|
1666 In Science
The year 1666 in science and technology involved some significant events. Events * December 22 – French Academy of Sciences first meets. Astronomy * Publication of Stanisław Lubieniecki's ''Theatrum Cometicum'' begins in Amsterdam, the first encyclopedia and atlas of comets. Botany * Establishment of Herrenhäuser Gärten, Hanover. Mathematics * Isaac Newton develops differential calculus. * Samuel Morland produces several designs of pocket calculating machine and also publishes ''A New Method of Cryptography''. Physics * Isaac Newton uses a prism to split sunlight into the component colours of the optical spectrum, assisting understanding of the nature of light. * Robert Hooke and Giovanni Alfonso Borelli both expound gravitation as an attractive force (Hooke's lecture "On gravity" at the Royal Society of London on March 21; Borelli's ''Theoricae Mediceorum planetarum ex causis physicis deductae'', published in Florence later in the year). Publications * Margaret Cavend ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Science
Science is a systematic endeavor that Scientific method, builds and organizes knowledge in the form of Testability, testable explanations and predictions about the universe. Science may be as old as the human species, and some of the earliest archeological evidence for scientific reasoning is tens of thousands of years old. The earliest written records in the history of science come from Ancient Egypt and Mesopotamia in around 3000 to 1200 Common Era, BCE. Their contributions to mathematics, astronomy, and medicine entered and shaped Greek natural philosophy of classical antiquity, whereby formal attempts were made to provide explanations of events in the Universe, physical world based on natural causes. After the fall of the Western Roman Empire, knowledge of History of science in classical antiquity, Greek conceptions of the world deteriorated in Western Europe during the early centuries (400 to 1000 CE) of the Middle Ages, but was preserved in the Muslim world during the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
London
London is the capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary down to the North Sea, and has been a major settlement for two millennia. The City of London, its ancient core and financial centre, was founded by the Roman Empire, Romans as ''Londinium'' and retains its medieval boundaries.See also: Independent city#National capitals, Independent city § National capitals The City of Westminster, to the west of the City of London, has for centuries hosted the national Government of the United Kingdom, government and Parliament of the United Kingdom, parliament. Since the 19th century, the name "London" has also referred to the metropolis around this core, historically split between the Counties of England, counties of Middlesex, Essex, Surrey, Kent, and Hertfordshire, which largely comprises Greater London ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, most populous country, with a Population of China, population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and Borders of China, borders fourteen countries by land, the List of countries and territories by land borders, most of any country in the world, tied with Russia. Covering an area of approximately , it is the world's third List of countries and dependencies by area, largest country by total land area. The country consists of 22 provinces of China, provinces, five autonomous regions of China, autonomous regions, four direct-administered municipalities of China, municipalities, and two special administrative regions of China, Special Administrative Regions (Hong Kong and Macau). The national capital is Beijing, and the List of cities in China by population, most populous cit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
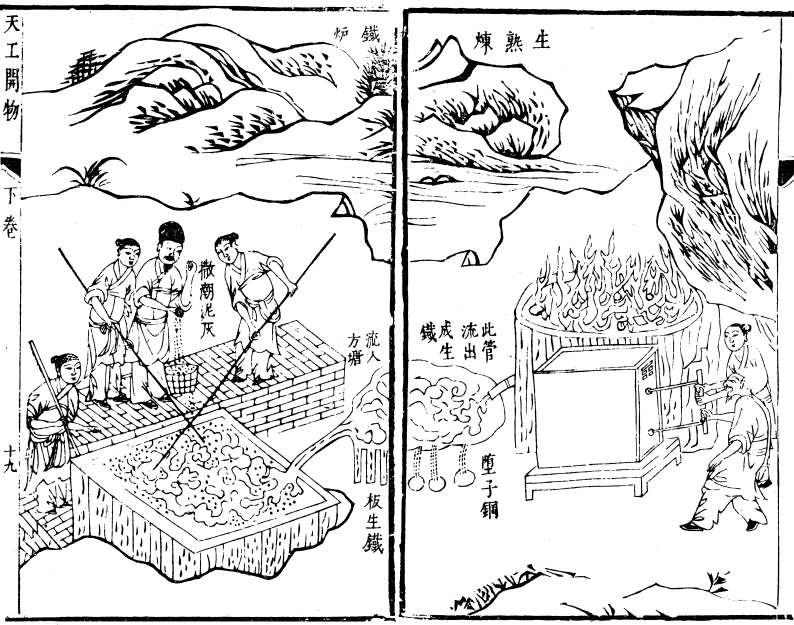
Song Yingxing
Song Yingxing ( Traditional Chinese: 宋應星; Simplified Chinese: 宋应星; Wade Giles: Sung Ying-Hsing; 1587-1666 AD) was a Chinese scientist and encyclopedist who lived during the late Ming Dynasty (1368–1644). He was the author of '' Tiangong Kaiwu'', an encyclopedia that covered a wide variety of technical subjects, including the use of gunpowder weapons.Needham, Volume 5, Part 7, 36. The British biochemist, sinologist, and historian Joseph Needham called Song Yingxing "The Diderot of China."Needham, Volume 5, Part 7, 102. Biography Song Yingxing was born in Yichun of Jiangxi in 1587 to a gentry family of reduced circumstances, he participated in the imperial examinations, and passed the provincial test in 1615, at the age of 28. He achieved only modest wealth and influence during his life. However, he was repeatedly unsuccessful in the metropolitan examination. Song sat for the test five times, the last being in 1631 at the age of 44. After this last failure, he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1582 In Science
The year 1582 in science and technology included a number of events, some of which are listed here. This year sees the introduction of the Gregorian calendar, promulgated by Pope Gregory XIII in the Papal bull ''Inter gravissimas'' on February 24 and based largely on the work of Christopher Clavius. Under the Habsburg monarchy in Spain, Portugal and Italy, together with the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, the year continues under the Julian calendar as normal until Thursday October 4, the next day becoming Friday October 15; France follows two months later, letting Sunday December 9 be followed by Monday December 20. Other countries switch in later years. Astronomy * Giovanni Antonio Magini publishes the ephemerides ''Ephemerides coelestium motuum''. Exploration * Richard Hakluyt publishes ''Divers Voyages Touching the Discoverie of America and the Ilands Adjacent unto the Same, Made First of all by our Englishmen''. Medicine * Urbain Hémard investigates the anatomy of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physicist
A physicist is a scientist who specializes in the field of physics, which encompasses the interactions of matter and energy at all length and time scales in the physical universe. Physicists generally are interested in the root or ultimate causes of phenomena, and usually frame their understanding in mathematical terms. Physicists work across a wide range of research fields, spanning all length scales: from sub-atomic and particle physics, through biological physics, to cosmological length scales encompassing the universe as a whole. The field generally includes two types of physicists: experimental physicists who specialize in the observation of natural phenomena and the development and analysis of experiments, and theoretical physicists who specialize in mathematical modeling of physical systems to rationalize, explain and predict natural phenomena. Physicists can apply their knowledge towards solving practical problems or to developing new technologies (also known as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genoa
Genoa ( ; it, Genova ; lij, Zêna ). is the capital of the Regions of Italy, Italian region of Liguria and the List of cities in Italy, sixth-largest city in Italy. In 2015, 594,733 people lived within the city's administrative limits. As of the 2011 Italian census, the Province of Genoa, which in 2015 became the Metropolitan City of Genoa, had 855,834 resident persons. Over 1.5 million people live in the wider metropolitan area stretching along the Italian Riviera. On the Gulf of Genoa in the Ligurian Sea, Genoa has historically been one of the most important ports on the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean: it is currently the busiest in Italy and in the Mediterranean Sea and twelfth-busiest in the European Union. Genoa was the capital of Republic of Genoa, one of the most powerful maritime republics for over seven centuries, from the 11th century to 1797. Particularly from the 12th century to the 15th century, the city played a leading role in the commercial trade in Euro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Giovanni Battista Baliani
Giovanni Battista Baliani (1582–1666) was an Italian mathematician, physicist and astronomer. Career He was born in Genoa. He was governor of Savona in 1647–1649 and captain of the Republic of Genoa's archers. For some 25 years, he held a correspondence with Galileo Galilei about the time's most innovative scientific theories and experiments.. However, Applebaum also calls Baliani's correspondence with Galileo "intermittent". For another discussion of the timing and content of letters dating from 1615 to 1639, see . Work At Savona, from the Priamar Fortress, he repeated Galileo's experiment of the Tower of Pisa, obtaining more precise measurements which allowed him to underline the effect of air attrition. He also conducted an experiment to show the heat generated by a pot full of water, which he had boiled after rotating it at high speed. His main work is entitled ''De motu naturali gravium, fluidorum et solidorum'' ("About the motion of bodies, fluids and solids"), publish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1736 In Science
The year 1736 in science and technology involved some significant events. Botany * Charles Marie de La Condamine, with François Fresneau Gataudière, makes the first scientific observations of rubber, in Ecuador. Earth sciences * June 19 – French Academy of Sciences expedition led by Pierre Louis Maupertuis, with Anders Celsius, begins work on measuring a meridian arc in the Torne Valley of Finland. Mathematics * June 8 – Leonhard Euler writes to James Stirling describing the Euler–Maclaurin formula, providing a connection between integrals and calculus. * Euler produces the first ''published'' proof of Fermat's "little theorem". * Sir Isaac Newton's ''Method of Fluxions'' (1671), describing his method of differential calculus, is first published (posthumously) and Thomas Bayes publishes a defense of its logical foundations against the criticism of George Berkeley (anonymously). Medicine * Early 1736 – The “Publick Workhouse and House of Correction” that is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English People
The English people are an ethnic group and nation native to England, who speak the English language, a West Germanic language, and share a common history and culture. The English identity is of Anglo-Saxon origin, when they were known in Old English as the ('race or tribe of the Angles'). Their ethnonym is derived from the Angles, one of the Germanic peoples who migrated to Great Britain around the 5th century AD. The English largely descend from two main historical population groups the West Germanic tribes (the Angles, Saxons, Jutes and Frisians) who settled in southern Britain following the withdrawal of the Romans, and the partially Romanised Celtic Britons already living there.Martiniano, R., Caffell, A., Holst, M. et al. Genomic signals of migration and continuity in Britain before the Anglo-Saxons. Nat Commun 7, 10326 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms10326 Collectively known as the Anglo-Saxons, they founded what was to become the Kingdom of England ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stephen Gray (scientist)
Stephen Gray (December 1666 – 7 February 1736) was an English dyer and astronomer who was the first to systematically experiment with electrical conduction. Until his work in 1729 the emphasis had been on the simple generation of static charges and investigations of the static phenomena (electric shocks, plasma glows, etc.). He also first made the distinction between conduction and insulation, and discovered the action-at-a-distance phenomenon of electrostatic induction. Early life Gray was born in Canterbury, Kent, and after some basic schooling, he was apprenticed to his father (and later his elder brother) in the cloth-dyeing trade. His interests lay with natural science and particularly with astronomy; he managed to educate himself in these developing disciplines, mainly through wealthy friends in the district, who gave him access to their libraries and scientific instruments. Science was very much a rich man's hobby at this time. He ground his own lenses and constr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxford Dictionary Of National Biography
The ''Dictionary of National Biography'' (''DNB'') is a standard work of reference on notable figures from British history, published since 1885. The updated ''Oxford Dictionary of National Biography'' (''ODNB'') was published on 23 September 2004 in 60 volumes and online, with 50,113 biographical articles covering 54,922 lives. First series Hoping to emulate national biographical collections published elsewhere in Europe, such as the '' Allgemeine Deutsche Biographie'' (1875), in 1882 the publisher George Smith (1824–1901), of Smith, Elder & Co., planned a universal dictionary that would include biographical entries on individuals from world history. He approached Leslie Stephen, then editor of the '' Cornhill Magazine'', owned by Smith, to become the editor. Stephen persuaded Smith that the work should focus only on subjects from the United Kingdom and its present and former colonies. An early working title was the ''Biographia Britannica'', the name of an earlier eig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |