|
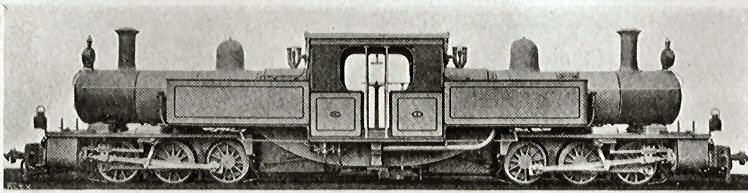
0-6-6-0
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, a wheel arrangement refers to a locomotive with two engine units mounted under a rigid locomotive frame, with the front engine unit pivoting and each engine unit with six coupled driving wheels without any leading or trailing wheels. The wheel arrangement was mostly used to describe Mallet locomotive types and in some occasions, Double Fairlie locomotives. A similar wheel arrangement exists for Double Fairlie, Meyer, Kitson-Meyer and Garratt locomotives, but on these types it is referred to as since both engine units are pivoting.Espitalier, T.J.; Day, W.A.J. (1943). ''The Locomotive in South Africa - A Brief History of Railway Development. Chapter II - The Adoption of the 3 ft. 6 in. Gauge on the Cape Government Railways'' (Continued). South African Railways and Harbours Magazine, August 1943. pp. 592-594. Overview The 0-6-6-0 wheel arrangement was used mostly on Mallet locomotives, on which the engine un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fairlie Locomotive
A Fairlie locomotive is a type of articulated locomotive, articulated steam locomotive that has the driving wheels on bogies. It was invented by Robert Francis Fairlie. The locomotive may be double-ended (a double Fairlie) or single ended (a single Fairlie). Most double-ended Fairlies had wheel arrangements of or . All were tank locomotives. While Fairlie locomotives are now used only on heritage railways, the majority of diesel locomotive, diesel and electric locomotives in the world follow the basic form of the Fairlie — two power trucks with all axles driven. Many also follow the Fairlie's double-ended concept, capable of being driven equally well in both directions. Development of the design In 1864, the Scottish people, Scottish engineer Robert Francis Fairlie published a pamphlet detailing his plans for a new type of articulated locomotive. He had become convinced that the conventional pattern of locomotive could be improved on, and that his proposed design would ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mallet Locomotive
A Mallet locomotive is a type of compound locomotive, compound articulated locomotive, articulated steam locomotive, invented by the Swiss engineer Anatole Mallet (1837–1919). The front of the locomotive is articulated on a bogie. The Compound steam engine, compound steam system fed steam at boiler pressure to high-pressure cylinders driving the rear set of driving wheels (rigidly connected to the boiler). The exhaust steam from these cylinders was fed into a low-pressure receiver and was then sent to low-pressure cylinders that powered the driving wheels on the swiveling bogie towards the front of locomotive. Compounding Steam under pressure is converted into mechanical energy more efficiently if it is used in a compound steam engine, compound engine; in such an engine, steam from a boiler is used in high-pressure (HP) cylinders and then under reduced pressure in a second set of cylinders. The lower-pressure steam occupies a larger volume and the low-pressure (LP) cylinders ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fairlie Locomotive
A Fairlie locomotive is a type of articulated locomotive, articulated steam locomotive that has the driving wheels on bogies. It was invented by Robert Francis Fairlie. The locomotive may be double-ended (a double Fairlie) or single ended (a single Fairlie). Most double-ended Fairlies had wheel arrangements of or . All were tank locomotives. While Fairlie locomotives are now used only on heritage railways, the majority of diesel locomotive, diesel and electric locomotives in the world follow the basic form of the Fairlie — two power trucks with all axles driven. Many also follow the Fairlie's double-ended concept, capable of being driven equally well in both directions. Development of the design In 1864, the Scottish people, Scottish engineer Robert Francis Fairlie published a pamphlet detailing his plans for a new type of articulated locomotive. He had become convinced that the conventional pattern of locomotive could be improved on, and that his proposed design would ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Whyte Notation
The Whyte notation is a classification method for steam locomotives, and some internal combustion locomotives and electric locomotives, by wheel arrangement. It was devised by Frederick Methvan Whyte, and came into use in the early twentieth century following a December 1900 editorial in ''American Engineer and Railroad Journal''. The notation was adopted and remains in use in North America and the United Kingdom to describe the wheel arrangements of steam locomotives, but for modern locomotives, multiple units and trams it has been supplanted by the UIC system in Europe and by the AAR system (essentially a simplification of the UIC system) in North America. However, geared steam locomotives do not use the notation. They are classified by their model and their number of trucks. Structure of the system Basic form The notation in its basic form counts the number of leading wheels, then the number of driving wheels, and finally the number of trailing wheels, numbers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saxon XV HTV
The Saxon Class XV HTV was a class of goods train steam locomotive operated by the Royal Saxon State Railways, which had been conceived for hauling trains and acting as banking engines for routes in the Ore Mountains. In 1925 the Deutsche Reichsbahn grouped them into their DRG Class 79.0. History The two locomotives were built in 1916 at the Sächsischen Maschinenfabrik, formerly Hartmann. The undercarriage of the locomotives was unusual. Instead of an alternative proposal for a twelve-coupled locomotive with sideways-sliding Gölsdorf axles, as was realised a year later in the shape of the Württemberg K, the Saxon Railways decided on a proposal by their head of the engineering department, Lindner, for a design that was unique in Germany: the Saxon XV HTV was given two, fixed, six-coupled drives. This was mainly because they had doubts about the suitability of the ''Gölsdorf'' system for twelve-couplers. The outside axles were designed as Klien-Lindner axles and could be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baltimore And Ohio Railroad Locomotives
On the Baltimore and Ohio Railroad, locomotives were always considered of great importance, and the railroad was involved in many experiments and innovations. History Early locomotives The name ''Tom Thumb (locomotive), Tom Thumb'' is forever associated with the B&O, as the first steam locomotive built in the United States for an American railroad. It was built strictly as a demonstrator, but it was succeeded by a series of similar locomotives (the "Grasshopper locomotive, Grasshoppers" and the "Crabs") designed by Ross Winans, the first head of motive power on the railroad. Early B&O designs were quite unlike those used on other roads, due to in-house design and the emphasis of pulling power. 4-2-0 locomotives from Norris (represented by the "Lafayette" reproduction in the B&O museum's collection) were the anomaly on a railroad which was already building eight-coupled (0-8-0) locomotives well before the Civil War. By the beginning of the war, new power on the railroad had become ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wheel Arrangement
In rail transport, a wheel arrangement or wheel configuration is a system of classifying the way in which wheels are distributed under a locomotive. Several notations exist to describe the wheel assemblies of a locomotive by type, position, and connections, with the adopted notations varying by country. Within a given country, different notations may also be employed for different kinds of locomotives, such as steam, electric, and diesel powered. Especially in steam days, wheel arrangement was an important attribute of a locomotive because there were many different types of layout adopted, each wheel being optimised for a different use (often with only some being actually "driven"). Modern diesel and electric locomotives are much more uniform, usually with all axles driven. Major notation schemes The main notations are the Whyte notation (based on counting the wheels), the AAR wheel arrangement notation (based on counting either the axles or the bogies), and the UIC classifi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
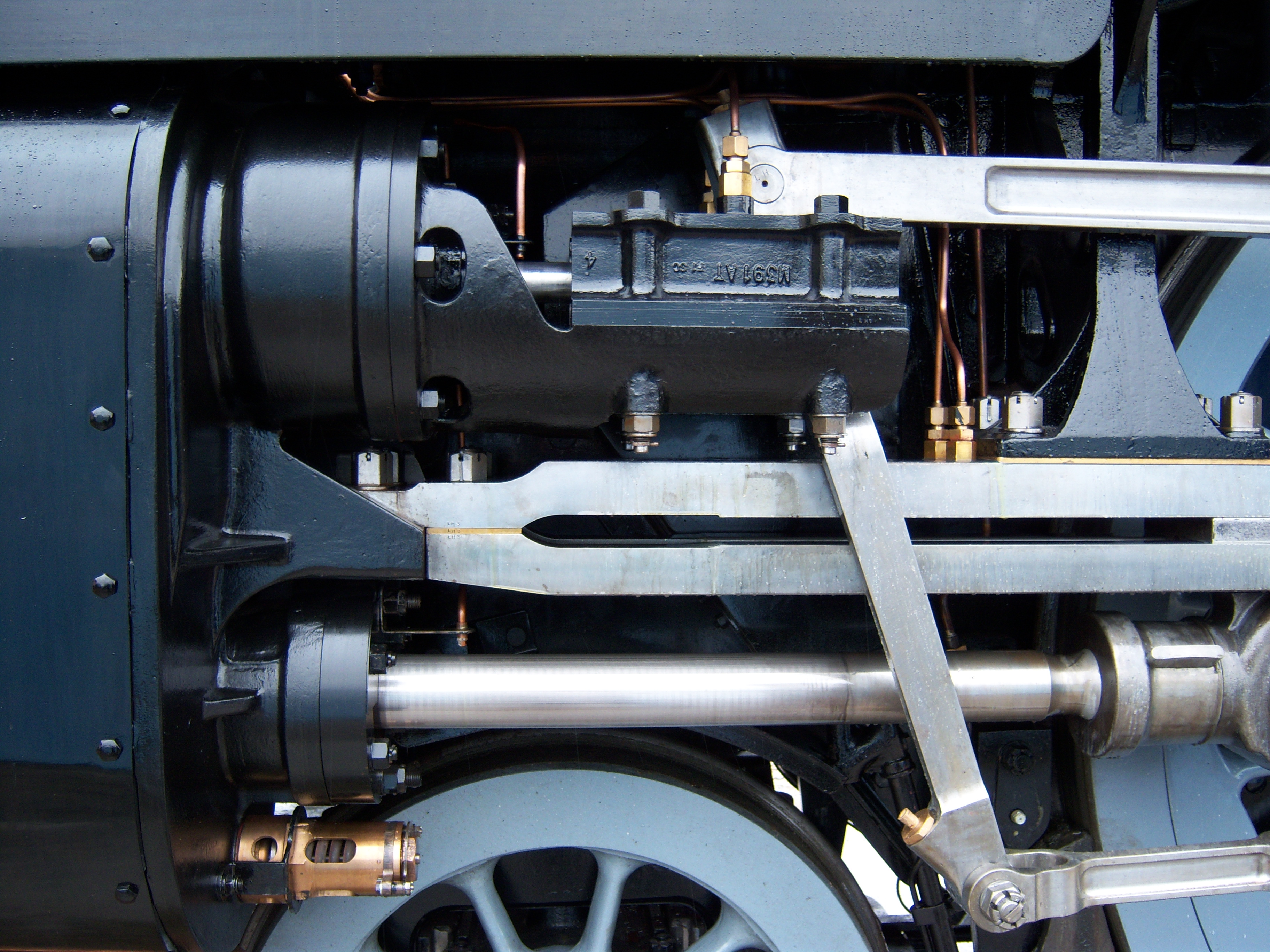
Cylinder (locomotive)
The cylinder is the power-producing element of the steam engine powering a steam locomotive. The cylinder (engine), cylinder is made pressure-tight with end covers and a piston; a valve distributes the steam to the ends of the cylinder. Cylinders were initially cast iron, but later made of steel. The cylinder casting includes other features such as (in the case of Stephenson's Rocket) valve ports and mounting feet. The last big American locomotives incorporated the cylinders as part of huge one-piece steel castings that were the Locomotive frame, main frame of the locomotive. Renewable wearing surfaces were needed inside the cylinders and provided by cast-iron bushings. The way the valve controlled the steam entering and leaving the cylinder was known as steam distribution and shown by the shape of the indicator diagram. What happened to the steam inside the cylinder was assessed separately from what happened in the boiler and how much friction the moving machinery had to cope wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pampanga Sugar Development Company
The Pampanga Sugar Development Company built the first Filipino-financed sugar central in Pampanga, Philippines. It was established in 1921 by several local families in Pampanga. It is the oldest running mill in the province. The Pasudeco Sugar Central was finished in March, 1921, to serve as a central purchasing and processing company for the surrounding sugar plantations. Financed by the Pampanga Sugar Development Company, it was constructed by the Honolulu Iron Works. Its existence became a catalyst for the exponential growth of San Fernando, the capital of the rich sugar-producing province of Pampanga. On July 12, 1939, two of the founders, Jose de Leon and Augusto Gonzalez, as well as Constabulary Captain Julian Olivas, were gunned down at the administrative offices of Pasudeco. At that time, de Leon and Gonzalez were the two richest men in Pampanga and the biggest Pasudeco shareholders. The 30-meter-high 1964 Chimney 3 was transferred to Capital Town gate in July 2022. Chi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baldwin Locomotive Works
The Baldwin Locomotive Works (BLW) was an American manufacturer of railway locomotives from 1825 to 1951. Originally located in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, it moved to nearby Eddystone, Pennsylvania, Eddystone in the early 20th century. The company was for decades the world's largest producer of steam locomotives, but struggled to compete when demand switched to diesel locomotives. Baldwin produced the last of its 70,000-plus locomotives in 1951, before merging with the Lima Locomotive Works, Lima-Hamilton Corporation on September 11, 1951, to form the Baldwin-Lima-Hamilton Corporation. The company has no relation to the E.M. Baldwin and Sons of New South Wales, Australia, a builder of small diesel locomotives for sugar cane railroads. History: 19th century Beginning Matthias W. Baldwin, the founder, was a jeweler and whitesmith, who, in 1825, formed a partnership with machinist David H. Mason, and began making bookbinders' tools and cylinders for calico printing. Baldwin t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arkhangelsk
Arkhangelsk (, ) is a types of inhabited localities in Russia, city and the administrative center of Arkhangelsk Oblast, Russia. It lies on both banks of the Northern Dvina near its mouth into the White Sea. The city spreads for over along the banks of the river and numerous islands of its river delta, delta. Arkhangelsk was the chief seaport of medieval and early modern Russia until 1703, when it was replaced by the newly founded Saint Petersburg. A Northern Railway (Russia), railway runs from Arkhangelsk to Moscow via Vologda and Yaroslavl, and air travel is served by the Talagi Airport and the smaller Vaskovo Airport. As of the Russian Census (2021), 2021 Census, the city's population was 301,199. Coat of arms The arms of the city display the Michael (archangel), Archangel Michael in the act of defeating the Devil. Legend states that this victory took place near where the city stands, hence its name, and that Michael still stands watch over the city to prevent the Devil's r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Murmansk
Murmansk () is a port city and the administrative center of Murmansk Oblast in the far Far North (Russia), northwest part of Russia. It is the world's largest city north of the Arctic Circle and sits on both slopes and banks of a modest fjord, Kola Bay, an estuarine inlet of the Barents Sea, with its bulk on the east bank of the inlet. The city is a major port of the Arctic Ocean and is about from the Norway–Russia border, border with Norway, from the Finland–Russia border, border with Finland and from Moscow. Benefiting from the North Atlantic Current, Murmansk resembles cities of its size across western Russia, with highway and railway access to the rest of Europe, and the northernmost trolleybus system on Earth. Its connectivity contrasts with the isolation of Arctic ports like the Siberian Dikson (urban-type settlement), Dikson on the shores of the Kara Sea, and Iqaluit, in the Canadian Arctic. Despite long, snowy winters, Murmansk's climate is moderated by the generall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |