|
1876 In Science
The year 1876 in science and technology involved some significant events, listed below. Astronomy * December 7 – First recorded observation of the Great White Spot on Saturn, made by American astronomer Asaph Hall, who uses it to calculate the planet's rotation period. Biology * Robert Koch demonstrates that ''Bacillus anthracis'' is the source of anthrax, the first bacterium conclusively shown to cause disease. * Koller's sickle in Bird, avian gastrulation is first described by August Rauber. * Francis Galton invents the silent dog whistle. * Meiosis is discovered and described for the first time in sea urchin eggs by the German biologist Oscar Hertwig. Chemistry * Josiah Willard Gibbs publishes ''On the Equilibrium of Heterogeneous Substances'', a compilation of his work on thermodynamics and physical chemistry which lays out the concept of Thermodynamic free energy, free energy to explain the physical basis of chemical equilibria. Exploration * May 24 – End of the Chal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oscar Hertwig
Oscar Hertwig (21 April 1849 in Friedberg – 25 October 1922 in Berlin) was a German embryologist and zoologist known for his research in developmental biology and evolution. Hertwig is credited as the first person to observe sexual reproduction at the cellular level, by looking at the cells of sea urchins under the microscope. Biography Hertwig was the elder brother of zoologist-professor Richard Hertwig (1850–1937). The Hertwig brothers were the most eminent scholars of Ernst Haeckel (and Carl Gegenbaur) from the University of Jena. They were independent of Haeckel's philosophical speculations but took his ideas in a positive way to widen their concepts in zoology. Initially, between 1879 and 1883, they performed embryological studies, especially on the theory of the coelom (1881), the fluid-filled body cavity. These problems were based on the phylogenetic theorems of Haeckel, i.e. the biogenic theory (German = biogenetisches Grundgesetz), and the " gastraea theory" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brain Tumor
A brain tumor (sometimes referred to as brain cancer) occurs when a group of cells within the Human brain, brain turn cancerous and grow out of control, creating a mass. There are two main types of tumors: malignant (cancerous) tumors and benign tumor, benign (non-cancerous) tumors. These can be further classified as primary tumors, which start within the brain, and metastasis, secondary tumors, which most commonly have spread from tumors located outside the brain, known as brain metastasis tumors. All types of brain tumors may produce symptoms that vary depending on the size of the tumor and the part of the brain that is involved. Where symptoms exist, they may include headaches, seizures, problems with visual perception, vision, vomiting and cognition, mental changes. Other symptoms may include difficulty walking, speaking, with sensations, or unconsciousness. The cause of most brain tumors is unknown, though up to 4% of brain cancers may be caused by CT scan radiation. Uncommo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
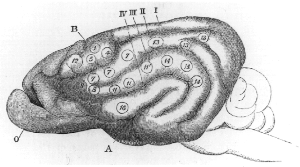
William Macewen
Sir William Macewen ( ; 22 June 1848 – 22 March 1924) was a Scottish surgeon. He was a pioneer in modern brain surgery, considered the ''father of neurosurgery'' and contributed to the development of bone graft surgery, the surgical treatment of hernia and of pneumonectomy (removal of the lungs). Career Macewen was born near Port Bannatyne, near Rothesay on the Isle of Bute, in western Scotland in 1848. He studied Medicine at the University of Glasgow, receiving a medical degree in 1872. He was greatly influenced by Joseph, Lord Lister (1827–1912), who revolutionised surgery by developing antisepsis, by the use of phenol, thus decreasing drastically the enormous mortality of surgical patients due to infections. By following Lister and adopting systematically the use of scrubbing (deep cleansing and disinfection of hands and arms), sterilisation of surgical tools, use of surgical gowns, and (recently discovered) anaesthesia, Macewen became one of the most innovati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
David Ferrier
Sir David Ferrier FRS (13 January 1843 – 19 March 1928) was a pioneering Scottish neurologist and psychologist. Ferrier conducted experiments on the brains of animals such as monkeys and in 1881 became the first scientist to be prosecuted under the Cruelty to Animals Act, 1876 which had been enacted following a major public debate over vivisection. Life Ferrier was born in Woodside, Aberdeen, the sixth child of David and Hannah; he was educated at Aberdeen Grammar School before studying for an MA at Aberdeen University (graduating in Classics in 1863), before studying psychophysiology in Germany and medicine at Edinburgh. As a medical student, he began to work as a scientific assistant to the influential free-thinking philosopher and psychologist Alexander Bain (1818–1903), one of the founders of associative psychology. Around 1860, psychology was finding its scientific foundation mainly in Germany, with the rigorous research of Hermann von Helmholtz (1821–1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hibernation
Hibernation is a state of minimal activity and metabolic reduction entered by some animal species. Hibernation is a seasonal heterothermy characterized by low body-temperature, slow breathing and heart-rate, and low metabolic rate. It is most commonly used to pass through winter months – called overwintering. Although traditionally reserved for "deep" hibernators such as rodents, the term has been redefined to include animals such as bears and is now applied based on active metabolic suppression rather than any absolute decline in body temperature. Many experts believe that the processes of daily torpor and hibernation form a continuum and use similar mechanisms. The equivalent during the summer months is aestivation. Hibernation functions to conserve energy when sufficient food is not available. To achieve this energy saving, an endothermic animal decreases its metabolic rate and thereby its body temperature. Hibernation may last days, weeks, or months—depending on t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karolina Olsson
Karolina Olsson (29 October 1861 – 5 April 1950), also known as "Soverskan på Oknö" ("The Sleeper of Oknö"), was a Swedish woman who purportedly remained in hibernation between 1876 and 1908 (32 years). This is believed to be the longest time that anyone has lived in this manner who then awoke without any residual symptoms. Life Olsson was born on 29 October 1861 in Oknö near Mönsterås, the second-eldest of five children; her siblings were all brothers. She suffered a head wound while outdoors at age 14 on 18 February 1876, but seemed to recover from it quickly. On 22 February, she complained of a toothache. Her family believed that her tooth was sore because of witchcraft, and she was ordered to go to bed. However, when she fell asleep, she did not wake up. Her father was a fisherman and unable to afford a doctor, and the family relied instead on the advice of friends and the town midwife. Olsson's mother force-fed her milk and sugar water. Finally, the neighbors paid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Factorization
In mathematics, factorization (or factorisation, see American and British English spelling differences#-ise, -ize (-isation, -ization), English spelling differences) or factoring consists of writing a number or another mathematical object as a product of several ''Factor (arithmetic), factors'', usually smaller or simpler objects of the same kind. For example, is an ''integer factorization'' of , and is a ''polynomial factorization'' of . Factorization is not usually considered meaningful within number systems possessing division ring, division, such as the real number, real or complex numbers, since any x can be trivially written as (xy)\times(1/y) whenever y is not zero. However, a meaningful factorization for a rational number or a rational function can be obtained by writing it in lowest terms and separately factoring its numerator and denominator. Factorization was first considered by Greek mathematics, ancient Greek mathematicians in the case of integers. They proved the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mersenne Prime
In mathematics, a Mersenne prime is a prime number that is one less than a power of two. That is, it is a prime number of the form for some integer . They are named after Marin Mersenne, a French Minim friar, who studied them in the early 17th century. If is a composite number then so is . Therefore, an equivalent definition of the Mersenne primes is that they are the prime numbers of the form for some prime . The exponents which give Mersenne primes are 2, 3, 5, 7, 13, 17, 19, 31, ... and the resulting Mersenne primes are 3, 7, 31, 127, 8191, 131071, 524287, 2147483647, ... . Numbers of the form without the primality requirement may be called Mersenne numbers. Sometimes, however, Mersenne numbers are defined to have the additional requirement that should be prime. The smallest composite Mersenne number with prime exponent ''n'' is . Mersenne primes were studied in antiquity because of their close connection to perfect numbers: the Euclid–Eule ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Édouard Lucas
__NOTOC__ François Édouard Anatole Lucas (; 4 April 1842 – 3 October 1891) was a French mathematician. Lucas is known for his study of the Fibonacci sequence. The related Lucas sequences and Lucas numbers are named after him. Biography Lucas was born in Amiens and educated at the École Normale Supérieure. He worked in the Paris Observatory and later became a professor of mathematics at the Lycée Saint Louis and the Lycée Charlemagne in Paris. Lucas served as an artillery officer in the French Army during the Franco-Prussian War of 1870–1871. In 1875, Lucas posed a challenge to prove that the only solution of the Diophantine equation :\sum_^ n^2 = M^2\; with ''N'' > 1 is when ''N'' = 24 and ''M'' = 70. This is known as the cannonball problem, since it can be visualized as the problem of taking a square arrangement of cannonballs on the ground and building a square pyramid out of them. It was not until 1918 that a proof (using elliptic functions) was found for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Challenger Expedition
The ''Challenger'' expedition of 1872–1876 was a scientific programme that made many discoveries to lay the foundation of oceanography. The expedition was named after the naval vessel that undertook the trip, . The expedition, initiated by William Benjamin Carpenter, was placed under the scientific supervision of Sir Charles Wyville Thomson—of the University of Edinburgh and Merchiston Castle School—assisted by five other scientists, including Sir John Murray (oceanographer), John Murray, a secretary-artist and a photographer. The Royal Society of London obtained the use of ''Challenger'' from the Royal Navy and in 1872 modified the ship for scientific tasks at Sheerness, equipping it with separate laboratories for natural history and chemistry. The expedition, led by Captain George Nares, sailed from Portsmouth, England, on 21 December 1872. Other naval officers included Commander John Maclear. – pages 19 and 20 list the civilian staff and naval officers and crew, along ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermodynamic Free Energy
In thermodynamics, the thermodynamic free energy is one of the state functions of a thermodynamic system. The change in the free energy is the maximum amount of work that the system can perform in a process at constant temperature, and its sign indicates whether the process is thermodynamically favorable or forbidden. Since free energy usually contains potential energy, it is not absolute but depends on the choice of a zero point. Therefore, only relative free energy values, or changes in free energy, are physically meaningful. The free energy is the portion of any first-law energy that is available to perform thermodynamic work at constant temperature, ''i.e.'', work mediated by thermal energy. Free energy is subject to irreversible loss in the course of such work. Since first-law energy is always conserved, it is evident that free energy is an expendable, second-law kind of energy. Several free energy functions may be formulated based on system criteria. Free energy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |