|
12th Infantry Division (Wehrmacht)
The 12th Infantry Division (German: "12. Infanteriedivision") – later known as the 12th Volksgrenadier Division – was a Wehrmacht military unit of Nazi Germany that fought during World War II. The division was formed in 1934. It participated in the invasion of Poland in 1939 and the 1940 campaign in France and the Low Countries. In the Soviet Union, the division joined Operation Barbarossa. The division was destroyed in the Soviet Operation Bagration in the summer of 1944. The division was re-activated in September 1944 and posted to the newly created Western Front. History and organisation Formation The division was formed in 1934 from Pomerania's Mecklenburger population, with its home station being in Schwerin. In order to hide Germany's remilitarisation – a breaking of the terms of the Treaty of Versailles – the unit was codenamed ''Infanterieführer II'' to disguise its size. It did not assume its bona-fide designation until the creation of the Wehrmacht was annou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infantry
Infantry, or infantryman are a type of soldier who specialize in ground combat, typically fighting dismounted. Historically the term was used to describe foot soldiers, i.e. those who march and fight on foot. In modern usage, the term broadly encompasses a wide variety of subspecialties, including light infantry, irregular infantry, heavy infantry, mountain infantry, motorized infantry, mechanized infantry, Airborne forces, airborne infantry, Air assault, air assault infantry, and Marines, naval infantry. Other subtypes of infantry, such as line infantry and mounted infantry, were once commonplace but fell out of favor in the 1800s with the invention of more accurate and powerful weapons. Etymology and terminology In English, use of the term ''infantry'' began about the 1570s, describing soldiers who march and fight on foot. The word derives from Middle French , from older Italian (also Spanish) ''infanteria'' (foot soldiers too inexperienced for cavalry), from Latin '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
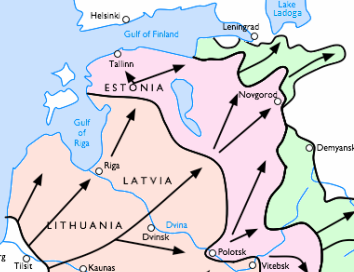
Demjansk Einkesselung
Demyansk () is an urban locality (a work settlement) and the administrative center of Demyansky District of Novgorod Oblast, Russia, located along the Yavon River. Municipally, it is incorporated as Demyanskoye Urban Settlement, the only urban settlement in the district. Population: History Demyansk was first mentioned in a chronicle in 1406 as Demon. The area was a part of Derevskaya Pyatina of Novgorod. Demon was a fortress protecting a waterway from Lake Ilmen upstream the Pola and the Yavon to Lake Seliger. The fortress was located close to the boundary between the Novgorod Republic and the Grand Duchy of Moscow, and it was at least twice sieged by Muscovite troops. In 1441, the Muscovites did not manage to conquer Demon, but in the 1470s they conquered and destroyed the fortress. After the subsequent fall of Novgorod, Demon was transferred to the Grand Duchy of Moscow. In the 17th century, Demon went into decline, and a new settlement was founded nearby, which was known ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heinz-Georg Lemm
Heinz-Georg Lemm (1 June 1919 – 17 November 1994) was a German Oberst (colonel) of the Wehrmacht and general in the who served as Chief of the Army Office. Career During World War II, Lemm served in the Wehrmacht and was a recipient of the Knight's Cross of the Iron Cross with Oak Leaves and Swords. He was promoted to Major 1943, 1944 and Oberst 1945. Lemm joined the in 1957 and commanded the 7th Panzergrenadier-Brigade of the 3rd Panzer-Division in Hamburg until 1963, when he was promoted to Brigadegeneral. In 1970 he was promoted to Generalmajor and commanded the 5th Panzer-Division in Diez. Promoted further in 1974, he was named Chief of the Troop Office of the , with the rank of . He was awarded the Great Cross of Merit with Star and the Legion of Merit; he retired in 1979. After this he became honorary president (''Ehrenpräsident'') of the Association of Knight's Cross Recipients. Awards *Iron Cross (1939) 2nd Class (6 October 1939) & 1st Class (31 December ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Army Group Centre
Army Group Centre () was the name of two distinct strategic German Army Groups that fought on the Eastern Front in World War II. The first Army Group Centre was created during the planning of Operation Barbarossa, Germany's invasion of the Soviet Union, as one of the three German Army formations assigned to the invasion. After Army Group North was trapped in the Courland Pocket in mid-1944, it was renamed to Army Group Courland and the first Army Group Centre was renamed "Army Group North". The second iteration of Army Group Centre was formed by the redesignation of Army Group A as the replacement for the first Army Group Centre. Formation and Command The army group was officially created by Adolf Hitler when he issued Führer Directive 21 on 18 December 1940, ordering German forces to prepare for an attack on Soviet Russia in 1941. The first commanding officer of Army Group Centre was Field Marshal Fedor von Bock, who would lead it until he was relieved on 18 December 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vitebsk
Vitebsk or Vitsyebsk (, ; , ; ) is a city in northern Belarus. It serves as the administrative center of Vitebsk Region and Vitebsk District, though it is administratively separated from the district. As of 2025, it has 358,927 inhabitants, making it the country's fourth-largest city. It is served by Vitebsk Vostochny Airport and Vitebsk Air Base. History Middle Ages Vitebsk developed from a river harbor where the Vićba River (Віцьба, from which it derives its name) flows into the larger Western Dvina, which is spanned in the city by the Kirov Bridge. Archaeological research indicates that Baltic tribes had settlements at the mouth of Vitba. In the 9th century, Slavic settlements of the tribal union of the Krivichs replaced them. According to the '' Chronicle of Michael Brigandine'' (1760), Princess Olga of Kiev founded Vitebsk (also recorded as Dbesk, Vidbesk, Videbsk, Vitepesk, or Vicibesk) in 974. Other versions give 947 or 914. Academician Boris Rybakov an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Byelorussian Soviet Socialist Republic
The Byelorussian Soviet Socialist Republic (BSSR, Byelorussian SSR or Byelorussia; ; ), also known as Soviet Belarus or simply Belarus, was a Republics of the Soviet Union, republic of the Soviet Union (USSR). It existed between 1920 and 1922 as an independent state, and afterwards as one of Republics of the Soviet Union, fifteen constituent republics of the USSR from 1922 to 1991, with its own legislation from 1990 to 1991. The republic was ruled by the Communist Party of Byelorussia. It was also known as the ''White Russian Soviet Socialist Republic''. Following the Treaty of Brest-Litovsk in March 1918, which ended Russia's involvement in World War I, the Belarusian Democratic Republic (BDR) was proclaimed under German occupation; however, as German troops left, the Socialist Soviet Republic of Byelorussia was established in its place by the Bolsheviks in December, and it was later merged with the Lithuanian Soviet Socialist Republic (1918–1919), Lithuanian Soviet Socia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Stalingrad
The Battle of Stalingrad ; see . rus, links=on, Сталинградская битва, r=Stalingradskaya bitva, p=stəlʲɪnˈɡratskəjə ˈbʲitvə. (17 July 19422 February 1943) was a major battle on the Eastern Front of World War II, beginning when Nazi Germany and its Axis allies attacked and became locked in a protracted struggle with the Soviet Union for control over the Soviet city of Stalingrad (now known as Volgograd) in southern Russia. The battle was characterized by fierce close-quarters combat and direct assaults on civilians in aerial raids; the battle epitomized urban warfare, being the single largest and costliest urban battle in military history. It was the bloodiest and fiercest battle of the entirety of World War II—and arguably in all of human history—as both sides suffered tremendous casualties amidst ferocious fighting in and around the city. The battle is commonly regarded as the turning point in the European theatre of World War II, as Germany ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hermann Göring
Hermann Wilhelm Göring (or Goering; ; 12 January 1893 – 15 October 1946) was a German Nazism, Nazi politician, aviator, military leader, and convicted war criminal. He was one of the most powerful figures in the Nazi Party, which governed Germany from 1933 to 1945. He also served as ''Oberkommando der Luftwaffe, Oberbefehlshaber der Luftwaffe'' (Supreme Commander of the Air Force), a position he held until the final days of the regime. He was born in Rosenheim, Kingdom of Bavaria, Bavaria. A veteran World War I fighter pilot Flying aces, ace, Göring was a recipient of the . He served as the last commander of Jagdgeschwader 1 (World War I), ''Jagdgeschwader'' 1 (JG I), the fighter wing once led by Manfred von Richthofen. An early member of the Nazi Party, Göring was among those wounded in Adolf Hitler's failed Beer Hall Putsch in 1923. While receiving treatment for his injuries, he developed an addiction to morphine that persisted until the last year of his life. Aft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Demyansk Pocket
The Demyansk Pocket (; ) was the name given to the pocket of German troops encircled by the Red Army around Demyansk, south of Leningrad, during World War II's Eastern Front. The pocket existed mainly from 8 February to 21 April 1942. A much smaller force was surrounded in the Kholm Pocket at the town of Kholm, about to the southwest. Both resulted from the German retreat after its defeat during the Battle of Moscow. The successful defence of Demyansk was achieved by using an airbridge and was a significant development in modern warfare. Its success was a major contributor to the decision by the Army High Command to try the same tactic during the Battle of Stalingrad, but it then failed to save the 6th Army, commanded by Friedrich Paulus. Encirclement The encirclement began as the Demyansk Offensive Operation, the first phase being carried out from 7 January until 20 May 1942 on the initiative of General Lieutenant Pavel Kurochkin, commander of Northwestern Front. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
3rd SS Panzer Division Totenkopf
The 3rd SS Panzer Division "Totenkopf" () was an elite division of the Waffen-SS of Nazi Germany during World War II, formed from the Standarten of the SS-TV. Its name, '' Totenkopf'', is German for "death's head"the skull and crossbones symboland it is thus sometimes referred to as the Death's Head Division. The division was formed through the expansion of ''Kampfgruppe Eicke'', a battle group named – in keeping with German military practice – after its commander, Theodor Eicke. Most of the battle group's personnel had been transferred to the Waffen-SS from concentration camp guard units, which were known collectively as ''SS-Totenkopfverbände''; others were former members of '' Selbstschutz'': ethnic German militias that had committed war crimes in Poland. The division became notorious for its brutality, and committed numerous war crimes, including the Le Paradis and Chasselay massacres. The remnants of the division surrendered on 9 May 1945 to American ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of Leningrad
The siege of Leningrad was a Siege, military blockade undertaken by the Axis powers against the city of Leningrad (present-day Saint Petersburg) in the Soviet Union on the Eastern Front (World War II), Eastern Front of World War II from 1941 to 1944. Leningrad, the country's second largest city, was besieged by Nazi Germany, Germany and Finland for 872 days, but never captured. The siege was the List of sieges, most destructive in history and possibly the List of battles by casualties#Sieges and urban combat, most deadly, causing an estimated 1.5 million deaths, from a prewar population of 3.2 million. It was not classified as a war crime at the time, but some historians have since classified it as a genocide due to the intentional destruction of the city and the systematic starvation of its civilian population. p. 334 In August 1941, Nazi Germany, Germany's Army Group North reached the suburbs of Leningrad as Finnish forces moved to encircle the city from the north. Land ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leningrad
Saint Petersburg, formerly known as Petrograd and later Leningrad, is the List of cities and towns in Russia by population, second-largest city in Russia after Moscow. It is situated on the Neva, River Neva, at the head of the Gulf of Finland on the Baltic Sea. The city had a population of 5,601,911 residents as of 2021, with more than 6.4 million people living in the Saint Petersburg metropolitan area, metropolitan area. Saint Petersburg is the List of European cities by population within city limits, fourth-most populous city in Europe, the List of cities and towns around the Baltic Sea, most populous city on the Baltic Sea, and the world's List of northernmost items#Cities and settlements, northernmost city of more than 1 million residents. As the former capital of the Russian Empire, and a Ports of the Baltic Sea, historically strategic port, it is governed as a Federal cities of Russia, federal city. The city was founded by Tsar Peter the Great on 27 May 1703 on the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |