|
1176
Year 1176 ( MCLXXVI) was a leap year starting on Thursday of the Julian calendar, the 1176th year of the Common Era (CE) and Anno Domini (AD) designations, the 176th year of the 2nd millennium, the 76th year of 12th century, and the 7th year of the 1170s decade. Events By place Byzantine Empire * Summer – Emperor Manuel I (Komnenos) assembles a Byzantine expeditionary force, and marches towards Iconium, the Seljuk capital. Meanwhile, hordes of Seljuk Turks destroy crops and poison water supplies, to make Manuel's march more difficult, and harass the Byzantine army, in order to force it into the Meander Valley. Kilij Arslan II, ruler of the Sultanate of Rum, hears of the expedition, and sends envoys to ask for peace. * September 17 – Battle of Myriokephalon: The Seljuk Turks defeat the Byzantine forces led by Manuel I, who are ambushed when moving through a narrow mountain pass near Lake Beyşehir. The Byzantines are dispersed and surrounded. They ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Legnano
The battle of Legnano was a battle between the imperial army of Frederick Barbarossa and the troops of the Lombard League on 29 May 1176, near the town of Legnano, in present-day Lombardy, Italy. Although the presence of the enemy nearby was already known to both sides, they suddenly met without having time to plan any strategy. The battle was crucial in the long war waged by the Holy Roman Empire in an attempt to assert its power over the municipalities of northern Italy, which decided to set aside their mutual rivalries and join in a military alliance symbolically led by Pope Alexander III, the Lombard League. The battle ended the fifth and last descent into Italy of Emperor Frederick Barbarossa, who after the defeat tried to resolve the Italian question by adopting a diplomatic approach. This resulted a few years later in the Peace of Constance (25 June 1183), with which the Emperor recognized the Lombard League and made administrative, political, and judicial concessions to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
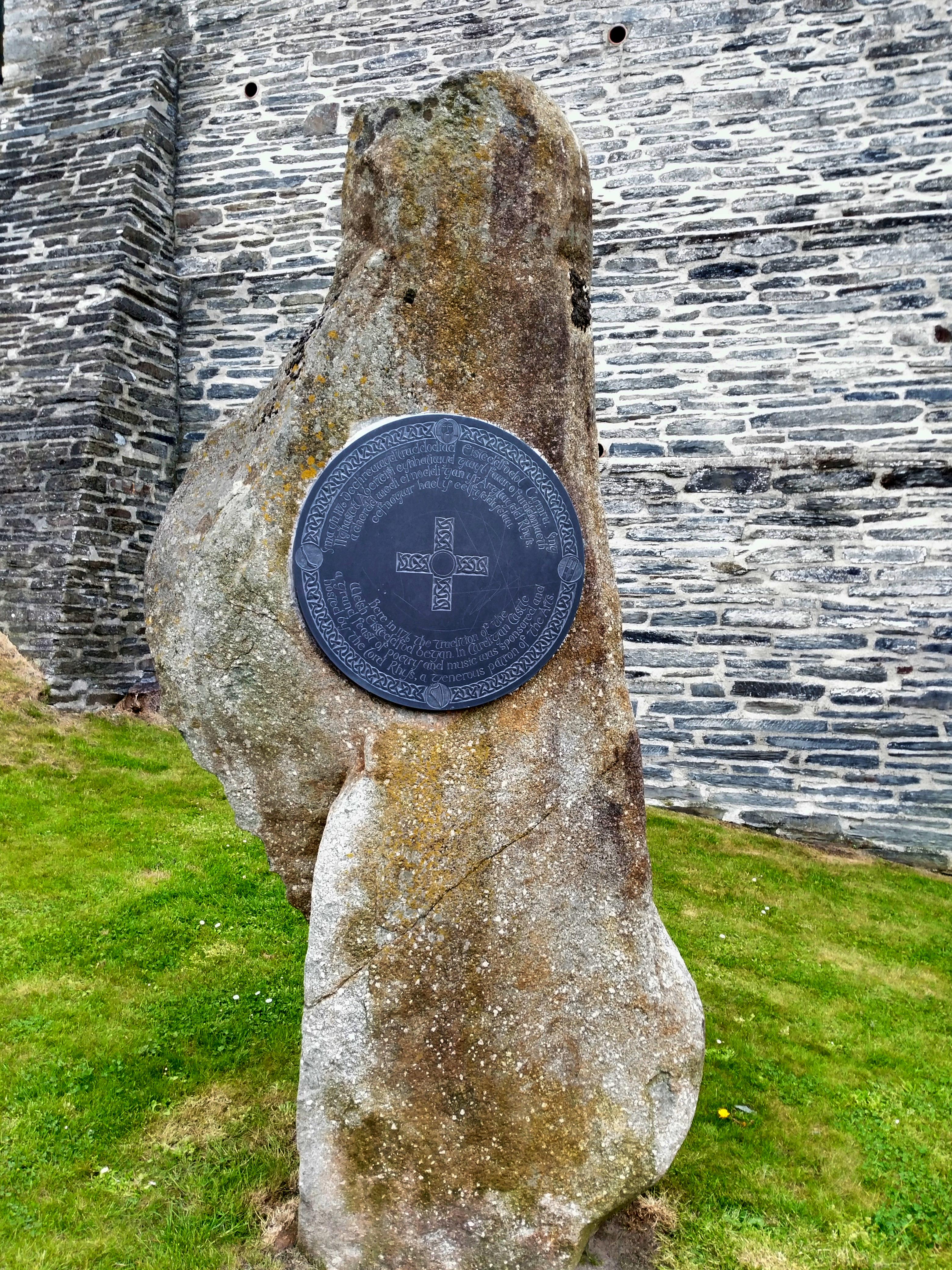
1176 Cardigan Eisteddfod
The 1176 Cardigan eisteddfod, as it is commonly described, was a cultural tournament involving bards and musicians, held in the grounds of Cardigan Castle, Cardigan, West Wales, by the Lord Rhys ap Gruffydd. Though the term ''eisteddfod'' was not commonly used until several centuries later, the 1176 gathering is commonly claimed to be the earliest recorded forerunner of the modern national eisteddfod event. Background Rhys ap Gruffydd became the ruler uniting the whole of Deheubarth, covering southwest Wales, in 1155. This had followed years of battles with the English King Henry II. Rhys was made Lord of Ystrad Tywi or, commonly, the Lord Rhys. There followed a period of relative peace and security. In the early 1170s Henry II sought friendship with Rhys and confirmed his leadership of Deheubarth. In 1171 Rhys rebuilt Cardigan Castle in stone, as a political and military statement, making it his chief residence. Welsh princes commonly patronised professional bards at the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Myriokephalon
The Battle of Myriokephalon (also known as the Battle of Myriocephalum, , or ''Düzbel Muharebesi'') was a battle between the Byzantine Empire and the Seljuk Turks in the mountains west of Iconium (Konya) in southwestern Turkey on 17 September 1176. The battle was a strategic reverse for the Byzantine forces, who were ambushed when moving through a mountain pass. In 1161, the Seljuk Sultan of Rum Kilij Arslan II and Byzantine Emperor Manuel I Komnenos concluded a peace agreement. Manuel wanted to achieve peace for his Anatolian provinces with the help of this treaty. Kilij Arslan needed to eliminate internal rivals and gather his strength. After the death of Nureddin Zangi in 1174, the Sultan conquered the Danishmend emirates and expelled his brother Shahinshah, the ruler of Ankara. The emirs fled to Manuel, who demanded the surrender of the captured territories of the Danishmendids to him, which the Sultan was obliged to do under the treaty. However, Kilij Arslan ignored Manu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eisteddfod
In Welsh culture, an ''eisteddfod'' is an institution and festival with several ranked competitions, including in poetry and music. The term ''eisteddfod'', which is formed from the Welsh morphemes: , meaning 'sit', and , meaning 'be', means, according to Hywel Teifi Edwards, "sitting-together." Edwards further defines the earliest form of the eisteddfod as a competitive meeting between bards and minstrels, in which the winner was chosen by a noble or royal patron.Hywel Teifi Edwards (2015), ''The Eisteddfod'', pages 5–6. The first documented instance of such a literary festival and competition took place under the patronage of Prince Rhys ap Gruffudd of the House of Dinefwr at Cardigan Castle in 1176. However, with the Edwardian Conquest of Wales, the closing of the bardic schools, and the Anglicization of the Welsh nobility, it fell into abeyance. The current format owes much to an 18th-century revival, first patronized and overseen by the London-based Gwyneddigion S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardigan Castle
Cardigan Castle () is a castle overlooking the River Teifi in Cardigan, Ceredigion, Wales. It is a Grade I listed building. The castle dates from the late 11th-century, though was rebuilt in 1244. Castle Green House was built inside the castle walls in the early 1800s. After falling into disrepair the castle was restored in the early 2000s and opened to the public in 2015. It is owned by Ceredigion County Council and now includes a heritage centre and open-air concert facilities. The castle's gardens are listed on the Cadw/ICOMOS Register of Parks and Gardens of Special Historic Interest in Wales. History The first motte-and-bailey castle (ca.1093) was built a mile away from the present site, probably about the time of the founding of the town by Roger de Montgomery, a Norman baron. In 1110, King Henry I of England took Cardigan from Prince Owain ap Cadwgan as a punishment, and gave the Lordship of Cardigan and the castle to Gilbert Fitz Richard. The forerunner of the pre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry II Of England
Henry II () was King of England The monarchy of the United Kingdom, commonly referred to as the British monarchy, is the form of government used by the United Kingdom by which a hereditary monarch reigns as the head of state, with their powers Constitutional monarchy, regula ... from 1154 until his death in 1189. During his reign he controlled Kingdom of England, England, substantial parts of Wales in the High Middle Ages, Wales and Lordship of Ireland, Ireland, and much of Kingdom of France, France (including Duchy of Normandy, Normandy, County of Anjou, Anjou, and Duchy of Aquitaine, Aquitaine), an area that altogether was later called the Angevin Empire, and also held power over Kingdom of Scotland, Scotland and the Duchy of Brittany. Henry was the eldest son of Geoffrey Plantagenet, Count of Anjou, and Empress Matilda, Matilda, daughter of Henry I of England. By the age of fourteen, he became politically and militarily involved in The Anarchy, his mother's efforts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Assize Of Northampton
The Assize of Northampton, largely based on the Assize of Clarendon of 1166, is among a series of measures taken by King Henry II of England that solidified the rights of the knightly tenants and made all possession of land subject to and guaranteed by royal law. The assize is believed to have been passed at a council held in Northampton in January 1176. Clarendon extended The assize confirmed the offences to be brought forward by the jury of presentment according to Clarendon, and added arson and forgery to the list. It also set down new and severe punishments that could be handed down, including the removal of an offender's right hand. Aftermath of revolt Following as it did the Revolt of 1173–74, the Assizes included a wide-ranging oath of fealty (Item 6), as well as items concerning castles (8 and 11), insisting especially that "the justices see to it that the castles which have been destroyed are utterly demolished." Administrative reforms The assize is connected wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
12th Century
The 12th century is the period from 1101 to 1200 in accordance with the Julian calendar. In the history of European culture, this period is considered part of the High Middle Ages and overlaps with what is often called the Golden Age' of the Cistercians". The Golden Age of Islam experienced significant development, particularly in Islamic Spain. In Song dynasty China, Jurchen campaigns against the Song dynasty, an invasion by Jurchens caused a political schism of north and south. The Khmer Empire of Cambodia flourished during this century, while the Fatimids of Egypt were overtaken by the Ayyubid dynasty. Following the expansions of the Ghaznavids and Ghurid dynasty, Ghurid Empire, the Muslim conquests in the Indian subcontinent took place at the end of the century. Events 1101–1109 *1101: In July, the Treaty of Alton is signed between Henry I of England and his older brother Robert Curthose, Robert, Duke of Normandy in which Robert agrees to recognize Henry as king of Eng ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
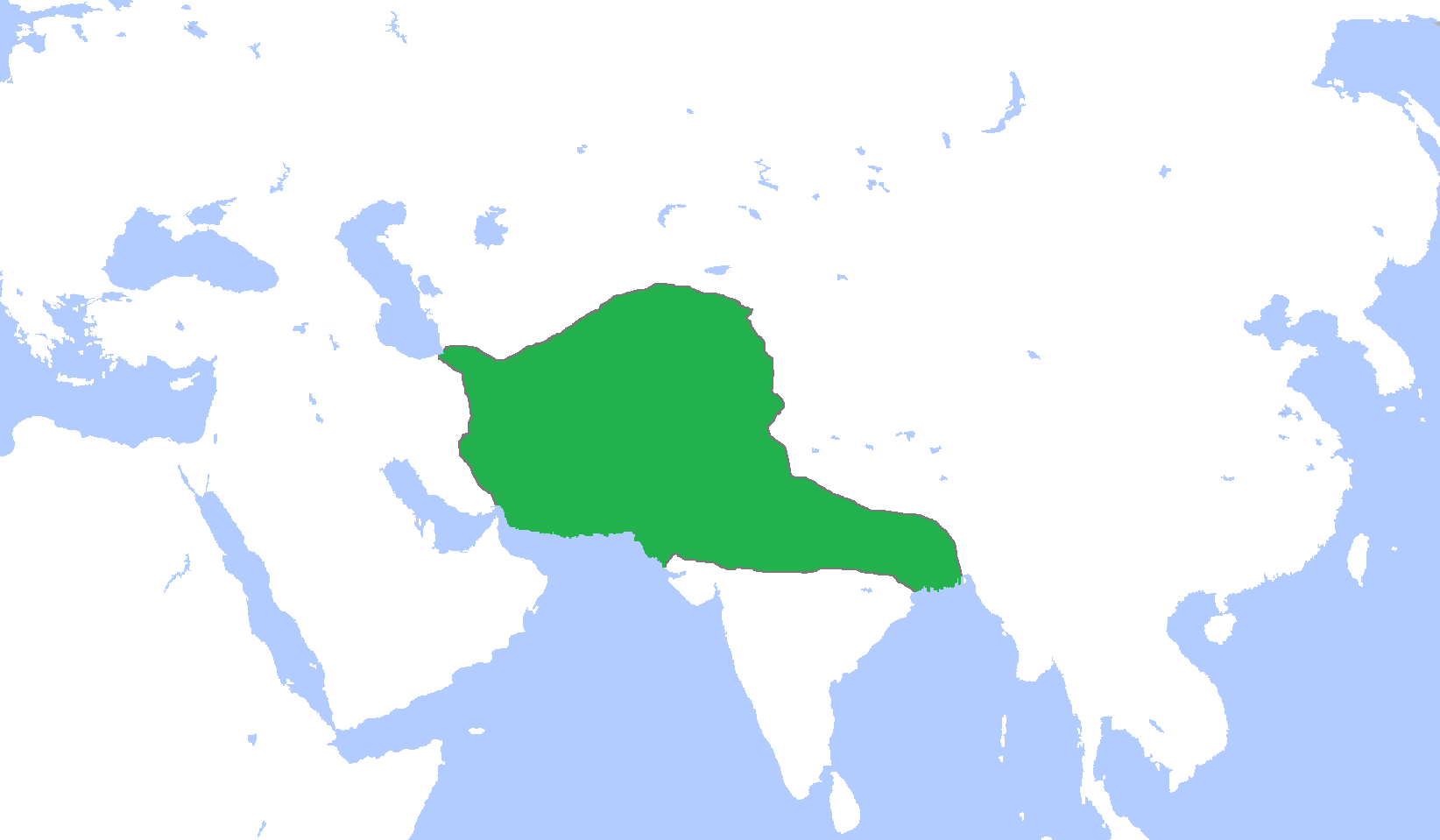
Manuel I Komnenos
Manuel I Komnenos (; 28 November 1118 – 24 September 1180), Latinized as Comnenus, also called Porphyrogenitus (; " born in the purple"), was a Byzantine emperor of the 12th century who reigned over a crucial turning point in the history of Byzantium and the Mediterranean. His reign saw the last flowering of the Komnenian restoration, during which the Byzantine Empire experienced a resurgence of military and economic power and enjoyed a cultural revival. Eager to restore his empire to its past glories as the great power of the Mediterranean world, Manuel pursued an energetic and ambitious foreign policy. In the process he made alliances with Pope Adrian IV and the resurgent West. He invaded the Norman Kingdom of Sicily, although unsuccessfully, being the last Eastern Roman emperor to attempt reconquests in the western Mediterranean. The passage of the potentially dangerous Second Crusade through his empire was adroitly managed. Manuel established a Byzantine protec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seljuq Dynasty
The Seljuk dynasty, or Seljukids ( ; , ''Saljuqian'',) alternatively spelled as Saljuqids or Seljuk Turks, was an Oghuz Turkic, Sunni Muslim dynasty that gradually became Persianate and contributed to Turco-Persian culture. The founder of the Seljuk dynasty, Seljuk Beg, was a descendant of a royal Khazar chief Tuqaq who served as advisor to the King of the Khazars. in West Asia and Central Asia. The Seljuks established the Seljuk Empire (1037–1194), the Sultanate of Kermân (1041–1186) and the Sultanate of Rum (1074–1308), which stretched from Iran to Anatolia and were the prime targets of the First Crusade. Early history The Seljuks originated from the Kinik branch of the Oghuz Turks, who in the 8th century lived on the periphery of the Muslim world; north of the Caspian Sea and Aral Sea in their Oghuz Yabgu State in the Kazakh Steppe of Turkestan. During the 10th century, Oghuz had come into close contact with Muslim cities. When Seljuk, the leader of the Seljuk clan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frederick I, Holy Roman Emperor
Frederick Barbarossa (December 1122 – 10 June 1190), also known as Frederick I (; ), was the Holy Roman Emperor from 1155 until his death in 1190. He was elected King of Germany in Frankfurt am Main, Frankfurt on 4 March 1152 and crowned in Aachen on 9 March 1152. He was crowned King of Italy on 24 April 1155 in Pavia and emperor by Pope Adrian IV on 18 June 1155 in Rome. Two years later, the term ' ("holy") first appeared in a document in connection with his empire. He was later formally crowned King of Burgundy, at Arles on 30 June 1178. His nickname of ' (meaning "Red Beard" in Italian) "was first used by the Republic of Florence, Florentines only in 1298 to differentiate the emperor from his grandson, Frederick II, Holy Roman Emperor, Frederick II ... and was never employed in medieval Germany" (the colour red was "also associated in the Middle Ages with malice and a hot temper"; in reality, Frederick's hair was "blond", although his beard was described by a contemporar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Assize Of Clarendon
The Assize of Clarendon was an act of Henry II of England in 1166 that began a transformation of English law and led to Jury trial, trial by jury in common law countries worldwide, and that established assize courts. Prior systems for deciding the winning party in a case, especially felony, felonies, included trial by ordeal, trial by battle, or compurgation, trial by compurgation (trial by oath), in which evidence, inspection, and inquiry was made under oath by laymen, knights or ordinary Franklin (class), freemen. After the Assize of Clarendon Jury trial, trial by jury developed, though some historians say beginnings of the jury system predate this act. The Assize of Clarendon did not lead to this change immediately; recourse to trial by combat was not officially rescinded until 1819 in the aftermath of the Ashford v Thornton, murder of Mary Ashford. The assize takes its name from Clarendon Palace, Wiltshire, the royal hunting lodge at which it was promulgated. Problems addre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |