|
12th Infantry Regiment (Poland)
12th Infantry Regiment (Polish language: 12 Pulk Piechoty, 12 pp) was an infantry regiment of the Polish Army. It existed from 1918 until 1939. Garrisoned in Wadowice, the unit belonged to the 6th Infantry Division from Kraków. The regiment celebrated its holiday on August 1, the anniversary of the 1920 Battle Of Leszniow, against the Red Army. During the 1939 Invasion of Poland, it belonged to Kraków Army, together with the 6th Infantry Division. Commandants * Colonel Jan Mischke (1918–1919), * Captain Franciszek Alter (1919), * Colonel Eugeniusz Stecz (1919), * Major Adam Smialowski (1919), * Colonel Edward Reyman (1919), * Captain Oswald Frank (1919), * Colonel Wandalin Doroszkiewicz (1919 – 10 1920), * Captain Wladyslaw Mielnik (1920), * Major Franciszek Alter (1920–1921), * Colonel Oswald Frank (1921–1927), * Colonel Jozef Cwiertniak (1927–1929), * Colonel Jozef Jaklicz (1929–1932), * Colonel Marian Raczynski (1932–1933), * Colonel Antoni Staic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polish Language
Polish (, , or simply , ) is a West Slavic languages, West Slavic language of the Lechitic languages, Lechitic subgroup, within the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family, and is written in the Latin script. It is primarily spoken in Poland and serves as the official language of the country, as well as the language of the Polish diaspora around the world. In 2024, there were over 39.7 million Polish native speakers. It ranks as the sixth-most-spoken among languages of the European Union. Polish is subdivided into regional Dialects of Polish, dialects. It maintains strict T–V distinction pronouns, Honorifics (linguistics), honorifics, and various forms of formalities when addressing individuals. The traditional 32-letter Polish alphabet has nine additions (, , , , , , , , ) to the letters of the basic 26-letter Latin alphabet, while removing three (x, q, v). Those three letters are at times included in an extended 35-letter alphabet. The traditional set compri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aleksander Stawarz
Aleksander StawarzW dziennikach personalnych M.S.Wojsk. z 1924, 1928 i 1932 r. jako datę urodzenia podano 7 lipca 1896 r. codename: Leśnik, Baca (7 August 1896, Nowy Targ - 28 January 1941, Auschwitz) was a Polish Army Colonel. In the First World War Stawarz served in Polish Legions. Since 1918 in the Polish Army he took part in the Polish-Bolshevik war, he distinguished himself during street fights in Minsk and the battle of Kalinówka. During the Second World War Stawarz was commander of the "2nd Highland Brigade" of the Army Karpaty. From 1939 until 1941 he was the founder and commander of the resistance unit "Dywizja Podhalańska", which was part of the ZWZ. He was arrested by the Gestapo and murdered in the German concentration camp Auschwitz Auschwitz, or Oświęcim, was a complex of over 40 concentration and extermination camps operated by Nazi Germany in occupied Poland (in a portion annexed into Germany in 1939) during World War II and the Holocaust. It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Military Units And Formations Established In 1918
A military, also known collectively as armed forces, is a heavily armed, highly organized force primarily intended for warfare. Militaries are typically authorized and maintained by a sovereign state, with their members identifiable by a distinct military uniform. They may consist of one or more military branches such as an army, navy, air force, space force, marines, or coast guard. The main task of a military is usually defined as defence of their state and its interests against external armed threats. In broad usage, the terms "armed forces" and "military" are often synonymous, although in technical usage a distinction is sometimes made in which a country's armed forces may include other paramilitary forces such as armed police. Beyond warfare, the military may be employed in additional sanctioned and non-sanctioned functions within the state, including internal security threats, crowd control, promotion of political agendas, emergency services and reconstruction, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infantry Regiments Of Poland
Infantry, or infantryman are a type of soldier who specialize in ground combat, typically fighting dismounted. Historically the term was used to describe foot soldiers, i.e. those who march and fight on foot. In modern usage, the term broadly encompasses a wide variety of subspecialties, including light infantry, irregular infantry, heavy infantry, mountain infantry, motorized infantry, mechanized infantry, Airborne forces, airborne infantry, Air assault, air assault infantry, and Marines, naval infantry. Other subtypes of infantry, such as line infantry and mounted infantry, were once commonplace but fell out of favor in the 1800s with the invention of more accurate and powerful weapons. Etymology and terminology In English, use of the term ''infantry'' began about the 1570s, describing soldiers who march and fight on foot. The word derives from Middle French , from older Italian (also Spanish) ''infanteria'' (foot soldiers too inexperienced for cavalry), from Latin '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1939 Infantry Regiment (Poland)
The Polish Infantry Regiment; (Polish: Pulk Piechoty) during World War 2 comprised on average some 2,900 men and 60 officers organised around 3 rifle battalions armed with either the Karabinek wz.29 or the Wz. 98, 7.92mm bolt-action rifles. Each 19-man squad was also issued the RKM wz.28 light machine gun. Other regimental weapons included the Polish version of the French Model 1897 75-mm field gun, the Wz. 35 anti-tank rifle, the Ckm wz.30 heavy machine gun A heavy machine gun (HMG) is significantly larger than light, medium or general-purpose machine guns. HMGs are typically too heavy to be man-portable (carried by one person) and require mounting onto a weapons platform to be operably stable or ..., the wz.31 81 mm mortar, and the wz.36 46mm light mortar/grenade launcher. Table of Organization and Equipment * 1 Recon Company **4 light machine guns **2 antitank rifles * 1 Antitank Company **9 37 mm antitank guns * 1 Pioneer Platoon * 1 Artillery Platoon **2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stanisław Szeptycki
Stanisław Maria Jan Teofil Szeptycki (3 November 1867 – 9 October 1950) was a Polish count, general and military commander. Biography Born in 1867 in Galicia, Austria-Hungary to the aristocratic Szeptycki family, he was the grandson of Polish playwright Aleksander Fredro, son of the count Jan Kanty Szeptycki and brother of Andrey Sheptytsky, Metropolitan Archbishop of the Ukrainian Greek Catholic Church (Stanisław was a Catholic of the Latin rite, his brother Andrey/Andrzej was also initially of the Latin Rite, but instead followed Greek Catholicism). Szeptycki joined the Austro-Hungarian Army, where he attained the rank of colonel. In 1914 he joined the Polish Legions, where he became commander of the Third Brigade, and from November 1916 to April 1917 commander of the entire Polish Legions formation. Following the Oath Crisis he commanded the German-aligned '' Polnische Wehrmacht''. Until February 1918 he was Austro-Hungarian governor general of Lublin, but resigned ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kalwaria Zebrzydowska
Kalwaria Zebrzydowska () is a town in southern Poland with 4,429 inhabitants (2007 estimate). As of 1999, it is situated in Lesser Poland or Małopolska (in Polish). Previously, the town was administered within the Voivodeship of Bielsko-Biała (1975–1998). Overview With a vision while viewing the neighbouring hills and valleys from the Castle of Lanckorona, on 1 December 1602, Mikołaj Zebrzydowski, the Voivode of Kraków commissioned the construction of a calvary, i.e. Roman Catholic monastery and the trails of the Passion of Christ modeled on the Calvary outside the city walls of Jerusalem. The town takes its name from the monastery that was constructed on the hills neighbouring Lanckorona and the last name of its founder Zebrzydowski. The town of Zebrzydów was established in 1617 in order to house the growing number of pilgrims visiting the Roman Catholic site of worship. The town rights were expanded and the town remapped by Jan Zebrzydowski in 1640, gaining the na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jozef Jaklicz
Jozef Jaklicz (1894–1974) was a soldier of the Austro-Hungarian Army and the Polish Legions in World War I, and officer of the Polish Army in the Second Polish Republic, nominated to the rank of General brygady. He fought in World War I, Polish–Soviet War, Polish–Ukrainian War and the Invasion of Poland. Jaklicz was born on 17 September 1894 in Kraków. After graduation from high school, he studied philosophy at the Jagiellonian University, and was active member of the Polish Sokol movement. In August 1914, Jaklicz joined 3rd Infantry Regiment of the Polish Legions. Promoted to the rank of company commander, he fought in Eastern Carpathians, Bessarabia and Volhynia. Following the creation of the Polish Auxiliary Corps, Jaklicz became a staff officer, and after its dissolution, he joined Polska Siła Zbrojna (Polnische Wehrmacht). In late 1918, Jaklicz entered the Polish Army, and was named commandant of a battalion of the 36th Academic Legion Infantry Regiment, which fought in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polish Army
The Land Forces () are the Army, land forces of the Polish Armed Forces. They currently contain some 110,000 active personnel and form many components of the European Union and NATO deployments around the world. Poland's recorded military history stretches back a millennium – since the 10th century (see List of Polish wars and History of the Polish Army). Poland's modern army was formed after Poland Partitions of Poland, regained independence following World War I in 1918. History 1918–1938 When Poland History of Poland (1918–1939), regained independence in 1918, it recreated its military which participated in the Polish–Soviet War of 1919–1921, and in the two smaller conflicts ( Polish–Ukrainian War (1918–1919) and the Polish–Lithuanian War (1919–1920)). Initially, right after the First World War, Poland had five military districts (1918–1921): * Poznań Military District (Poznański Okręg Wojskowy), HQ in Poznań * Kraków Military District (Krakowski ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Franciszek Alter
Franciszek Alter (22 November 1889 in Lviv – 23 January 1945 in Garmisch-Partenkirchen) was a Polish general. Career Franciszek Alter began his career as an officer in the Austro-Hungarian Army, reaching the rank of captain. He fought in the Polish Army during the Polish-Soviet War. He was promoted to general in March 1939. During the German invasion of Poland, he commanded the 25th Infantry Division (part of the Army Poznań). His division took part in the battle of Bzura and the defense of Warsaw, where it capitulated on 28 September. Death Alter refused to sign the Volksliste, and was imprisoned in the Oflag VII-A Murnau. In the Oflag, he fell ill, and died in early 1945, on 23 January. Awards Alter was awarded with the Silver Cross of the Virtuti Militari, the Knight's Cross of the Polonia Restituta, the Cross of Valour (four times) and the Cross of Independence Cross of Independence () was the second highest Polish military decoration between World Wars I a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
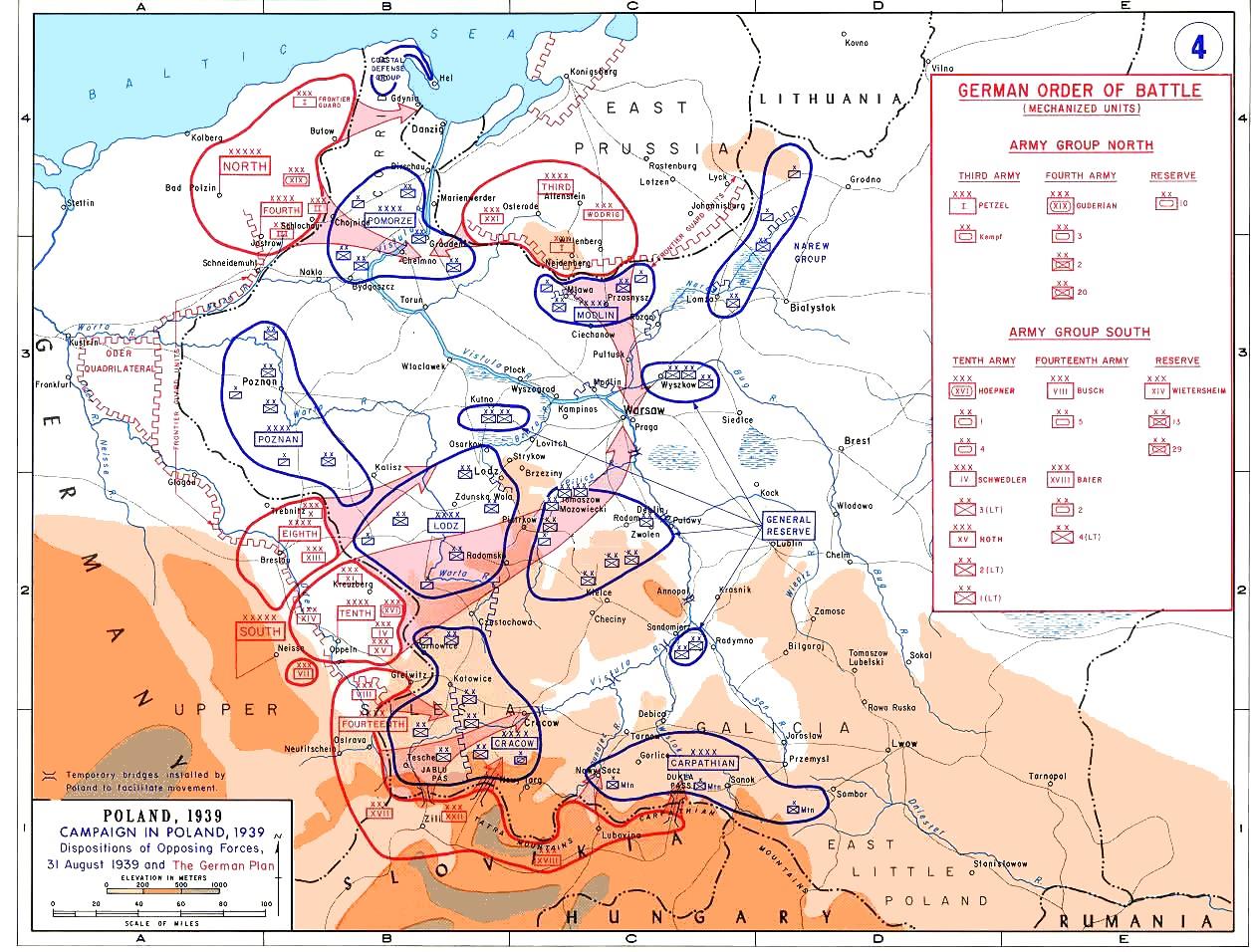
Kraków Army
Kraków Army () was one of the List of Polish armies, Polish armies which took part in the Invasion of Poland (1939), Polish Defensive War of 1939. It was officially created on March 23, 1939 as the main pivot of Polish defence. It was commanded by Gen. Antoni Szylling. Originally, Kraków Army was to be made of seven infantry divisions, two cavalry brigades and one mountain brigade. On September 1, 1939, General Szylling had the force which consisted of five infantry divisions, two cavalry brigades and one brigade of mountain infantry. Altogether, the army was made of 59 battalions, 29 squadrons, 352 cannons, 90 tanks, two armoured trains and 44 planes. These forces were not enough to halt German advance, especially in the area north of Częstochowa, where Kraków Army connected with Łódź Army. Main thrust of Wehrmacht panzer units was directed there, and this area was defended only by the Polish 7th I.D., which was destroyed in the early days of September 1939, opening the way t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |