|
1268
Year 1268 ( MCCLXVIII) was a leap year starting on Sunday of the Julian calendar. Events By topic War and politics * February 18 – Battle of Rakvere: The Livonian Order is defeated by Dovmont of Pskov. * April 4 – A five-year Byzantine–Venetian peace treaty is concluded between Venetian envoys and Emperor Michael VIII Palaiologos. It is ratified by the Doge of Venice Reniero Zeno on June 30. * August 23 – Battle of Tagliacozzo: The army of Charles of Anjou defeats the Ghibellines supporters of Conradin of Hohenstaufen, marking the fall of the Hohenstaufen Family from the Imperial and Sicilian thrones, and leading to the new chapter of Angevin domination in Southern Italy. * October 29 – Conradin, the last legitimate male heir of the Hohenstaufen Dynasty of Kings of Germany and Holy Roman Emperors, is executed, along with his companion Frederick I, Margrave of Baden, by Charles I of Sicily, a political rival and ally to the hostile Roman C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
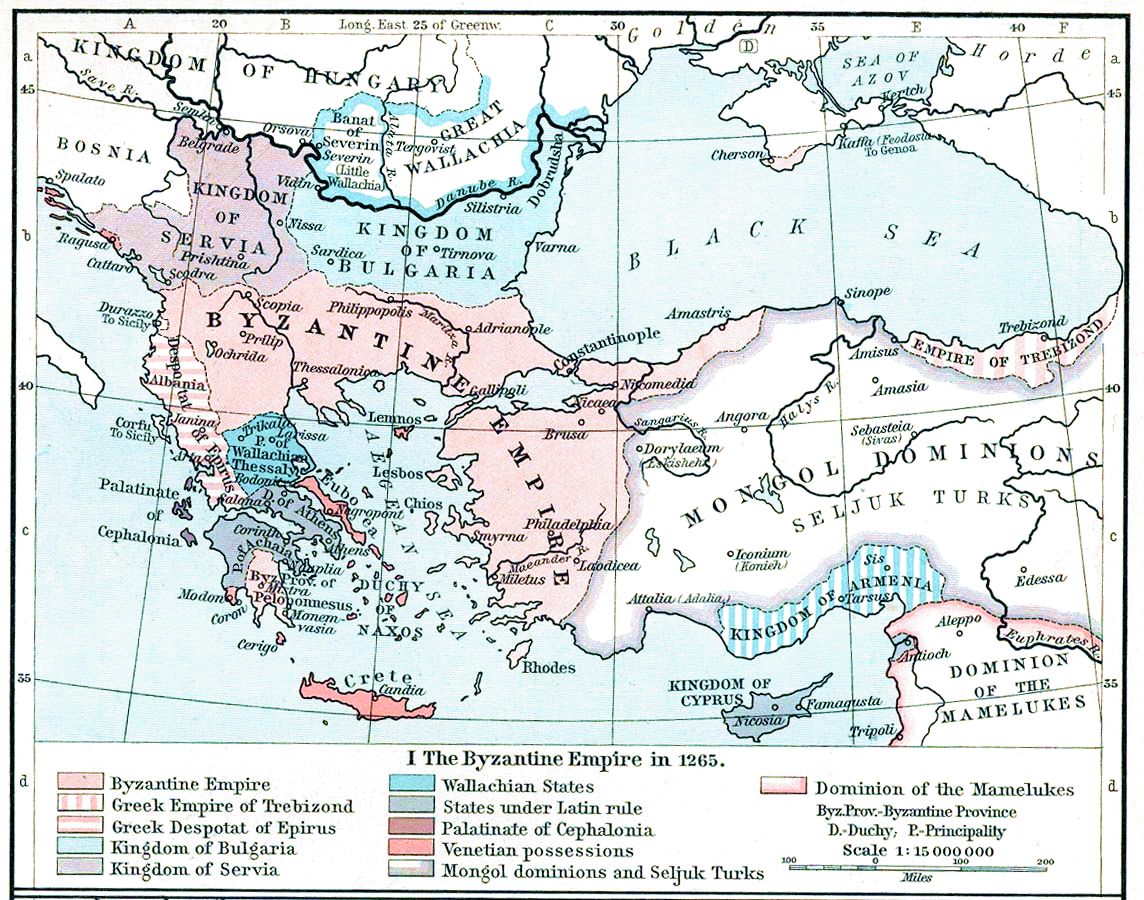
Byzantine–Venetian Treaty Of 1268
In 1268, the Byzantine Empire and the Republic of Venice agreed to temporarily end hostilities which had erupted after the Byzantine recovery of Constantinople by Emperor Michael VIII Palaiologos in 1261. Venice had enjoyed a privileged position in the Constantinople-based Latin Empire established by the Fourth Crusade in 1204, while Palaiologos had allied with Venice's main commercial rival, the Republic of Genoa, against them. The loss of Constantinople to Palaiologos was a heavy blow to Venice's political and commercial position in the East, as it cut off access to the Black Sea, and gave the Genoese privileged access instead. A naval war against Genoa and Byzantium followed, but despite a significant Venetian victory at the Battle of Settepozzi in 1263, it failed to produce decisive results. Nevertheless, Palaiologos became dissatisfied with the Genoese military performance, and the two allies grew increasingly mistrustful towards each other, leading the Byzantine emperor to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Konradin
Conrad III (25 March 1252 – 29 October 1268), called ''the Younger'' or ''the Boy'', but usually known by the diminutive Conradin (, ), was the last direct heir of the House of Hohenstaufen. He was Duke of Swabia (1254–1268) and nominal King of Jerusalem (1254–1268) and King of Sicily, Sicily (1254–1258). After Battle of Tagliacozzo, his attempt to reclaim the Kingdom of Sicily for the Hohenstaufen dynasty failed, he was captured and beheaded. Early childhood Conradin was born in Landshut, Wolfstein, Bavaria, to Conrad IV of Germany and Elisabeth of Bavaria, Queen of Germany, Elisabeth of Bavaria. Though he never succeeded his father as King of the Romans, Roman-German king, he was recognized as king of Sicily and Jerusalem by supporters of the Hohenstaufens in 1254. Having lost his father in 1254, he grew up at the court of his uncle and guardian, Louis II, Duke of Bavaria. His guardians were able to hold Swabia for him. Jerusalem was held by a relative from the royal h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reniero Zeno
Coat of arms of Reniero Zeno Silver Grosso of Doge Raniero Zeno, 1253–1268, Venice. Reniero Zeno () (died 7 July 1268) was the 45th Doge of Venice, reigning from 1 January 1253 until his death in 1268. Life The first references to Reniero Zeno in historical sources describe him as a diplomat in France and Italy, where he was excommunicated for having pushed Bologna to avoid paying tributes to the Papal States. In 1240 he helped Doge Jacopo Tiepolo during the siege of Ferrara, in 1242 put down a revolt in Zara and in 1244 he was named ''capitano generale da Mar'' (fleet commander) of the Republic of Venice. He was also the ''podestà'' (Chief Magistrate) of numerous Italian cities. After the death of Marino Morosini, Zeno, who was then ''podestà'' of Fermo, was elected Doge with 21 out of 41 votes. In 1256–1259 he, already lifted from the excommunication, helped Pope Alexander IV and Treviso in the war for the Marca Trevigiana against the Ghibelline warlord Ezzelino IV ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles I Of Sicily
Charles I (early 1226/12277 January 1285), commonly called Charles of Anjou or Charles d'Anjou, was King of Sicily from 1266 to 1285. He was a member of the royal Capetian dynasty and the founder of the House of Anjou-Sicily. Between 1246 and 1285, he was Count of Provence and County of Forcalquier, Forcalquier in the Holy Roman Empire and Count of Anjou and Count of Maine, Maine in France. In 1272 he was proclaimed Kingdom of Albania (medieval), King of Albania, in 1277 he purchased a claim to the Kingdom of Jerusalem, and in 1278 he became Prince of Achaea after the previous ruler, William of Villehardouin, died without heirs. The youngest son of Louis VIII of France and Blanche of Castile, Charles was destined for a Church career until the early 1240s. He acquired Provence and Forcalquier through his marriage to their heiress, Beatrice of Provence, Beatrice. His attempts to restore central authority brought him into conflict with his mother-in-law, Beatrice of Savoy, and th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Of Anjou
Charles I (early 1226/12277 January 1285), commonly called Charles of Anjou or Charles d'Anjou, was King of Sicily from 1266 to 1285. He was a member of the royal Capetian dynasty and the founder of the House of Anjou-Sicily. Between 1246 and 1285, he was Count of Provence and Forcalquier in the Holy Roman Empire and Count of Anjou and Maine in France. In 1272 he was proclaimed King of Albania, in 1277 he purchased a claim to the Kingdom of Jerusalem, and in 1278 he became Prince of Achaea after the previous ruler, William of Villehardouin, died without heirs. The youngest son of Louis VIII of France and Blanche of Castile, Charles was destined for a Church career until the early 1240s. He acquired Provence and Forcalquier through his marriage to their heiress, Beatrice. His attempts to restore central authority brought him into conflict with his mother-in-law, Beatrice of Savoy, and the nobility. He relinquished control of Forcalquier to his mother-in-law in 1248, al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frederick I, Margrave Of Baden
Frederick I of Baden (1249 – October 29, 1268), a member of the House of Zähringen, was List of rulers of Baden, Margrave of Baden and of March of Verona, Verona, as well as claimant List of rulers of Austria, Duke of Austria from 1250 until his death.Regesten der Markgrafen von Baden und Hachberg, 1050-1515. Innsbruck 1892 As a fellow campaigner of the Hohenstaufen king Conradin, he likewise was beheaded at the behest of King Charles I of Naples. Claim to Austria He was born in Austrian Alland, the only son of the Duchy of Swabia, Swabian margrave Herman VI, Margrave of Baden, Herman VI of Baden (c.1226–1250) and his wife Gertrude of Austria, Gertrude (1226–1288), niece and heiress of the late House of Babenberg, Babenberg duke Frederick II, Duke of Austria, Frederick II of Austria. As Duke Frederick II of Austria had been killed at the 1246 Battle of the Leitha River, the ducal line of the Babenberg dynasty had become extinct. Margrave Herman VI of Baden, through his mar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hohenstaufen
The Hohenstaufen dynasty (, , ), also known as the Staufer, was a noble family of unclear origin that rose to rule the Duchy of Swabia from 1079, and to royal rule in the Holy Roman Empire during the Middle Ages from 1138 until 1254. The dynasty's most prominent rulers – Frederick I (1155), Henry VI (1191) and Frederick II (1220) – ascended the imperial throne and also reigned over Italy and Burgundy. The non-contemporary name of 'Hohenstaufen' is derived from the family's Hohenstaufen Castle on Hohenstaufen mountain at the northern fringes of the Swabian Jura, near the town of Göppingen. Under Hohenstaufen rule, the Holy Roman Empire reached its greatest territorial extent from 1155 to 1268. Name The name Hohenstaufen was first used in the 14th century to distinguish the 'high' (''hohen'') conical hill named Staufen in the Swabian Jura (in the district of Göppingen) from the village of the same name in the valley below. The new name was applied to the hill c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Wesenberg (1268)
The Battle of Wesenberg, Rakvere or Rakovor (; ) was fought on 18 February 1268 between the combined forces of Danish Estonia, the Bishopric of Dorpat, the Livonian Order, and local Estonian militias on one side, and the forces of Novgorod and Pskov, led by Dmitry of Pereslavl, on the other. Medieval accounts of the battle vary with both sides claiming victory; however, the Livonian victory is seen as more plausible as Novgorodian-Pskovian forces retreated out of Danish Estonia, with Livonian Knights launching a retaliatory attack on Izborsk and Pskov soon afterward, in June 1269. Account of the ''Livonian Rhymed Chronicle'' According to the ''Livonian Rhymed Chronicle'', the only contemporary primary source describing the battle whose text survives in unaltered form to the present day, the combined forces of the two Russian republics invaded the territory of Danish Estonia in January 1268 where they commenced with looting of the countryside. The Danish vassals requested reinfor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Tagliacozzo
The Battle of Tagliacozzo was fought on 23 August 1268 between the Ghibelline supporters of Conradin of Hohenstaufen and the Guelph army of Charles of Anjou. The battle represented the last act of Hohenstaufen power in Italy. The capture and execution of Conradin several months after the battle also marked the fall of the family from the Imperial and Sicilian thrones, leading to the new chapter of Angevin domination in Southern Italy. Antecedents The German emperors of the Hohenstaufen line, who had inherited the kingdom of Sicily from its Norman rulers in 1197, had continually attempted to consolidate their more long-standing claims to northern Italy as well—an ambition which was vehemently opposed by many northern Italian states and by the Papacy. The resulting struggle between the Papacy and the Holy Roman Empire split the loyalties of many Italians and led to factionalism, the resulting factions being termed the Guelphs and Ghibellines. The death of the German empe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dovmont Of Pskov
Daumantas, Domantas or Dovmont (; Christian name: ''Timothy'' (Тимофей); died 20 May 1299) was Prince of Pskov from 1266 to 1299. During his term in office, Pskov became '' de facto'' independent from Novgorod. He is venerated as a saint in the Eastern Orthodox Church with his feast day observed on 20 May. In Lithuania Until 1265, Daumantas was Duke of Nalšia, a northern province of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, and was an ally of King Mindaugas. Mindaugas' and Daumantas' wives were sisters. In spite of the family relationship, Daumantas chose to ally himself with Mindaugas' nephew Treniota, who was Duke of Samogitia. Treniota had been steadily increasing his personal power within the kingdom as he tried to spark an all-Balts rebellion against the Teutonic Knights and the Livonian Order. In 1263, Daumantas assassinated Mindaugas and two of his sons. It has been suggested that he acted in collusion with Treniota. As a result, the Grand Duchy of Lithuania relapsed into ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michael VIII Palaiologos
Michael VIII Palaiologos or Palaeologus (; 1224 – 11 December 1282) reigned as Byzantine emperor from 1261 until his death in 1282, and previously as the co-emperor of the Empire of Nicaea from 1259 to 1261. Michael VIII was the founder of the Palaiologos, Palaiologan dynasty that would rule the Byzantine Empire until the Fall of Constantinople in 1453. He Reconquest of Constantinople, recovered Constantinople from the Latin Empire in 1261 and transformed the Empire of Nicaea into a Byzantine Empire under the Palaiologos dynasty, restored Byzantine Empire. His reign saw considerable recovery of Byzantine power, including the enlargement of the Byzantine army and Byzantine navy, navy. It also included the reconstruction of the city of Constantinople, and the increase of its population. His re-establishment of the University of Constantinople contributed to the Palaeologan Renaissance, a cultural flowering between the 13th and 15th centuries. It was also at this time that the fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |