|
132nd Infantry Division (Wehrmacht)
The 132nd Infantry Division (German: ''132. Infanterie-Division'') was a Nazi Germany, German division (military), division in World War II. It was formed on 5 October 1940 in Landshut, as part of the Aufstellungswelle#11th_wave, 11th Wave of Wehrmacht mobilization, and was destroyed in the Courland Pocket in 1945. In May 1941 the units of this division participated in the suppression of the May 1941 Sanski Most revolt, Serb uprising in Sanski Most in the Independent State of Croatia, a fascist puppet state created from Kingdom of Yugoslavia, Yugoslav territory. Following operations in the Balkans, the division participated in Operation Barbarossa as part of Army Group South. The division was held in reserve and did not see combat in the Soviet Union until July 27, 1941, near Koziatyn in Ukraine. The division was then involved in operations south of Kiev along the Dnieper River and later was diverted to the Crimea, where it served on the Isthmus of Perekop, Battle of the Kerch Peni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infantry
Infantry, or infantryman are a type of soldier who specialize in ground combat, typically fighting dismounted. Historically the term was used to describe foot soldiers, i.e. those who march and fight on foot. In modern usage, the term broadly encompasses a wide variety of subspecialties, including light infantry, irregular infantry, heavy infantry, mountain infantry, motorized infantry, mechanized infantry, Airborne forces, airborne infantry, Air assault, air assault infantry, and Marines, naval infantry. Other subtypes of infantry, such as line infantry and mounted infantry, were once commonplace but fell out of favor in the 1800s with the invention of more accurate and powerful weapons. Etymology and terminology In English, use of the term ''infantry'' began about the 1570s, describing soldiers who march and fight on foot. The word derives from Middle French , from older Italian (also Spanish) ''infanteria'' (foot soldiers too inexperienced for cavalry), from Latin '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kiev
Kyiv, also Kiev, is the capital and most populous List of cities in Ukraine, city of Ukraine. Located in the north-central part of the country, it straddles both sides of the Dnieper, Dnieper River. As of 1 January 2022, its population was 2,952,301, making Kyiv the List of European cities by population within city limits, seventh-most populous city in Europe. Kyiv is an important industrial, scientific, educational, and cultural center. It is home to many High tech, high-tech industries, higher education institutions, and historical landmarks. The city has an extensive system of Transport in Kyiv, public transport and infrastructure, including the Kyiv Metro. The city's name is said to derive from the name of Kyi, one of its four legendary founders. During History of Kyiv, its history, Kyiv, one of the oldest cities in Eastern Europe, passed through several stages of prominence and obscurity. The city probably existed as a commercial center as early as the 5th century. A Slav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rudolf Sintzenich
Rudolf Sintzenich (13 July 1889 – 24 December 1948) was a general in the Wehrmacht of Nazi Germany during World War II who commanded several divisions. He was a recipient of the Knight's Cross of the Iron Cross. Awards and decorations (excerpt) * Iron Cross (1914), 2nd and 1st Class * Military Merit Order (Bavaria), 4th Class with Swords * Wound Badge (1914) in Black * Honour Cross of the World War 1914/1918 with Swords * Sudetenland Medal * West Wall Medal * Repetition Clasp 1939 to the Iron Cross 1914, 2nd and 1st Class * War Merit Cross (1939), 2nd Class with Swords * Eastern Front Medal * Order of the Crown of King Zvonimir, I. Class with Star * Knight's Cross of the Iron Cross on 15 August 1940 as ''Generalmajor is the Germanic languages, Germanic variant of major general, used in a number of Central Europe, Central and Northern European countries. Austria Belgium Denmark is the second lowest general officer rank in the Royal Danish Army and R ...'' and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
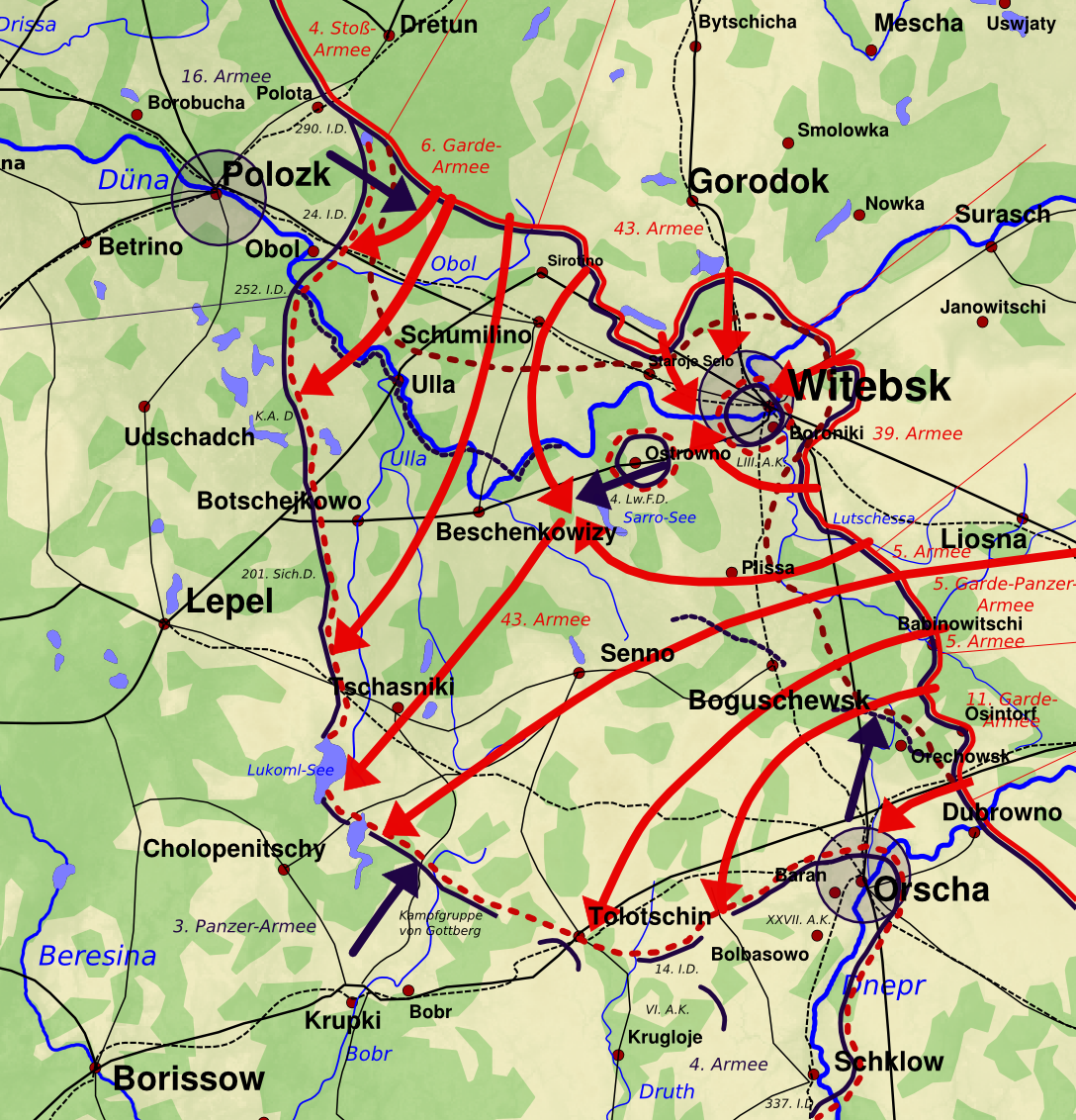
Operation Bagration
Operation Bagration () was the codename for the 1944 Soviet Byelorussian strategic offensive operation (), a military campaign fought between 22 June and 19 August 1944 in Byelorussian Soviet Socialist Republic, Soviet Byelorussia in the Eastern Front (World War II), Eastern Front of World War II, just over two weeks after the start of Operation Overlord in the west. It was during this operation that Nazi Germany was forced to fight simultaneously on two major fronts for the first time since the war began. The Soviet Union destroyed 28 of the divisions of Army Group Centre and completely shattered the German front line. The overall engagement is the largest defeat in German military history, with around 450,000 German casualties, while setting the stage for the subsequent isolation of 300,000 German soldiers in the Courland Pocket. On 22 June 1944, the Red Army attacked Army Group Centre in Byelorussia, with the objective of encircling and destroying its main component armies. By ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Army Group Centre
Army Group Centre () was the name of two distinct strategic German Army Groups that fought on the Eastern Front in World War II. The first Army Group Centre was created during the planning of Operation Barbarossa, Germany's invasion of the Soviet Union, as one of the three German Army formations assigned to the invasion. After Army Group North was trapped in the Courland Pocket in mid-1944, it was renamed to Army Group Courland and the first Army Group Centre was renamed "Army Group North". The second iteration of Army Group Centre was formed by the redesignation of Army Group A as the replacement for the first Army Group Centre. Formation and Command The army group was officially created by Adolf Hitler when he issued Führer Directive 21 on 18 December 1940, ordering German forces to prepare for an attack on Soviet Russia in 1941. The first commanding officer of Army Group Centre was Field Marshal Fedor von Bock, who would lead it until he was relieved on 18 December 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of Leningrad
The siege of Leningrad was a Siege, military blockade undertaken by the Axis powers against the city of Leningrad (present-day Saint Petersburg) in the Soviet Union on the Eastern Front (World War II), Eastern Front of World War II from 1941 to 1944. Leningrad, the country's second largest city, was besieged by Nazi Germany, Germany and Finland for 872 days, but never captured. The siege was the List of sieges, most destructive in history and possibly the List of battles by casualties#Sieges and urban combat, most deadly, causing an estimated 1.5 million deaths, from a prewar population of 3.2 million. It was not classified as a war crime at the time, but some historians have since classified it as a genocide due to the intentional destruction of the city and the systematic starvation of its civilian population. p. 334 In August 1941, Nazi Germany, Germany's Army Group North reached the suburbs of Leningrad as Finnish forces moved to encircle the city from the north. Land ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake Ladoga
Lake Ladoga is a freshwater lake located in the Republic of Karelia and Leningrad Oblast in northwestern Russia, in the vicinity of Saint Petersburg. It is the largest lake located entirely in Europe, the second largest lake in Russia after Lake Baikal, and the List of lakes by area, 14th largest freshwater lake by area in the world. It is comparable in size to Lake Ontario. ''Ladoga Lacus'', a methane lake on Saturn's moon Titan (moon), Titan, is named after the lake. Etymology In one of Nestor the Chronicler, Nestor's chronicles from the 12th century a lake called "the Great Nevo" is mentioned, a clear link to the Neva River and possibly further to Finnish language, Finnish ''nevo'' 'sea' or ''neva'' 'bog, quagmire'.:ru:Поспелов, Евгений Михайлович, Evgeny Pospelov: ''Geographical names of the world. Toponymic dictionary.'' Second edition. Astrel, Moscow 2001, pp. 106f. Ancient Norse sagas and Hanseatic treaties both mention a city made of lakes named ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sinyavino Offensive
The Sinyavino offensives were a series of Soviet offensives in 1941–1943 during World War II around the Sinyavino Heights, east of Leningrad, to lift the Siege of Leningrad. The area was only fully liberated during the Leningrad–Novgorod offensive in January 1944. List of battles First Sinyavino offensive (1941) The first Sinyavino offensive was a Soviet counterattack during the German Encirclement of Leningrad between 10 and 26 September 1941. It was executed by the 54th Army which attacked from the east and by the Leningrad Front's 115th Rifle Division and 4th Marines Brigade which attacked from the region of Nevskaya Dubrovka in Leningrad. The 54th Army Detachment advanced some 6-10 km, but was then surrounded and nearly entirely destroyed. The Leningrad Front troops made a forced crossing over the Neva River and occupied the Neva Bridgehead, but failed to advance any further. The Commander of the 54th Army, Marshal Grigory Kulik was relieved of command for the fa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operation Nordlicht (1942)
Operation Nordlicht (German, 'Northern Light') was devised by the German high command, the ''Oberkommando des Heeres'' ("High Command of the Army") after a year-long battle for Leningrad when Adolf Hitler ordered a final assault on the besieged city. The main objective of the operation was to capture Leningrad using forces of Army Group North under Field Marshal Georg von Küchler, and thereby bring an end to the siege and free up hundreds of thousands of troops. Meanwhile, the Germans were also preparing for the Battle of Stalingrad. Both attacks on Leningrad in the North and on Stalingrad in the South were synchronized by the Germans so as to confuse the Soviets. Operation Nordlicht was to begin on 23 August 1942 with a massive artillery bombardment of Leningrad, following with aerial bombardments by the Luftwaffe. But when the Soviets launched the Sinyavino Offensive on 19 August, the forces that were intended to be used for Nordlicht were transferred from the planned offensive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Army Group North
Army Group North () was the name of three separate army groups of the Wehrmacht during World War II. Its rear area operations were organized by the Army Group North Rear Area. The first Army Group North was deployed during the invasion of Poland and subsequently renamed Army Group B. The second Army Group North was created on 22 June 1941 from the former Army Group C and used in the northern sector of the Eastern Front from 1941 to January 1945. By then, this second Army Group North had gotten trapped in the Courland Pocket and was accordingly redesignated Army Group Courland. On the same day, the former Army Group Center, which was now defending the northernmost sector of the contiguous Eastern Front, was renamed Army Group North, assuming the status of the third and final iteration of the army group. First deployment of Army Group North: September – October 1939 The staff of Army Group North was formally assembled on 2 September 1939 from the headquarters of 2nd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maxim Gorky Fortresses
Armoured Coastal Batteries #30 and #35, commonly known in English as Maxim Gorky I and Maxim Gorky II, were coastal battery, coastal batteries used by the Soviet Union during the Crimean Campaign of World War II. The Operation Barbarossa, invading German forces nicknamed them after the famous Soviet author and political activist Maxim Gorky. Maxim Gorky I Maxim Gorky I () was located east of Ljabimorka, at (north of Severnaya Bay which formed Sevastopol's harbor), and contained two twin gun turrets which could fire four Obukhovskii 12"/52 Pattern 1907 gun, 30.5 cm guns. Once the Germans had broken through the Perekop Isthmus in October 1941, they advanced on Sevastopol but were confronted by Maxim Gorky I. They deployed the 80 cm rail gun Schwerer Gustav to destroy it. On June 6, 1942, heavy guns and Karl-Gerät siege mortars managed to make direct hits on the battery which destroyed one of the gun turrets and damaged the other. None of these were successful in eliminating t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of Sevastopol (1941–1942)
The siege of Sevastopol, also known as the defence of Sevastopol () or the Battle for Sevastopol (; ), was a military engagement that took place on the Eastern Front of the Second World War. The campaign was fought by the Axis powers of Germany and Romania against the Soviet Union for control of Sevastopol, a port in Crimea on the Black Sea. On 22 June 1941, the Axis invaded the Soviet Union during Operation Barbarossa, with Axis land forces reaching the Crimean peninsula in the autumn of 1941 and overrunning most of the area. The only objective not in Axis hands was Sevastopol. Several attempts were made to secure the city in October and November 1941. A major attack was planned for late November, but heavy rains delayed it until 17 December 1941. Under the command of Erich von Manstein, Axis forces were unable to capture Sevastopol during this first operation. Soviet forces launched an amphibious landing on the Crimean peninsula at Kerch in December 1941 to relieve the siege ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |