|
1049
Year 1049 ( MXLIX) was a common year starting on Sunday of the Julian calendar. Events By place Byzantine Empire * Spring – Pecheneg Revolt: Emperor Constantine IX decides to transfer 15,000 Pecheneg warriors from their positions in the Balkans to the eastern front. Upon approaching the Bosporus, the Pechenegs decide to turn back, and march through Bulgaria, until they reach the Byzantine city of Serdia. Later, joined by followers, the Pecheneg tribes raise the banner of revolt in Thrace. Europe * January 13 – Theodwin, prince-bishop of Liège, defeats Count Dirk IV of West Frisia near Dordrecht and restores imperial authority in the Rhine Delta. * The Republic of Pisa successfully completes the conquest of Sardinia, from the Andalusian occupiers. British Isles * Viking Irish raiders ally with King Gruffydd ap Rhydderch of Gwent in raiding along the River Severn. Africa * The Banu Hilal, a confederation of tribes of Arabia, begin their invasi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pope Leo IX
Pope Leo IX (, , 21 June 1002 – 19 April 1054), born Bruno von Egisheim-Dagsburg, was the head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 12 February 1049 to his death in 1054. Leo IX is considered to be one of the most historically significant popes of the Middle Ages; he was instrumental in the precipitation of the Great Schism of 1054, considered the turning point in which the Catholic and Eastern Orthodox Churches formally separated. Leo IX favoured traditional morality in his reformation of the Catholic Church. One of his first public acts was to hold the Easter synod of 1049; he joined Emperor Henry III in Saxony and accompanied him to Cologne and Aachen. He also summoned a meeting of the higher clergy in Reims in which several important reforming decrees were passed. At Mainz, he held a council at which the Italian and French as well as the German clergy were represented, and ambassadors of the Byzantine emperor were present. Here too, simony and clerical m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dirk IV, Count Of Holland
Dirk IV (ca. 1020/1030 – 13 January 1049) was Count of Holland from 1039 to 1049 (which was called Frisia at that time). Dirk's date of birth is unknown but it was probably ca. 1030 or shortly before, he was described as "adolescent" at the time of his death. His base of operations was the stronghold his father built at Vlaardingen. Contemporary chroniclers referred to him (in Latin) as "''Theodericus de Phlardirtinga''" (Vlaardingen) and as margrave thereof. The exact extent of his domain is not known, but at one time or another it stretched north to at least Rijnsburg and east to roughly Aalburg. Dirk IV continued the policy of his father Dirk III to enlarge his possessions, developing and colonizing the low-lying peat areas of Holland and Utrecht. As a result, he came into conflict with the bishop of Utrecht, other bishops and monasteries in the surrounding area. Because of this, Emperor Henry III personally led an expedition against him in 1046, forcing Dirk to return some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gruffydd Ap Rhydderch
Gruffudd ap Rhydderch (d. AD 1055) was a king of Gwent and part of the kingdom of Morgannwg in south Wales, and later king of Deheubarth. Gruffudd was the son of Rhydderch ab Iestyn, who had been able to take over the kingdom of Deheubarth from 1023 to 1033. He received the lordship of Caerleon in 1031 and strengthened its fortifications.Jermyn, Anthony.4: Caerleon Through the Centuries to the Year 2000". 2010 Accessed 13 February 2013. Already king of part of Morgannwg, Gruffudd became involved with Deheubarth when that kingdom was taken over from Hywel ab Edwin by Gruffudd ap Llywelyn, already king of Gwynedd, in 1044. Gruffudd ap Rhydderch was, however, able to expel him in 1045 and became king of Deheubarth himself. He was said to be a powerful king who stoutly resisted raids by the Danes and attacks by Gruffudd ap Llywelyn. In 1055, however, Gruffudd ap Llywelyn killed him in battle and recaptured Deheubarth. In 1049 he is reported raiding up the River Severn Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dordrecht
Dordrecht (), historically known in English as Dordt (still colloquially used in Dutch, ) or Dort, is a List of cities in the Netherlands by province, city and List of municipalities of the Netherlands, municipality in the Western Netherlands, located in the Provinces of the Netherlands, province of South Holland. It is the province's fifth-largest city after Rotterdam, The Hague, Leiden, and Zoetermeer, with a population of . The municipality covers the entire Dordrecht Island, also often called ''Het Eiland van Dordt'' ("the Island of Dordt"), bordered by the rivers Oude Maas, Beneden Merwede, Nieuwe Merwede, Hollands Diep, and Dordtsche Kil. Dordrecht is the largest and most important city in the Drechtsteden and is also part of the Randstad, the main conurbation in the Netherlands. Dordrecht is the oldest city in Holland and has a rich history and culture. Etymology The name Dordrecht comes from ''Thuredriht'' (circa 1120), ''Thuredrecht'' (circa 1200). The name seems to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theodwin Of Liège
Theodwin (Latin ''Dietwinus'') was prince-bishop of Liège from 1048 to 1075.Philibert Schmitz, "Theoduin", in ''Biographie Nationale de Belgique''vol. 24(Brussels, 1929), 757-758. Life Originally from Bavaria, Theodwin was named by Henry III, Holy Roman Emperor, Henry III to succeed Wazo of Liège, Wazo as bishop of Liège. In 1049 he led the imperial victory over Dirk IV, Count of Holland, Dirk IV of Frisia. In 1050-1051 he wrote to Henry I of France encouraging him to take firm action against Berengar of Tours. In 1066, Theodwin ceded city rights to Huy, the oldest such charter to survive from what is now Belgium. On 23 March 1075 Pope Gregory VII wrote to him reproachfully about the lax clerical discipline in his diocese, urging him to leave the Abbey of Saint-Hubert unmolested.Brigitte Meijns, "Papal Bulls as Instruments of Reform: the Reception of the Protection Bulls of Gregory VII in the Dioceses of Liège and Thérouanne (1074–1077)", ''Church History (journal), Church H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Common Year Starting On Sunday
A common year starting on Sunday is any non-leap year (i.e. a year with 365 days) that begins on Sunday, January 1, 1 January, and ends on Sunday, December 31, 31 December. Its dominical letter hence is A. The most recent year of such kind was 2023, and the next one will be 2034 in the Gregorian calendar, or, likewise, 2018 and 2029 in the obsolete Julian calendar, see #Applicable years, below for more. Any common year that starts on a Sunday has two Friday the 13ths: those two in this common year January 13, occur in January and October 13, October. This year has four months (January, April, July and October) which begin on a weekend-day. Calendars Applicable years Gregorian Calendar In the (currently used) Gregorian calendar, alongside Common year starting on Monday, Monday, Common year starting on Wednesday, Wednesday, Common year starting on Friday, Friday or Common year starting on Saturday, Saturday, the fourteen types of year (seven common, seven leap) repeat in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tribes Of Arabia
The tribes of Arabia () have inhabited the Arabian Peninsula for thousands of years and traditionally trace their ancestry to one of two forefathers: Adnan, whose descendants originate from Hejaz, West Arabia, Syrian Desert, North Arabia, East Arabia, and Najd#History, Central Arabia; or Qahtanite, Qahtan, whose descendants originate from South Arabia. Further, it is held in the Abrahamic religions—particularly Islam—that the Arab people are descended from Abraham through his son Ishmael. From the 7th century onward, concurrent with the spread of Islam, many of these tribes' members began migrating and settling in the various regions that were subdued during the early Muslim conquests, including the Arab migrations to the Levant, Levant, Arab conquest of Mesopotamia, Mesopotamia, Arab conquest of Egypt, Egypt, Muslim conquest of Khuzestan, Khuzestan, the Arab migrations to the Maghreb, Maghreb, and Islamization of the Sudan region, Sudan. This phenomenon triggered a process of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Banu Hilal
The Banu Hilal () was a confederation of Arab tribes from the Najd region of the central Arabian Peninsula that emigrated to the Maghreb region of North Africa in the 11th century. They ruled the Najd, and campaigned in the borderlands between Iraq and Syria. When the Fatimid Caliphate became the rulers of Egypt and the founders of Cairo in 969, they confined the Bedouin in the south before sending them to Central North Africa (Libya, Tunisia and Algeria) and then to Morocco. Historians estimate the total number of Arab nomads who migrated to the Maghreb in the 11th century to be to 500,000 to 700,000 to 1,000,000. Historian Mármol Carvajal estimated that more than a million Hilalians migrated to the Maghreb between 1051 and 1110, and estimated that the Hilalian population in the Maghreb at his time in 1573 was at 4,000,000 individuals, excluding other Arab tribes and other Arabs already present. Origin The Banu Hilal originated in Najd in the central Arabian Peninsula, som ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
River Severn
The River Severn (, ), at long, is the longest river in Great Britain. It is also the river with the most voluminous flow of water by far in all of England and Wales, with an average flow rate of at Apperley, Gloucestershire. It rises in the Cambrian Mountains in mid Wales, at an altitude of , on the Plynlimon massif, which lies close to the Ceredigion/Powys border near Llanidloes. The river then flows through Shropshire, Worcestershire and Gloucestershire. The county towns of Shrewsbury, Worcester, England, Worcester and Gloucester lie on its course. The Severn's major tributaries are the River Vyrnwy, Vyrnwy, the River Tern, Tern, the River Teme, Teme, the Warwickshire Avon, and the River Stour, Worcestershire, Worcestershire Stour. By convention, the River Severn is usually considered to end, and the Severn Estuary to begin, after the Prince of Wales Bridge, between Severn Beach in South Gloucestershire and Sudbrook, Monmouthshire. The total area of the estuary's draina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Gwent
Gwent () was a medieval Welsh kingdom, lying between the Rivers Wye and Usk. It existed from the end of Roman rule in Britain in about the 5th century until the Norman invasion of Wales in the 11th century. Along with its neighbour Glywysing, it seems to have had a great deal of cultural continuity with the earlier Silures, Miranda Aldhouse-Green &al. ''Gwent In Prehistory and Early History: The Gwent County History'', Vol.1. 2004. . keeping their own courts and diocese separate from the rest of Wales until their conquest by Gruffydd ap Llywelyn. Although it recovered its independence after his death in 1063, Gwent was the first of the Welsh kingdoms to be overrun following the Norman conquest. History Establishment The area has been occupied since the Paleolithic, with Mesolithic finds at Goldcliff and evidence of growing activity throughout the Bronze and Iron Age. Gwent came into being after the Romans had left Britain, and was a successor state drawing on the cultur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
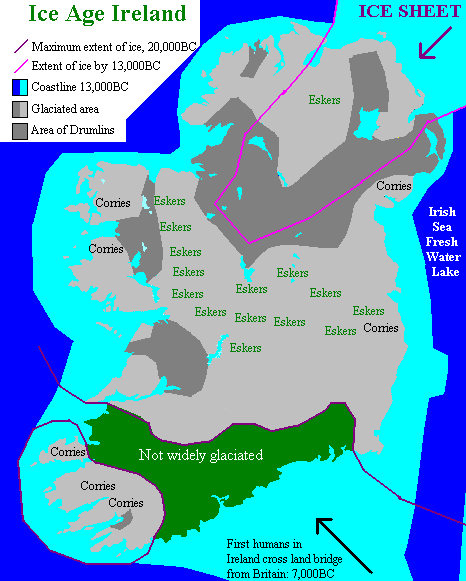
History Of Ireland (800–1169)
The first evidence of human presence in Ireland dates to around 34,000 years ago, with further findings dating the presence of ''Homo sapiens'' to around 10,500 to 7,000 BC. The receding of the ice after the Younger Dryas cold phase of the Quaternary, around 9700 BC, heralds the beginning of Prehistoric Ireland, which includes the archaeological periods known as the Mesolithic, the Neolithic from about 4000 BC, and the Copper Age beginning around 2500 BC with the arrival of the Beaker Culture. The Irish Bronze Age proper begins around 2000 BC and ends with the arrival of the Iron Age of the Celtic Hallstatt culture, beginning about 600 BC. The subsequent La Tène culture brought new styles and practices by 300 BC. Greek and Roman writers give some information about Ireland during the Classical period (see " protohistoric" period), by which time the island may be termed "Gaelic Ireland". By the late 4th century CE Christianity had begun to gradually subsume or replace the earli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al-Andalus
Al-Andalus () was the Muslim-ruled area of the Iberian Peninsula. The name refers to the different Muslim states that controlled these territories at various times between 711 and 1492. At its greatest geographical extent, it occupied most of the peninsula as well as Septimania under Umayyad rule. These boundaries changed through a series of conquests Western historiography has traditionally characterized as the ''Reconquista'',"Para los autores árabes medievales, el término Al-Andalus designa la totalidad de las zonas conquistadas – siquiera temporalmente – por tropas arabo-musulmanas en territorios actualmente pertenecientes a Portugal, España y Francia" ("For medieval Arab authors, Al-Andalus designated all the conquered areas – even temporarily – by Arab-Muslim troops in territories now belonging to Spain, Portugal and France"), García de Cortázar, José Ángel. ''V Semana de Estudios Medievales: Nájera, 1 al 5 de agosto de 1994'', Gobie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |