|
15-Cis-phytoene Desaturase
15-''cis''-phytoene desaturases (''PDS'', ''plant-type phytoene desaturases'') (, ''15-cis-phytoene:plastoquinone oxidoreductase''), are enzymes involved in the carotenoid biosynthesis in plants and cyanobacteria. Phytoene desaturases are membrane-bound enzymes localized in plastids and introduce two double bonds into their colorless substrate phytoene by dehydrogenation and isomerize two additional double bonds. This reaction starts a biochemical pathway involving three further enzymes ( zeta-carotene isomerase, zeta-carotene desaturase and carotene cis-trans isomerase) called the poly-cis pathway and leads to the red colored lycopene. The homologous phytoene desaturase found in bacteria and fungi ( CrtI) converts phytoene directly to lycopene by an all-trans pathway. Biochemistry PDS converts 15-''cis''-phytoene into 9,15,9'-tri-''cis''-ζ-carotene through reduction of the enzymes non-covalently bound FAD cofactor. This conversion introduces two additional double bonds at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Crystallography
X-ray crystallography is the experimental science of determining the atomic and molecular structure of a crystal, in which the crystalline structure causes a beam of incident X-rays to diffract in specific directions. By measuring the angles and intensities of the X-ray diffraction, a crystallographer can produce a three-dimensional picture of the density of electrons within the crystal and the positions of the atoms, as well as their chemical bonds, crystallographic disorder, and other information. X-ray crystallography has been fundamental in the development of many scientific fields. In its first decades of use, this method determined the size of atoms, the lengths and types of chemical bonds, and the atomic-scale differences between various materials, especially minerals and alloys. The method has also revealed the structure and function of many biological molecules, including vitamins, drugs, proteins and nucleic acids such as DNA. X-ray crystallography is still the prima ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phytoene Desaturation PLOS ONE
Phytoene () is a 40-carbon intermediate in the biosynthesis of carotenoids. The synthesis of phytoene is the first committed step in the synthesis of carotenoids in plants. Phytoene is produced from two molecules of geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate (GGPP) by the action of the enzyme phytoene synthase. The two GGPP molecules are condensed together followed by removal of diphosphate and proton shift leading to the formation of phytoene. Dietary phytoene and phytofluene are found in a number of human tissues including the liver, lung, breast, prostate, colon, and skin. Accumulation of these carotenoids in the skin may protect the skin by several mechanisms: acting as UV absorbers, as antioxidants, and as anti-inflammatory agents. Structure Phytoene is a symmetric molecule containing three conjugated double bonds. Phytoene has a UV-Vis absorption spectrum ''typical'' for a triply conjugated system with its main absorption maximum in the UVB range at 286 nm and with '' ε1% of 91 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phytoene Desaturase (zeta-carotene-forming)
Phytoene desaturase (zeta-carotene-forming) (, ''CrtIa'', ''2-step phytoene desaturase (ambiguous)'', ''two-step phytoene desaturase (ambiguous)'') is an enzyme with List of enzymes, systematic name ''15-cis-phytoene:acceptor oxidoreductase (zeta-carotene-forming)''. This enzyme catalysis, catalyses the following chemical reaction : 15-cis-phytoene + 2 acceptor \rightleftharpoons all-trans-zeta-carotene + 2 reduced acceptor (overall reaction) : (1a) 15-cis-phytoene + acceptor \rightleftharpoons all-trans-phytofluene + reduced acceptor : (1b) all-trans-phytofluene + acceptor \rightleftharpoons all-trans-zeta-carotene + reduced acceptor The enzyme is involved in carotenoid biosynthesis. See also * Phytoene desaturase (lycopene-forming) * Phytoene desaturase (neurosporene-forming) * 15-Cis-phytoene desaturase * Phytoene desaturase (3,4-didehydrolycopene-forming) References External links * {{Portal bar, Biology, border=no EC 1.3.99 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phytoene Desaturase (neurosporene-forming)
Phytoene desaturase (neurosporene-forming) (, ''3-step phytoene desaturase'', ''three-step phytoene desaturase'', ''phytoene desaturase (ambiguous)'', ''CrtI (ambiguous)'') is an enzyme with systematic name ''15-cis-phytoene:acceptor oxidoreductase (neurosporene-forming)''. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction : 15-''cis''-phytoene + 3 acceptor \rightleftharpoons all-''trans''-neurosporene + 3 reduced acceptor (overall reaction) : (1a) 15-''cis''-phytoene + acceptor \rightleftharpoons all-''trans''-phytofluene + reduced acceptor : (1b) all-''trans''-phytofluene + acceptor \rightleftharpoons all-''trans''-''zeta''-carotene + reduced acceptor : (1c) all-''trans''-''zeta''-carotene + acceptor \rightleftharpoons all-''trans''-neurosporene + reduced acceptor This enzyme is involved in carotenoid biosynthesis. See also * Phytoene desaturase (lycopene-forming) * 15-Cis-phytoene desaturase * Phytoene desaturase (zeta-carotene-forming) Phytoene desaturase (zeta-car ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
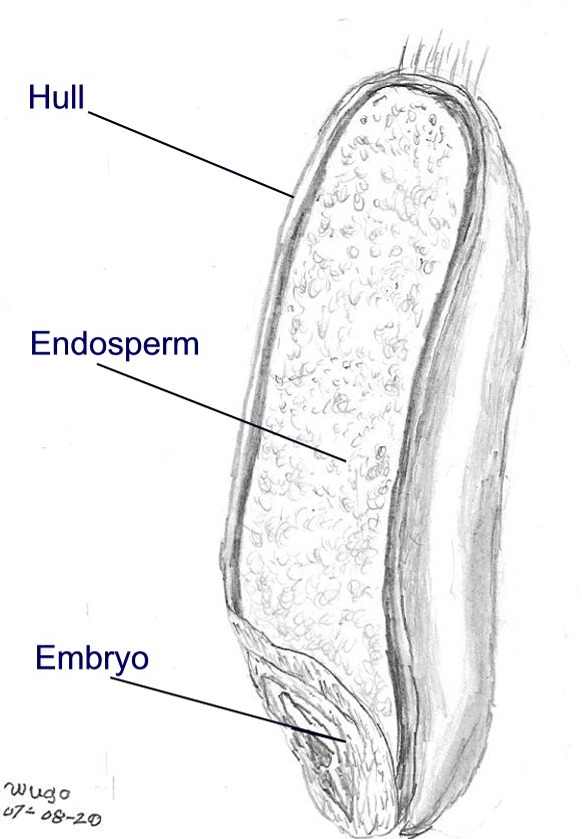
Endosperm
The endosperm is a tissue produced inside the seeds of most of the flowering plants following double fertilization. It is triploid (meaning three chromosome sets per nucleus) in most species, which may be auxin-driven. It surrounds the Embryo#Plant embryos, embryo and provides nutrition in the form of starch, though it can also contain Vegetable oil, oils and protein. This can make endosperm a source of nutrition in animal diet. For example, wheat endosperm is ground into flour for bread (the rest of the grain is included as well in whole wheat flour), while barley endosperm is the main source of sugars for beer production. Other examples of endosperm that forms the bulk of the edible portion are coconut "meat" and coconut "water", and Maize, corn. Some plants, such as certain orchids, lack endosperm in their seeds. Ancestral flowering plants have seeds with small embryos and abundant endosperm. In some modern flowering plants the embryo occupies most of the seed and the endosperm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Golden Rice
Golden rice is a variety of rice ('' Oryza sativa'') produced through genetic engineering to biosynthesize beta-carotene, a precursor of vitamin A, in the edible parts of the rice. It is intended to produce a fortified food to be grown and consumed in areas with a shortage of dietary vitamin A. Genetically modified golden rice can produce up to 23 times as much beta-carotene as the original golden rice. Golden rice is generally considered to be safe, with the FDA, Health Canada, International Rice Research Institute and the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation supporting its use. It has been met with significant opposition from some environmental and anti-globalisation activists, alleging risks regarding biodiversity and expressing concerns about unforeseen health effects and socioeconomic impacts. In 2016, 107 Nobel laureates wrote an open letter to Greenpeace and its supporters, asking them to abandon their campaign against genetically modified crops in general and golden ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sequence Homology
Sequence homology is the homology (biology), biological homology between DNA sequence, DNA, RNA sequence, RNA, or Protein primary structure, protein sequences, defined in terms of shared ancestry in the evolutionary history of life. Two segments of DNA can have shared ancestry because of three phenomena: either a speciation event (orthologs), or a Gene duplication, duplication event (paralogs), or else a Horizontal gene transfer, horizontal (or lateral) gene transfer event (xenologs). Homology among DNA, RNA, or proteins is typically inferred from their nucleotide or amino acid sequence similarity. Significant similarity is strong evidence that two sequences are related by evolutionary changes from a common ancestral sequence. Sequence alignment, Alignments of multiple sequences are used to indicate which regions of each sequence are homologous. Identity, similarity, and conservation The term "percent homology" is often used to mean "sequence similarity”, that is the percen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rice
Rice is a cereal grain and in its Domestication, domesticated form is the staple food of over half of the world's population, particularly in Asia and Africa. Rice is the seed of the grass species ''Oryza sativa'' (Asian rice)—or, much less commonly, ''Oryza glaberrima'' (African rice). Asian rice was domesticated in China some 13,500 to 8,200 years ago; African rice was domesticated in Africa about 3,000 years ago. Rice has become commonplace in many cultures worldwide; in 2023, 800 million tons were produced, placing it third after sugarcane and maize. Only some 8% of rice is traded internationally. China, India, and Indonesia are the largest consumers of rice. A substantial amount of the rice produced in developing nations is lost after harvest through factors such as poor transport and storage. Rice yields can be reduced by pests including insects, rodents, and birds, as well as by weeds, and by List of rice diseases, diseases such as rice blast. Traditional rice polyc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CRISPR
CRISPR (; acronym of clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats) is a family of DNA sequences found in the genomes of prokaryotic organisms such as bacteria and archaea. Each sequence within an individual prokaryotic CRISPR is derived from a DNA fragment of a bacteriophage that had previously infected the prokaryote or one of its ancestors. These sequences are used to detect and destroy DNA from similar bacteriophages during subsequent infections. Hence these sequences play a key role in the antiviral (i.e. anti- phage) defense system of prokaryotes and provide a form of heritable, acquired immunity. CRISPR is found in approximately 50% of sequenced bacterial genomes and nearly 90% of sequenced archaea. Cas9 (or "CRISPR-associated protein 9") is an enzyme that uses CRISPR sequences as a guide to recognize and open up specific strands of DNA that are complementary to the CRISPR sequence. Cas9 enzymes together with CRISPR sequences form the basis of a technology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluridone
Fluridone is an organic compound that is used as aquatic herbicide often used to control invasive plants. It is used in the United States to control hydrilla and Eurasian watermilfoil among other species. Fluridone is sold as a solution and as a slow release solid because the herbicide level must be maintained for several weeks. The compound is a colorless solid.Franz Müller and Arnold P. Applebyki "Weed Control, 2. Individual Herbicides" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry 2010 The compound was first reported as a possible herbicide for cotton fields in 1976. It was registered with the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency in 1986 and has low toxicity to animals with no restrictions on swimming or drinking in treated water bodies. Fluridone breaks down in the environment over days or weeks with the major degradation product being N-methyl formamide. The half-life of fluridone in soils and sediments has been estimated at nine months. Fluridone degradation in soil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
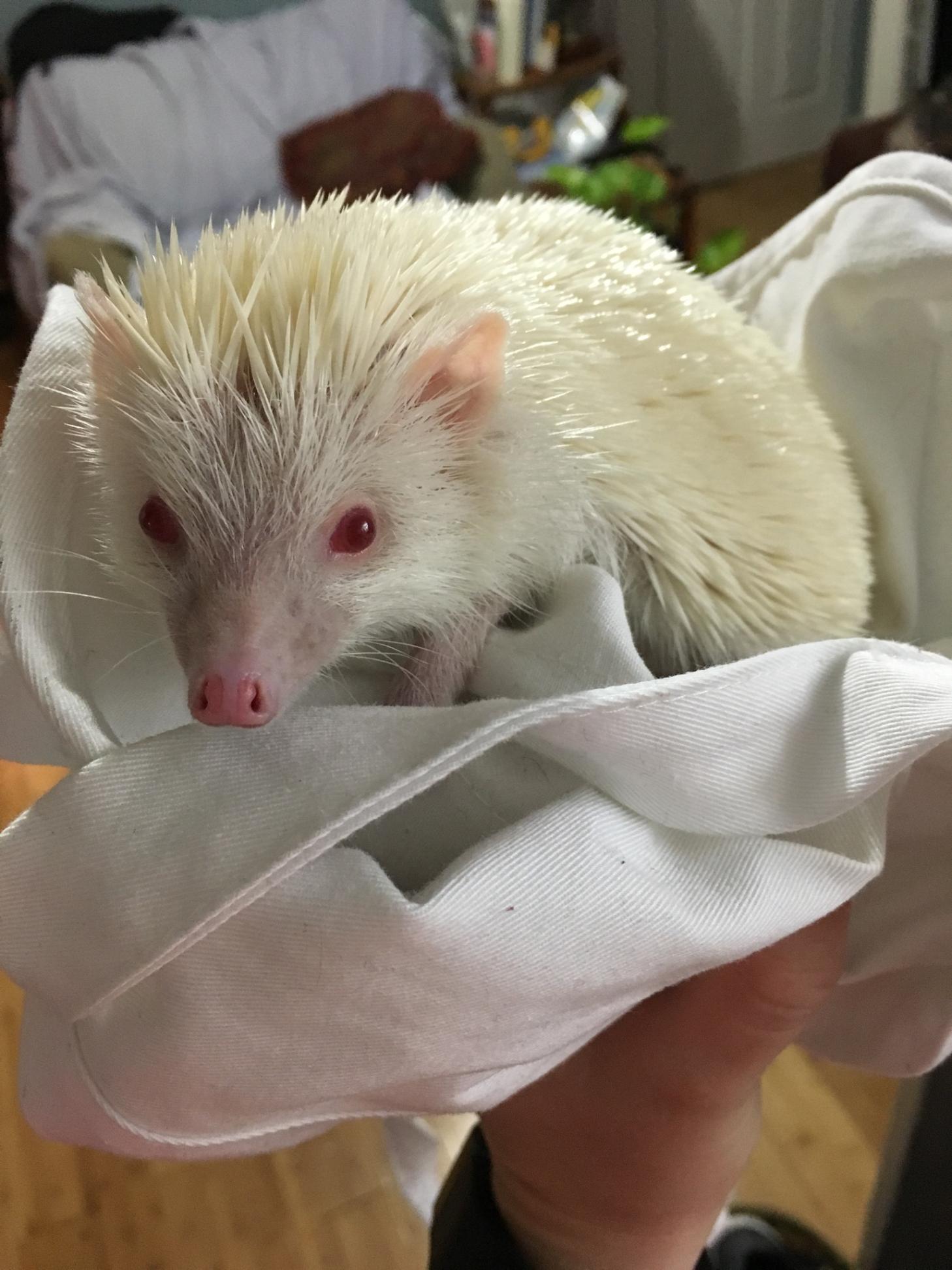
Albinism
Albinism is the congenital absence of melanin in an animal or plant resulting in white hair, feathers, scales and skin and reddish pink or blue eyes. Individuals with the condition are referred to as albinos. Varied use and interpretation of the terms mean that written reports of albinistic animals can be difficult to verify. Albinism can reduce the survivability of an animal; for example, it has been suggested that albino alligators have an average survival span of only 24 hours due to the lack of protection from UV radiation and their lack of camouflage to avoid predators. It is a common misconception that all albino animals have characteristic pink or red eyes (resulting from the lack of pigment in the Iris (anatomy), iris allowing the blood vessels of the retina to be visible); this is not the case for some forms of albinism. Familiar albino animals include in-bred strains of laboratory animals (rats, mice and rabbits), but populations of naturally occurring albino animals ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |