|
1,2-Dimorpholinoethane
1,2-Dimorpholinoethane is an organic chemical and specifically a nitrogen-oxygen heterocyclic compound. At room temperature it is a solid with a melting point of 75 °C. It has two tertiary amines in the same molecule meaning it is ideal for use as a polyurethane catalyst. It has the CAS Registry Number 1723-94-0 and is TSCA and REACH registered and on EINECS with the number 217-026-5. The IUPAC name is 4-(2-morpholin-4-ylethyl)morpholine and the chemical formula C10H20N2O2. Synonyms Section reference. * 4,4'-Ethylenedimorpholine * 4,4'-(Ethane-1,2-diyl)bismorpholine * Morpholine, 4,4'-(1,2-ethanediyl)bis- * 1,2-Di-N-morpholinylethane * Morpholine,4,4'-(1,2-ethanediyl)bis- * Morpholine, 4,4'-ethylenedi- Uses and synthesis As the molecule has two tertiary nitrogen atoms in the molecule, the substance finds use as a catalyst for polyurethane including PU foams. 1,2-Dimorpholinoethane has been used to make transition metal complexes. As there are two nitrogen atoms in the mol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heterocyclic Compound
A heterocyclic compound or ring structure is a cyclic compound that has atoms of at least two different elements as members of its ring(s). Heterocyclic organic chemistry is the branch of organic chemistry dealing with the synthesis, properties, and applications of organic heterocycles. Examples of heterocyclic compounds include all of the nucleic acids, the majority of drugs, most biomass (cellulose and related materials), and many natural and synthetic dyes. More than half of known compounds are heterocycles. 59% of US FDA-approved drugs contain nitrogen heterocycles. Classification The study of organic heterocyclic chemistry focuses especially on organic unsaturated derivatives, and the preponderance of work and applications involves unstrained organic 5- and 6-membered rings. Included are pyridine, thiophene, pyrrole, and furan. Another large class of organic heterocycles refers to those fused to benzene rings. For example, the fused benzene derivatives of py ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toxic Substances Control Act Of 1976
The Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA) is a United States law, passed by the United States Congress, Congress in 1976 and administered by the United States United States Environmental Protection Agency, Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), that regulates chemicals not regulated by other U.S. federal statutes, including chemicals already in commerce and the introduction of new chemicals.Auer, Charles, Frank Kover, James Aidala, Marks Greenwood“Toxic Substances: A Half Century of Progress.”EPA Alumni Association. March 2016. When the TSCA was put into place, all existing chemicals were considered to be safe for use and subsequently Grandfather Clause, grandfathered in. Its three main objectives are to assess and regulate new commercial chemicals before they enter the market, to regulate chemicals already existing in 1976 that posed an "unreasonable risk of injury to health or the environment", as for example Polychlorinated biphenyl, PCBs, lead, mercury and radon, and to re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
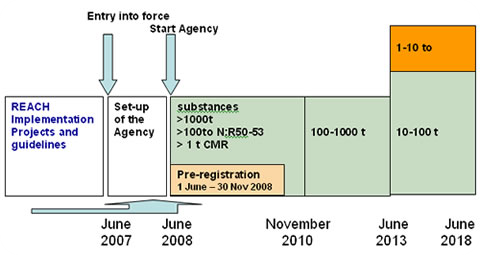
Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation And Restriction Of Chemicals
Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) is a European Union regulation dating from 18 December 2006, amended on 16 December 2008 by Regulation (EC) No 1272/2008. REACH addresses the production and use of chemical substances, and their potential impacts on both human health and the environment. Its 849 pages took seven years to pass, and it has been described as the most complex legislation in the Union's history and the most important in 20 years. It is the strictest law to date regulating chemical substances and will affect industries throughout the world. REACH entered into force on 1 June 2007, with a phased implementation over the next decade. The regulation also established the European Chemicals Agency, which manages the technical, scientific and administrative aspects of REACH. Overview When REACH is fully in force, it will require all companies manufacturing or importing chemical substances into the European Union in quantities of o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transition Metal
In chemistry, a transition metal (or transition element) is a chemical element in the d-block of the periodic table (groups 3 to 12), though the elements of group 12 (and less often group 3) are sometimes excluded. The lanthanide and actinide elements (the f-block) are called inner transition metals and are sometimes considered to be transition metals as well. They are lustrous metals with good electrical and thermal conductivity. Most (with the exception of group 11 and group 12) are hard and strong, and have high melting and boiling temperatures. They form compounds in any of two or more different oxidation states and bind to a variety of ligands to form coordination complexes that are often coloured. They form many useful alloys and are often employed as catalysts in elemental form or in compounds such as coordination complexes and oxides. Most are strongly paramagnetic because of their unpaired d electrons, as are many of their compounds. All of the elements that are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Denticity
In coordination chemistry, denticity () refers to the number of donor groups in a given ligand that bind to the central metal atom in a coordination complex. In many cases, only one atom in the ligand binds to the metal, so the denticity equals one, and the ligand is said to be unidentate or monodentate. Ligands with more than one bonded atom are called multidentate or polydentate. The denticity of a ligand is described with the Greek letter κ ('kappa'). For example, κ6-EDTA describes an EDTA ligand that coordinates through 6 non-contiguous atoms. Denticity is different from hapticity because hapticity refers exclusively to ligands where the coordinating atoms are contiguous. In these cases the η ('eta') notation is used. Bridging ligands use the μ ('mu') notation. Classes Polydentate ligands are chelating agents and classified by their denticity. Some atoms cannot form the maximum possible number of bonds a ligand could make. In that case one or more binding si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ligand
In coordination chemistry, a ligand is an ion or molecule with a functional group that binds to a central metal atom to form a coordination complex. The bonding with the metal generally involves formal donation of one or more of the ligand's electron pairs, often through Lewis acids and bases, Lewis bases. The nature of metal–ligand bonding can range from covalent bond, covalent to ionic bond, ionic. Furthermore, the metal–ligand bond order can range from one to three. Ligands are viewed as Lewis bases, although rare cases are known to involve Lewis acids and bases, Lewis acidic "ligands". Metals and metalloids are bound to ligands in almost all circumstances, although gaseous "naked" metal ions can be generated in a high vacuum. Ligands in a complex dictate the reactivity (chemistry), reactivity of the central atom, including ligand substitution rates, the reactivity of the ligands themselves, and redox. Ligand selection requires critical consideration in many practical are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catalysis
Catalysis () is the increase in rate of a chemical reaction due to an added substance known as a catalyst (). Catalysts are not consumed by the reaction and remain unchanged after it. If the reaction is rapid and the catalyst recycles quickly, very small amounts of catalyst often suffice; mixing, surface area, and temperature are important factors in reaction rate. Catalysts generally react with one or more reactants to form intermediates that subsequently give the final reaction product, in the process of regenerating the catalyst. The rate increase occurs because the catalyst allows the reaction to occur by an alternative mechanism which may be much faster than the noncatalyzed mechanism. However the noncatalyzed mechanism does remain possible, so that the total rate (catalyzed plus noncatalyzed) can only increase in the presence of the catalyst and never decrease. Catalysis may be classified as either homogeneous, whose components are dispersed in the same phase (usual ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heterocyclic Compounds With 2 Rings
A heterocyclic compound or ring structure is a cyclic compound that has atoms of at least two different elements as members of its ring(s). Heterocyclic organic chemistry is the branch of organic chemistry dealing with the synthesis, properties, and applications of organic heterocycles. Examples of heterocyclic compounds include all of the nucleic acids, the majority of drugs, most biomass (cellulose and related materials), and many natural and synthetic dyes. More than half of known compounds are heterocycles. 59% of US FDA-approved drugs contain nitrogen heterocycles. Classification The study of organic heterocyclic chemistry focuses especially on organic unsaturated derivatives, and the preponderance of work and applications involves unstrained organic 5- and 6-membered rings. Included are pyridine, thiophene, pyrrole, and furan. Another large class of organic heterocycles refers to those fused to benzene rings. For example, the fused benzene derivatives of pyridin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tertiary Amines
In chemistry, amines (, ) are organic compounds that contain carbon-nitrogen bonds. Amines are formed when one or more hydrogen atoms in ammonia are replaced by alkyl or aryl groups. The nitrogen atom in an amine possesses a lone pair of electrons. Amines can also exist as hetero cyclic compounds. Aniline is the simplest aromatic amine, consisting of a benzene ring bonded to an amino group. Amines are classified into three types: primary (1°), secondary (2°), and tertiary (3°) amines. Primary amines (1°) contain one alkyl or aryl substituent and have the general formula RNH2. Secondary amines (2°) have two alkyl or aryl groups attached to the nitrogen atom, with the general formula R2NH. Tertiary amines (3°) contain three substituent groups bonded to the nitrogen atom, and are represented by the formula R3N. The functional group present in primary amines is called the amino group. Classification of amines Amines can be classified according to the nature and number o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |