|
134th Infantry Division (Wehrmacht)
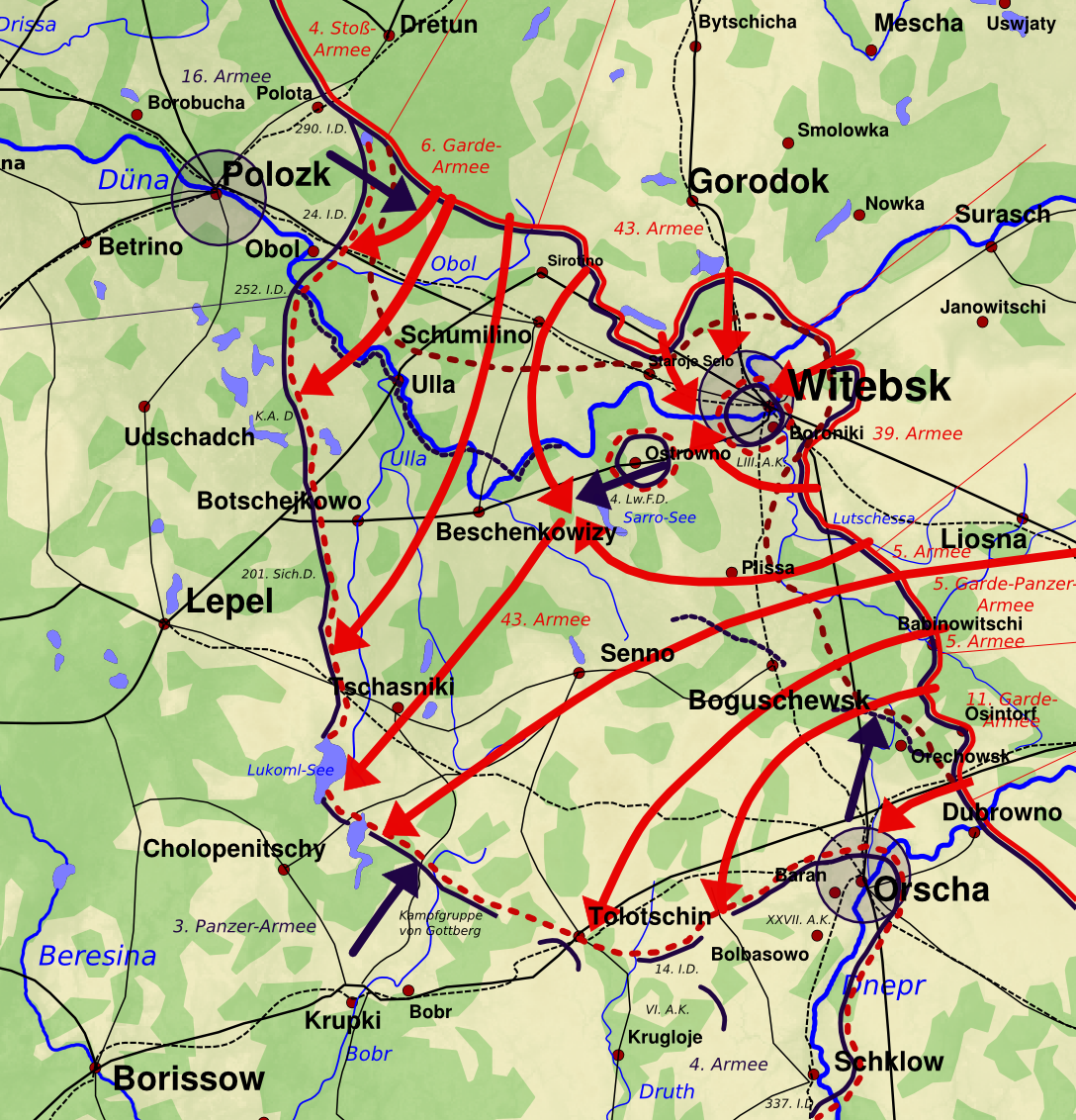
The 134th Infantry Division () was a Nazi Germany, German division (military), division in World War II. It was formed in October 1940. From June 1941, the 134th Infantry Division took part in the invasion of the Soviet Union as part of the Army Group Center. In December 1941, the division was involved in the Battle of Moscow. Together with the 45th Infantry Division (Wehrmacht), 45th Infantry Division, she was temporarily surrounded as part of the 2nd Army at Livny and lost a large part of her artillery. The division was destroyed in the Soviet Bobruysk Offensive, part of Operation Bagration in the summer of 1944.Tessin, pp. 15–16 Orders of Battle ''134. Infanterie-Division'' 1940 *''Infanterie-Regiment 439'' *''Infanterie-Regiment 445'' *''Infanterie-Regiment 446'' *''Artillerie-Regiment 134'' *''Aufklärungs-Abteilung 134'' *''Pionier-Bataillon 134'' *''Panzerjäger-Abteilung 134'' *''Divisions-Nachrichten-Abteilung 134'' *''Divisions-Nachschubführer 134'' ''134. Infanteri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infantry
Infantry, or infantryman are a type of soldier who specialize in ground combat, typically fighting dismounted. Historically the term was used to describe foot soldiers, i.e. those who march and fight on foot. In modern usage, the term broadly encompasses a wide variety of subspecialties, including light infantry, irregular infantry, heavy infantry, mountain infantry, motorized infantry, mechanized infantry, Airborne forces, airborne infantry, Air assault, air assault infantry, and Marines, naval infantry. Other subtypes of infantry, such as line infantry and mounted infantry, were once commonplace but fell out of favor in the 1800s with the invention of more accurate and powerful weapons. Etymology and terminology In English, use of the term ''infantry'' began about the 1570s, describing soldiers who march and fight on foot. The word derives from Middle French , from older Italian (also Spanish) ''infanteria'' (foot soldiers too inexperienced for cavalry), from Latin '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Division (military)
A division is a large military unit or Formation (military), formation, usually consisting of between 10,000 and 25,000 soldiers. In most armies, a division is composed of several regiments or brigades; in turn, several divisions typically make up a corps. Historically, the division has been the default combined arms unit capable of independent Military tactics, operations. Smaller combined arms units, such as the American regimental combat team (RCT) during World War II, were used when conditions favored them. In recent times, modern Western militaries have begun adopting the smaller brigade combat team (similar to the RCT) as the default combined arms unit, with the division to which they belong being less important. A similar word, ''Divizion, //'', is also used in Slavic languages (such as Russian, Serbo-Croatian, and Polish) for a battalion-size artillery or cavalry unit. In naval usage "division (naval), division" has a completely different range of meanings. Aboard ship ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infantry Divisions Of Germany During World War II
Infantry, or infantryman are a type of soldier who specialize in ground combat, typically fighting dismounted. Historically the term was used to describe foot soldiers, i.e. those who march and fight on foot. In modern usage, the term broadly encompasses a wide variety of subspecialties, including light infantry, irregular infantry, heavy infantry, mountain infantry, motorized infantry, mechanized infantry, airborne infantry, air assault infantry, and naval infantry. Other subtypes of infantry, such as line infantry and mounted infantry, were once commonplace but fell out of favor in the 1800s with the invention of more accurate and powerful weapons. Etymology and terminology In English, use of the term ''infantry'' began about the 1570s, describing soldiers who march and fight on foot. The word derives from Middle French , from older Italian (also Spanish) ''infanteria'' (foot soldiers too inexperienced for cavalry), from Latin '' īnfāns'' (without speech, newbo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hans Schlemmer
__NOTOC__ Johann Schlemmer (18 January 1893 – 26 June 1973) was a German general during World War II who commanded the LXXV Army Corps. He was a recipient of the Knight's Cross of the Iron Cross with Oak Leaves. Schlemmer surrendered to Allied troops in Italy in 1945. Life and career Johann Schlemmer was born in Nesselwang in Bavaria on 18 January 1893. Joining the German Army in 1913, he served in World War I as a lieutenant in the Bavarian Artillery. He remained in the army after 1918. At the outbreak of World War II he commanded first a battalion, then a regiment, of mountain artillery, before being promoted to general officer rank, commanding the 134th Infantry Division. He ended the war as a General of Mountain Troops, commanding the LXXV Army Corps in Italy. He surrendered to Allied troops in Italy in 1945. Awards and decorations * Iron Cross (1914) 2nd Class (9 November 1914) & 1st Class (17 December 1916) * Clasp to the Iron Cross (1939) 2nd Class (2 October 193 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Livny
Livny (, ) is a town in Oryol Oblast, Russia. As of 2018, it had a population of 47,221. :ru:Ливны#cite note-2018AA-3 History The town is believed to have originated in 1586 as Ust-Livny, a wooden fort on the bank of the Livenka River, although some believe that a town had existed on the spot previous to the Mongol invasion of Rus'. The fortress was important in guarding the southern border of the Grand Duchy of Moscow in the case of a Crimean Tatar raid along the Muravsky Trail. Thirty years later, Ivan the Terrible sent prince Masalsky to build a town of Livny under the umbrella of a garrison stationed in the fort. It was pillaged and burnt by the Tatars on many occasions. In 1606, the citizens of Livny raised a rebellion against Boris Godunov, killing his governor and proclaiming their allegiance to False Dmitry I. Two years later, Ivan Bolotnikov chose it as a base of his military operations against Vasily IV. In 1618, the wooden town was burnt by the Coss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
45th Infantry Division (Wehrmacht)
The 45th Infantry Division () was an infantry division of the army of Nazi Germany during World War II. Towards the end of the war, the division was reassembled into a second iteration, the 45th Volksgrenadier Division () History 45th Infantry Division With the annexation of Austria in 1938 by Nazi Germany, what was once the 4th Austrian Division was incorporated into the Wehrmacht (German Army) and re-designated the 45th Infantry Division. In the 1939 Invasion of Poland, the division was on the right wing of Gerd von Rundstedt's Army Group South. On 22 June 1941, the 45th Infantry Division began Operation Barbarossa by starting the 9-day long siege of the Brest Fortress.Christian Ganzer: ''German and Soviet Losses as an Indicator of the Length and Intensity of the Battle for the Brest Fortress (1941).'' In: The Journal of Slavic Military Studies, Volume 27, Issue 3, p. 449-466. In March 1942 the Red Army defeated the division at Livny, Russia and captured the archive of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
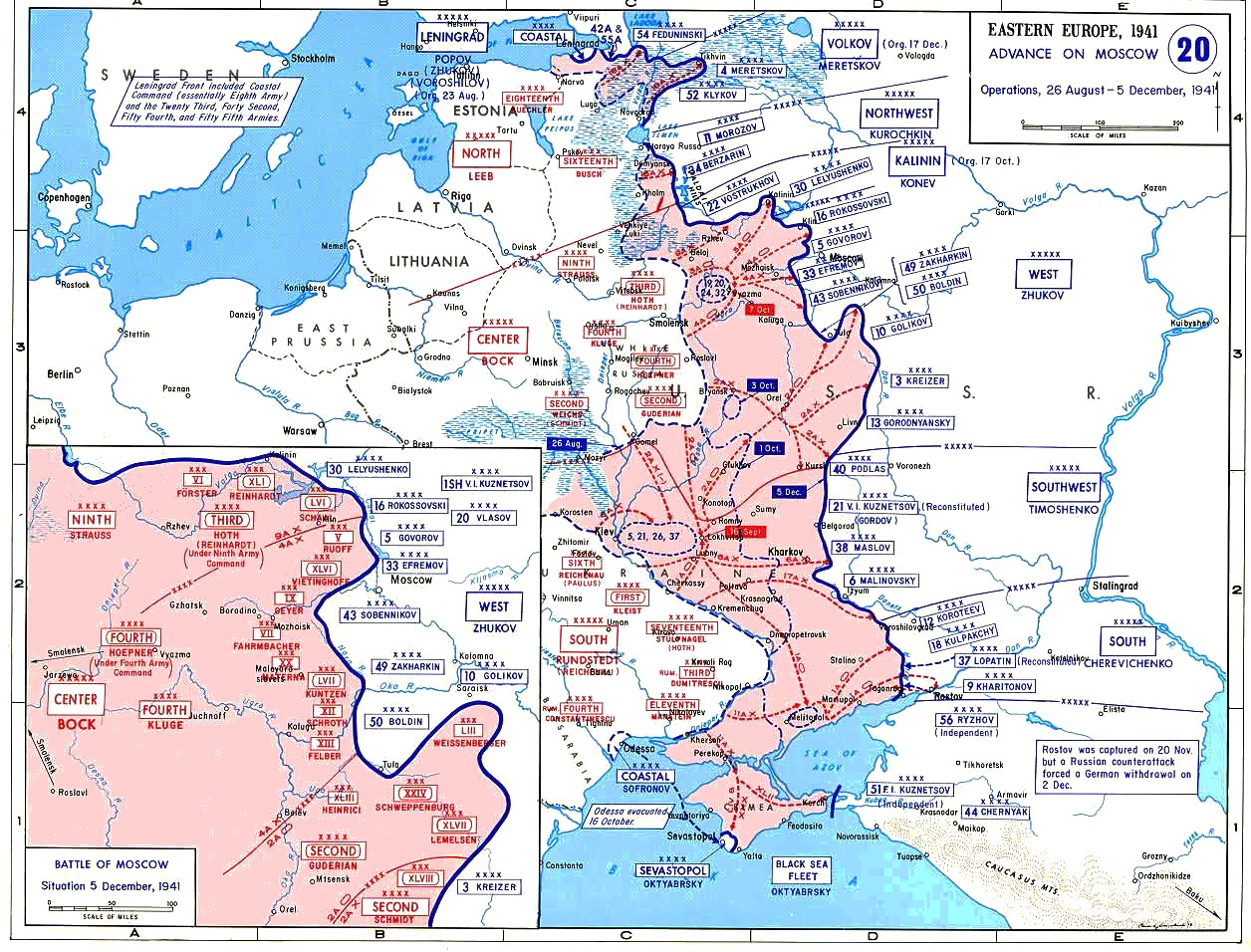
Battle Of Moscow
The Battle of Moscow was a military campaign that consisted of two periods of strategically significant fighting on a sector of the Eastern Front during World War II, between October 1941 and January 1942. The Soviet defensive effort frustrated Hitler's attack on Moscow, the capital and largest city of the Soviet Union. Moscow was one of the primary military and political objectives for Axis forces in their invasion of the Soviet Union. The German Strategic Offensive, named Operation Typhoon, called for two pincer offensives, one to the north of Moscow against the Kalinin Front by the 3rd and 4th Panzer Armies, simultaneously severing the Moscow–Leningrad railway, and another to the south of Moscow Oblast against the Western Front south of Tula, by the 2nd Panzer Army, while the 4th Army advanced directly towards Moscow from the west. Initially, the Soviet forces conducted a strategic defence of Moscow Oblast by constructing three defensive belts, deploying newly r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany, officially known as the German Reich and later the Greater German Reich, was the German Reich, German state between 1933 and 1945, when Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party controlled the country, transforming it into a Totalitarianism, totalitarian dictatorship. The Third Reich, meaning "Third Realm" or "Third Empire", referred to the Nazi claim that Nazi Germany was the successor to the earlier Holy Roman Empire (800–1806) and German Empire (1871–1918). The Third Reich, which the Nazis referred to as the Thousand-Year Reich, ended in May 1945, after 12 years, when the Allies of World War II, Allies defeated Germany and entered the capital, Berlin, End of World War II in Europe, ending World War II in Europe. After Hitler was appointed Chancellor of Germany in 1933, the Nazi Party began to eliminate political opposition and consolidate power. A 1934 German referendum confirmed Hitler as sole ''Führer'' (leader). Power was centralised in Hitler's person, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Army (Wehrmacht)
The German Army (, 'army') is the land component of the armed forces of Federal Republic of Germany, Germany. The present-day German Army was founded in 1955 as part of the newly formed West German together with the German Navy, ''Marine'' (German Navy) and the German Air Force, ''Luftwaffe'' (German Air Force). , the German Army had a strength of 63,047 soldiers. History Overview A German army equipped, organized, and trained following a single doctrine and permanently unified under one command was created in 1871 during the unification of Germany under the leadership of Prussia. From 1871 to 1919, the title ''German Army (German Empire), Deutsches Heer'' (German Army) was the official name of the German land forces. Following the German defeat in World War I and the end of the German Empire, the main army was dissolved. From 1921 to 1935 the name of the German land forces was the ''Reichswehr, Reichsheer'' (Army of the Realm) and from 1935 to 1945 the name ''German Army (We ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
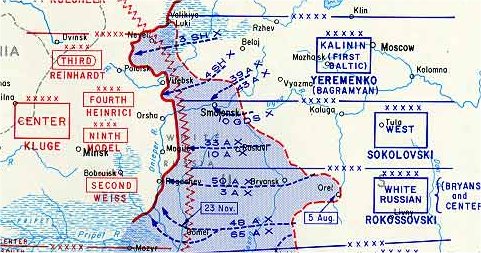
Operation Bagration
Operation Bagration () was the codename for the 1944 Soviet Byelorussian strategic offensive operation (), a military campaign fought between 22 June and 19 August 1944 in Byelorussian Soviet Socialist Republic, Soviet Byelorussia in the Eastern Front (World War II), Eastern Front of World War II, just over two weeks after the start of Operation Overlord in the west. It was during this operation that Nazi Germany was forced to fight simultaneously on two major fronts for the first time since the war began. The Soviet Union destroyed 28 of the divisions of Army Group Centre and completely shattered the German front line. The overall engagement is the largest defeat in German military history, with around 450,000 German casualties, while setting the stage for the subsequent isolation of 300,000 German soldiers in the Courland Pocket. On 22 June 1944, the Red Army attacked Army Group Centre in Byelorussia, with the objective of encircling and destroying its main component armies. By ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Smolensk (1943)
The second Smolensk operation (code naming "Alexander Suvorov, Suvorov";Istomin (1975), pp. 20–21 7 August – 2 October 1943) was a Soviet strategic offensive operation conducted by the Red Army as part of the Summer-Autumn Campaign of 1943. Staged almost simultaneously with the Lower Dnieper Offensive (13 August – 22 September), the offensive lasted two months and was led by General Andrei Yeremenko, commanding the Kalinin Front, and Vasily Sokolovsky, commanding the Western Front (Soviet Union), Western Front. Its goal was to clear the German presence from the Smolensk and Bryansk regions. Smolensk had been under German occupation since the first Battle of Smolensk (1941), Battle of Smolensk in 1941. Despite an impressive German defense, the Red Army was able to stage several breakthroughs, liberating several major cities, including Smolensk and Roslavl. As a result of this operation, the Red Army was able to start planning for the liberation of Belarus. However, the overa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |