|
1204 Deaths
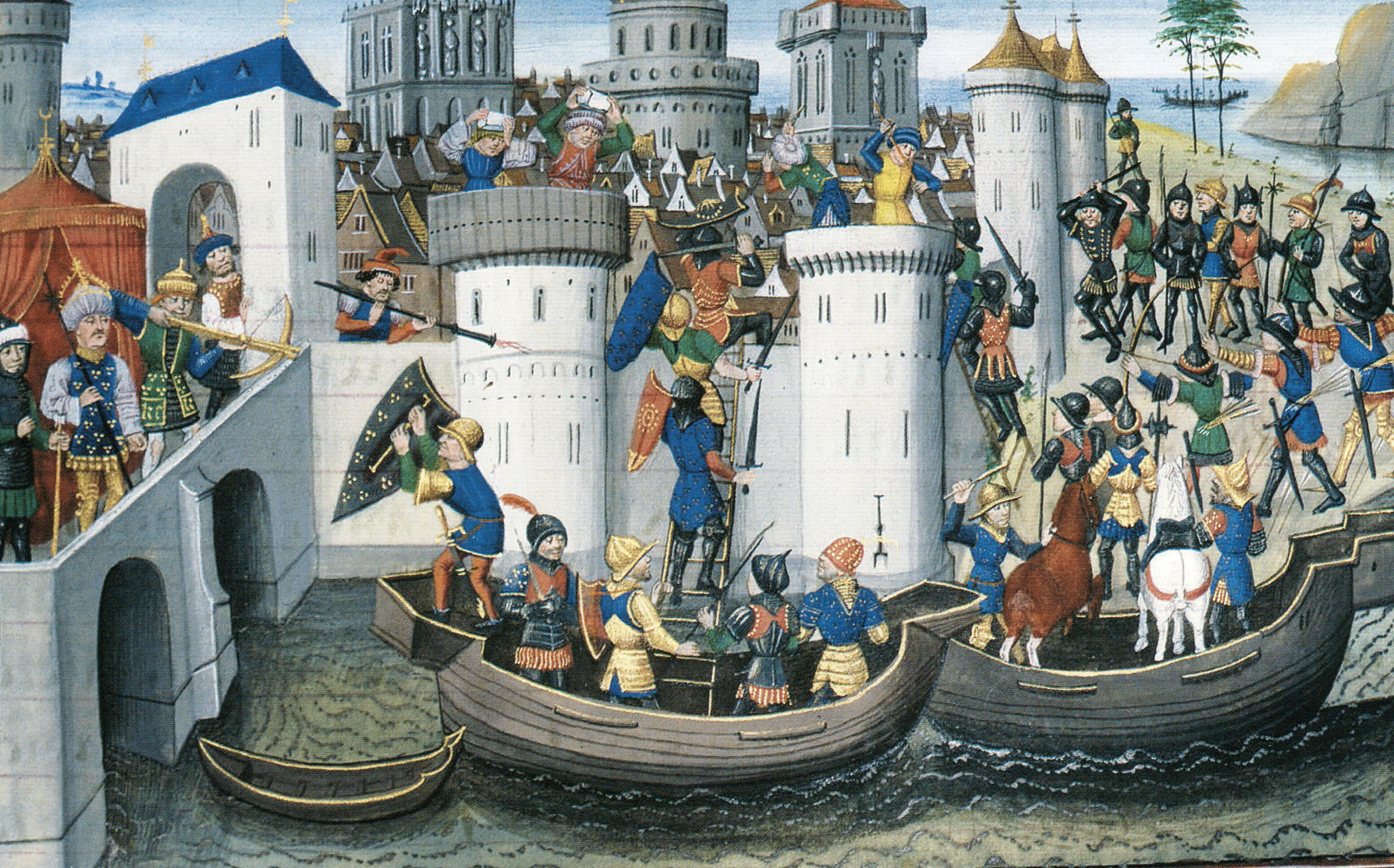
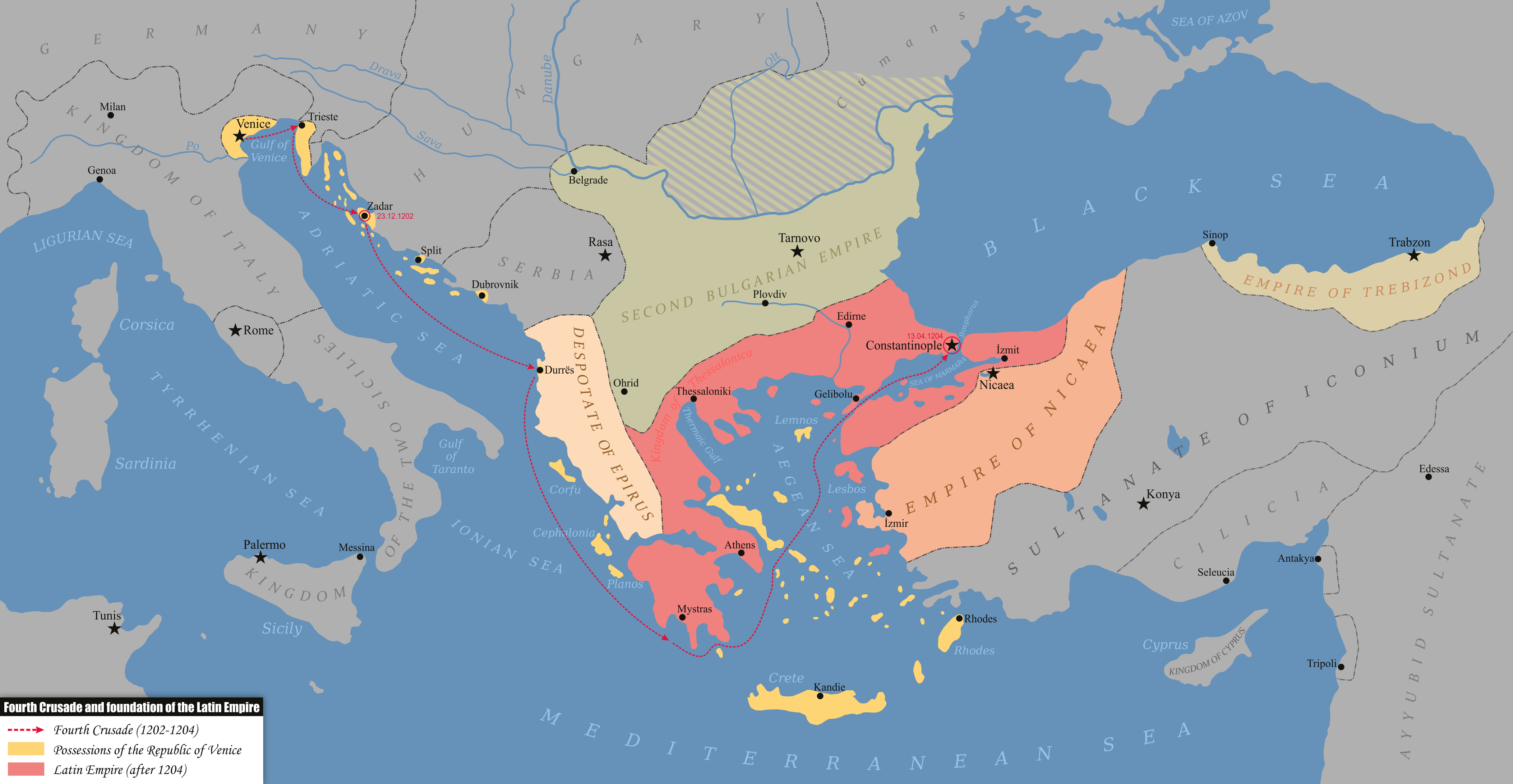
Year 1204 ( MCCIV) was a leap year starting on Thursday of the Julian calendar. Events * January 27– 28 – Byzantine emperor Alexios IV Angelos is overthrown in a revolution. * February 5 – Alexios V Doukas is crowned Byzantine emperor. * April 12 – Sack of Constantinople: Crusaders enter Constantinople by storm and start pillaging the city as part of the Fourth Crusade. Forces of the Republic of Venice seize the antique statues that will become the horses of Saint Mark. * May 16 – Baldwin, Count of Flanders, is crowned emperor of the Latin Empire a week after his election by the members of the Fourth Crusade. * Theodore I Laskaris flees to Nicaea after the capture of Constantinople, and establishes the Empire of Nicaea; Byzantine successor states are also established in Epirus and Trebizond. * Boniface I, Marquis of Montferrat, a leader of the Fourth Crusade, founds the Kingdom of Thessalonica. * The writings of French theologian Amalric o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Numerals
Roman numerals are a numeral system that originated in ancient Rome and remained the usual way of writing numbers throughout Europe well into the Late Middle Ages. Numbers are written with combinations of letters from the Latin alphabet, each with a fixed integer value. The modern style uses only these seven: The use of Roman numerals continued long after the Fall of the Western Roman Empire, decline of the Roman Empire. From the 14th century on, Roman numerals began to be replaced by Arabic numerals; however, this process was gradual, and the use of Roman numerals persisted in various places, including on clock face, clock faces. For instance, on the clock of Big Ben (designed in 1852), the hours from 1 to 12 are written as: The notations and can be read as "one less than five" (4) and "one less than ten" (9), although there is a tradition favouring the representation of "4" as "" on Roman numeral clocks. Other common uses include year numbers on monuments and buildin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horses Of Saint Mark
The Horses of Saint Mark (), also known as the Triumphal Quadriga or Horses of the Hippodrome of Constantinople, is a set of bronze statues of four horses, originally part of a monument depicting a quadriga (a four-horse carriage used for chariot racing). The horses were placed on the façade, on the loggia above the porch, of St Mark's Basilica in Venice, northern Italy, after the Siege of Constantinople (1204), sack and looting of Constantinople in 1204. They remained there until looted by Napoleon in 1797 but were returned in 1815. The sculptures have been removed from the façade and placed in the interior of St Mark's for conservation purposes, with replicas in their position on the loggia. Origins The sculptures date from classical antiquity. Many scholars believe they were sculpted in the 2nd or 3rd century AD, noting similarities to the Equestrian Statue of Marcus Aurelius in Rome (c. 175 AD). But some say the evident technical expertise and naturalistic rendering of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amalric Of Bena
Amalric of Bena (; ; died ) was a French theologian, philosopher and sect leader, after whom the Amalricians are named. Reformers such as Martin Luther considered him to be a proto-Protestant. Biography Amalric was born in the latter part of the 12th century at Bennes, a village between Ollé and Chauffours in the diocese of Chartres. Amalric taught philosophy and theology at the University of Paris and enjoyed a great reputation as a subtle dialectician; his lectures developing the philosophy of Aristotle attracted a large audience. In 1204 his doctrines were condemned by the university and, on a personal appeal to Pope Innocent III, the sentence was ratified, Amalric being ordered to return to Paris and recant his errors. His death was caused, it is said, by grief at the humiliation to which he had been subjected. In 1209, ten of his followers were burnt before the gates of Paris and Amalric's own body was exhumed and burnt and the ashes given to the winds. The doctrines ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theology
Theology is the study of religious belief from a Religion, religious perspective, with a focus on the nature of divinity. It is taught as an Discipline (academia), academic discipline, typically in universities and seminaries. It occupies itself with the unique content of analyzing the supernatural, but also deals with religious epistemology, asks and seeks to answer the question of revelation. Revelation pertains to the acceptance of God, gods, or deity, deities, as not only transcendent or above the natural world, but also willing and able to interact with the natural world and to reveal themselves to humankind. Theologians use various forms of analysis and argument (Spirituality, experiential, philosophy, philosophical, ethnography, ethnographic, history, historical, and others) to help understanding, understand, explanation, explain, test, critique, defend or promote any myriad of List of religious topics, religious topics. As in philosophy of ethics and case law, arguments ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Thessalonica
The Kingdom of Thessalonica () was a short-lived Crusader State founded after the Fourth Crusade over conquered Byzantine lands in today's territory of Northern Greece and Thessaly. History Background After the fall of Constantinople to the crusaders in 1204, Boniface of Montferrat, the leader of the crusade, was expected by both the Crusaders and the defeated Byzantines to become the new emperor. However, the Venetians felt that Boniface was too closely tied to the Byzantine Empire, as his brother Conrad had married into the Byzantine imperial family. The Venetians wanted an emperor whom they could control more easily, and with their influence, Baldwin of Flanders was elected as emperor of the new Latin Empire. Establishment Boniface reluctantly accepted this, and set out to conquer Thessalonica, the second-largest Byzantine city after Constantinople. At first he had to compete with Emperor Baldwin, who also wanted the city. He then went on to capture the city later ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boniface I, Marquis Of Montferrat
Boniface I, usually known as Boniface of Montferrat (; ; c. 1150 – 4 September 1207), was the ninth Marquis of Montferrat (from 1192), a leader of the Fourth Crusade (1201–04) and the king of Thessalonica (from 1205). Early life Boniface was the third son of William V of Montferrat and Judith of Babenberg, born after his father's return from the Second Crusade. He was a younger brother of William "Longsword", Count of Jaffa and Ascalon, and of Conrad I of Jerusalem. His youthful exploits in the late 1170s are recalled in the famous "epic letter", ''Valen marques, senher de Monferrat'', by his good friend and court troubadour, Raimbaut de Vaqueiras. These included the rescue of the heiress Jacopina of Ventimiglia from her uncle Count Otto, who was intending to deprive her of her inheritance and send her to Sardinia. Boniface arranged a marriage for her. When Albert of Malaspina (husband of one of Boniface's sisters) abducted Saldina de Mar, a daughter of a prominent G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Empire Of Trebizond
The Empire of Trebizond or the Trapezuntine Empire was one of the three successor rump states of the Byzantine Empire that existed during the 13th through to the 15th century. The empire consisted of the Pontus, or far northeastern corner of Anatolia, and portions of southern Crimea. The Trapezuntine Empire was formed in 1204 with the help of Queen Tamar of Georgia after the Georgian expedition in Chaldia and Paphlagonia, which was commanded by Alexios Komnenos a few weeks before the Sack of Constantinople. Alexios later declared himself emperor and established himself in Trebizond (now Trabzon in Turkey). Alexios and David Komnenos, grandsons and last male descendants of the deposed emperor Andronikos I Komnenos, pressed their claims as Roman emperors against Alexios V Doukas. While the rulers of Trebizond bore the title of emperor until the end of their state in 1461, their rivals, the Laskarids in Nikaia and the Palaiologoi in Constantinople contested their claim to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Despotate Of Epirus
The Despotate of Epirus () was one of the Greek Rump state, successor states of the Byzantine Empire established in the aftermath of the Fourth Crusade in 1204 by a branch of the Angelos dynasty. It claimed to be the legitimate successor of the Byzantine Empire during the subsequent struggle for Constantinople, along with the Empire of Nicaea and the Empire of Trebizond; its rulers briefly proclaiming themselves as Emperors in 1227–1242 (during which it is most often called the Empire of Thessalonica). The term "Despotate of Epirus" is, like "Byzantine Empire" itself, a modern historiographic convention and not a name in use at the time. The Despotate was centred on the region of Epirus, encompassing also Albania and the western portion of Greek Macedonia and also included Thessaly and western Greece as far south as Nafpaktos. Through a policy of aggressive expansion under Theodore Komnenos Doukas the Despotate of Epirus also briefly came to incorporate central Macedonia (regi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived History of the Roman Empire, the events that caused the fall of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th centuryAD, it endured until the fall of Constantinople to the Ottoman Empire in 1453. The term 'Byzantine Empire' was coined only after its demise; its citizens used the term 'Roman Empire' and called themselves 'Romans'. During the early centuries of the Roman Empire, the western provinces were Romanization (cultural), Latinised, but the eastern parts kept their Hellenistic culture. Constantine the Great, Constantine I () legalised Christianity and moved the capital to Constantinople. Theodosius I, Theodosius I () made Christianity the state religion and Greek gradually replaced Latin for official use. The empire adopted a defensive strategy and, throughout its remaining history, expe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Empire Of Nicaea
The Empire of Nicaea (), also known as the Nicene Empire, was the largest of the three Byzantine Greeks, Byzantine Greek''A Short history of Greece from early times to 1964'' by Walter Abel Heurtley, W. A. Heurtley, H. C. Darby, C. W. Crawley, C. M. Woodhouse (1967), p. 55: "There in the prosperous city of Nicaea, Theodoros Laskaris, the son in law of a former Byzantine Emperor, establish a court that soon become the Small but reviving Greek empire." rump states founded by the aristocracy of the Byzantine Empire that fled when Constantinople was occupied by Western European and Republic of Venice, Venetian armed forces during the Fourth Crusade, a military event known as the Sack of Constantinople. Like the other Byzantine rump states that formed due to the 1204 fracturing of the empire, such as the Empire of Trebizond and the Despotate of Epirus, it was a continuation of the eastern half of the Roman Empire that survived well into the Middle Ages. A fourth state, known in histori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nicaea
Nicaea (also spelled Nicæa or Nicea, ; ), also known as Nikaia (, Attic: , Koine: ), was an ancient Greek city in the north-western Anatolian region of Bithynia. It was the site of the First and Second Councils of Nicaea (the first and seventh Ecumenical councils in the early history of the Christian Church), the Nicene Creed (which comes from the First Council). It was also the capital city of the Empire of Nicaea following the Fourth Crusade in 1204, until the recapture of Constantinople by the Byzantines in 1261. Nicaea was also the capital of the Ottomans from 1331 to 1335. The ancient city is located within the modern Turkish city of İznik (whose modern name derives from Nicaea's), and is situated in a fertile basin at the eastern end of Lake Ascanius, bounded by ranges of hills to the north and south. It is situated with its west wall rising from the lake itself, providing both protection from siege from that direction, as well as a source of supplies which would ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theodore I Laskaris
Theodore I Laskaris or Lascaris (; 1175November 1221) was the first emperor of Nicaea—a successor state of the Byzantine Empire—from 1205 to his death. Although he was born to an obscure aristocratic family, his mother was related to the imperial Komnenos clan. He married Anna, a younger daughter of Emperor Alexios III Angelos in 1200. He received the title of despot before 1203, demonstrating his right to succeed his father-in-law on the throne. The Fourth Crusade forced AlexiosIII to flee from Constantinople in 1203. Theodore was imprisoned by the crusaders (commonly referred to as "Latins" by the Byzantines), but he escaped. After crossing the Bosporus into Asia Minor (in present-day Turkey), he started to organise the local Greeks' resistance against the Latins in Bithynia in his father-in-law's name. He concluded an alliance with the Seljuq sultan of Rum, but he could not stop the Latins' expansion. Neither could he prevent a claimant to the imperial t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |