. Jagdish Mohanty of IIT Kanpur and Australian National University, Canberra. In 1981, the Institute moved to its present campus near Chandrasekharpur, Bhubaneswar. It was taken over by the Department of Atomic Energy, India on 25 March 1985 and started functioning as an autonomous body. Re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Geophysical Research Institute
The National Geophysical Research Institute (NGRI) is a geoscientific research organization established in 1961 under the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), India's largest Research and Development organization. It is supported by more than 200 scientists and other technical staff whose research activities are published in several journals of national and international interest. Research areas covered by this institute include hydrocarbon and coal exploration, mineral exploration, deep seismic sounding studies, exploration and management of groundwater resources, earthquake hazard assessment, structure of Earth's interior and its evolution (theoretical studies), geophysical instrument development and geothermal exploration. The major facilities available at NGRI include: *Laser Ablation Multi-Collector Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometer (LA-MC-ICPMS) with clean chemistry laboratory facility. *Mineral Physics Laboratory with high-pressure Diamon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northeast India
Northeast India, officially the North Eastern Region (NER), is the easternmost region of India representing both a geographic and political Administrative divisions of India, administrative division of the country. It comprises eight States and union territories of India, states—Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland and Tripura (commonly known as the "Seven Sisters"), and the "brother" state of Sikkim. The region shares an international border of 5,182 kilometres (3,220 mi) (about 99 per cent of its total geographical boundary) with several neighbouring countries – it borders China to the north, Myanmar to the east, Bangladesh to the south-west, Nepal to the west, and Bhutan to the north-west. It comprises an area of , almost 8 per cent of that of India. The Siliguri Corridor connects the region to the Mainland India, rest of mainland India. The states of North Eastern Region are officially recognised under the North Eastern Council (NEC), co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burma Microplate
The Burma plate is a minor tectonic plate or microplate located in Southeast Asia, sometimes considered a part of the larger Eurasian plate. The Andaman Islands, Nicobar Islands, and northwestern Sumatra are located on the plate. This island arc separates the Andaman Sea from the main Indian Ocean to the west. To its east lies the Sunda plate, from which it is separated along a transform boundary, running in a rough north–south line through the Andaman Sea. This boundary between the Burma and Sunda plates is a marginal seafloor spreading centre, which has led to the opening up of the Andaman Sea (from a southerly direction) by "pushing out" the Andaman-Nicobar-Sumatra island arc from mainland Asia, a process which began in earnest approximately 4 million years ago. To the west is the much larger India plate, which is subducting beneath the western facet of the Burma plate. This extensive subduction zone has formed the Sunda Trench. Tectonic history In models of the recon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sagaing Fault
The Sagaing Fault is a major fault in Myanmar, a mainly continental right-lateral transform fault between the Indian plate and Sunda plate. It links the divergent boundary in the Andaman Sea with the zone of active continental collision along the Himalayan front. It passes through the populated cities of Mandalay, Yamethin, Pyinmana, the capital Naypyidaw, Toungoo and Pegu before dropping off into the Gulf of Martaban, running for a total length of over . Discovery and early studies A partial visualization of an active fault trace that aligns with the present-day Sagaing Fault trace was recorded by Fritz Noetling, a geologist, in the book ''The Miocene of Burma'' published in 1900. In 1913, Thomas Henry Digges La Touche of the Geological Survey of India acknowledged the existence of a plate boundary feature along the Shan Plateau's western margin in Mandalay, including the one dividing metamorphic stratas of the Sagaing Hills from the Central Tertiary Basin. While analysing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |