|
1477 Deaths
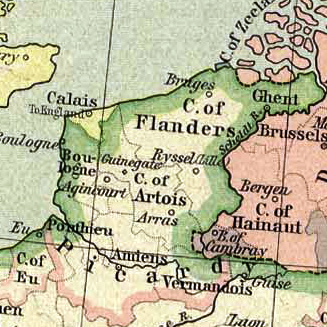
Year 1477 ( MCDLXXVII) was a common year starting on Wednesday of the Julian calendar. Events January–December * January 5 – Battle of Nancy: Charles the Bold of Burgundy is again defeated, and this time is killed; this marks the end of the Burgundian Wars. * February? – Volcano Bardarbunga erupts in Iceland, with a VEI of 6. * February 11 – Mary of Burgundy, the daughter of Charles the Bold, is forced by her disgruntled subjects to sign the '' Great Privilege'', by which the Flemish cities recover all the local and communal rights which have been abolished by the decrees of the dukes of Burgundy, in their efforts to create a centralized state in the Low Countries. * February 27 – Uppsala University is founded, becoming the first university in Sweden and all of Scandinavia. * August 19 – Mary of Burgundy marries Maximilian I, Holy Roman Emperor, in Ghent, bringing her Flemish and Burgundian lands into the Holy Roman Empire, and detaching ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uppsala University
Uppsala University (UU) () is a public university, public research university in Uppsala, Sweden. Founded in 1477, it is the List of universities in Sweden, oldest university in Sweden and the Nordic countries still in operation. Initially founded in the 15th century, the university rose to significance during the rise of Swedish Empire, Sweden as a great power at the end of the 16th century and was then given relative financial stability with a large donation from Monarchy of Sweden, King Gustavus Adolphus of Sweden, Gustavus Adolphus in the early 17th century. Uppsala also has an important historical place in Swedish national culture, and national identity, identity for the Swedish establishment: in historiography, religion, literature, politics, and music. Many aspects of Swedish academic culture in general, such as the white student cap, originated in Uppsala. It shares some peculiarities, such as the student nation system, with Lund University and the University of Helsink ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Colonialism
Russian imperialism is the political, economic and cultural influence, as well as military power, exerted by Russia and its predecessor states, over other countries and territories. It includes the conquests of the Tsardom of Russia, the Russian Empire, the imperialism of the Soviet Union, and the #Contemporary Russian imperialism, neo-imperialism of the Russian Federation. Some Postcolonialism, postcolonial scholars have noted the lack of attention given to Russian and Soviet imperialism in the discipline. After the Fall of Constantinople (1453), Principality of Moscow, Moscow named itself Moscow, third Rome, the third Rome, following the Roman Empire, Roman and Byzantine Empires. Beginning in the 1550s, Russia conquered, on average, territory the size of the Netherlands every year for 150 years. This included Russian conquest of Siberia, Siberia, Russian conquest of Central Asia, central Asia, Russian conquest of the Caucasus, the Caucasus and parts of Eastern Europe. Russia en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
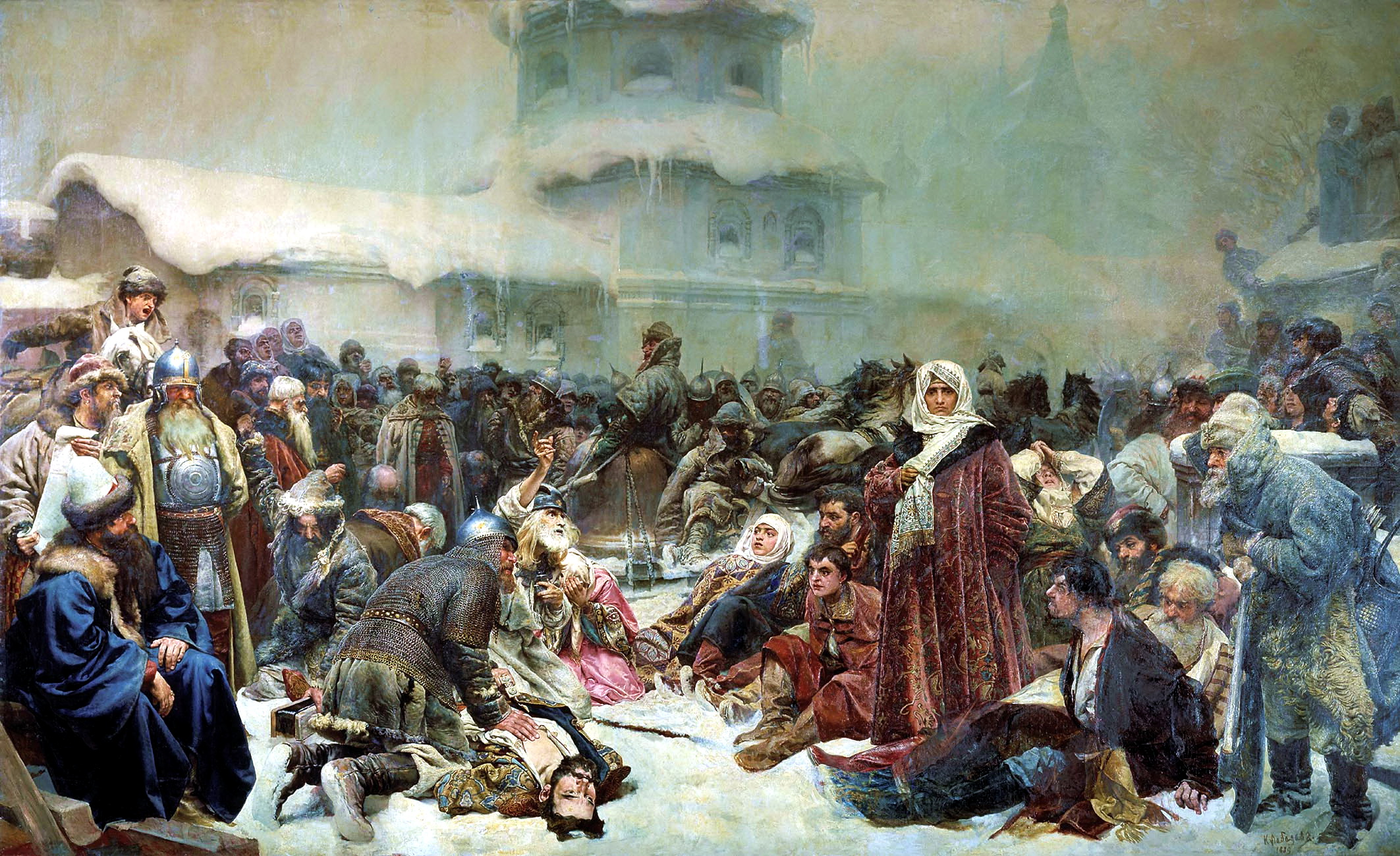
Novgorod Republic
The Novgorod Republic () was a medieval state that existed from the 12th to 15th centuries in northern Russia, stretching from the Gulf of Finland in the west to the northern Ural Mountains in the east. Its capital was the city of Novgorod. The republic prospered as the easternmost trading post of the Hanseatic League, and its people were much influenced by the culture of the Byzantines, with the Novgorod school of icon painting producing many fine works. Novgorod won its independence in 1136 after the Novgorodians deposed their prince and the Novgorod ''veche'' began to elect and dismiss princes at its own will. The ''veche'' also elected the '' posadnik'', who was the chief executive of the city, and the archbishop of Novgorod, subject to approval by the Russian metropolitan. The '' tysyatsky'' was also elected by the ''veche'', who was originally the military commander, and served the interests of the common people. Novgorodian nobles known as boyars dominated the ''vech ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ivan III Of Russia
Ivan III Vasilyevich (; 22 January 1440 – 27 October 1505), also known as Ivan the Great, was Grand Prince of Moscow and Sovereign of all Russia, all Russia from 1462 until his death in 1505. Ivan served as the co-ruler and regent for his blind father Vasily II before he officially ascended the throne. He multiplied the territory of his state through conquest, purchase, inheritance and the seizure of lands from his dynastic relatives, and laid the foundations of the centralized Russian state. He also renovated the Kremlin, Moscow Kremlin and introduced a new Sudebnik of 1497, legal code. Ivan is credited with ending the dominance of the Tatars over Russia; his Great Stand on the Ugra River, victory over the Great Horde in 1480 formally restored its independence. Ivan began using the title tsar, and used the title tentatively until the House of Habsburg, Habsburgs recognized it. While officially using "tsar" in his correspondence with other monarchs, he was satisfied with the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Westminster
Westminster is the main settlement of the City of Westminster in Central London, Central London, England. It extends from the River Thames to Oxford Street and has many famous landmarks, including the Palace of Westminster, Buckingham Palace, Westminster Abbey, Westminster Cathedral, Trafalgar Square and much of the West End of London, West End cultural centre including the entertainment precinct of West End theatre. The name () originated from the informal description of the abbey church and royal peculiar of St Peter's (Westminster Abbey), west of the City of London (until the English Reformation there was also an Eastminster abbey, on the other side of the City of London, in the East End of London). The abbey's origins date from between the 7th and 10th centuries, but it rose to national prominence when rebuilt by Edward the Confessor in the 11th century. With the development of the old palace alongside the abbey, Westminster has been the home of Governance of England, Engla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dictes And Sayings Of The Philosophers
''Dicts and Sayings of the Philosophers'' ("The Sayings of the Philosophers") is an incunabulum, or early printed book. The Middle English work is a translation, by Anthony Woodville, 2nd Earl Rivers, Anthony Woodville, of a wisdom literature compendium written in Arabic by the medieval Arab scholar al-Mubashshir ibn Fatik, titled ''Mukhtār al-ḥikam wa-maḥāsin al-kalim'' (مختار الحكم ومحاسن الكلم) which had been translated into several languages. Woodville based his version on an earlier French translation. His translation would come to be printed by William Caxton in 1477 as either the first, or one of the earliest, books printed in the English language.''Dictionary of National Biography, DNB'', p. 383 History of original and earlier translations The Arabic original is known as ''Mukhtār al-ḥikam wa-maḥāsin al-kalim'' ('Compendium of Maxims and Aphorisms'), and was written toward the middle of the eleventh century by a Syrian-born emir of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anthony Woodville, 2nd Earl Rivers
Anthony Woodville, 2nd Earl Rivers (c. 144025 June 1483), was an English nobleman, courtier, bibliophile and writer. He was the brother of Queen Elizabeth Woodville who married King Edward IV. He was one of the leading members of the Woodville family, which came to prominence during the reign of King Edward IV. After Edward's death, he was arrested and then executed by the Duke of Gloucester (the future King Richard III) as part of a power struggle between Richard and the Woodvilles. His English translation of '' The Dictes and Sayings of the Philosophers'' is one of the first books printed in England. This presents a detailed biography. Origins He was the eldest son to survive childhood of Richard Woodville, 1st Earl Rivers, by his wife Jacquetta of Luxembourg. His sister was Elizabeth Woodville, who married King Edward IV and became queen. Career Like his father, he was originally a Lancastrian, fighting on that side at the Battle of Towton, but later became a Yorki ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Caxton
William Caxton () was an English merchant, diplomat and writer. He is thought to be the first person to introduce a printing press into Kingdom of England, England in 1476, and as a Printer (publishing), printer to be the first English retailer of printed books. His parentage and date of birth are not known for certain, but he may have been born between 1415 and 1424, perhaps in the Weald or wood land of Kent, perhaps in Hadlow or Tenterden. In 1438 he was apprenticed to Robert Large, a wealthy London silk Mercery, mercer. Shortly after Large's death, Caxton moved to Bruges, Belgium, a wealthy cultured city in which he was settled by 1450. Successful in business, he became governor of the Company of Merchant Adventurers of London; on his business travels, he observed the new printing industry in Cologne, which led him to start a printing press in Bruges in collaboration with Colard Mansion. When Margaret of York, sister of Edward IV, married the Charles the Bold, Duke of Burgund ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
November 18
Events Pre-1600 * 326 – The old St. Peter's Basilica is consecrated by Pope Sylvester I. * 401 – The Visigoths, led by king Alaric I, cross the Alps and invade northern Italy. * 1095 – The Council of Clermont begins: called by Pope Urban II, it led to the First Crusade to the Holy Land. * 1105 – Maginulfo is elected Antipope Sylvester IV in opposition to Pope Paschal II. * 1210 – Pope Innocent III excommunicates Holy Roman Emperor Otto IV for invading the Kingdom of Sicily after promising to recognize papal control over it. * 1302 – Pope Boniface VIII issues the Papal bull '' Unam sanctam'', claiming spiritual supremacy for the papacy. * 1421 – St Elizabeth's flood: A dike in the Grote Hollandse Waard in the Netherlands breaks, killing about 10,000 people. * 1493 – Christopher Columbus first sights the island now known as Puerto Rico. 1601–1900 *1601 – Tiryaki Hasan Pasha, an Ottoman provincial governor, ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire, also known as the Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation after 1512, was a polity in Central and Western Europe, usually headed by the Holy Roman Emperor. It developed in the Early Middle Ages, and lasted for a millennium until its Dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire, dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars. For most of its history the Empire comprised the entirety of the modern countries of Germany, Czechia, Austria, the Netherlands, Belgium, Switzerland, Slovenia, and Luxembourg, most of north-central Italy, and large parts of modern-day east France and west Poland. On 25 December 800, Pope Leo III crowned the Frankish king Charlemagne Roman emperor, reviving the title more than three centuries after the fall of the Western Roman Empire in 476. The title lapsed in 924, but was revived in 962 when Otto I, OttoI was crowned emperor by Pope John XII, as Charlemagne's and the Carolingian Empire's successor. From 962 until the 12th century, the empire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ghent
Ghent ( ; ; historically known as ''Gaunt'' in English) is a City status in Belgium, city and a Municipalities of Belgium, municipality in the Flemish Region of Belgium. It is the capital and largest city of the Provinces of Belgium, province of East Flanders, and the third largest in the country, after Brussels and Antwerp. It is a Port of Ghent, port and Ghent University, university city. The city originally started as a settlement at the confluence of the Rivers Scheldt and Leie. In the Late Middle Ages Ghent became one of the largest and richest cities of northern Europe, with some 50,000 people in 1300. After the late 16th century Ghent became a less important city, resulting in an extremely well-preserved historic centre, that now makes Ghent an important destination of tourism. The municipality comprises the city of Ghent proper and the surrounding suburbs of Afsnee, Desteldonk, Drongen, Gentbrugge, Ledeberg, Mariakerke, East Flanders, Mariakerke, Mendonk, Oostakker, S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |