|
17th Infantry (The Loyal Regiment)
The 17th Infantry (The Loyal Regiment) was an infantry regiment of the Bengal Army, later of the united British Indian Army. It was formed at Phillour in 1858 by Major J. C. Innes from men of the 3rd, 36th and 61st Bengal Native Infantry regiments who remained loyal to the British East India Company during the Indian Mutiny, and designated ''The Loyal Purbiah Regiment''.''Quarterly Indian Army List January'' 1919, p. 1086 These men were designated as Purbiyas, ''Purbiah'', or ''Poorbeah'' meaning Easterners and were recruited from the region stretching from Agra to Bihar. It was subsequently re-designated as follows:- *17th Regiment of Bengal Native Infantry – 1861 *17th (The Loyal Purbiah) Regiment of Bengal Native Infantry – 1864 *17th (The Loyal Purbiah) Regiment of Bengal Infantry –1885 *17th (The Loyal Regiment) of Bengal Infantry – 1898 *17th Musalman Rajput Infantry (The Loyal Regiment) – 1902 Its final designation came in 1903 with the Kitchener reforms of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Raj
The British Raj ( ; from Hindustani language, Hindustani , 'reign', 'rule' or 'government') was the colonial rule of the British The Crown, Crown on the Indian subcontinent, * * lasting from 1858 to 1947. * * It is also called Crown rule in India, * * * * or direct rule in India. * Quote: "Mill, who was himself employed by the British East India company from the age of seventeen until the British government assumed direct rule over India in 1858." * * The region under British control was commonly called India in contemporaneous usage and included areas directly administered by the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, United Kingdom, which were collectively called ''Presidencies and provinces of British India, British India'', and areas ruled by indigenous rulers, but under British British paramountcy, paramountcy, called the princely states. The region was sometimes called the Indian Empire, though not officially. As ''India'', it was a founding member of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kitchener Reforms
The Indian Army was the force of British India, until national independence in 1947. Formed in 1895 by uniting the three Presidency armies, it was responsible for the defence of both British India and the princely states, which could also have their own armies. As stated in the ''Imperial Gazetteer of India'', the "British Government has undertaken to protect the dominions of the Native princes from invasion and even from rebellion within: its army is organized for the defence not merely of British India, but of all possessions under the suzerainty of the King-Emperor." The Indian Army was a vital part of the British Empire's military forces, especially in World War I and World War II. The Indian Presidency armies were originally under East India Company command, and comprised the Bengal Army, Madras Army, and Bombay Army. After the Indian Rebellion of 1857, all company troops were transferred to the British Crown. In 1879, the Presidency armies were integrated into a system of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Honourable East India Company Regiments
''The Honourable'' (Commonwealth English) or ''The Honorable'' (American English; see spelling differences) (abbreviation: ''Hon.'', ''Hon'ble'', or variations) is an honorific style that is used as a prefix before the names or titles of certain people, usually with official governmental or diplomatic positions. Use by governments International diplomacy In international diplomatic relations, representatives of foreign states are often styled as ''The Honourable''. Deputy chiefs of mission, , consuls-general, consuls and honorary consuls are always given the style. All heads of consular posts, whether they are honorary or career postholders, are accorded the style according to the State Department of the United States. However, the style ''Excellency'' instead of ''The Honourable'' is used for ambassadors and high commissioners only. Africa Democratic Republic of the Congo In the Democratic Republic of the Congo, the prefix 'Honourable' or 'Hon.' is used for members of bot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Indian Army Infantry Regiments
British may refer to: Peoples, culture, and language * British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories and Crown Dependencies. * British national identity, the characteristics of British people and culture * British English, the English language as spoken and written in United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland and, more broadly, throughout the British Isles * Celtic Britons, an ancient ethno-linguistic group * Brittonic languages, a branch of the Insular Celtic language family (formerly called British) ** Common Brittonic, an ancient language Other uses *People or things associated with: ** Great Britain, an island ** British Isles, an island group ** United Kingdom, a sovereign state ** British Empire, a historical global colonial empire ** Kingdom of Great Britain (1707–1800) ** United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland (1801–1922) * British Raj, colonial India under the British Empire * British Hong Kong, colonial H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
11th Indian Division
The 11th Indian Division was an infantry division of the British Indian Army during World War I. It was formed in December 1914 with two infantry brigades already in Egypt and a third formed in January 1915. After taking part in the Actions on the Suez Canal, the division was dispersed as its brigades were posted away. The division was commanded throughout its existence by Major-General Alexander Wallace. History The pre-war 22nd (Lucknow) Brigade and the 32nd (Imperial Service) Brigade (formed in October 1914) were posted to Egypt to help defend the Suez Canal. The 11th Indian Division was formed on 24 December 1914 with these two brigades, and little else in terms of divisional troops. A third brigade ( 31st) was formed in January 1915 with other units already in Egypt. The division beat off Turkish attempts to cross the Suez Canal on 3–4 February 1915 in the Actions on the Suez Canal. Thereafter, the division was dissolved in May 1915 with its brigades posted t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
8th Lucknow Division
The 8th (Lucknow) Division was a formation of the British Indian Army's Northern Army that was first formed as a result of the Kitchener reforms of the Indian Army in 1903. The Division remained in India on internal security duties during World War I, though the 8th (Lucknow) Cavalry Brigade was transferred to the 1st Indian Cavalry Division and served in France on the Western Front, and the 22nd Lucknow Infantry Brigade served as part of the 11th Indian Division in Egypt. Division formation in 1914 8th (Lucknow) Cavalry Brigade :''Commander: Major General Cookson'' *1st King's Dragoon Guards *16th Cavalry *36th Jacob's Horse * 39th Central India Horse 22nd (Lucknow) Brigade :''Commander: Major General A. Wilson'' *3rd Battalion, Royal Fusiliers *1st Battalion, King's Own Scottish Borderers *17th Infantry (The Loyal Regiment) *36th Sikhs *74th Punjabis *U Battery, Royal Horse Artillery * V Brigade, Royal Field Artillery **63rd, 64th and 73rd Batteries Fyzabad Brigade :''Comm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
22nd (Lucknow) Brigade
The Lucknow Brigade was an infantry brigade of the British Indian Army formed in 1907 as a result of the Kitchener Reforms. It was mobilized as 22nd (Lucknow) Brigade at the outbreak of the First World War as part of Indian Expeditionary Force E. It served in Egypt in 1915 before being broken up in January 1916. The brigade was reformed in India in 1917 for internal security duties and to aid the expansion of the Indian Army in the last year of the war. It remained part of the British Indian Army between the wars under several designations and was the 6th (Lucknow) Infantry Brigade in September 1939. History The Kitchener Reforms, carried out during Herbert Kitchener, 1st Earl Kitchener, Lord Kitchener's tenure as Commander-in-Chief, India (1902–09), completed the unification of the three former Presidency armies, the Frontier Force (other), Punjab Frontier Force, the Hyderabad Contingent and other local forces into one British Indian Army, Indian Army. Kitchener ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting took place mainly in European theatre of World War I, Europe and the Middle Eastern theatre of World War I, Middle East, as well as in parts of African theatre of World War I, Africa and the Asian and Pacific theatre of World War I, Asia-Pacific, and in Europe was characterised by trench warfare; the widespread use of Artillery of World War I, artillery, machine guns, and Chemical weapons in World War I, chemical weapons (gas); and the introductions of Tanks in World War I, tanks and Aviation in World War I, aircraft. World War I was one of the List of wars by death toll, deadliest conflicts in history, resulting in an estimated World War I casualties, 10 million military dead and more than 20 million wounded, plus some 10 million civilian de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sudan Campaign
The Mahdist War (; 1881–1899) was fought between the Mahdist Sudanese, led by Muhammad Ahmad bin Abdullah, who had proclaimed himself the "Mahdi" of Islam (the "Guided One"), and the forces of the Khedivate of Egypt, initially, and later the forces of Britain. After four years, the Mahdist rebels overthrew the Ottoman-Egyptian administration with the fall of Khartoum and gained control over Sudan. The Mahdist State launched several unsuccessful invasions of their neighbours, expanding the scale of the conflict to also include the Italian Empire, the Congo Free State and the Ethiopian Empire. They also faced significant internal rebellion. Anglo-Egyptian forces reconquered Sudan in 1898 and the Mahdist state collapsed following defeat at the battle of Omdurman. The last organised resistance from the Mahdists ended the next year, leading to the creation of Anglo-Egyptian Sudan (1899–1956), a ''de jure'' condominium of the British Empire, and the Kingdom of Egypt, in which Br ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
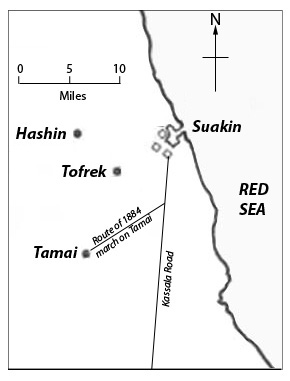
Suakin
Suakin or Sawakin (, Beja: ''Oosook'') is a port city in northeastern Sudan, on the west coast of the Red Sea. It was formerly the region's chief port, but is now secondary to Port Sudan, about north. Suakin used to be considered the height of medieval luxury on the Red Sea, but the old city built of coral is now in ruins. In 1983, the adjacent historic mainland town, known as the Geyf, had a population of 18,030 and the 2009 population was estimated at 43,337. Ferries run daily from Suakin to Jeddah in Saudi Arabia. Etymology The Beja name for Suakin is ''Oosook''. This is possibly from the Arabic word ''suq'', meaning market. In Beja, the locative case for this is ''isukib'', whence Suakin might have derived.Berg, RobertSuakin: Time and Tide. ''Saudi Aramco World.'' The spelling on Admiralty charts in the late 19th century was "Sauakin", but in the popular press "Suakim" was predominant. History Ancient Suakin was likely Ptolemy's Port of Good Hope, Limen Evangelis, whic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Tofrek
The Battle of Tofrek was fought on 22 March 1885 some 5 miles inland from the port of Suakin on the Red Sea coast of Sudan. A contingent of some 3,000 troops from the British and Indian Suakin Expedition#Second expedition, "Suakin Field Force" led by Major General John McNeill (British Army officer), Sir John Carstairs McNeill (under the overall command of General Gerald Graham) was attacked by a Mahdist War, Mahdist force under the leadership of Osman Digna. The Mahdists were heavily defeated, losing some 1,000 of their 2,000 fighters as compared to the loss of 70 British and Indian soldiers plus over 100 casualties. Background The sacking of Khartoum and the killing of Charles George Gordon, General Gordon and the massacre of thousands of civilians at the hands of Muhammad Ahmad, Mahdist warriors in January 1885, together with the failure of the relief effort of Garnet Wolseley, 1st Viscount Wolseley, General Wolseley's Nile Expedition, prompted the British government to revive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Anglo-Afghan War
The Second Anglo-Afghan War (Dari: جنگ دوم افغان و انگلیس, ) was a military conflict fought between the British Raj and the Emirate of Afghanistan from 1878 to 1880, when the latter was ruled by Sher Ali Khan of the Barakzai dynasty, the son of former Emir Dost Mohammad Khan (Emir of Afghanistan), Dost Mohammad Khan. The war was part of the Great Game between the British Empire, British and Russian empire, Russian empires. The war was split into two campaigns – the first began in November 1878 with the British Raj, British invasion of Afghanistan from British Raj, India. The British were quickly victorious and forced the Amir – Sher Ali Khan to flee. Ali's successor Mohammad Yaqub Khan immediately sued for peace and the Treaty of Gandamak was then signed on 26 May 1879. The British sent an envoy and mission led by Louis Cavagnari, Sir Louis Cavagnari to Kabul, but on 3 September this mission was massacred and the conflict was reignited by Mohammad Ayub Khan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |