|
10th Infantry Division (France)
The 10th Infantry Division (10e DI) was an infantry Division (military), division of the French Army which took part in the First World War, and Second World War. History The division was created by the decree of 28 September 1873. Located in the 13th military region (Clermont-Ferrand), it was made up of two brigades. At the beginning of the First World War, it was mobilised in the 5th Military Region and formed part of the 5th Army Corps (France), 5th Army Corps from August 1914 to November 1918. On 10 May 1940 the 10th DI, under the orders of General Sisteron, was attached to the reserve of the French General Headquarters, then on 16 May to the 23rd Army Corps and on 16 June 1940 to the 2nd Army (France), 2nd Army, with which it capitulated on 25 June and was subsequently disbanded. After the Normandy landings, the division was reconstituted, mainly of troops of Parisian French Forces of the Interior, FFI/Francs-Tireurs et Partisans, Francs-Tireurs and Partisans (French C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infantry
Infantry, or infantryman are a type of soldier who specialize in ground combat, typically fighting dismounted. Historically the term was used to describe foot soldiers, i.e. those who march and fight on foot. In modern usage, the term broadly encompasses a wide variety of subspecialties, including light infantry, irregular infantry, heavy infantry, mountain infantry, motorized infantry, mechanized infantry, Airborne forces, airborne infantry, Air assault, air assault infantry, and Marines, naval infantry. Other subtypes of infantry, such as line infantry and mounted infantry, were once commonplace but fell out of favor in the 1800s with the invention of more accurate and powerful weapons. Etymology and terminology In English, use of the term ''infantry'' began about the 1570s, describing soldiers who march and fight on foot. The word derives from Middle French , from older Italian (also Spanish) ''infanteria'' (foot soldiers too inexperienced for cavalry), from Latin '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nevers
Nevers ( , ; , later ''Nevirnum'' and ''Nebirnum'') is a city and the Prefectures in France, prefecture of the Nièvre Departments of France, department in the Bourgogne-Franche-Comté Regions of France, region in central France. It was the principal city of the former provinces of France, province of Nivernais. It is south-southeast of Paris. History Nevers first enters written history as Noviodunum, a town held by the Aedui at Ancient Rome, Roman contact. The quantities of medals and other Roman antiquities found on the site indicate the importance of the place, and in 52 BCE, Julius Caesar made Noviodunum, which he describes as in a convenient position on the banks of the Loire, a depot (''B. G.'' vii. 55). There, he had his hostages, corn and military chest, with the money in it allowed him from home for the war, his own and his army's baggage and a great number of horses which had been bought for him in Spain and Italy. After his failure before Gergovia, the Aedui at Nov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Occupation Zone
The French occupation zone in Germany (, ) was one of the Allied-occupied areas in Germany after World War II. Background In the aftermath of the Second World War, Winston Churchill, Franklin D. Roosevelt and Joseph Stalin met at the Yalta Conference to discuss Germany's post-war occupation, which included among other things coming to a final determination of the inter-zonal borders. Originally, there were to be only three zones, with the French excluded. French General Charles de Gaulle, who by this point was the leader of the Provisional Government of the French Republic, was not invited to Yalta. Deeply offended by this snub, the French leader nevertheless worked tirelessly to restore his nation's honour in the aftermath of the German occupation. Key to this was ensuring a French occupation of substantial German territories – in de Gaulle's view, only a French occupation of Germany could restore the honour of France. He therefore vehemently demanded that a zone be alloc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Koblenz
Koblenz ( , , ; Moselle Franconian language, Moselle Franconian: ''Kowelenz'') is a German city on the banks of the Rhine (Middle Rhine) and the Moselle, a multinational tributary. Koblenz was established as a Roman Empire, Roman military post by Nero Claudius Drusus, Drusus . Its name originates from the Latin ', meaning "(at the) confluence". The actual confluence is today known as the "Deutsches Eck, German Corner", a symbol of the unification of Germany that features an Emperor William monuments, equestrian statue of Emperor William I. The city celebrated its 2,000th anniversary in 1992. The city ranks as the third-largest city by population in Rhineland-Palatinate, behind Mainz and Ludwigshafen am Rhein. Its usual-residents' population is 112,000 (). Koblenz lies in a narrow flood plain between high hill ranges, some reaching mountainous height, and is served by an express rail and autobahn network. It is part of the populous Rhineland. Name Historic spellings include ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atlantic Pockets
In World War II, the Atlantic pockets were locations along the coasts of the Netherlands, Belgium and France chosen as strongholds by the occupying German forces, to be defended as long as possible against land attack by the Allies. The locations are known in German as (lit. "Atlantic strongholds") but are known in English as "Atlantic pockets". Six of the Atlantic pockets were captured by the Allies between June and October 1944. Others were placed under siege. Three surrendered in April 1945, and the remainder in May 1945. Designation as fortresses On 19 January 1944 Adolf Hitler declared eleven places along the Atlantic Wall to be fortresses (''Festungen''), to be held until the last man or the last round, calling them (lit. "Atlantic strongholds"). The ports were: IJmuiden, the Hoek van Holland, Dunkirk, Boulogne-sur-Mer, Le Havre, Cherbourg, Saint-Malo, Brest, Lorient, Saint-Nazaire and the Gironde estuary. In February and March 1944 three more coastal areas we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
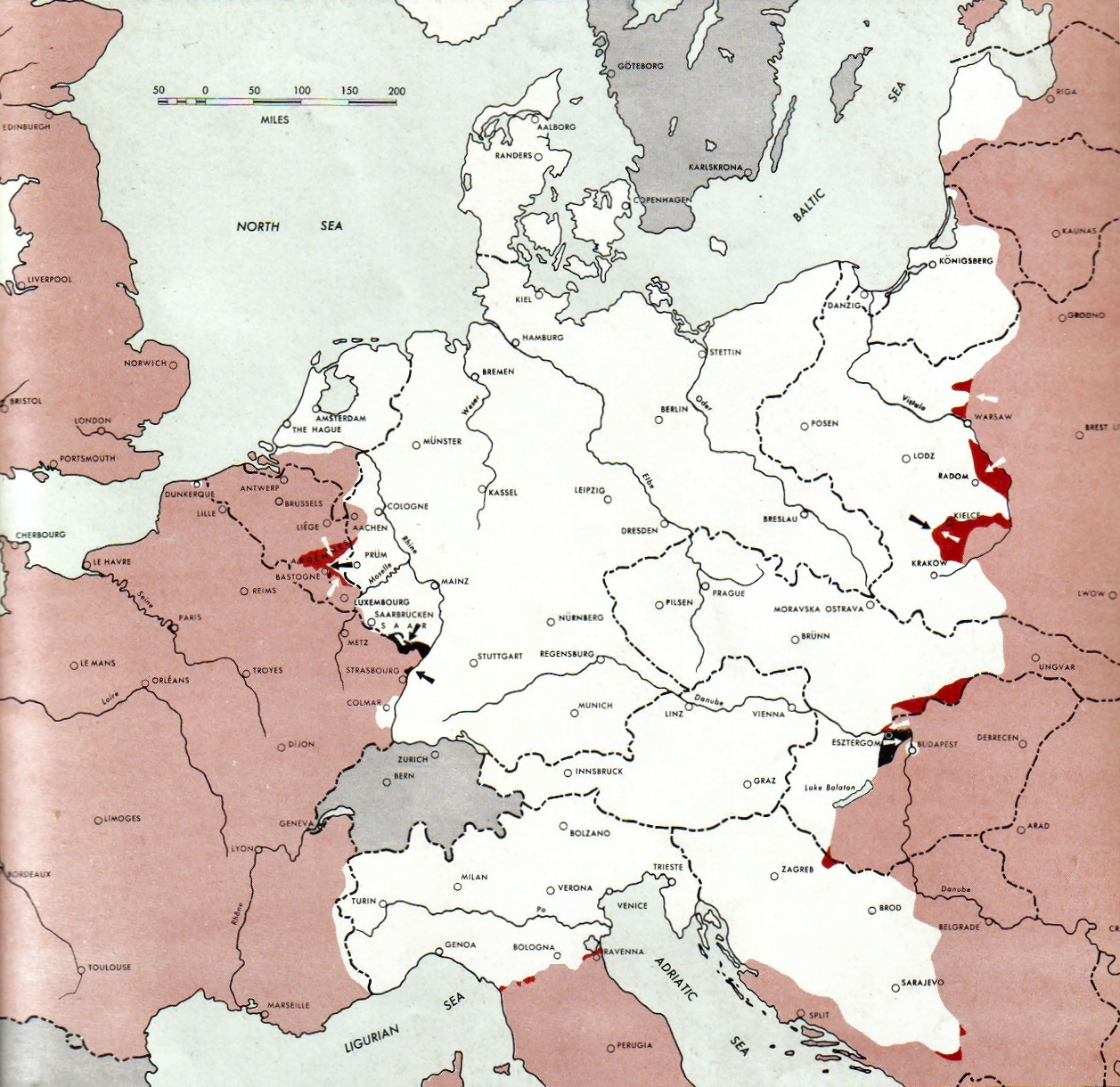
Colmar Pocket
The Colmar Pocket (; ) was the area held in central Alsace, France, by the German Nineteenth Army from November 1944 to February 1945, against the U.S. 6th Army Group (6th AG) during World War II. It was formed when 6th AG liberated southern and northern Alsace and adjacent eastern Lorraine, but could not clear central Alsace. During Operation Nordwind in December 1944, the 19th Army attacked north out of the Pocket in support of other German forces attacking south from the Saar into northern Alsace. In late January and early February 1945, the French First Army (reinforced by the U.S. XXI Corps) cleared the Pocket of German forces. Background Formation of the Pocket A German bridgehead on the west bank of the Rhine long and deep was isolated in November 1944 when the German defenses in the Vosges Mountains The Vosges ( , ; ; Franconian (linguistics), Franconian and ) is a range of medium mountains in Eastern France, near its France–Germany border, border with G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Liberation Army
__NOTOC__ The French Liberation Army ( ; AFL) was the reunified French Army that arose from the merging of the Armée d'Afrique with the prior Free French Forces (; FFL) during World War II. The military force of Free France, it participated in the Italian and Tunisian campaigns before joining in the Liberation of France with other Western Allies of World War II. It went on to join the Western Allied invasion of Germany. History The French Liberation Army was created in January 1943 when the Army of Africa () led by General Giraud was combined with the Free French Forces of General de Gaulle. The AFL participated in the campaigns of Tunisia and Italy; during the Italian campaign the AFL was known as the French Expeditionary Corps in Italy ( ''en Italie or CEFI)'' making a quarter of the troops deployed. The AFL was key in the liberation of Corsica, the first French metropolitan department to be liberated. The troops that landed 2 months after D-Day were the 2nd Armor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean De Lattre De Tassigny
Jean Joseph Marie Gabriel de Lattre de Tassigny (2 February 1889 – 11 January 1952) was a French ''général d'armée'' during World War II and the First Indochina War. He was posthumously elevated to the dignity of Marshal of France in 1952. As an officer during World War I, he fought in various battles, including at Battle of Verdun, Verdun, and was wounded in action, wounded five times, surviving the war with eight citations, the Legion of Honour, and the Military Cross. During the Interwar period, he took part in the Rif War in French Morocco, Morocco, where he was again wounded in action. He went on to serve in the Ministry of War (France), Ministry of War and the staff of ''Conseil supérieur de la guerre'' under the vice president ''Général d'armée'' Maxime Weygand. Early in World War II, from May to June 1940, he was the youngest French general. He led 14th Infantry Division (France), the 14th Infantry Division during the Battle of France in the battles of Rethel, C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1st Army (France)
The First Army () was a field army of France that fought during World War I and World War II. It was also active during the Cold War. World War I On mobilization in August 1914, General Auguste Dubail was put in the charge of the First Army, which comprised the 7th Army Corps (France), 7th, 8th Army Corps (France), 8th, 13th Army Corps (France), 13th, 14th Army Corps (France), 14th, and 21st Army Corps (France), 21st Army Corps, two divisions of cavalry and one reserve infantry division. It was massed between Belfort and the general line Mirecourt-Lunéville with headquarters at Epinal. First Army then took part, along with the French Second Army, in the Invasion of Lorraine. The First Army intended to take the strongly defended town of Sarrebourg. Kingdom of Bavaria, Bavarian Crown Prince Rupprecht, commander of the 6th Army (German Empire), German Sixth Army, was tasked with stopping the French invasion. The French attack was repulsed by Rupprecht and his stratagem of preten ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
4th Battalion Of Foot Chasseurs , or The Fourth of July
{{Disambiguation ...
Fourth or the fourth may refer to: * the ordinal form of the number 4 * ''Fourth'' (album), by Soft Machine, 1971 * Fourth (angle), an ancient astronomical subdivision * Fourth (music), a musical interval * ''The Fourth'', a 1972 Soviet drama See also * * * 1/4 (other) * 4 (other) * The fourth part of the world (other) * Forth (other) * Quarter (other) * Independence Day (United States) Independence Day, known colloquially as the Fourth of July, is a federal holiday in the United States which commemorates the ratification of the Declaration of Independence by the Second Continental Congress on July 4, 1776, establishing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
46th Infantry Regiment (France)
The 46th Infantry Regiment an infantry regiment of the French Army. During the whole of the First World War it was part of the 10th Infantry Division. It was initially based in Paris. It saw action during the First World War, particularly during the Argonne offensive, where, in October 1914—along with the rest of the division—it saw heavy fighting and suffered heavy casualties. It took part in the Battle of Vauquois in February the following year, where, the regimental band—playing the ''Marseillaise'' for the 46th, 76th, and 89th as they attacked—were among the first to be killed. The regiment's standard bearer was Collignon, a former councillor of state, while its adjutant was Maurice Cazeneuve, tenor of the Opéra-Comique. Both were killed in action at Vauquois. During the Battle of Verdun in May it was commanded by Lieutenant Gustave Cohen. After the end of the Second World War, the regiment was disbanded on 30 April 1946, becoming the 46th Infantry Battalion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |