|
1827 In Science
The year 1827 in science and technology involved some significant events, listed below. Chemistry * April 7 – John Walker (inventor), John Walker begins selling his invention, the "Lucifer" friction match, in England. * Aluminium isolated by Friedrich Wöhler. * William Prout classifies the components of food into the three main divisions of carbohydrates, fats and proteins. * Zeise's salt is the first platinum/olefin complex, an early example of organometallic chemistry. Exploration * William Edward Parry reaches 82°45'N, which will remain for 49 years the highest latitude attained. Geology * Gideon Mantell publishes his ''Illustrations of the Geology of Sussex'', including the first use of the binomial ''Megalosaurus bucklandii''. * George Julius Poulett Scrope, G. Poulett Scrope publishes his ''Memoir on the Geology of Central France, including the volcanic formations…'', extending by detailed observation his work on volcanology. History of science * John Farey Jr., J ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Megalosaurus Bucklandii
''Megalosaurus'' (meaning "great lizard", from Ancient Greek, Greek , ', meaning 'big', 'tall' or 'great' and , ', meaning 'lizard') is an extinct genus of large carnivorous theropod dinosaurs of the Middle Jurassic Epoch (Bathonian stage, 166 million years ago) of southern England. Although fossils from other areas have been assigned to the genus, the only certain remains of ''Megalosaurus'' come from Oxfordshire and date to the late Middle Jurassic. The earliest remains of ''Megalosaurus'' were described in the 17th century, and were initially interpreted as the remains of elephants or giants. ''Megalosaurus'' was named in 1824 by William Buckland, becoming the first genus of (non-avian) dinosaur to be validly named. The type species is ''M. bucklandii'', named in 1827 by Gideon Mantell, after Buckland. In 1842, ''Megalosaurus'' was one of three genera on which Richard Owen based his Dinosauria, along with ''Iguanodon'' and ''Hylaeosaurus''. On Owen's directions a model was ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wellcome Institute
The Wellcome Institute for the History of Medicine (1968–1999) was a London centre for the study and teaching of medical history. It consisted of the Wellcome Library and an Academic Unit. The former was and is a world-class library collection owned and managed by the Wellcome Trust and staffed by librarians including academic librarians who held honorary lectureships at University College London. The Academic Unit was a group of university staff appointed at University College London that conducted a programme of university teaching, thesis supervision, seminars, conferences and publications. Directors of the Wellcome Historical Medical Museum and of the Wellcome Institute for the History of Medicine * 1913–1936 Henry S. Wellcome, LLD, DSc, FRS (Founder and Director) * 1913–1925 C. J. S. Thompson, MBE (Curator) * 1925–1934 L. W. G. Malcolm, MSc, PhD, FRSE (Conservator) * 1934–1947 Captain Peter J. Johnston-Saint, MA, FRSE (Conservator) ( photo) * 1941–194Dr S. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Adams (physician)
Robert Adams (1791 – 13 January 1875) was an Irish surgeon and was three times President of the Royal College of Surgeons in Ireland (RCSI), in 1840, 1860 and 1867. Early life and education Adams was born in 1791 in Dublin, Ireland and studied at Trinity College Dublin between 1810 and 1814. He received his Bachelor of Arts, B.A. in 1814. He began his medical school, medical training under William Hartigan and George Stewart, leading Dublin surgeons. He was elected a fellow of the RCSI in 1818 and then went abroad to complete his medical and surgical training. Adams did not take the M.B. degree until 1842. In that year he became an M.D., and in 1861 received the newly instituted qualification of Master in Surgery. The greater part of Adams' anatomical studies were undertaken in the RCSI under Abraham Colles. In 1816, he obtained the Letters Testimonial, and on 2 November 1818, he was promoted to Membership of the College. He was elected surgeon to the Jervis Street Hospital and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edinburgh
Edinburgh is the capital city of Scotland and one of its 32 Council areas of Scotland, council areas. The city is located in southeast Scotland and is bounded to the north by the Firth of Forth and to the south by the Pentland Hills. Edinburgh had a population of in , making it the List of towns and cities in Scotland by population, second-most populous city in Scotland and the List of cities in the United Kingdom, seventh-most populous in the United Kingdom. The Functional urban area, wider metropolitan area had a population of 912,490 in the same year. Recognised as the capital of Scotland since at least the 15th century, Edinburgh is the seat of the Scottish Government, the Scottish Parliament, the Courts of Scotland, highest courts in Scotland, and the Palace of Holyroodhouse, the official residence of the Monarchy of the United Kingdom, British monarch in Scotland. It is also the annual venue of the General Assembly of the Church of Scotland. The city has long been a cent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
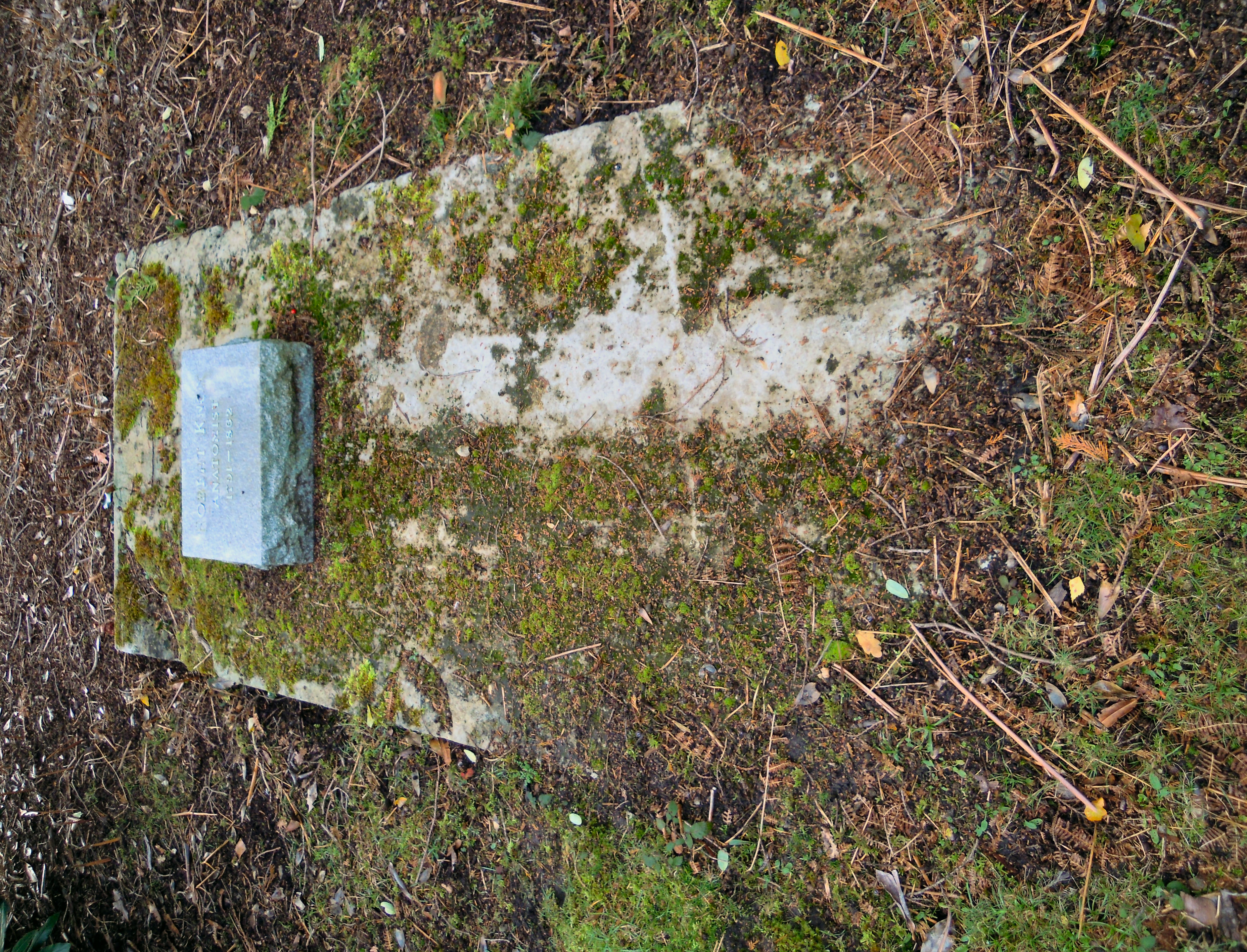
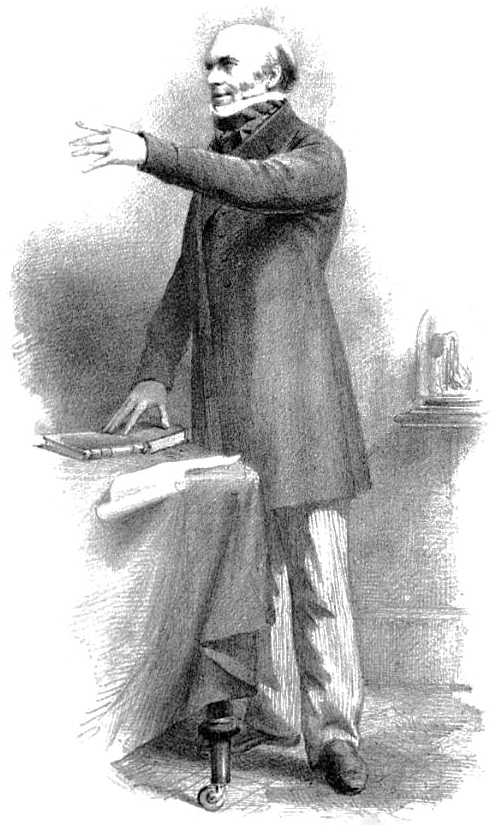
Robert Knox (surgeon)
Robert Knox (4 September 1791 – 20 December 1862) was a Scottish anatomist and ethnologist best known for his involvement in the Burke and Hare murders. Born in Edinburgh, Scotland, Knox eventually partnered with anatomist and former teacher John Barclay (anatomist), John Barclay and became a lecturer on anatomy in the city, where he introduced the theory of transcendental anatomy. However, Knox's incautious methods of obtaining cadavers for dissection before the passage of the Anatomy Act 1832 and disagreements with professional colleagues ruined his career in Scotland. Following these developments, he moved to London, though this did not revive his career. Knox's views on humanity gradually shifted over the course of his lifetime, as his initially positive views (influenced by the ideals of Étienne Geoffroy Saint-Hilaire) gave way to a more pessimistic view. Knox also devoted the latter part of his career to studying and theorising on evolution and ethnology; during this ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dissection
Dissection (from Latin ' "to cut to pieces"; also called anatomization) is the dismembering of the body of a deceased animal or plant to study its anatomical structure. Autopsy is used in pathology and forensic medicine to determine the cause of death in humans. Less extensive dissection of plants and smaller animals preserved in a formaldehyde solution is typically carried out or demonstrated in biology and natural science classes in middle school and high school, while extensive dissections of cadavers of adults and children, both fresh and preserved are carried out by medical students in medical schools as a part of the teaching in subjects such as anatomy, pathology and forensic medicine. Consequently, dissection is typically conducted in a morgue or in an anatomy lab. Dissection has been used for centuries to explore anatomy. Objections to the use of cadavers have led to the use of alternatives including virtual dissection of computational anatomy, computer models. In the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burke And Hare
The Burke and Hare murders were a series of sixteen murders committed over a period of about ten months in 1828 in Edinburgh, Scotland. They were undertaken by William Burke and William Hare, who sold the corpses to Robert Knox for dissection at his anatomy lectures. Edinburgh was a leading European centre of anatomical study in the early 19th century, in a time when the demand for cadavers led to a shortfall in legal supply. Scottish law required that corpses used for medical research should only come from those who had died in prison, suicide victims, or from foundlings and orphans. The shortage of corpses led to an increase in body snatching by what were known as "resurrection men". Measures to ensure graves were left undisturbed—such as the use of mortsafes—exacerbated the shortage. When a lodger in Hare's house died, he turned to his friend Burke for advice; they decided to sell the body to Knox. They received what was, for them, the generous sum of £7 10 s. A little ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antoine Clot
Antoine Barthelemy Clot (7 November 1793 – 28 August 1868) was a French doctor known as Clot Bey while practicing in Egypt. Early life and education He was born at Grenoble. In 1823, he graduated in medicine and surgery at Montpellier. His thesis for Doctor of Surgery was entitled ''Dangers of the Instrumental Manipulation in Obstetrical Delivery.'' Efforts in Egypt During the French occupation of Egypt, Napoleon designated Kasr al-Aini a hospital for his troops in 1799, and then afterwards proposed the opening of a school to teach local Egyptian students the medicine required to treat the troops. This is how, after practicing for a time at Marseille, Clot was invited by Muhammad Ali, Viceroy of Egypt to direct the Kasr al-Aini (Qasral-‘Ayni) School of Medicine at the Army hospital of Abou Zabel which later transferred to Cairo. The Viceroy of Egypt was determined to keep his army in good health and had sent emissaries to recruit doctors in Europe. On 24 January 1825, C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Egypt
Egypt ( , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a country spanning the Northeast Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to northern coast of Egypt, the north, the Gaza Strip of Palestine and Israel to Egypt–Israel barrier, the northeast, the Red Sea to the east, Sudan to Egypt–Sudan border, the south, and Libya to Egypt–Libya border, the west; the Gulf of Aqaba in the northeast separates Egypt from Jordan and Saudi Arabia. Cairo is the capital, list of cities and towns in Egypt, largest city, and leading cultural center, while Alexandria is the second-largest city and an important hub of industry and tourism. With over 109 million inhabitants, Egypt is the List of African countries by population, third-most populous country in Africa and List of countries and dependencies by population, 15th-most populated in the world. Egypt has one of the longest histories o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qasr El Eyni Hospital
Qasr El Eyni Hospital () is a research and teaching hospital in Cairo, Egypt. This hospital is affiliated with the Cairo University Faculty of Medicine. The hospital was founded on March 11, 1827. History In 1827, a medical school was established and attached to a military hospital in Abu Zaabal. The French doctor Antoine Clot Bey ( Antoine Clot) became the first director of the medical school and hospital. In 1837, the medical school and hospital were moved to Qasr El Eyni Street in Cairo. The hospital was renamed as "Qasr El Eyni hospital". In 1838, The first school for midwifery was established in Qasr El Eyni Hospital. In 1848, Clot Bey resigned and went back to France. In 1850, Abbas I appointed Wilhelm Griesinger as the director. In 1851, Griesinger's assistant Theodor Bilharz discovered the first known blood flukes, ''Schistosoma haematobium'' and '' Schistosoma mansoni,'' and with it the disease bilharzia (schistosomiasis). In 1855, Clot Bey was re-appointed di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |