|
1873 In Science
The year 1873 in science and technology involved some significant events, listed below. Chemistry * Jacobus Henricus van 't Hoff and Joseph Achille Le Bel, working independently, develop a model of chemical bonds, chemical bonding that explains the chirality experiments of Pasteur and provides a physical cause for optical activity in chiral compounds Exploration * The Austro-Hungarian North Pole Expedition discovers Franz-Josef Land Mathematics * Charles Hermite proves that the mathematical constant ''e (mathematical constant), e'' is a transcendental number * Henri Brocard introduces the Brocard points, Brocard triangle and Brocard circle Meteorology * September 15 – agreement for establishment of the International Meteorological Organization. Physics * February 20 – English electrical engineer Willoughby Smith publishes his discovery of the photoconductivity of the element selenium * June 14 – Johannes Diderik van der Waals defends his thesis, Over de Continuiteit v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematical Association
The Mathematical Association is a professional society concerned with mathematics education in the UK. History It was founded in 1871 as the Association for the Improvement of Geometrical Teaching and renamed to the Mathematical Association in 1897. It was the first teachers' subject organisation formed in England. In March 1927, it held a three-day meeting in Grantham to commemorate the bicentenary of the death of Sir Isaac Newton, attended by Sir J. J. Thomson (discoverer of the electron), Sir Frank Watson Dyson – the Astronomer Royal, Sir Horace Lamb, and G. H. Hardy. In 1951, Mary Cartwright became the first female president of the Mathematical Association. In the 1960s, when comprehensive education was being introduced, the Association was in favour of the 11-plus system. For maths teachers training at university, a teaching award that was examined was the Diploma of the Mathematical Association, later known as the Diploma in Mathematical Education of the Mathema ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gibbs Free Energy
In thermodynamics, the Gibbs free energy (or Gibbs energy as the recommended name; symbol is a thermodynamic potential that can be used to calculate the maximum amount of Work (thermodynamics), work, other than Work (thermodynamics)#Pressure–volume work, pressure–volume work, that may be performed by a closed system, thermodynamically closed system at constant temperature and pressure. It also provides a necessary condition for processes such as chemical reactions that may occur under these conditions. The Gibbs free energy is expressed as G(p,T) = U + pV - TS = H - TS where: * U is the internal energy of the system * H is the enthalpy of the system * S is the entropy of the system * T is the temperature of the system * V is the volume of the system * p is the pressure of the system (which must be equal to that of the surroundings for mechanical equilibrium). The Gibbs free energy change (, measured in joules in International System of Units, SI) is the ''maximum'' amount of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Association For The Advancement Of Science
The British Science Association (BSA) is a Charitable organization, charity and learned society founded in 1831 to aid in the promotion and development of science. Until 2009 it was known as the British Association for the Advancement of Science (BA). The current Chief Executive is Hannah Russell. The BSA's mission is to get more people engaged in the field of science by coordinating, delivering, and overseeing different projects that are suited to achieve these goals. The BSA "envisions a society in which a diverse group of people can learn and apply the sciences in which they learn." and is managed by a professional staff located at their Head Office in the Wellcome Wolfson Building. The BSA offers a wide variety of activities and events that both recognise and encourage people to be involved in science. These include the British Science Festival, British Science Week, the CREST Awards, For Thought, The Ideas Fund, along with regional and local events. History Foundation Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecule
A molecule is a group of two or more atoms that are held together by Force, attractive forces known as chemical bonds; depending on context, the term may or may not include ions that satisfy this criterion. In quantum physics, organic chemistry, and biochemistry, the distinction from ions is dropped and ''molecule'' is often used when referring to polyatomic ions. A molecule may be homonuclear, that is, it consists of atoms of one chemical element, e.g. two atoms in the oxygen molecule (O2); or it may be heteronuclear, a chemical compound composed of more than one element, e.g. water (molecule), water (two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom; H2O). In the kinetic theory of gases, the term ''molecule'' is often used for any gaseous particle regardless of its composition. This relaxes the requirement that a molecule contains two or more atoms, since the noble gases are individual atoms. Atoms and complexes connected by non-covalent interactions, such as hydrogen bonds or ionic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Clerk Maxwell
James Clerk Maxwell (13 June 1831 – 5 November 1879) was a Scottish physicist and mathematician who was responsible for the classical theory of electromagnetic radiation, which was the first theory to describe electricity, magnetism and light as different manifestations of the same phenomenon. Maxwell's equations for electromagnetism achieved the Unification (physics)#Unification of magnetism, electricity, light and related radiation, second great unification in physics, where Unification (physics)#Unification of gravity and astronomy, the first one had been realised by Isaac Newton. Maxwell was also key in the creation of statistical mechanics. With the publication of "A Dynamical Theory of the Electromagnetic Field" in 1865, Maxwell demonstrated that electric force, electric and magnetic fields travel through space as waves moving at the speed of light. He proposed that light is an undulation in the same medium that is the cause of electric and magnetic phenomena. (Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
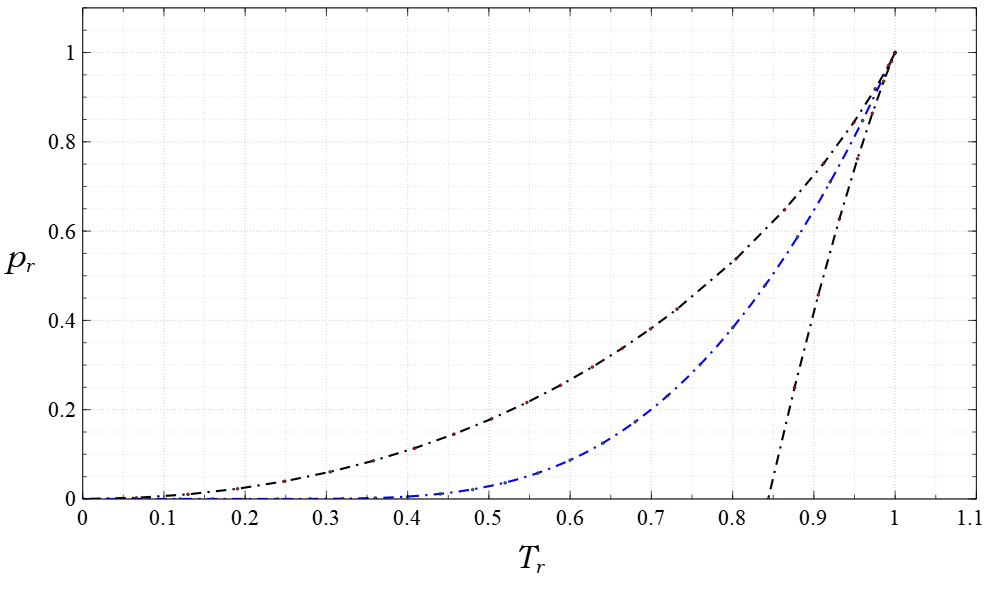
Van Der Waals Equation
The van der Waals equation is a mathematical formula that describes the behavior of real gases. It is an equation of state that relates the pressure, volume, Avogadro's law, number of molecules, and temperature in a fluid. The equation modifies the ideal gas law in two ways: first, it considers particles to have a finite diameter (whereas an ideal gas consists of point particles); second, its particles interact with each other (unlike an ideal gas, whose particles move as though alone in the volume). The equation is named after Dutch physicist Johannes Diderik van der Waals, who first derived it in 1873 as part of his doctoral thesis. Van der Waals based the equation on the idea that fluids are composed of discrete particles, which few scientists believed existed. However, the equation accurately predicted the behavior of a fluid around its Critical point (thermodynamics), critical point, which had been discovered a few years earlier. Its qualitative and quantitative agreement w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Condensation
Condensation is the change of the state of matter from the gas phase into the liquid phase, and is the reverse of vaporization. The word most often refers to the water cycle. It can also be defined as the change in the state of water vapor to liquid water when in contact with a liquid or solid surface or cloud condensation nuclei within the atmosphere. When the transition happens from the gaseous phase into the solid phase directly, the change is called deposition. Condensation is usually associated with water. Initiation Condensation is initiated by the formation of atomic/molecular clusters of that species within its gaseous volume—like rain drop or snow flake formation within clouds—or at the contact between such gaseous phase and a liquid or solid surface. In clouds, this can be catalyzed by water-nucleating proteins, produced by atmospheric microbes, which are capable of binding gaseous or liquid water molecules. Reversibility scenarios A few distinct rev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leiden University
Leiden University (abbreviated as ''LEI''; ) is a Public university, public research university in Leiden, Netherlands. Established in 1575 by William the Silent, William, Prince of Orange as a Protestantism, Protestant institution, it holds the distinction of being the oldest university in the Netherlands of today. During the Dutch Golden Age scholars from around Europe were attracted to the Dutch Republic for its climate of intellectual tolerance. Individuals such as René Descartes, Rembrandt, Christiaan Huygens, Hugo Grotius, Benedictus Spinoza, and later Baron d'Holbach were active in Leiden and environs. The university has seven academic faculties and over fifty subject departments, housing more than forty national and international research institutes. Its historical primary campus consists of several buildings spread over Leiden, while a second campus located in The Hague houses a liberal arts college (Leiden University College The Hague) and several of its faculties. It i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johannes Diderik Van Der Waals
Johannes Diderik van der Waals (; 23 November 1837 – 8 March 1923) was a Dutch theoretical physicist who received the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1910 "for his work on the equation of state for gases and liquids". Van der Waals started his career as a schoolteacher. He became the first physics professor of the University of Amsterdam when its status was upgraded to Municipal University in 1877. His name is primarily associated with the van der Waals equation, an equation of state that describes the behavior of gases and their condensation to the liquid phase. His name is also associated with van der Waals forces (forces between stable molecules), with van der Waals molecules (small molecular clusters bound by van der Waals forces), and with the van der Waals radius (size of molecules). James Clerk Maxwell once said that, "there can be no doubt that the name of Van der Waals will soon be among the foremost in molecular science." In his 1873 thesis, Van der Waals noted the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nature (journal)
''Nature'' is a British weekly scientific journal founded and based in London, England. As a multidisciplinary publication, ''Nature'' features Peer review, peer-reviewed research from a variety of academic disciplines, mainly in science and technology. It has core editorial offices across the United States, continental Europe, and Asia under the international scientific publishing company Springer Nature. ''Nature'' was one of the world's most cited scientific journals by the Science Edition of the 2022 ''Journal Citation Reports'' (with an ascribed impact factor of 50.5), making it one of the world's most-read and most prestigious academic journals. , it claimed an online readership of about three million unique readers per month. Founded in the autumn of 1869, ''Nature'' was first circulated by Norman Lockyer and Alexander MacMillan (publisher), Alexander MacMillan as a public forum for scientific innovations. The mid-20th century facilitated an editorial expansion for the j ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Selenium
Selenium is a chemical element; it has symbol (chemistry), symbol Se and atomic number 34. It has various physical appearances, including a brick-red powder, a vitreous black solid, and a grey metallic-looking form. It seldom occurs in this elemental state or as pure ore compounds in Earth's crust. Selenium ( ) was discovered in 1817 by , who noted the similarity of the new element to the previously discovered tellurium (named for the Earth). Selenium is found in :Sulfide minerals, metal sulfide ores, where it substitutes for sulfur. Commercially, selenium is produced as a byproduct in the refining of these ores. Minerals that are pure selenide or selenate compounds are rare. The chief commercial uses for selenium today are glassmaking and pigments. Selenium is a semiconductor and is used in photocells. Applications in electronics, once important, have been mostly replaced with silicon semiconductor devices. Selenium is still used in a few types of Direct current, DC power surge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |