|
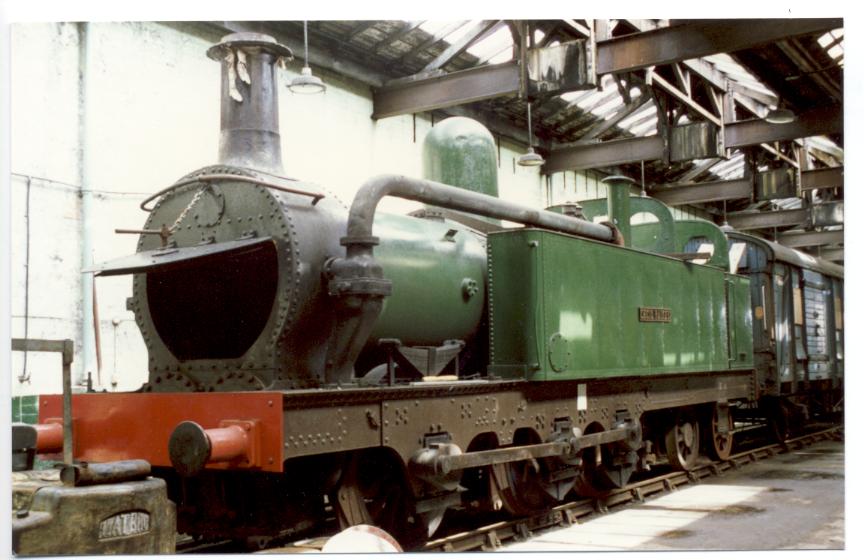
0-6-4
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, represents the wheel arrangement of no leading wheels, six powered and coupled driving wheels on three axles, and four trailing wheels on two axles. Overview This wheel arrangement has only been used for tank locomotives and Single Fairlies. The earliest known example was the Moel Tryfan narrow gauge locomotive, built for use on the North Wales Narrow Gauge Railways. It was a Single Fairlie type, built by the Vulcan Foundry near Manchester in 1875. It was followed by the R class and S class, built by the Avonside Engine Company of England for the New Zealand Railways Department between 1878 and 1881. Usage Australia The South Australian Railways K class locomotives were introduced in 1884, designed by William Thow. They were noted to run more smoothly bunker-first. After the electrification of the Mersey Railway in England, four of its 0-6-4T locomotives were sold to J & A Brown of New South Wales, A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NZR S Class
The NZR S class (later WAGR I class) was a class of seven 0-6-4T Fairlie locomotive, single Fairlie steam locomotives operated by New Zealand's New Zealand Railways Department, Railways Department (NZR) between 1882 and 1927. History During the 1870s, the railway network in New Zealand was a fragmented system of light railway lines built in rough country where short, Grade (slope), steep grades and Minimum railway curve radius, tight curves were common. The Fairlie type of steam locomotive was well-suited to working in such conditions. Earlier double-ended engines (known as Double Fairlies) suffered from frame breakages while operating in the Wanganui region, leading to the requirement for conventional engines with Fairlie's maneuverability. The Avonside Engine Company of Bristol, England was able to solve the problem by providing both the NZR R class, R and S classes of Single Fairlies, 18 of the former in 1878-79 and 7 of the latter in 1880-81.T. A. McGavin, ''Steam Locomotives ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mersey Railway
The Mersey Railway was the passenger railway connecting the communities of Liverpool and Birkenhead, England. It is currently a part of the Merseyrail network. It was extended further into the Wirral Peninsula, which lies on the opposite bank of the River Mersey to Liverpool. Both sides of the river were connected via the Mersey Railway Tunnel. The railway opened in 1886 with four stations using steam locomotives hauling unheated wooden carriages; in the next six years the line was extended with the opening of three more stations. Using the first tunnel under the Mersey, the line is the world's oldest underground railway outside London. Because the steam locomotives created a polluted atmosphere in the tunnel despite the forced ventilation system, many passengers reverted back to using the river ferries making the railway bankrupt by 1900. Recovery came after the railway adopted electric traction in 1903. The Mersey Railway remained independent after the Railways Act 1921, rail ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NZR R Class
The NZR R class was a class of early 0-6-4T single Fairlie steam locomotives operated by New Zealand's Railways Department (NZR) between 1879 and 1936. Introduction In the 1870s New Zealand's railway network was a small, fragmented system of light railway lines built in rough country where short, steep grades and tight curves were common. The Fairlie type of steam locomotive was well-suited to working in such conditions. In 1872, the first Fairlie locomotives arrived from England, the E class. Gradually the number of these double-ended engines (known as Double Fairlies) grew to 10, and came to include the B class of 1874. There was still a need for orthodox engines with Fairlie manoeuvrability. The Avonside Engine Company of Bristol, England solved the problem by providing both the R and S classes of Single Fairlie engines; 18 of the former in 1878-79 and 7 of the latter in 1880-81.T. A. McGavin, ''Steam Locomotives of New Zealand, Part One: 1863 to 1900'' (Wellington: N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
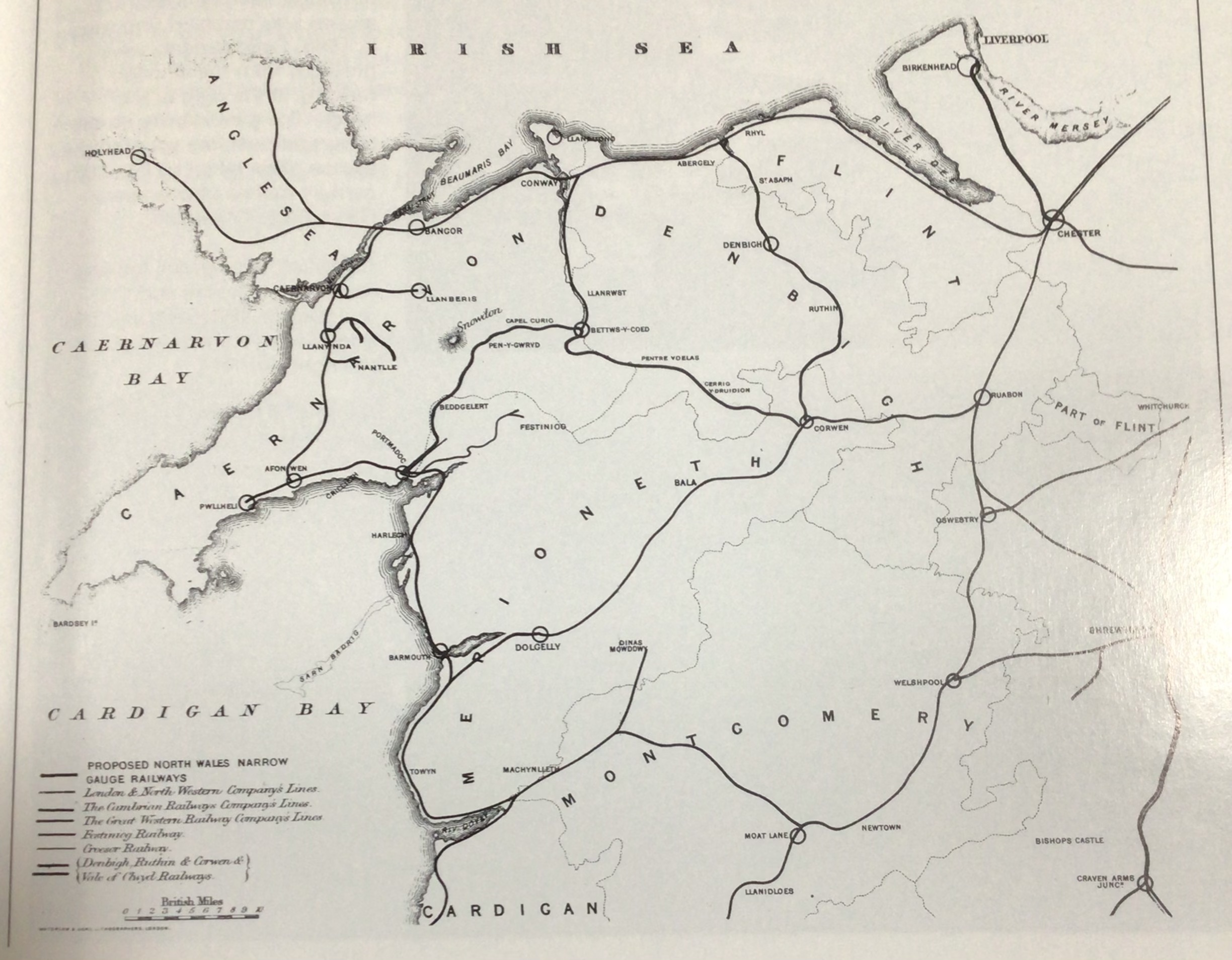
North Wales Narrow Gauge Railways
The North Wales Narrow Gauge Railways (NWNGR) was a railway company that planned to build a number of inter-connected narrow-gauge railways across North Wales. The first two of these lines – jointly known as the "Moel Tryfan Undertaking" – were authorised by act of Parliament, the (35 & 36 Vict. c. clxxv) and were built and opened in the 1870s. The original main line ran from Dinas railway station, Dinas Junction to Bryngwyn Station, Bryngwyn and opened in 1877. The second line was a branch from Tryfan Junction to Rhyd Ddu railway station, South Snowdon, though shortly after opening, the company designated the Tryfan Junction to Bryngwyn section as the branch, and the Dinas Junction to South Snowdon section as the main line. Routes built The company completed construction of two lines, The first, opened in 1877, was approximately long, running south-east from a junction with the London and North Western Railway's Carnarvonshire Railway, Caernarfon to Afon Wen branch at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Australian Railways K Class (narrow Gauge)
The South Australian Railways K class (narrow gauge) comprised a single locomotive. The design, by South Australian Railways Locomotive Engineer William Thow, was very similar to that of the South Australian Railways K class (broad gauge), broad-gauge K class, but it was smaller and lighter. It was allocated number 52 within the sequence allocated to the larger locomotives. The locomotive was built in 1883, five years after the first broad-gauge K class locomotive and a year before the last of the 18 such locomotives entered service. No. 52 was built by Dübs and Company of Glasgow, whereas Beyer, Peacock and Company, of Manchester, built all the broad-gauge class. The broad-gauge design was moderately "shrunk" to meet the smaller loading gauge of lines and the lower load-bearing capacity of track compared with the broad gauge. Some key specifications are compared in the table below. A major design weakness of the broad-gauge K class was the lack of a Leading whe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moel Tryfan (locomotive)
''Moel Tryfan'' was a narrow gauge steam locomotive built for use on the North Wales Narrow Gauge Railways (NWNGRs) in 1874/5. The locomotive was an single Fairlie locomotive built by the Vulcan Foundry near Manchester. It spent its entire working life on the NWNGRs and its successors the Welsh Highland Railway (WHR) and the Ffestiniog Railway (FfR). History North Wales Narrow Gauge Railways The North Wales Narrow Gauge Railways built two gauge railways, connecting , near Caernarfon, with , and . Two identical locomotives were ordered from the Vulcan Foundry to work the new railway. They were built to Fairlie's patent for articulated locomotives and were designed by George Percival Spooner, son of Charles Eaton Spooner, the manager of the nearby FfR. The locomotives were the first s in the British Isles. They were named ''Moel Tryfan'' and ''Snowdon Ranger''. ''Moel Tryfan'' was named after the local mountain where the slate quarries that provided most of the railwa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Whyte Notation
The Whyte notation is a classification method for steam locomotives, and some internal combustion locomotives and electric locomotives, by wheel arrangement. It was devised by Frederick Methvan Whyte, and came into use in the early twentieth century following a December 1900 editorial in ''American Engineer and Railroad Journal''. The notation was adopted and remains in use in North America and the United Kingdom to describe the wheel arrangements of steam locomotives, but for modern locomotives, multiple units and trams it has been supplanted by the UIC system in Europe and by the AAR system (essentially a simplification of the UIC system) in North America. However, geared steam locomotives do not use the notation. They are classified by their model and their number of trucks. Structure of the system Basic form The notation in its basic form counts the number of leading wheels, then the number of driving wheels, and finally the number of trailing wheels, numbers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fairlie Locomotive
A Fairlie locomotive is a type of articulated locomotive, articulated steam locomotive that has the driving wheels on bogies. It was invented by Robert Francis Fairlie. The locomotive may be double-ended (a double Fairlie) or single ended (a single Fairlie). Most double-ended Fairlies had wheel arrangements of or . All were tank locomotives. While Fairlie locomotives are now used only on heritage railways, the majority of diesel locomotive, diesel and electric locomotives in the world follow the basic form of the Fairlie — two power trucks with all axles driven. Many also follow the Fairlie's double-ended concept, capable of being driven equally well in both directions. Development of the design In 1864, the Scottish people, Scottish engineer Robert Francis Fairlie published a pamphlet detailing his plans for a new type of articulated locomotive. He had become convinced that the conventional pattern of locomotive could be improved on, and that his proposed design would ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Avonside Engine Company
The Avonside Engine Company was a locomotive manufacturer in Avon Street, St Philip's, Bristol, England between 1864 and 1934. However the business originated with an earlier enterprise Henry Stothert and Company. Origins The firm was originally started by Henry Stothert in 1837 as Henry Stothert and Company. Henry was the son of George Stothert (senior), founder of the nearby Bath engineering firm of Stothert & Pitt. Henry's brother, also named George, was manager of the same firm. The company was given an order for two broad gauge () Firefly class express passenger engines ''Arrow'' and ''Dart'', with driving wheels, delivered for the opening of the Great Western Railway (GWR) from Bristol to Bath on 31 August 1840. This was soon followed by an order for eight smaller Sun class engines with driving wheels. Stothert, Slaughter and Company Edward Slaughter joined the company in 1841, when it became known as Stothert, Slaughter and Company. By 1844 their works were nam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wheel Arrangement
In rail transport, a wheel arrangement or wheel configuration is a system of classifying the way in which wheels are distributed under a locomotive. Several notations exist to describe the wheel assemblies of a locomotive by type, position, and connections, with the adopted notations varying by country. Within a given country, different notations may also be employed for different kinds of locomotives, such as steam, electric, and diesel powered. Especially in steam days, wheel arrangement was an important attribute of a locomotive because there were many different types of layout adopted, each wheel being optimised for a different use (often with only some being actually "driven"). Modern diesel and electric locomotives are much more uniform, usually with all axles driven. Major notation schemes The main notations are the Whyte notation (based on counting the wheels), the AAR wheel arrangement notation (based on counting either the axles or the bogies), and the UIC classifi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Driving Wheel
On a steam locomotive, a driving wheel is a powered wheel which is driven by the locomotive's pistons (or turbine, in the case of a steam turbine locomotive). On a conventional, non-articulated locomotive, the driving wheels are all coupled together with side rods (also known as coupling rods); normally one pair is directly driven by the main rod (or connecting rod) which is connected to the end of the piston rod; power is transmitted to the others through the side rods. On diesel and electric locomotives, the driving wheels may be directly driven by the traction motors. Coupling rods are not usually used, and it is quite common for each axle to have its own motor. Jackshaft drive and coupling rods were used in the past (e.g. in the Swiss Crocodile locomotive) but their use is now confined to shunter locomotives. On an articulated locomotive or a duplex locomotive, driving wheels are grouped into sets with wheels within each set linked together. Diameter Drivin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country comprising mainland Australia, the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania and list of islands of Australia, numerous smaller islands. It has a total area of , making it the list of countries and dependencies by area, sixth-largest country in the world and the largest in Oceania. Australia is the world's flattest and driest inhabited continent. It is a megadiverse countries, megadiverse country, and its size gives it a wide variety of landscapes and Climate of Australia, climates including deserts of Australia, deserts in the Outback, interior and forests of Australia, tropical rainforests along the Eastern states of Australia, coast. The ancestors of Aboriginal Australians began arriving from south-east Asia 50,000 to 65,000 years ago, during the Last Glacial Period, last glacial period. By the time of British settlement, Aboriginal Australians spoke 250 distinct l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |