|
1922 Philippine Senate Elections
Senatorial elections were held on June 6, 1922 in the Philippines under the Jones Law provisions. It was controversial when Senate President Manuel L. Quezon accused Sergio Osmeña of autocratic leadership and for his failure in handling the economic crisis which began in 1919. This resulted to the Nacionalista Party to be split. Quezon-Osmeña spilt In 1921, the economic crisis that began in 1919 began to worsen in the Philippine Islands. From 1919 to 1921, there were floods in parts of the country resulting in a rice crisis. The Philippine National Bank lost due to mismanagement and the government deficit was more than which led to the raising of taxes. During these period, all government-owned corporations suffered losses. The economic crisis led to massive discontent and criticism to the standing party, the Nacionalista Party. When Warren G. Harding, then elected U.S. president, sent the Wood-Forbes Mission for the Philippine Islands in April 1921, Quezon became worried ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Senate Of The Philippines
The Senate of the Philippines () is the upper house of Congress of the Philippines, Congress, the bicameral legislature of the Philippines, with the House of Representatives of the Philippines, House of Representatives as the lower house. The Senate is composed of 24 senators who are elected at-large (the country forms one district in Philippine Senate elections, senatorial elections) under a Plurality block voting, plurality-at-large voting system. Senators serve six-year terms with a maximum of two consecutive terms, with half of the senators elected in staggered elections every three years. When the Senate was restored by the Constitution of the Philippines, 1987 Constitution, the 24 senators who were elected in 1987 served until 1992. In 1992, the 12 candidates for the Senate obtaining the highest number of votes served until 1998, while the next 12 served until 1995. This is in accordance with the transitory provisions of the Constitution. Thereafter, each senator electe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
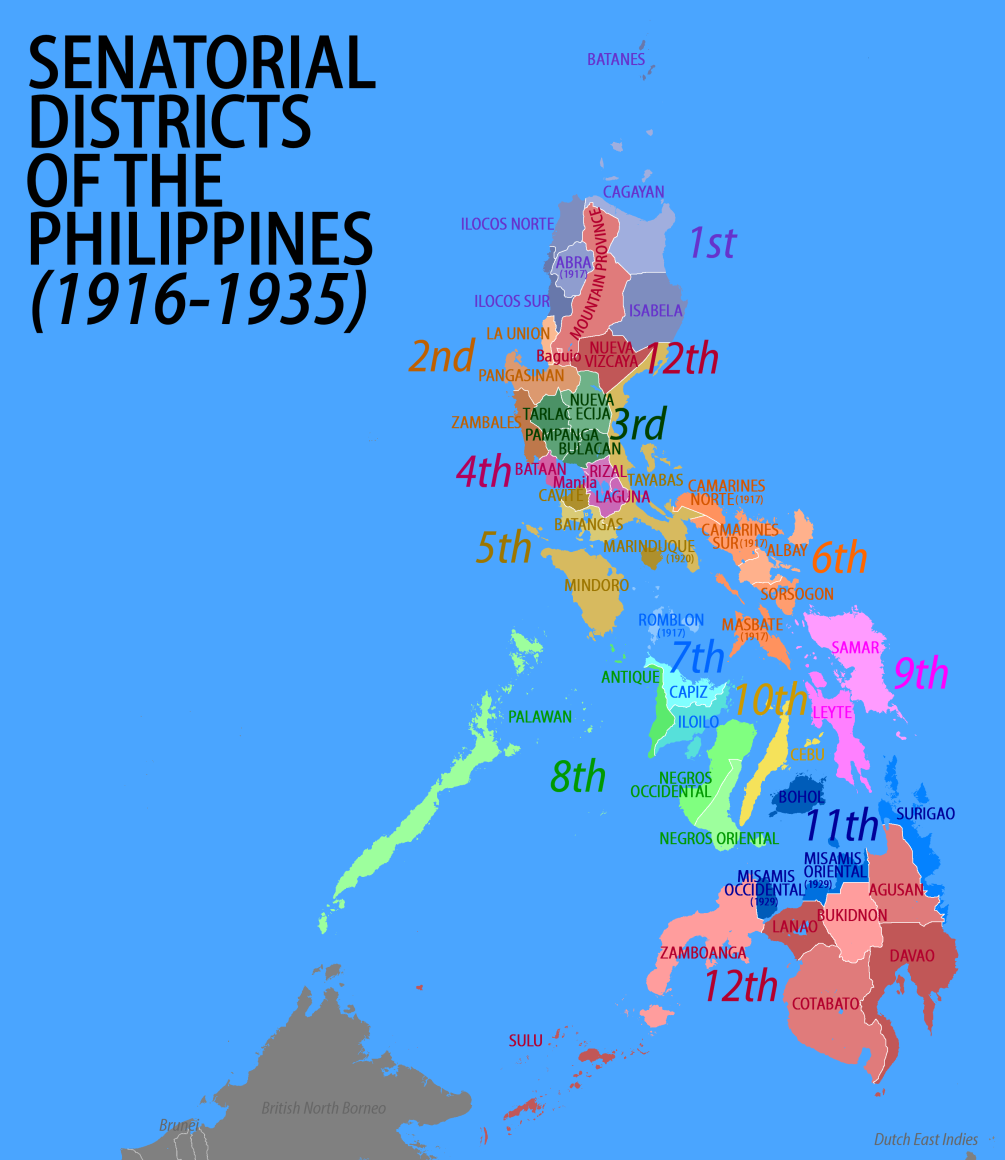
Senatorial Districts Of The Philippines
The senatorial districts of the Philippines were the representations of the provinces of the Philippines in the Philippine Senate from 1916 to 1935. History The enactment of the Philippine Autonomy Act (popularly known as "Jones Law") in August 1916 by the United States Congress provided for the creation of a bicameral legislature consisting of a lower chamber (House of Representatives) and an upper chamber (Senate). Until then the Philippine Commission held the executive power and some legislative powers over the American colony. The system of government of the Philippines in its early years of transition to democratic self-government was deliberately structured to emulate the American model. The Philippines thus followed the American system of electing the members of the 24-seat senate by district. The districts were organized and numbered in a roughly north–south fashion, much like the present administrative regions. The first eleven districts were composed of estab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philippine Senate Elections
Elections to the Senate of the Philippines are done via plurality-at-large voting; a voter can vote for up to twelve candidates, with the twelve candidates with the highest number of votes being elected. The 24-member Senate uses staggered elections, with only one-half of its members up for election at any given time, except for special elections, which are always held concurrently with regularly scheduled elections. Manner of choosing candidates With the advent of the nominal multi-party system in 1987, political parties have not been able to muster enough candidates to fill their 12-person slate. This means they have to join coalitions or alliances in order to present a full slate. If a slate is still not complete, "guest candidates" may be invited, even from rival slates. A guest candidate may not be compelled to join the campaign rallies of the slate that invited him/her. A party may even not include their entire ticket to a coalition slate, or assign their candidates to com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philippine Elections
Elections in the Philippines are of several types. The president, vice-president, and the senators are elected for a six-year term, while the members of the House of Representatives, governors, vice-governors, members of the Sangguniang Panlalawigan (provincial board members), mayors, vice-mayors, members of the Sangguniang Panlungsod/ members of the Sangguniang Bayan (city/municipal councilors), barangay officials, and the members of the Sangguniang Kabataan (youth councilors) are elected to serve for a three-year term. Congress has two chambers. The House of Representatives has 316 seats since 2022, of which 80% are contested in single seat electoral districts and 20% are allotted to party-lists according to a modified Hare quota with remainders disregarded and a three-seat cap. These party list seats are only accessible to marginalized and under-represented groups and parties, local parties, and sectoral wings of major parties that represent the marginalized. The Con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Politics Of The Philippines
Politics in the Philippines are governed by a Separation of powers, three-branch system of government. The country is a democracy, with a President of the Philippines, president who is directly Elections in the Philippines, elected by the people and serves as both the head of state and the head of government. The president serves as the leader of the executive branch and is a powerful political figure. A president may only hold office for one six-year term. The bicameral Congress of the Philippines, Congress consists of two separate bodies: the Senate of the Philippines, Senate, with members elected at-large across the country, and the larger House of Representatives of the Philippines, House of Representatives, with members chosen mostly from specific geographic districts. The Congress performs legislative functions. The Judiciary of the Philippines, judiciary is overseen by the Supreme Court of the Philippines and has extensive Judicial review, review jurisdiction over judgmen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commission On Elections (Philippines)
The Commission on Elections (), abbreviated as , is one of the three Constitutional Commission#Philippines, constitutional commissions of the Philippines. Its principal role is to enforce all laws and regulations relative to the conduct of elections in the Philippines. The other two Constitutional Commissions are the Commission on Audit (Philippines), Commission on Audit and Civil Service Commission (Philippines), Civil Service Commission. Functions According to Article IX-C, Section 2 of the 1987 Constitution of the Philippines, the Commission on Elections (COMELEC) shall exercise the following powers and functions: # Enforce and administer all laws and regulations relative to the conduct of an election, plebiscite, initiative, referendum, and recall. # Exercise exclusive original jurisdiction over all contests relating to the elections, returns, and qualifications of all elective regional, provincial, and city officials, and appellate jurisdiction over all contests involving ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
6th Philippine Legislature
The 6th Philippine Legislature was the meeting of the legislature of the Philippines under the sovereign control of the United States from 1922 to 1925. Sessions Leadership Senate * President: Manuel L. Quezon ( 5th District, Nacionalista Colectivista) * President pro tempore: Sergio Osmeña ( 10th District, Nacionalista Unipersonalista) * Majority Floor Leader: Francisco Enage ( 9th District, Nacionalista Colectivista) House of Representatives * Speaker: Manuel Roxas ( Capiz–1st, Nacionalista Colectivista) * Speaker pro tempore: Antonio de las Alas ( Batangas–1st, Nacionalista Colectivista) * Majority Floor Leader: Benigno Aquino Sr. ( Tarlac–2nd, Nacionalista Unipersonalista) Members Senate The following are the terms of the elected senators of this Legislature, according to the date of election: * For senators elected on June 3, 1919: June 3, 1919 – June 2, 1925 * For senators elected on June 6, 1922: June 6, 1922 – June 5, 1928 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Progresista Party
The Progresista Party ( Filipino and Spanish: ''Partido Progresista''; ) was a political party in the Philippines during the early 20th century. Formed in 1900 as the Federalist Party (Partido Federalista), the party originally had the Philippines becoming a U.S. state as one of its original platforms, which was later rescinded. Origins as the Partido Federalista After the defeat of the Filipinos by the Americans on the Philippine–American War (then known as the Philippine Insurrection), the Americans assessed the situation; the United States Congress passed the Philippine Organic Act of 1902 creating the Philippine Assembly. While the assembly had nationalists who wanted independence from the United States, most delegates pursued statehood within the U.S. These delegates, led by Pedro Paterno, formed the Partido Federalista (Federalist Party or the Federalistas) on December 23, 1900. On that meeting, the party platform of the recognition of U.S. sovereignty, establishment of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Democrata Party
The Democrata Party, also known as ''Partido Democrata Nacional'' () was a political party in the early 20th century Philippines, when the Philippines was an insular territory of the United States. It functioned as an opposition party against the ruling Nacionalista Party. History The Democrata Party came from the remnants of the Progresista Party, which had been defeated by the Nacionalistas. Juan Sumulong founded the Democrata party in 1917, espousing "''absolute and immediate independence''". In the 1922 election, the Nacionalistas were split into two camps: Senate President Manuel L. Quezon pushed for collective leadership, calling Speaker Sergio Osmeña's leadership style as "''unipersonal''", a charge Osmeña denied. Thus, Quezon and his allies were the "Colectivistas", while Osmeña and his allies were the "Unipersonalistas". Osmeña decided to run for the Senate, directly challenging Quezon's authority. This led to the Nacionalistas losing their majority in the House ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First-past-the-post Voting
First-past-the-post (FPTP)—also called choose-one, first-preference plurality (FPP), or simply plurality—is a single-winner voting rule. Voters mark one candidate as their favorite, or first-preference, and the candidate with more first-preference votes than any other candidate (a ''plurality'') is elected, even if they do not have more than half of votes (a '' majority''). FPP has been used to elect part of the British House of Commons since the Middle Ages before spreading throughout the British Empire. Throughout the 20th century, many countries that previously used FPP have abandoned it in favor of other electoral systems, including the former British colonies of Australia and New Zealand. FPP is still officially used in the majority of US states for most elections. However, the combination of partisan primaries and a two-party system in these jurisdictions means that most American elections behave effectively like two-round systems, in which the first round ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Governor-General Of The Philippines
The governor-general of the Philippines (; ; ) was the title of the Executive (government), government executive during the colonial period of the Philippines, first by History of the Philippines (1521–1898), the Spanish in Mexico City and later Madrid as "Captain General"– , ) from 1565–1898 and the History of the Philippines (1898–1946), United States (1898–1946), and briefly by British occupation of Manila, Great Britain (1762–1764) and Japanese occupation of the Philippines, Japan (1942–1945). They were also the representative of the Executive (government), executive of the ruling power. On November 15, 1935, the Commonwealth of the Philippines was established as a transitional government to prepare the country for independence from American control. The governor-general was replaced by an elected Filipino people, Filipino List of presidents of the Philippines, president of the Philippine Commonwealth, as the Executive (government), chief executive of the Phil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philippines's 12th Senatorial District
Philippines's 12th senatorial district, officially the Twelfth Senatorial District of the Philippine Islands (), was one of the twelve senatorial districts of the Philippines in existence between 1916 and 1935. Unlike the first eleven districts which elected two members each to the Senate of the Philippines, the upper chamber of the bicameral Philippine Legislature under the Insular Government of the Philippine Islands, the two senators from this district were appointed by the Governor-General of the Philippines to serve indefinite terms in the 4th Philippine Legislature, 4th to 10th Philippine Legislature, 10th legislatures. The district was created under the 1916 Jones Law (Philippines), Jones Law to represent the non-Christian tribes of the northern Luzon provinces of Mountain Province and Nueva Vizcaya, the city of Baguio, and the Moro people and other non-Christian tribes of the Department of Mindanao and Sulu provinces of Agusan (province), Agusan, Bukidnon, Cotabato (historic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |