|
168th Infantry Division (Wehrmacht)
The 168th Infantry Division () was an Infantry Division, infantry division of the Nazi Germany, German German Army (1935–1945), Heer during World War II. It was active between 1939 and 1945. History The 168th Infantry Division was formed in the Görlitz area on 1 December 1939 as a division of the seventh ''Aufstellungswelle''. It initially consisted of the Infantry Regiments 417 and 429, as well as the Light Artillery Detachment 248. The latter was soon transferred to the 164th Infantry Division (Wehrmacht), 164th Infantry Division, and the 168th was strengthened to full division strength by the addition of a third regiment, numbered 442, and a full Artillery Regiment, numbered 248. The division's deployment took from December 1939 until May 1940. During this time, the 168th Infantry Division remained at home, in Wehrkreis VIII in Silesia. The first divisional commander was Wolf Boysen. On 11 January 1940, Hans Mundt replaced Boysen as divisional commander. In June 1940, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Army (Wehrmacht)
The German Army (, 'army') is the land component of the armed forces of Federal Republic of Germany, Germany. The present-day German Army was founded in 1955 as part of the newly formed West German together with the German Navy, ''Marine'' (German Navy) and the German Air Force, ''Luftwaffe'' (German Air Force). , the German Army had a strength of 63,047 soldiers. History Overview A German army equipped, organized, and trained following a single doctrine and permanently unified under one command was created in 1871 during the unification of Germany under the leadership of Prussia. From 1871 to 1919, the title ''German Army (German Empire), Deutsches Heer'' (German Army) was the official name of the German land forces. Following the German defeat in World War I and the end of the German Empire, the main army was dissolved. From 1921 to 1935 the name of the German land forces was the ''Reichswehr, Reichsheer'' (Army of the Realm) and from 1935 to 1945 the name ''German Army (We ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silesia
Silesia (see names #Etymology, below) is a historical region of Central Europe that lies mostly within Poland, with small parts in the Czech Silesia, Czech Republic and Germany. Its area is approximately , and the population is estimated at 8,000,000. Silesia is split into two main subregions, Lower Silesia in the west and Upper Silesia in the east. Silesia’s culture reflects its complex history and diverse influences, blending Polish, Czech, and German elements. The region is known for its distinctive Silesian language (still spoken by a minority in Upper Silesia), richly decorated folk National costumes of Poland, costumes, hearty regional Silesian cuisine, cuisine, and a mix of Gothic, Baroque, and industrial-era Silesian architecture, architecture seen in its cities and towns. The largest city of the region is Wrocław. Silesia is situated along the Oder River, with the Sudeten Mountains extending across the southern border. The region contains many historical landmarks ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
17th Army (Wehrmacht)
The German Seventeenth Army () was a field army of Nazi Germany during World War II. Operation Barbarossa On 22 June 1941, the 17th Army was part of Army Group South when Nazi Germany launched Operation Barbarossa and invaded the Soviet Union. From 1 July, the Hungarian "Mobile Corps" (''Gyorshadtest'') was subordinated to the 17th Army. Along with 1st Panzer Army, the 17th Army encircled Soviet forces in central Ukraine during the Battle of Uman. Approximately 100,000 Soviet troops were captured. The 17th Army participated in the Battle of Kiev (1941), Battle of Kiev. Army Group South was ordered to resume the offensive, with the objective of capturing Rostov-on-Don, the gateway to the Caucasus oil fields, and Kharkov, a major center of heavy industry for the Soviet Union. In October 1941, the army came under the command of Hermann Hoth, who was convicted post-war in the High Command Trial. Hoth was an active supporter of the Eastern Front (World War II), war of annihilation (') ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
12th Army (Wehrmacht)
The 12th Army (German: ''12. Armee'') was a World War II field army of the Wehrmacht. History Campaign in the west The 12th Army was activated on October 13, 1939, with General Wilhelm List in command. First seeing defensive action along the Siegfried Line, the army was part of Rundstedt's Army Group A responsible for the Ardennes offensive. It had under its command seven infantry divisions and one mountain division in May 1940. After the breakthrough on the Meuse near Sedan, the infantry divisions fought their way to the Aisne. In the ensuing Fall Rot the army marched to the Swiss border and secured the demarcation line with Zone libre. For the rest of 1940 the army was assigned to occupation duties in France. Balkan campaign In February 1941, an agreement between Field Marshal List and the Bulgarian General Staff allowed the passage of German troops. On the night of February 28, German Army units crossed the Danube from Romania and took up strategic positions in Bulgaria. On ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
XXIX Army Corps (Wehrmacht)
The XXIX Army Corps () was an infantry corps of the German Army during World War II, active from 1940 to 1945. Operational history The corps was formed on 20 May 1940 in ''Wehrkreis'' IV with a home station at Naumburg, which was changed to Bautzen on 8 June. It was initially part of the ''Oberkommando des Heeres'' Reserve, becoming part of 9th Army of Army Group A in northern France by July. It transferred to the 17th Army of Army Group B in the General Government during March and April 1941 in preparation for Operation Barbarossa, the German invasion of the Soviet Union. The corps transferred to the 6th Army with Army Group B in May, fighting with the army as part of Army Group South when the invasion began on 22 June. It Included the 111th, 299th, and 56th Infantry Divisions on 1 May. The corps participated in actions along the Bug River, the Battle of Kiev, and at Belgorod between June and December, continuing to fight at Belgorod until July 1942. In August the corps w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
XVII Army Corps (Wehrmacht)
XVII Army Corps () was a corps in the German Army during World War II. The corps was formed in Vienna on 1 April 1938 after the Annexation of Austria. Invasion of Poland At the beginning of the war in September 1939, the Corps, under the leadership of General Werner Kienitz, was assigned to the 14th Army in south Poland with the 44th and 45th Infantry Division. Together with the VIII Army Corps, XVII corps advanced from the Teschen area to the north of the Vistula via Pszczyna to Kraków. It then participated in the successful attack of the XVIII Corps on Lviv under General Eugen Beyer, which concluded the campaign. Battle of France Between 11 and 13 November 1939, the Corps was transferred to France, and from January 1940 onwards it was placed under reserve in the 2nd Army. During the second phase of the Western campaign, XVII Corps was transferred in June 1940 to the 12th Army and deployed for the attack on the Aisne. Invasion of Russia When Operation Barbarossa, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Army Group B
Army Group B () was the name of four distinct German Army Group, army group commands that saw action during World War II. The first Army Group B was created on 12 October 1939 (from the former Army Group North) and fought in the Battle of France on the northern flank. It was responsible for a part of the German invasion of Belgium (1940), German invasion of Belgium and the majority of the German invasion of the Netherlands. In the later stage of that campaign ("Fall Rot, Case Red"), it again advanced on the German right flank towards the Somme (river), Somme river, the city of Paris and the France–Spain border, Franco-Spanish border. After 16 August 1940, it was deployed to East Prussia and to the General Government in Occupation of Poland (1939–1945), German-occupied Poland. When Operation Barbarossa began on 22 June 1941, Army Group B was renamed on the same day to become "Army Group Center". The second Army Group B came into existence on 9 July 1942, when Army Group South ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
18th Army (Wehrmacht)
The 18th Army (German: ''18. Armee'') was a World War II field army in the German ''Wehrmacht''. Formed in November 1939 in Military Region (''Wehrkreis'') VI, the 18th Army was part of the offensive into the Netherlands (Battle of the Netherlands) and Belgium (Battle of Belgium) during Fall Gelb and later moved into France in 1940. The 18th Army was then moved East and participated in Operation Barbarossa in 1941. The Army was a part of the Army Group North until early 1945, when it was subordinated to Army Group Kurland. In October 1944, the army was encircled by the Red Army offensives and spent the remainder of the war in the Courland Pocket The Courland Pocket was a Pocket (military), pocket located on the Courland Peninsula in Latvia on the Eastern Front (World War II), Eastern Front of World War II from 9 October 1944 to 10 May 1945. Army Group North of the ''Wehrmacht'' were .... History On 22 July 1940, the 18th Army consisted of XXVI Corps ( 161st and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
XXXXIV Army Corps (Wehrmacht)
German XXXXIV. Corps (XXXXIV. Armeekorps) was a corps in the German Army during World War II. History The General Command XXXXIV. Armee Korps was established on 15 April 1940 in the Wehrkreis XVII (Vienna) and took part in the Battle of France in the section of the 6th Army. After the breakthrough over the Aisne, it advanced towards the Loire and occupied Orléans. In July 1940, the Corps was transferred to the General Government (Poland) and placed under the command of the 4th Army. After the start of Operation Barbarossa (June 1941), again under the command of the 6th Army, the XXXXIV Army Corps, composed of the 9th, 262nd, 297th and 57th Infantry Divisions, operated on the Southern Bug, and took Sokal and Krystynopol. During the Battle of Brody (1941), the XXXXIV Corps was subjected to strong counter-attacks by the Soviet 15th Mechanized Corps. After withstanding the attack, the advance towards Koziatyn continued. In August 1941, during the Battle of Uman, the corps wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
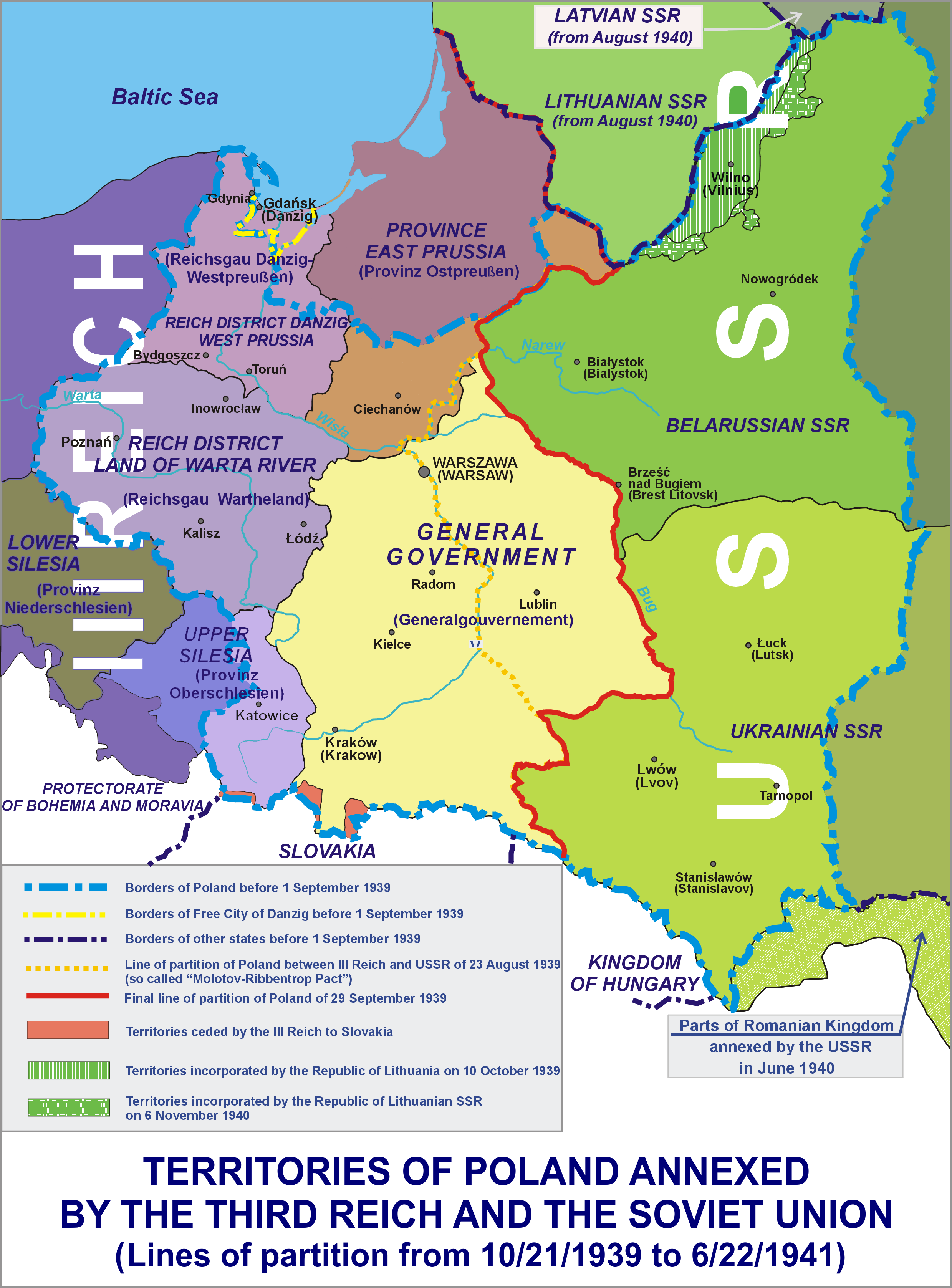
Occupation Of Poland (1939–1945)
During World War II, Poland was occupied by Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union following the invasion in September 1939, and it was formally concluded with the defeat of Germany by the Allies in May 1945. Throughout the entire course of the occupation, the territory of Poland was divided between Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union (USSR), both of which intended to eradicate Poland's culture and subjugate its people. In the summer-autumn of 1941, the lands which were annexed by the Soviets were overrun by Germany in the course of the initially successful German attack on the USSR. After a few years of fighting, the Red Army drove the German forces out of the USSR and crossed into Poland from the rest of Central and Eastern Europe. Sociologist Tadeusz Piotrowski argues that both occupying powers were hostile to the existence of Poland's sovereignty, people, and the culture and aimed to destroy them. Before Operation Barbarossa, Germany and the Soviet Union coordinated th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
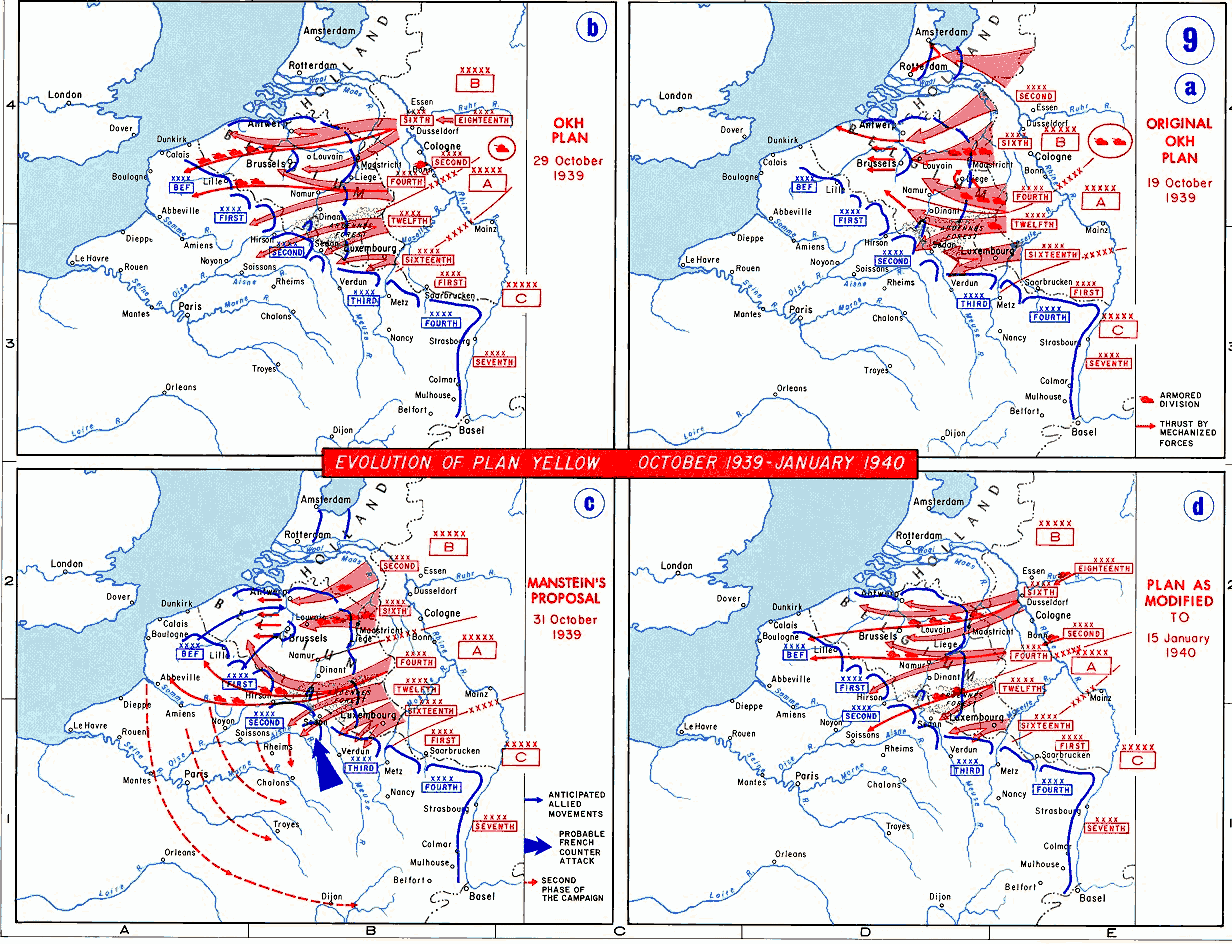
Battle Of France
The Battle of France (; 10 May – 25 June 1940), also known as the Western Campaign (), the French Campaign (, ) and the Fall of France, during the Second World War was the Nazi Germany, German invasion of the Low Countries (Belgium, Luxembourg and the Netherlands) and French Third Republic, France. The plan for the invasion of the Low Countries and France was called (Case Yellow or the Manstein plan). (Case Red) was planned to finish off the French and British after the Dunkirk evacuation, evacuation at Dunkirk. The Low Countries and France were defeated and occupied by Axis troops down to the Demarcation line (France), Demarcation line. On 3 September 1939, French declaration of war on Germany (1939), France and United Kingdom declaration of war on Germany (1939), Britain declared war on Nazi Germany, over the German invasion of Poland on 1 September. In early September 1939, the French army began the limited Saar Offensive but by mid-October had withdrawn to the start line ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Army Group C
Army Group C () was an army group of the German Wehrmacht during World War II. In its first deployment between 1939 and 1941, its main assignment was the defense of the Franco-German border during the Phony War and the Western Campaign, after which it was moved to East Prussia to become Army Group North. When Army Group C was recreated from 1943 to 1945, it was used to coordinate German forces on the Italian front. History 1939–1941 Army Group C was first formed in Frankfurt on 26 August 1939, from Army Group Command 2 (itself formed on 1 October 1919 as ''Reichswehrgruppenkommando'') in Frankfurt/Main. The only commander of the army group throughout its first tenure of service was Wilhelm Ritter von Leeb, who had been reactivated from retirement upon the outbreak of the war.Meyer, Georg (1985). Leeb, Wilhelm Ritter von'' In: ''Neue Deutsche Biographie'' (in German). Vol. 14, Duncker & Humblot, Berlin, ISBN 3428001958, pp. 51–53.Between September 1939 and June 1940, Army ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |