|
183rd Tunnelling Company
The 183rd Tunnelling Company was one of the tunnelling companies of the Royal Engineers created by the British Army during World War I. The tunnelling units were occupied in offensive and defensive mining involving the placing and maintaining of mines under enemy lines, as well as other underground work such as the construction of deep dugouts for troop accommodation, the digging of subways, saps (a narrow trench dug to approach enemy trenches), cable trenches and underground chambers for signals and medical services.The Tunnelling Companies RE , access date 25 April 2015 Background By January 1915 it had become evident to the BEF at the[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting took place mainly in European theatre of World War I, Europe and the Middle Eastern theatre of World War I, Middle East, as well as in parts of African theatre of World War I, Africa and the Asian and Pacific theatre of World War I, Asia-Pacific, and in Europe was characterised by trench warfare; the widespread use of Artillery of World War I, artillery, machine guns, and Chemical weapons in World War I, chemical weapons (gas); and the introductions of Tanks in World War I, tanks and Aviation in World War I, aircraft. World War I was one of the List of wars by death toll, deadliest conflicts in history, resulting in an estimated World War I casualties, 10 million military dead and more than 20 million wounded, plus some 10 million civilian de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herbert Kitchener, 1st Earl Kitchener
Field Marshal Horatio Herbert Kitchener, 1st Earl Kitchener (; 24 June 1850 – 5 June 1916) was a British Army officer and colonial administrator. Kitchener came to prominence for his imperial campaigns, his involvement in the Second Boer War, and his central role in the early part of the First World War. Kitchener was credited in 1898 for having won the Battle of Omdurman and securing control of the Sudan, for which he was made Baron Kitchener of Khartoum. As Chief of Staff (1900–1902) in the Second Boer WarAnon."Kitchener of Khartoum, Viscount" in ''Debrett's peerage, baronetage, knightage, and companionage'', London: Dean & Son, 1903, p. 483-484. he played a key role in Lord Roberts' conquest of the Boer Republics, then succeeded Roberts as commander-in-chief – by which time Boer forces had taken to guerrilla fighting and British forces imprisoned Boer and African civilians in concentration camps. His term as commander-in-chief (1902–1909) of the Army in India ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Battalions Of The South Wales Borderers
This is a list of battalions of the South Wales Borderers from its formation in 1881 until its final amalgamation in 1969. Origin of the regiment First formed in 1689 and originally known by the names of its colonels, the 24th Foot received its number in 1751 and its subtitle '(2nd Warwickshire)' in 1782. The 2nd Battalion existed from 1804 to 1814 and was reformed in 1858.Frederick, pp. 292–4. Under the 'Localisation of the Forces' scheme introduced in 1872 by the Cardwell Reforms, each regiment of the line established a permanent depot in a county or region, to which the local militia and volunteer battalions were affiliated. The 24th Foot's links to Warwickshire were tenuous, and it was assigned to Sub-District No 25 (Counties of Cardigan, Radnor and Monmouth) in South Wales. The depot was at Brecon, already the headquarters of the Royal South Wales Borderers Militia (Royal Brecon and Radnor Rifles).''Army List'', various dates. Under the Childers Reforms of 1881 the lin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wales
Wales ( ) is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is bordered by the Irish Sea to the north and west, England to the England–Wales border, east, the Bristol Channel to the south, and the Celtic Sea to the south-west. , it had a population of 3.2 million. It has a total area of and over of Coastline of Wales, coastline. It is largely mountainous with its higher peaks in the north and central areas, including Snowdon (), its highest summit. The country lies within the Temperate climate, north temperate zone and has a changeable, Oceanic climate, maritime climate. Its capital and largest city is Cardiff. A distinct Culture of Wales, Welsh culture emerged among the Celtic Britons after the End of Roman rule in Britain, Roman withdrawal from Britain in the 5th century, and Wales was briefly united under Gruffudd ap Llywelyn in 1055. After over 200 years of war, the Conquest of Wales by Edward I, conquest of Wales by King Edward I o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint-Omer
Saint-Omer (; ; Picard: ''Saint-Onmé'') is a commune and sub-prefecture of the Pas-de-Calais department in France. It is west-northwest of Lille on the railway to Calais, and is located in the Artois province. The town is named after Saint Audomar, who brought Christianity to the area. The canalised section of the river Aa begins at Saint-Omer, reaching the North Sea at Gravelines in northern France. Below its walls, the Aa connects with the Neufossé Canal, which ends at the river Lys. History Saint-Omer first appeared in the writings during the 7th century under the name of Sithiu (Sithieu or Sitdiu), around the Saint-Bertin abbey founded on the initiative of Audomar, (Odemaars or Omer). Omer, bishop of Thérouanne, in the 7th century established the Abbey of Saint Bertin, from which that of Notre-Dame was an offshoot. Rivalry and dissension, which lasted till the French Revolution, soon sprang up between the two monasteries, becoming especially virulent when ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spring R
Spring(s) may refer to: Common uses * Spring (season), a season of the year * Spring (device), a mechanical device that stores energy * Spring (hydrology), a natural source of water * Spring (mathematics), a geometric surface in the shape of a helically coiled tube * Spring (political terminology), often used to name periods of political liberalization * Springs (tide), in oceanography, the maximum tide, occurs twice a month during the full and new moon Places * Spring (Milz), a river in Thuringia, Germany * Spring, Alabel, a barangay unit in Alabel, Sarangani Province, Philippines * Șpring, a commune in Alba County, Romania * Șpring (river), a river in Alba County, Romania * Springs, Gauteng, South Africa * Springs, the location of Dubai British School, Dubai * Spring Village, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines * Spring Village, Shropshire, England United States * Springs, New York, a part of East Hampton, New York * Springs, Pennsylvania, an unincorporated community * Spri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Bluff (Ypres)
The Actions of the Bluff were local operations in 1916 carried out in Flanders during the First World War by the German 4th Army and the British Second Army. The Bluff is a mound near St Eloi, south-east of Ypres in Belgium, created from a spoil heap made during the digging of the Ypres– Comines Canal before the war. From 14 to 15 February and on 2 March 1916, the Germans and the British fought for control of the Bluff, the Germans capturing the mound and defeating counter-attacks only for the British to recapture it and a stretch of the German front line, after pausing to prepare a set-piece attack. The fighting at the Bluff was one of nine sudden attacks for local gains made by the Germans or the British between the appointment of Sir Douglas Haig as commander in chief of the British Expeditionary Force (BEF), and the beginning of the Battle of the Somme. The BEF was at a tactical disadvantage, on low boggy ground, easily observed from German positions. A retirement to mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
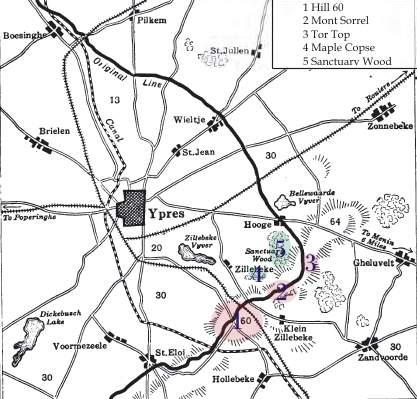
Sanctuary Wood Cemetery
Sanctuary Wood Cemetery is a Commonwealth War Graves Commission (CWGC) cemetery for the dead of the First World War, 5 km east of Ypres, Belgium, near Hooge in the municipality of Zillebeke. Located off the main Ypres-Menin Road on ''Canadalaan'' (Canada Lane). The Canadian Hill 62 Memorial is 100 metres further down the road from the cemetery. Sanctuary Wood itself was named by British troops in November 1914 when it was used to shelter troops. Fighting took place in it in September 1915 and it was fought over by Canadian and German soldiers during the Battle of Mount Sorrel in early June 1916. Three small Commonwealth cemeteries were established in it between May and August 1915 but were largely obliterated during the Battle of Mount Sorrel. When the war finished, traces of one of them were found, containing 137 graves, and became the core of the present Sanctuary Wood Cemetery. It was greatly expanded between 1927 and 1932 with graves being moved in from surrounding ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RE Grave, Railway Wood
RE Grave, Railway Wood is a Commonwealth War Graves Commission (CWGC) memorial and war grave located in the Ypres Salient on the Western Front. It is located on the Bellewaerde Ridge near Zillebeke, about 4 kilometres east of Ypres, and a little north of Hooge. The area of the ''Cambridge Road'' sector, halfway in between Wieltje and Hooge, was the site of intensive underground fighting in the First World War. The Liverpool Scottish Memorial, Railway Wood is located nearby. History The Royal Engineers grave at Railway Wood marks the site where twelve soldiers (eight Royal Engineers of the 177th Tunnelling Company and four attached infantrymen) were killed between November 1915 and August 1917 whilst tunnelling under the hill near Hooge during the defence of Ypres. The men were trapped underground and their bodies not recovered, and after the war, the memorial was erected on the hill. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
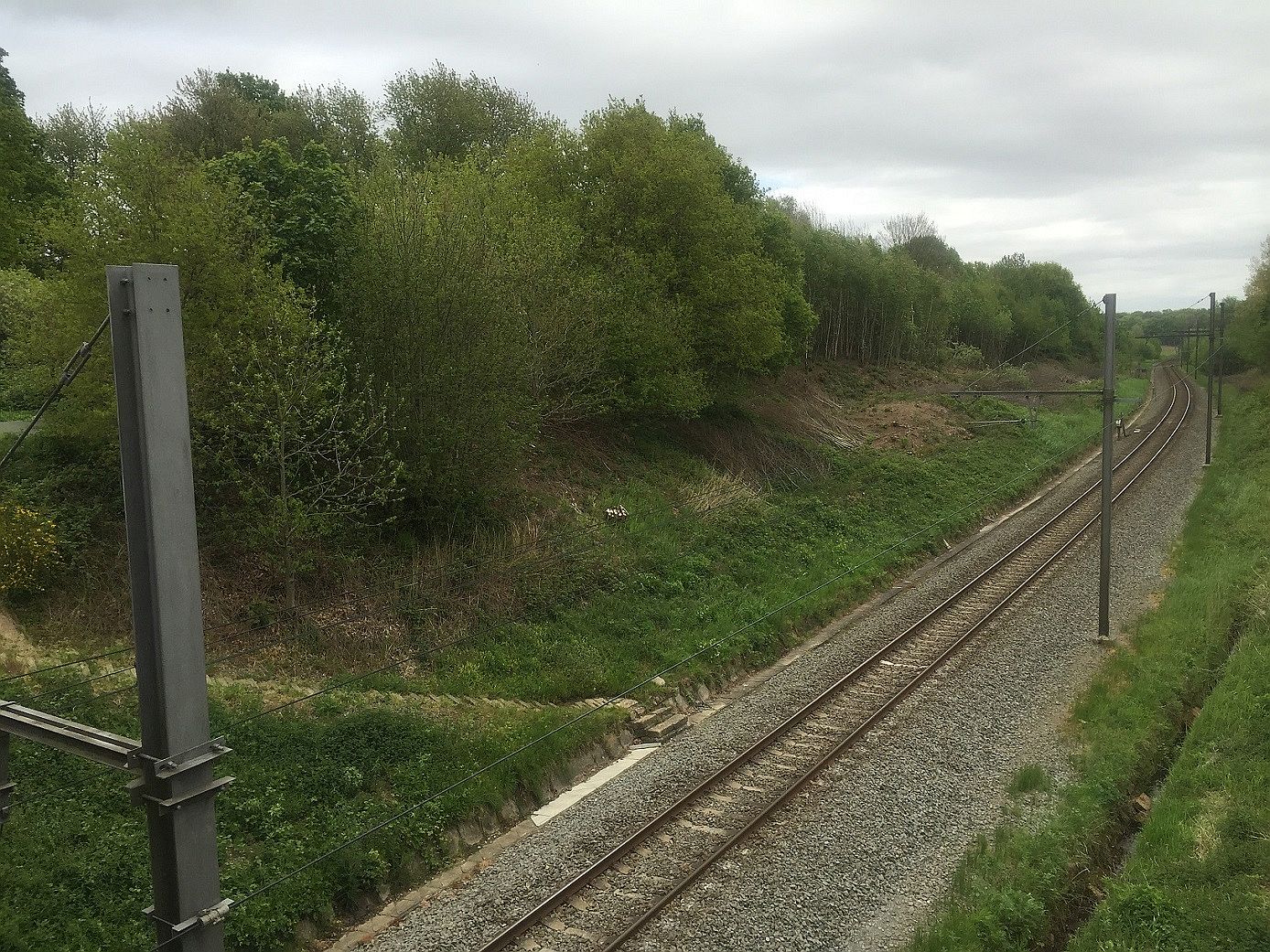
Hill 60 (Ypres)
Hill 60 is a World War I battlefield memorial site and park in the Zwarteleen area of Zillebeke south of Ypres, Belgium. It is located about from the centre of Ypres and is directly on the railway line to Comines. Before the First World War the hill was known locally as (Lover's Knoll). The site comprises two areas of raised land separated by the railway line; the northern area was known by soldiers as ''Hill 60'' while the southern part was known as ''The Caterpillar''. Background Origin The high ground of Hill 60, south of Zillebeke, was created in the 1850s by spoil dumped from the cutting of the railway line between Ypres and Comines-Warneton, Comines. The line opened in March 1854 and formed part of the La Madeleine–Comines List of railway lines in France, railway from the French Nord-Pas-de-Calais regions of France, region into Belgian Flanders. The earth excavated during the building of the railway was dumped on either side of the embankment and formed hillocks. On ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hooge In World War I
In World War I, the area around Hooge on Bellewaerde Ridge, about east of Ypres in Flanders in Belgium, was one of the easternmost sectors of the Ypres Salient and was the site of much fighting between German and Allied forces. Within a radius of Hooge are the sites of Château Wood, Sanctuary Wood, Railway Wood and Menin Road. There are four Commonwealth War Graves Commission (CWGC) war cemeteries in this area and several museums and memorials. Hill 62 and Mount Sorrel (Also Mont Sorrel) are further south, while the sites known to British and Commonwealth soldiers as Stirling Castle and Clapham Junction are further east. Background Hooge For much of the war, Hooge was one of the easternmost sectors of the Ypres Salient, being almost constantly exposed to enemy attacks from three sides. After the First Battle of Ypres in 1914, the front line of the salient ran through the Hooge area and there was almost constant fighting in the region over the next three years, durin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
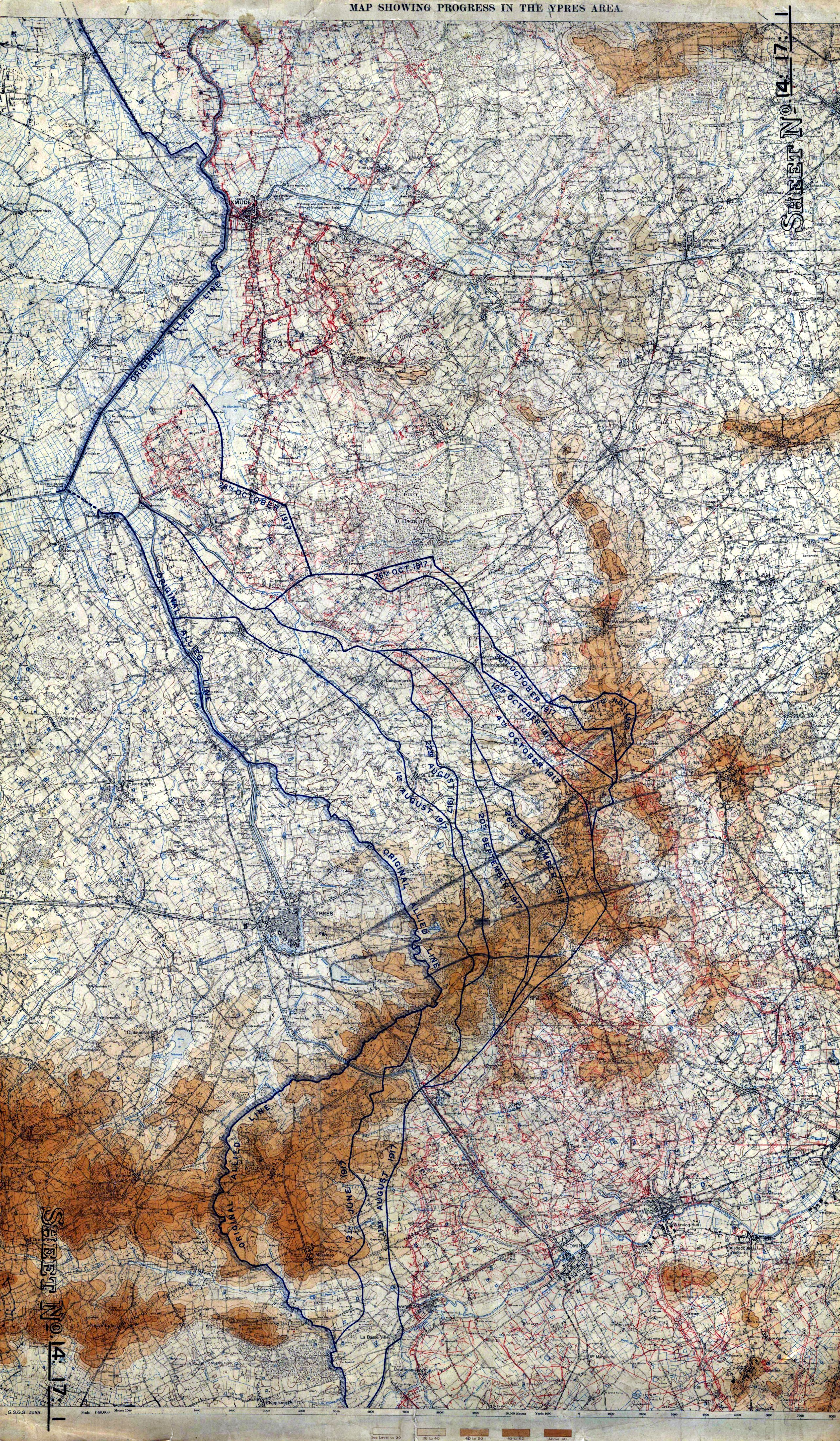
Ypres Salient
The Ypres Salient, around Ypres, in Belgium, was the scene of several battles and a major part of the Western Front during World War I. Location Ypres lies at the junction of the Ypres–Comines Canal and the Ieperlee. The city is overlooked by Kemmel Hill in the south-west and from the east by low hills running south-west to north-east with Wytschaete ( Wijtschate), Hill 60 to the east of Verbrandenmolen, Hooge, Polygon Wood and Passchendaele ( Passendale). The high point of the ridge is at Wytschaete, from Ypres, while at Hollebeke the ridge is distant and recedes to at Polygon Wood. Wytschaete is about above the plain; on the Ypres–Menin road at Hooge, the elevation is about and at Passchendaele. The rises are slight, apart from the vicinity of Zonnebeke, which has a From Hooge and to the east, the slope is near Hollebeke, it is heights are subtle but have the character of a saucer lip around Ypres. The main ridge has spurs sloping east and one is particularly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |