|
1709 In Literature
This article contains information about the literary events and publications of 1709. Events *February 1 or 2 – Alexander Selkirk, the inspiration for ''Robinson Crusoe'', is rescued from the Juan Fernández Islands, where he was marooned, and begins his return to civilization. *April 12 – The magazine '' The Tatler'' is founded in London by Richard Steele, writing as Isaac Bickerstaff. On July 8 "Mrs. (Phoebe) Crackenthorpe" (perhaps Delarivier Manley) begins publication of ''The Female Tatler''. *April 26 – An act of the General Assembly of the Church of Scotland provides for public libraries in presbyteries. *May–October 20 – Delarivier Manley's ''roman à clef'' ''The New Atalantis (Secret Memoirs and Manners of Several Persons of Quality, of both Sexes, From The New Atalantis, an Island in the Mediterranean)'' is published in London (in two volumes, anonymously), purporting to be translated from Italian. Its satire of the Whigs is so scurrilous that the author i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Satire
Satire is a genre of the visual, literary, and performing arts, usually in the form of fiction and less frequently non-fiction, in which vices, follies, abuses, and shortcomings are held up to ridicule, often with the intent of exposing or shaming the perceived flaws of individuals, corporations, government, or society itself into improvement. Although satire is usually meant to be humorous, its greater purpose is often constructive social criticism, using wit to draw attention to both particular and wider issues in society. Satire may also poke fun at popular themes in art and film. A prominent feature of satire is strong irony or sarcasm—"in satire, irony is militant", according to literary critic Northrop Frye— but parody, burlesque, exaggeration, juxtaposition, comparison, analogy, and double entendre are all frequently used in satirical speech and writing. This "militant" irony or sarcasm often professes to approve of (or at least accept as natural) th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nicholas Rowe (writer)
Nicholas Rowe (; 20 June 1674 – 6 December 1718) was an English dramatist, poet and miscellaneous writer who was appointed Poet Laureate in 1715. His plays and poems were well-received during his lifetime, with one of his translations described as one of the greatest productions in English poetry. He was also considered the first editor of the works of William Shakespeare. Life Nicholas Rowe was born in Little Barford, Bedfordshire, England, son of John Rowe (d. 1692), barrister and sergeant-at-law, and Elizabeth, daughter of Jasper Edwards, on 20 June 1674. His family possessed a considerable estate at Lamerton in Devonshire. His father practised law and published Benlow's and Dallison's Reports during the reign of King James II. The future Poet Laureate was educated first at Highgate School, and then at Westminster School under the guidance of Richard Busby. In 1688, Rowe became a King's Scholar, which was followed by his entrance into Middle Temple in 1691. His en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shakespeare's Editors
Shakespeare's editors were essential in the development of the modern practice of producing printed books and the evolution of textual criticism. The 17th-century folio collections of the plays of William Shakespeare did not have editors in the modern sense of the term. In the best understanding of contemporary consensus scholarship, the plays to be included in the First Folio ( 1623) were gathered together or "compiled" by John Heminges and Henry Condell, two long-time colleagues of Shakespeare in the King's Men. The play manuscripts may have been proofread and prepared for printing by Edward Knight, the "book-keeper" or prompter of the company. The task of proofreading and correcting the actual printed pages of the Folio was left to the compositors and printers in the print-shop, yielding the uneven and often defective text that is the First Folio. Even less is known about the creation of the Second (1632), Third ( 1663–64), and Fourth Folios (1685) than about the First; se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
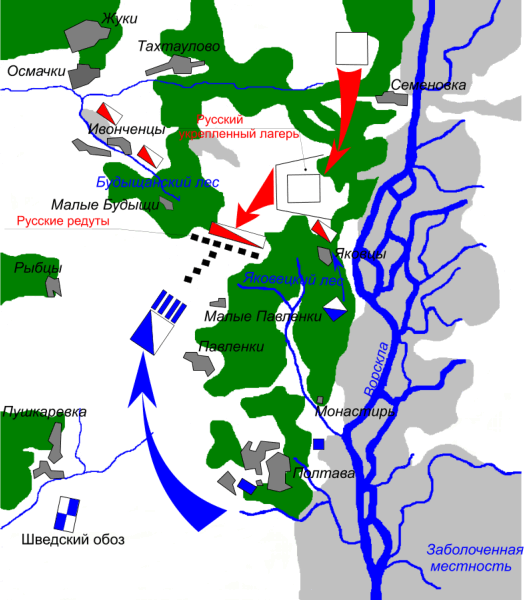
Battle Of Poltava
The Battle of Poltava took place 8 July 1709, was the decisive and largest battle of the Great Northern War. The Russian army under the command of Tsar Peter I defeated the Swedish army commanded by Carl Gustaf Rehnskiöld. The battle would lead to the Swedish Empire losing its status as a European great power and also marked the beginning of Russian supremacy in eastern Europe. During the course of six years in the initial stages of the war, King Charles XII and the Swedish Empire had defeated almost all participants in the anti-Swedish coalition, which initially consisted of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth, Denmark-Norway and the Tsardom of Russia. The latter, under , was the only one still fighting. Charles therefore chose to invade Russia in the autumn of 1707 and march towards Moscow with a large Swedish army. However, the campaign was complicated by harsh weather conditions and by Russian scorched earth tactics and surprise attacks, which forced Charles to interr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gustaf Adlerfelt
Gustaf Adlerfelt (1671 – June 28, 1709) was a Swedish historical writer born near Stockholm, brother of Pehr Adlerfelt. He was appointed by Charles XII "gentleman of the court" and afterwards accompanied him to his military campaigns, and writing a journal on them. He continues this work until his death in 1709 when he was killed by a cannonball in the Battle of Poltava The Battle of Poltava took place 8 July 1709, was the decisive and largest battle of the Great Northern War. The Russian army under the command of Tsar Peter I defeated the Swedish army commanded by Carl Gustaf Rehnskiöld. The battle would l .... References 1671 births 1709 deaths 17th-century Swedish nobility Caroleans 17th-century Swedish writers 17th-century male writers Swedish military writers 18th-century Swedish nobility Deaths by cannonball Writers from Stockholm {{Sweden-writer-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
June 28
Events Pre-1600 *1098 – Fighters of the First Crusade defeat Kerbogha, Kerbogha of Mosul at the Battle of Antioch (1098), battle of Antioch. *1360 – Muhammed VI, Sultan of Granada, Muhammed VI becomes the tenth Nasrid dynasty, Nasrid king of Emirate of Granada, Granada after killing his brother-in-law Ismail II, Sultan of Granada, Ismail II. *1461 – Edward, Earl of March, is crowned King Edward IV of England. *1495 – A French force heavily defeats a much larger Neapolitan and Spanish army at the battle of Seminara, leading to the creation of the Tercios by Gonzalo de Córdoba. *1519 – Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor, Charles V is elected Emperor of the Holy Roman Empire. *1575 – Sengoku period of Japan: The combined forces of Oda Nobunaga and Tokugawa Ieyasu are victorious in the Battle of Nagashino. 1601–1900 *1635 – Guadeloupe becomes a French colony. *1651 – The Battle of Berestechko between Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jacob Tonson
Jacob Tonson, sometimes referred to as Jacob Tonson the Elder (12 November 1655 – 17 March 1736), was an eighteenth-century English bookseller and publisher. Tonson published editions of John Dryden and John Milton, and is best known for having obtained a copyright on the plays of William Shakespeare by buying up the rights of the heirs of the publisher of the Fourth Book, Folio after the Statute of Anne went into effect. He was also the founder of the famous Kit-Cat Club. His nephew, Jacob Tonson the Younger (1682–1735), was his business partner. The business was continued by the younger Tonson's son, Jacob Tonson (1714–1767). History Scholars have not always been sure of Tonson's birthdate, and it has in the past been listed as occurring in 1655 or 1656. But the register of christenings in the parish of St Andrew Holborn (parish), St Andrew Holborn demonstrates that Tonson was born on 12 November 1655 and baptised on 18 November 1655. The register lists Tonson as the "s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Dryden
John Dryden (; – ) was an English poet, literary critic, translator, and playwright who in 1668 was appointed England's first Poet Laureate of the United Kingdom, Poet Laureate. He is seen as dominating the literary life of Restoration (England), Restoration England to such a point that the period came to be known in literary circles as the Age of Dryden. Romantic era, Romantic writer Sir Walter Scott called him "Glorious John". Early life Dryden was born in the village rectory of Aldwincle near Thrapston in Northamptonshire, where his maternal grandfather was the rector of All Saints Church, Aldwincle, All Saints. He was the eldest of fourteen children born to Erasmus Dryden and wife Mary Pickering, paternal grandson of Sir Erasmus Dryden, 1st Baronet, Sir Erasmus Dryden, 1st BaroneSir Erasmus Dryden, 1st Baronet, t (1553–1632), and wife Frances Wilkes, Puritan landowning gentry who supported the Puritan cause and Parliament. He was a second cousin once removed of Jonath ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander Pope
Alexander Pope (21 May 1688 Old Style and New Style dates, O.S. – 30 May 1744) was an English poet, translator, and satirist of the Age of Enlightenment, Enlightenment era who is considered one of the most prominent English poets of the early 18th century. An exponent of Augustan literature, Pope is best known for his satirical and discursive poetry including ''The Rape of the Lock'', ''The Dunciad'', and ''An Essay on Criticism,'' and for his translations of Homer. Pope is often quoted in ''The Oxford Dictionary of Quotations'', some of his verses having entered common parlance (e.g. "damning with faint praise" or "An Essay on Criticism, to err is human; to forgive, divine"). Life Alexander Pope was born in London on 21 May 1688 during the year of the Glorious Revolution. His father (Alexander Pope, 1646–1717) was a successful linen merchant in the Strand, London. His mother, Edith (née Turner, 1643–1733), was the daughter of William Turner, Esquire, of York. Both pare ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
May 2
Events Pre-1600 * 1194 – King Richard I of England gives Portsmouth its first royal charter. * 1230 – William de Braose is hanged by Prince Llywelyn the Great. * 1536 – Anne Boleyn, Queen of England, is arrested and imprisoned on charges of adultery, incest, treason and witchcraft. * 1559 – John Knox returns from exile to Scotland to become the leader of the nascent Scottish Reformation. *1568 – Mary, Queen of Scots, escapes from Lochleven Castle. 1601–1900 * 1611 – The King James Version of the Bible is published for the first time in London, England, by printer Robert Barker. * 1625 – Afonso Mendes, appointed by Pope Gregory XV as Latin Patriarch of Ethiopia, arrives at Beilul from Goa. * 1670 – King Charles II of England grants a permanent charter to the Hudson's Bay Company to open up the fur trade in North America. * 1808 – Outbreak of the Peninsular War: The people of Madrid rise up in rebellion against Fre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxford Dictionary Of National Biography
The ''Dictionary of National Biography'' (''DNB'') is a standard work of reference on notable figures from History of the British Isles, British history, published since 1885. The updated ''Oxford Dictionary of National Biography'' (''ODNB'') was published on 23 September 2004 in 60 volumes and online, with 50,113 biographical articles covering 54,922 lives. First series Hoping to emulate national biography, biographical collections published elsewhere in Europe, such as the (1875), in 1882 the publisher George Murray Smith, George Smith (1824–1901), of Smith, Elder & Co., planned a universal dictionary that would include biographical entries on individuals from world history. He approached Leslie Stephen, then editor of the ''Cornhill Magazine'', owned by Smith, to become the editor. Stephen persuaded Smith that the work should focus only on subjects from the United Kingdom and its present and former colonies. An early working title was the ''Biographia Britannica'', the na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |