|
111th Rifle Corps
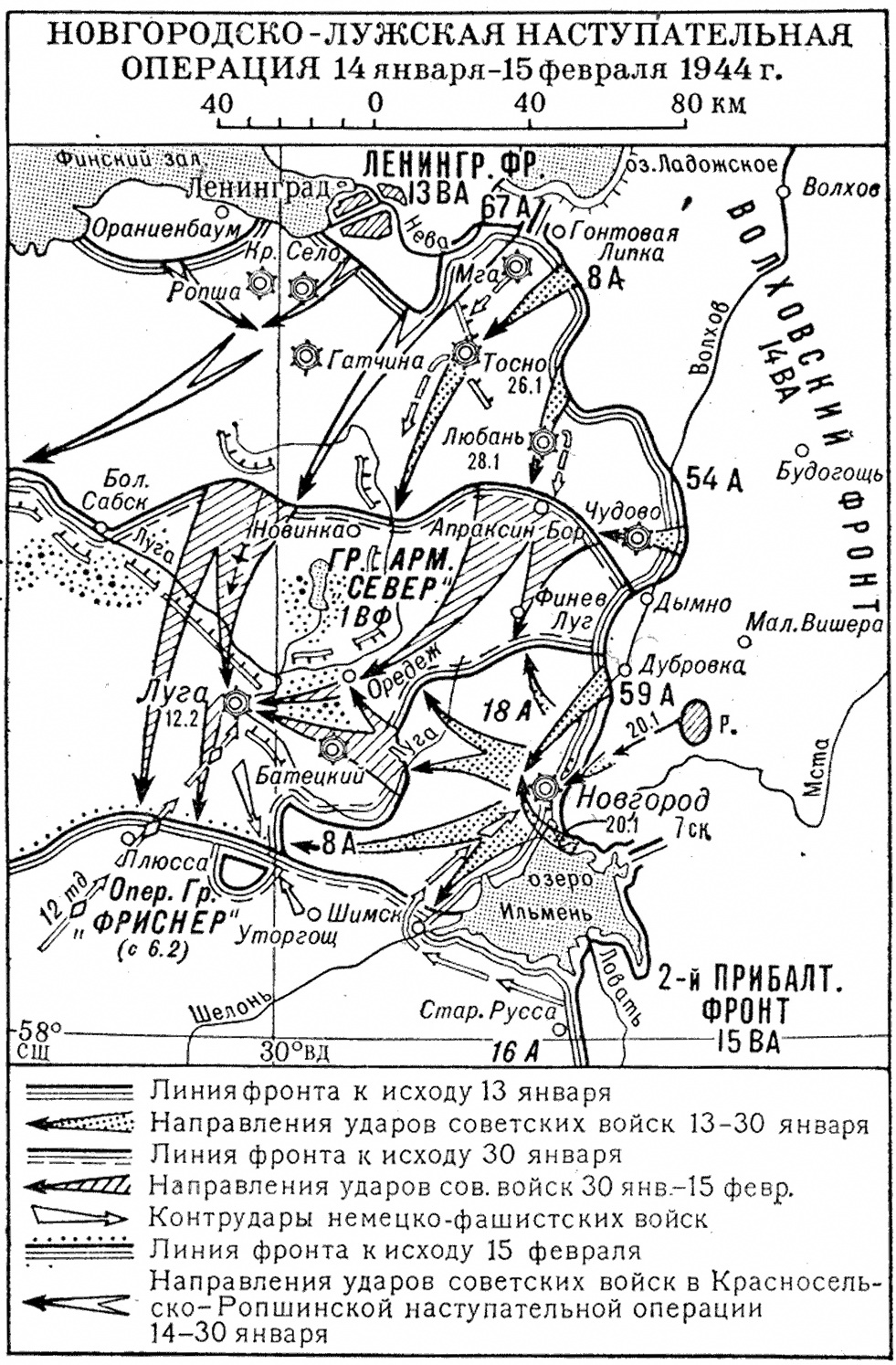
The 111th Rifle Corps () was an infantry corps of the Red Army during World War II. Its headquarters was formed with the 54th Army of the Volkhov Front in mid-November 1943, and with its assigned divisions fought in the Leningrad–Novgorod Offensive during January and February 1944. The corps then fought in failed attempts to break the Panther Line for the next several months and the Pskov-Ostrov Offensive in July. Its headquarters was transferred to the 67th Army and with a different set of divisions fought in the Riga Offensive in September. During late 1944 and early 1945 it served on garrison duty in southern Estonia and Latvia, then participated in the disarmament and collection of German prisoners of the war surrendered in the Courland Pocket in early May. Postwar, the corps was disbanded in early 1946. World War II The headquarters of the 111th Rifle Corps was formed in early November 1943 under the command of Major General Boris Rozhdestvensky, who led it for th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a Federation, federal union of Republics of the Soviet Union, fifteen national republics; in practice, both Government of the Soviet Union, its government and Economy of the Soviet Union, its economy were highly Soviet-type economic planning, centralized until its final years. It was a one-party state governed by the Communist Party of the Soviet Union, with the city of Moscow serving as its capital as well as that of its largest and most populous republic: the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic, Russian SFSR. Other major cities included Saint Petersburg, Leningrad (Russian SFSR), Kyiv, Kiev (Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic, Ukrainian SSR), Minsk (Byelorussian Soviet Socialist Republic, Byelorussian SSR), Tas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
53rd Rifle Brigade
{{Numberdis ...
53 may refer to: * 53 (number) * one of the years 53 BC, AD 53, 1953, 2053 * FiftyThree, an American privately held technology company that specializes in tools for mobile creation and visual thinking * 53rd Regiment Alabama Cavalry * 53rd Regiment of Foot (other) * 53rd Division (other) * ''53'' (Jacky Terrasson album), 2019 * "Fifty Three", a song by Karma to Burn from the album ''Arch Stanton'', 2014 * Fifth Third Bank Fifth Third Bank (5/3 Bank), the principal subsidiary of Fifth Third Bancorp is an American bank holding company headquartered in Cincinnati, Ohio. Fifth Third is one of the largest consumer banks in the Midwestern United States, Fifth Third B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1st Shock Army
The 1st Shock Army (russian: 1-я ударная армия) was a field army established by the Soviet Union's Red Army during World War II. The 1st Shock Army was created in late 1941 and fought in the northern areas of Russia and the Baltic States until the surrender of Germany in 1945. The Army was created in accordance with prewar doctrine that called for Shock Armies to 'overcome difficult defensive dispositions in order to create a tactical penetration of sufficient breadth and depth to permit the commitment of mobile formations for deeper exploitation.' However, as the war went on, Shock Armies lost this specific role and reverted, in general, to ordinary frontline formations. History The 1st Shock Army was formed as part of the Reserve of the Supreme High Command (RVGK, the Stavka reserve) at Zagorsk (now Sergiyev Posad) in the Moscow Military District in November 1941. Taking part in the Battle of Moscow in December 1941, on 1 December the Army consisted of the 133rd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
14th Guards Rifle Corps
14 (fourteen) is a natural number following 13 and preceding 15. In relation to the word "four" ( 4), 14 is spelled "fourteen". In mathematics * 14 is a composite number. * 14 is a square pyramidal number. * 14 is a stella octangula number. * In hexadecimal, fourteen is represented as E * Fourteen is the lowest even ''n'' for which the equation φ(''x'') = ''n'' has no solution, making it the first even nontotient (see Euler's totient function). * Take a set of real numbers and apply the closure and complement operations to it in any possible sequence. At most 14 distinct sets can be generated in this way. ** This holds even if the reals are replaced by a more general topological space. See Kuratowski's closure-complement problem * 14 is a Catalan number. * Fourteen is a Companion Pell number. * According to the Shapiro inequality 14 is the least number ''n'' such that there exist ''x'', ''x'', ..., ''x'' such that :\sum_^ \frac < \frac where ''x'' = ''x'', ''x' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leningrad Front
The Leningrad Front (russian: Ленинградский фронт) was formed during the 1941 German approach on Leningrad (now Saint Petersburg) by dividing the Northern Front into the Leningrad Front and Karelian Front on August 27, 1941. History The Leningrad Front was immediately given the task of containing the German drive towards Leningrad and defending the city from the approaching Army Group North. By September 1941, German forces to the south were effectively stopped on the outskirts of Leningrad, initiating the two-and-a-half-year-long siege of Leningrad. Although Finnish forces to the north stopped at the old Finnish–Soviet border, the Leningrad front suffered severe losses on the Finnish Front. From September 8, soldiers of the front were forced to conduct operations under the conditions of a blockade, with very little supply. Some supplies did reach the city however via the lake Road of Life. During the blockade, the front executed various offensive and de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
225th Rifle Division
The 225th Rifle Division was an infantry division of the Red Army, formed in December 1941 from the remnants of the pre-war 3rd Tank Division and based on the ''shtat'' (table of organization and equipment) of July 29, 1941. The 3rd Tank's single rifle regiment was joined by two reserve rifle regiments, and its howitzer regiment was converted to a standard artillery regiment. As part of 52nd Army in Volkhov Front it took part in largely local fighting in the Novgorod area, seeing combat in several abortive attempts to retake the city until it finally played a main role in its liberation in January 1944 and received its name as a battle honor. Following this victory, the 225th advanced toward Pskov, now as part of 54th Army. When the summer offensive began, it helped breach the German defenses of the Panther Line in the Pskov area and then advanced through Latvia, eventually reaching Riga. When 3rd Baltic Front was disbanded, the division was reassigned to the 21st Army, which wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
21st Infantry Division (Wehrmacht)
The 21st Infantry Division was a German military unit which fought during World War II. History The 21st Infantry Division (Germany) was formed in 1934 in Elbing, East Prussia, by expanding the 3rd Prussian Infantry Regiment of the 1st Division of the old Reichswehr. As this was a direct breach of the terms of the Treaty of Versailles, its existence was initially concealed; it was formally designated as the 21st Infantry Division in October 1935. Its East Prussian origin informed the adoption of the divisional symbol, a figure holding a shield bearing the black cross of the Teutonic Knights. Mobilised in the 1st wave in 1939, the division took part in the German invasion of Poland and the following year's invasion of France. For the next four years, it fought on the Eastern Front, largely as part of Army Group North, assigned to Eighteenth Army. After being involved in series of defensive battles and retreats to Riga as the Soviet army conquered their territory, late 1944 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
80th Rifle Division (Soviet Union)
The 80th Rifle Division (russian: 80-я стрелковая дивизия) was a rifle division of the Red Army, formed twice. The division was first formed in 1923 and was stationed in eastern Ukraine. It was destroyed in mid-1941 in the Battle of Uman. Its second formation was formed from a People's Militia division in Leningrad, fighting in the siege of that city from September. In early 1944 it fought in the Leningrad–Novgorod Offensive, which ended the siege. The division then served with the 59th Army in its westward advance, and was disbanded postwar. 1st formation The division was established in 1923 in the Ukrainian Military District, initially as a territorial rifle division. The division's initial composition was: *410th Rifle Regiment *467th Rifle Regiment *519th Rifle Regiment *346th Artillery Regiment It remained a part of the Ukrainian Military District until 1935 when the eastern half of the Ukraine was used to create the Kharkiv Military District and th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
18th Rifle Division (Soviet Union)
The 18th Rifle Division was an infantry division of the Soviet Union's Red Army during the Russian Civil War, Polish–Soviet War, Winter War and World War II. The division was formed a total of five times during this period. First Formation The 18th Rifle Division was formed on 26 November 1918 at Arkhangelsk from troops from Archangel, Belsky and Kotlassky areas. During the period from November 1918 to May 1921 the division was part of the 6th Army, 7th Army, 15th Army, 4th Army, Reserve Group of the Western Front, 3rd Army, 15th Army, 9th Army, and 11th Armies. It participated in the liberation of Archangel and Onega. In the spring of 1920 the division was part of the Western Front and took part in the invasion of Poland. After being defeated at the Battle of Warsaw the division retreated to East Prussia where it was briefly interned. In November 1920 the division was assigned to the Caucasus Front where it participated in the battles with the white-green in the Kuban ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Porkhov
Porkhov (russian: По́рхов) is a town and the administrative center of Porkhovsky District in Pskov Oblast, Russia, located on the Shelon River, east of Pskov, the administrative center of the oblast. Population: History The fortress of Porkhov is believed to have been founded in 1239 by Alexander Nevsky. The timber fortress was sacked by Algirdas (Olgierd) in 1356 and fell in flames in 1387. The Novgorod Republic immediately rebuilt its fortifications in limestone downstream. In 1428, Grand Duke of Lithuania Vytautas destroyed the western wall by artillery fire and entered Porkhov. Two years later, the Novgorodians augmented the fortress and rebuilt its walls. After the fall of Novgorod to the Muscovites in 1478, the fortress lost its military importance. Porkhov was the second most important town of Shelon Pyatina, after Russa. It was not, however, a significant economical center—there were only seventy-six homesteads there in the 15th century and almost al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soltsy
Soltsy (russian: Сольцы́) is a town and the administrative center of Soletsky District in Novgorod Oblast, Russia, located on the left bank of the Shelon River, southwest of Veliky Novgorod, the administrative center of the oblast. Population: History Soltsy, whose name owes to the nearby salt water springs, was first mentioned in a chronicle in 1390 and in the following played an important role as an intermediate station on the trade route connecting Novgorod and Pskov. In 1471, the Battle of Shelon between Muscovite forces led by Ivan III and the army of the Novgorod Republic took place near Soltsy, which marked the end of political independence of the Novgorod Republic. Soltsy eventually became a part of the Moscow State. In the course of the administrative reform carried out in 1708 by Peter the Great, the territory was included into Ingermanland Governorate (known since 1710 as Saint Petersburg Governorate). In 1727, separate Novgorod Governorate was split o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |