|
1611 In Science
The year 1611 in science and technology involved some significant events. Astronomy * February 27 – Sunspots are observed by telescope by Frisian astronomers Johannes Fabricius and David Fabricius and Johannes publishes the results of these observations in ''De Maculis in Sole observatis'' in Wittenberg later this year. Such early discoveries are overlooked however, and the first sighting is claimed a few months later by Galileo Galilei and Christoph Scheiner. Mathematics * Johannes Kepler produces Kepler's conjecture on sphere packing."On the six-cornered snowflake". Technology * Completion of Cordouan lighthouse on the Gironde estuary (designed by Louis de Foix), the first wave-swept light. Births * January 28 – Johannes Hevelius, German astronomer (died 1687) * March 1 – John Pell, English mathematician (died 1685) * Willem Piso, Dutch physician and naturalist (died 1678) * Georg Marcgrave, German naturalist, explorer of Brazil (died 1644) Deaths * August 9 � ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Science
Science is a systematic endeavor that Scientific method, builds and organizes knowledge in the form of Testability, testable explanations and predictions about the universe. Science may be as old as the human species, and some of the earliest archeological evidence for scientific reasoning is tens of thousands of years old. The earliest written records in the history of science come from Ancient Egypt and Mesopotamia in around 3000 to 1200 Common Era, BCE. Their contributions to mathematics, astronomy, and medicine entered and shaped Greek natural philosophy of classical antiquity, whereby formal attempts were made to provide explanations of events in the Universe, physical world based on natural causes. After the fall of the Western Roman Empire, knowledge of History of science in classical antiquity, Greek conceptions of the world deteriorated in Western Europe during the early centuries (400 to 1000 CE) of the Middle Ages, but was preserved in the Muslim world during the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johannes Hevelius
Johannes Hevelius Some sources refer to Hevelius as Polish: * * * * * * * Some sources refer to Hevelius as German: * * * * *of the Royal Society * (in German also known as ''Hevel''; pl, Jan Heweliusz; – 28 January 1687) was a councillor and mayor of Gdańsk (Danzig), in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. As an astronomer, he gained a reputation as "the founder of lunar topography", and described ten new constellations, seven of which are still used by astronomers. Etymology According to the Polish Academy of Sciences (1975) the origin of the name goes back to the surname Hawke, a historical alternative spelling for the English word hawk, which changed into ''Hawelke'' or ''Hawelecke''. In Poland he is known as ''Jan Heweliusz''. Other versions of the name include Hewel, Hevel, Hevelke or Hoefel, Höwelcke, Höfelcke. According to Feliks Bentkowski (1814), during his early years he also signed as Hoefelius. Along with the Latinized version of his name, Ludwig G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1611 In Science
The year 1611 in science and technology involved some significant events. Astronomy * February 27 – Sunspots are observed by telescope by Frisian astronomers Johannes Fabricius and David Fabricius and Johannes publishes the results of these observations in ''De Maculis in Sole observatis'' in Wittenberg later this year. Such early discoveries are overlooked however, and the first sighting is claimed a few months later by Galileo Galilei and Christoph Scheiner. Mathematics * Johannes Kepler produces Kepler's conjecture on sphere packing."On the six-cornered snowflake". Technology * Completion of Cordouan lighthouse on the Gironde estuary (designed by Louis de Foix), the first wave-swept light. Births * January 28 – Johannes Hevelius, German astronomer (died 1687) * March 1 – John Pell, English mathematician (died 1685) * Willem Piso, Dutch physician and naturalist (died 1678) * Georg Marcgrave, German naturalist, explorer of Brazil (died 1644) Deaths * August 9 � ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
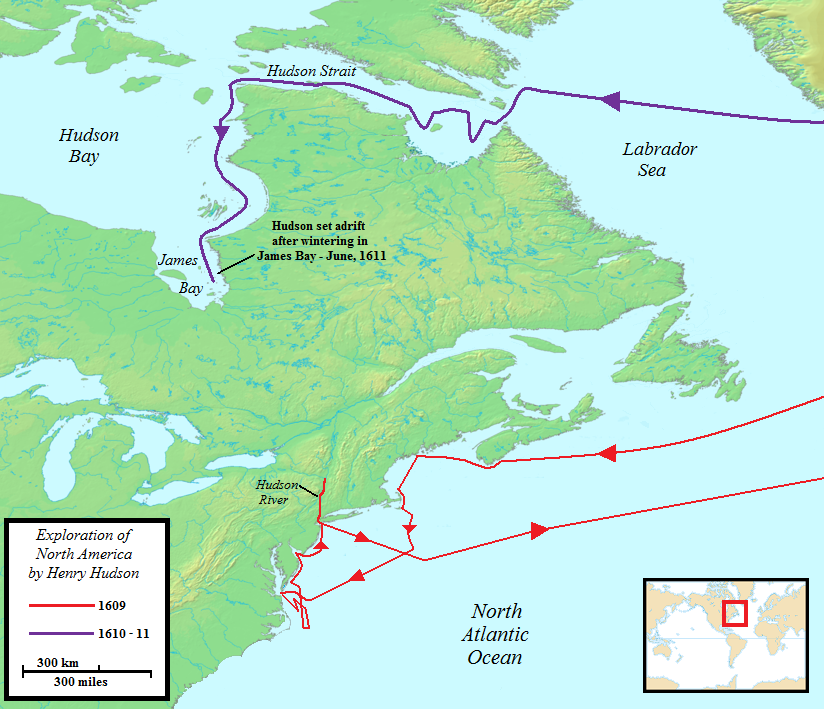
Henry Hudson
Henry Hudson ( 1565 – disappeared 23 June 1611) was an English sea explorer and navigator during the early 17th century, best known for his explorations of present-day Canada and parts of the northeastern United States. In 1607 and 1608, Hudson made two attempts on behalf of English merchants to find a rumoured Northeast Passage to Cathay via a route above the Arctic Circle. In 1609, he landed in North America on behalf of the Dutch East India Company and explored the region around the modern New York metropolitan area. Looking for a Northwest Passage to Asia on his ship '' Halve Maen'' ("Half Moon"), he sailed up the Hudson River, which was later named after him, and thereby laid the foundation for Dutch colonization of the region. On his final expedition, while still searching for the Northwest Passage, Hudson became the first European to see Hudson Strait and the immense Hudson Bay. In 1611, after wintering on the shore of James Bay, Hudson wanted to pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematician
A mathematician is someone who uses an extensive knowledge of mathematics in their work, typically to solve mathematical problems. Mathematicians are concerned with numbers, data, quantity, mathematical structure, structure, space, Mathematical model, models, and mathematics#Calculus and analysis, change. History One of the earliest known mathematicians were Thales of Miletus (c. 624–c.546 BC); he has been hailed as the first true mathematician and the first known individual to whom a mathematical discovery has been attributed. He is credited with the first use of deductive reasoning applied to geometry, by deriving four corollaries to Thales' Theorem. The number of known mathematicians grew when Pythagoras of Samos (c. 582–c. 507 BC) established the Pythagoreans, Pythagorean School, whose doctrine it was that mathematics ruled the universe and whose motto was "All is number". It was the Pythagoreans who coined the term "mathematics", and with whom the study of mathemat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English People
The English people are an ethnic group and nation native to England, who speak the English language, a West Germanic language, and share a common history and culture. The English identity is of Anglo-Saxon origin, when they were known in Old English as the ('race or tribe of the Angles'). Their ethnonym is derived from the Angles, one of the Germanic peoples who migrated to Great Britain around the 5th century AD. The English largely descend from two main historical population groups the West Germanic tribes (the Angles, Saxons, Jutes and Frisians) who settled in southern Britain following the withdrawal of the Romans, and the partially Romanised Celtic Britons already living there.Martiniano, R., Caffell, A., Holst, M. et al. Genomic signals of migration and continuity in Britain before the Anglo-Saxons. Nat Commun 7, 10326 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms10326 Collectively known as the Anglo-Saxons, they founded what was to become the Kingdom of England ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Blagrave
John Blagrave of Reading (d. 1611) was an English Tudor mathematician, astronomer and designer of astronomical and mathematical instruments. His astrolabe designs, which he described in his writings, were advanced for Britain. He devoted himself to mathematical study and was called, by Anthony à Wood, "the flower of mathematicians of his age" Biography John Blagrave was born as the second son to John Blagrave of Bullmarsh and Anne (daughter of Sir Anthony Hungerford of Down Ampney) in Berkshire at an unknown date sometime in the 1560s. The Blagraves were a branch of that landed gentry family of Calcot Park, Berkshire. He was educated in Reading School and went to St John's College, Oxford for an education in mathematics, though he never received a degree. Blagrave married the widow Dorothy Gunter (daughter of Simon Gunter of Milton Lilbourne in Wiltshire). He had no issue himself but had a step-daughter, Jane, from his wife. In 1591, his father gave him a lease on some Southc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1644 In Science
The year 1644 AD in science and technology involved some significant events. Mathematics * The Basel problem is posed by Pietro Mengoli, and will puzzle mathematicians until solved by Leonhard Euler in 1735. Technology * Jacob van Eyck collaborates with the bellfounding duo Pieter and François Hemony to create the first tuned carillon in Zutphen. Publications * Jan Baptist van Helmont publishes ''Dageraad ofte Nieuwe Opkomst der Geneeskunst'' ("Daybreak, or the New Rise of Medicine"). Births * 25 September – Ole Rømer, Danish astronomer who makes the first quantitative measurements of the speed of light (died 1710) Deaths * 2 July – William Gascoigne, English scientist (born 1610) * 30 December – Jan Baptist van Helmont, Flemish chemist (born 1580 __NOTOC__ Events January–June * January 31 – Portuguese succession crisis of 1580: The death of Henry, King of Portugal, with no direct heirs, leads to conflict between his potential successors, incl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Georg Marcgrave
Georg Marcgrave (originally german: Georg Marggraf, also spelled ''"Marcgraf" "Markgraf"'') (1610 – 1644) was a German naturalist and astronomer, whose posthumously published ''Historia Naturalis Brasiliae'' was a major contribution to early modern science. Life Born in Liebstadt in the Electorate of Saxony, Marcgrave studied botany, astronomy, mathematics, and medicine in Germany and Switzerland until 1636 when he journeyed to Leiden in the Netherlands. In 1637, he was appointed astronomer of a company being formed to sail to the Dutch Brazil. He was accompanied by Willem Piso, a physician. He afterward entered the service of Dutch Brazil's governor, Johan Maurits van Nassau-Siegen, whose patronage provided him with the means of exploring a considerable part of Brazil. He arrived in Brazil in early 1638 and undertook the first zoological, botanical, and astronomical expedition there, exploring various parts of the colony to study its natural history and geography. Travelin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1678 In Science
{{Science year nav, 1678 The year 1678 in science and technology involved some significant events. Astronomy * Edmund Halley publishes a catalogue of 341 southern stars—the first systematic southern sky survey. Physics * Christiaan Huygens publishes his ''Traité de la Lumière/Treatise on Light'', which states his principle of wavefront sources. * Robert Hooke discovers the fundamental law of elasticity when he finds that the stress (force) exerted is proportional to the strain (elongation) produced. Zoology * Publication of ''English Spiders'' by Martin Lister, the first book devoted to spiders. Births * April 14 – Abraham Darby I, ironmaster (died 1717) * July 16 – Jakob Hermann, mathematician (died 1733) * October 27 – Pierre Raymond de Montmort, mathematician (died 1719) * November 26 – Jean-Jacques d'Ortous de Mairan, geophysicist (died 1771) * December 2 – Nicolaas Kruik (Cruquius), cartographer and meteorologist (died 1754) * ''unknown'' – Pierre Fau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Willem Piso
Willem Piso (in Dutch Willem Pies, in Latin Gulielmus Piso, also called Guilherme Piso in Portuguese) (1611 in Leiden – 28 November 1678 in Amsterdam) was a Dutch physician and naturalist who participated as an expedition doctor in Dutch Brazil from 1637 – 1644, sponsored by count Johan Maurits van Nassau-Siegen and the Dutch West India Company. Piso became one of the founders of tropical medicine. Life and career Piso was born in Leiden to church organist Hermann Pies and Cornelia van Liesvelt. He studied in Leiden and received a degree in medicine from Caen in 1633 and settled in Amsterdam as a doctor. In 1637, he was offered a position in the Dutch West India Company as a physician to Count Johan Maurits van Nassau-Siegen (1604-1679), governor of Dutch Brazil. He left for Brazil along with the astronomer Georg Marcgrave and the painters Albert Eckhout and Frans Post. There, he recommended the consumption of fresh fish, vegetables, and fruits after discove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1685 In Science
The year 1685 in science and technology involved some significant events. Mathematics * Adam Adamandy Kochański publishes an approximation for squaring the circle. Physiology and medicine * Charles Allen publishes the first book in English on dentistry, The Operator for the Teeth'. * Govert Bidloo publishes an atlas of human anatomy, ''Ontleding des menschelyken lichaams'', with plates by Gerard de Lairesse. Technology * Menno van Coehoorn publishes his principal treatise on fortification, ''Nieuwe Vestingbouw op een natte of lage horisont'', in Leeuwarden. Births * August 18 – Brook Taylor, English mathematician (died 1731) * November 17 – Pierre Gaultier de Varennes et de la Vérendrye, French Canadian explorer (died 1749) Deaths * February 2 – Pierre Bourdelot, French physician, anatomist, freethinker, abbé and libertine (born 1610) * November 23 – Bernard de Gomme, military engineer in England (born 1620) * December 12 – John Pell, English mathematician ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |