|
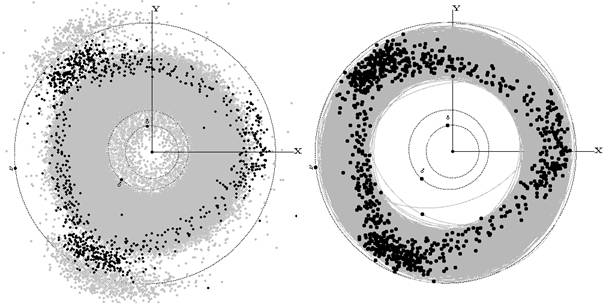
153 Hilda
153 Hilda is a large asteroid in the outer main belt, with a diameter of 170 km. The spectrum matches that of a P-type asteroid. It was discovered by Johann Palisa on 2 November 1875, from the Austrian Naval Observatory at Pula, now Croatia. The name was chosen by the astronomer Theodor von Oppolzer, who named it after one of his daughters. It is the largest member of the hilda family, a collisional family of asteroids in the Hilda region. Orbit and family Hilda gives its name to an asteroid group called the Hilda group (or ''Hildas'' for short). It is not a true asteroid family, since the members are not physically related, but rather share similar orbital elements. The Hildas are locked in a 2:3 orbital resonance with Jupiter; since Jupiter takes 11.9 years to orbit the Sun while Hilda takes 7.9 years, Jupiter orbits the Sun twice for every 3 orbits that Hilda completes. There are over 1,100 other objects known to be in a 2:3 resonance with Jupiter. The asteroid is, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apparent Magnitude
Apparent magnitude () is a measure of the Irradiance, brightness of a star, astronomical object or other celestial objects like artificial satellites. Its value depends on its intrinsic luminosity, its distance, and any extinction (astronomy), extinction of the object's light caused by interstellar dust along the sightline, line of sight to the observer. Unless stated otherwise, the word ''magnitude'' in astronomy usually refers to a celestial object's apparent magnitude. The magnitude scale likely dates to before the ancient Ancient Greek astronomy#Astronomy in the Greco-Roman and Late Antique eras, Roman astronomer Ptolemy, Claudius Ptolemy, whose Star catalogue, star catalog popularized the system by listing stars from First-magnitude star, 1st magnitude (brightest) to 6th magnitude (dimmest). The modern scale was mathematically defined to closely match this historical system by Norman Robert Pogson, Norman Pogson in 1856. The scale is reverse logarithmic scale, logarithmic: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jupiter
Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the List of Solar System objects by size, largest in the Solar System. It is a gas giant with a Jupiter mass, mass more than 2.5 times that of all the other planets in the Solar System combined and slightly less than one-thousandth the mass of the Sun. Its diameter is 11 times that of Earth and a tenth that of the Sun. Jupiter orbits the Sun at a distance of , with an orbital period of . It is the List of brightest natural objects in the sky, third-brightest natural object in the Earth's night sky, after the Moon and Venus, and has been observed since prehistoric times. Its name derives from that of Jupiter (god), Jupiter, the chief deity of ancient Roman religion. Jupiter was the first of the Sun's planets to form, and its inward migration during the primordial phase of the Solar System affected much of the formation history of the other planets. Jupiter's atmosphere consists of 76% hydrogen and 24% helium by mass, with a denser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
P-type Asteroids (Tholen)
P-type (primitive-type) asteroids have low albedo and a featureless reddish Asteroid spectral types, spectrum. It has been suggested that they have a composition of organic-rich silicates, carbon and anhydrous silicates, possibly with water ice in their interior. P-type asteroids are found in the outer asteroid belt and beyond. There are about 33 known P-type asteroids, depending on the classification, including 46 Hestia, 65 Cybele, 76 Freia, 87 Sylvia, 153 Hilda, 476 Hedwig and, in some classifications, 107 Camilla. Taxonomy An early system of asteroid taxonomy was established in 1975 from the doctoral thesis work of David J. Tholen. This was based upon observations of a group of 110 asteroids. The U-type classification was used as a miscellaneous class for asteroids with unusual spectra that did not fit into the C-type asteroid, C and S-type asteroid classifications. In 1976, some of these U-type asteroids with unusual moderate albedo levels were labeled as M-type asteroid, M-t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Objects Observed By Stellar Occultation
Object may refer to: General meanings * Object (philosophy), a thing, being, or concept ** Object (abstract), an object which does not exist at any particular time or place ** Physical object, an identifiable collection of matter * Goal, an aim, target, or objective * Object (grammar), a sentence element, such as a direct object or an indirect object Science, technology, and mathematics Computing * 3D model, a representation of a physical object * Object (computer science), a language mechanism for binding data with methods that operate on that data ** Object-orientation (other), in which concepts are represented as objects *** Object-oriented programming (OOP), in which an object is an instance of a class or array ** Object (IBM i), the fundamental unit of data storage in the IBM i operating system * Object file, the output of a compiler or other translator program (also known as "object code") * HTML object element Mathematics * Object (mathematics), an abstrac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Articles Containing Video Clips
Article often refers to: * Article (grammar), a grammatical element used to indicate definiteness or indefiniteness * Article (publishing) An article or piece is a written work published in a Publishing, print or electronic media, electronic medium, for the propagation of news, research results, academic analysis or debate. News A news article discusses current or recent news of e ..., a piece of nonfictional prose that is an independent part of a publication Article(s) may also refer to: Government and law * Elements of treaties of the European Union * Articles of association, the regulations governing a company, used in India, the UK and other countries; called articles of incorporation in the US * Articles of clerkship, the contract accepted to become an articled clerk * Articles of Confederation, the predecessor to the current United States Constitution * Article of impeachment, a formal document and charge used for impeachment in the United States * Article of ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Named Minor Planets
Named may refer to something that has been given a name. Named may also refer to: * named (computing), a widely used DNS server * Naming (parliamentary procedure) * The Named (band), an American industrial metal group In literature: * ''The Named'', a fantasy novel by Marianne Curley * The Named, a fictional race of prehistoric big cats, depicted in ''The Books of the Named'' series by Clare Bell See also * Name (other) * Names (other) Names are words or terms used for identification. Names may also refer to: * ''Names'' (EP), by Johnny Foreigner * ''Names'' (journal), an academic journal of onomastics * The Names (band), a Belgian post-punk band * ''The Names'' (novel), b ... * Naming (other) {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Discoveries By Johann Palisa
Discoveries may refer to: Media Film and television * ''Discoveries'' (film), a 1939 British film * ''Discoveries'' (TV series), a Canadian youth science television series * "Discoveries", a Series D episode of the television series ''QI'' (2006) * "Discoveries" (''Hotel Portofino''), a 2022 TV episode Literature * ''Discoveries'' (Robertson Davies), a 2002 book by Robertson Davies * ''Abrams Discoveries'', a series of illustrated non-fiction books published by Harry N. Abrams * ''Discoveries'', a work by William Butler Yeats, written in 1907 * ''Discoveries'', a magazine published by Cedars-Sinai Medical Center Music * ''Discoveries'' (Cannonball Adderley album), 1955 * ''Discoveries'' (Josh Nelson album), 2011 * ''Discoveries'' (Northlane album), 2011 Other uses * Discoveries (horse), a racehorse See also * Age of Discoveries * Discovery (other) * Explorations (other) Exploration is the process of discovery. Exploration or explorations may ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hilda Asteroids
The Hilda asteroids (adj. ''Hildian'') are a List of minor-planet groups#Other groups out to the orbit of Jupiter, dynamical group of more than 6,000 asteroids located beyond the asteroid belt but within Jupiter's orbit, in a 3:2 orbital resonance with Jupiter. The namesake is the asteroid 153 Hilda. Hildas move in their elliptical orbits in such a fashion that they arrive closest to Jupiter's orbit (i.e. at their Apsis#Perihelion_and_aphelion, aphelion) just when either one of Jupiter's , or Lagrange points arrives there. On their next orbit their aphelion will synchronize with the next Lagrange point in the –– sequence. Since , and are 120° apart, by the time a Hilda completes an orbit, Jupiter will have completed 360° − 120° or two-thirds of its own orbit. A Hilda's orbit has a semi-major axis between 3.7 and 4.2 Astronomical unit, AU (the average over a long time span is 3.97), an eccentricity (orbit), eccentricity less than 0.3, and an inclination less ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rotation Period
In astronomy, the rotation period or spin period of a celestial object (e.g., star, planet, moon, asteroid) has two definitions. The first one corresponds to the '' sidereal rotation period'' (or ''sidereal day''), i.e., the time that the object takes to complete a full rotation around its axis relative to the background stars ( inertial space). The other type of commonly used "rotation period" is the object's '' synodic rotation period'' (or ''solar day''), which may differ, by a fraction of a rotation or more than one rotation, to accommodate the portion of the object's orbital period around a star or another body during one day. Measuring rotation For solid objects, such as rocky planets and asteroids, the rotation period is a single value. For gaseous or fluid bodies, such as stars and giant planets, the period of rotation varies from the object's equator to its pole due to a phenomenon called differential rotation. Typically, the stated rotation period for a giant pl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Light Curve
In astronomy, a light curve is a graph (discrete mathematics), graph of the Radiance, light intensity of a celestial object or region as a function of time, typically with the magnitude (astronomy), magnitude of light received on the ''y''-axis and with time on the ''x''-axis. The light is usually in a particular frequency interval or frequency band, band. Light curves can be periodic, as in the case of eclipsing binary, eclipsing binaries, Cepheid variables, other periodic variables, and Methods of detecting extrasolar planets#Transit photometry, transiting extrasolar planets; or aperiodic, like the light curve of a nova, cataclysmic variable star, supernova, gravitational microlensing, microlensing event, or binary as observed during occultation events. The study of a light curve and other observations can yield considerable information about the physical process that produces such a light curve, or constrain the physical theories about it. Variable stars Graphs of the ap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orbital Eccentricity
In astrodynamics, the orbital eccentricity of an astronomical object is a dimensionless parameter that determines the amount by which its orbit around another body deviates from a perfect circle. A value of 0 is a circular orbit, values between 0 and 1 form an elliptic orbit, 1 is a parabolic escape orbit (or capture orbit), and greater than 1 is a hyperbola. The term derives its name from the parameters of conic sections, as every Kepler orbit is a conic section. It is normally used for the isolated two-body problem, but extensions exist for objects following a rosette orbit through the Galaxy. Definition In a two-body problem with inverse-square-law force, every orbit is a Kepler orbit. The eccentricity of this Kepler orbit is a non-negative number that defines its shape. The eccentricity may take the following values: * Circular orbit: * Elliptic orbit: * Parabolic trajectory: * Hyperbolic trajectory: The eccentricity is given by e = \sqrt where ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecliptic
The ecliptic or ecliptic plane is the orbital plane of Earth's orbit, Earth around the Sun. It was a central concept in a number of ancient sciences, providing the framework for key measurements in astronomy, astrology and calendar-making. From the perspective of an observer on Earth, the Sun's movement around the celestial sphere over the course of a year traces out a path along the ecliptic against the fixed stars, background of stars – specifically the Zodiac constellations. The planets of the Solar System can also be seen along the ecliptic, because their orbital planes are very close to Earth's. The Moon's orbital plane is also similar to Earth's; the ecliptic is so named because the ancients noted that eclipses only occur when the Moon is crossing it. The ecliptic is an important Plane of reference, reference plane and is the basis of the ecliptic coordinate system. Ancient scientists were able to calculate Earth's axial tilt by comparing the ecliptic plane to that of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |