|
й»ѓе®—зѕІ
Huang Zongxi (; September 24, 1610 – August 12, 1695), courtesy name Taichong (), was a Chinese naturalist, political theorist, philosopher, and soldier during the latter part of the Ming dynasty into the early part of the Qing dynasty, Qing. He was the son an adherent of the Donglin Movement who died in prison. In 1626, the teenaged Huang became a disciple of the philosopher Liu Zongzhou. In 1631, he started studying Chinese history. Huang was politically active as a Ming loyalist until his retirement in 1649, spending the rest of his life in study. A warrant for his arrest was issued after the rise to power of Ruan Dacheng, but he avoided capture through uncertain ways. He may have fled China to seek political refuge in Japan. Huang's political text ''Waiting for the Dawn (book), Waiting for the Dawn'' condemns selfish autocratic rule, and declares that the world should belong to the people. He argued that all laws and regulatory bodies should be an outgrowth of local needs, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yuyao
Yuyao () is a county-level city in the northeast of Zhejiang province, China. It is under the jurisdiction of the sub-provincial city of Ningbo. It is located west of central Ningbo, east of Hangzhou, bordering Hangzhou Bay in the north. Yuyao covers an area of . Demographics As of the 2020 census, its population was 1,254,032. Its built-up (or metro) area with the county-level city of Cixi largely conurbated, had 3,083,520 inhabitants. However, recently the migrated workers and their families have increase the total population to about 1.6 million, but they do not show up in the official census and other related statistics data. Geography and climate Yuyao lies in a subtropical monsoon zone, rich in sunshine and rain fall, warm and humid, distinct in the four seasons. The mean annual sunshine is 2,061 hours and the annual rate of sunshine is 47%. The mean annual temperature is 16 degrees Celsius, and the coldest months perennially are January and February, the hottest are Ju ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
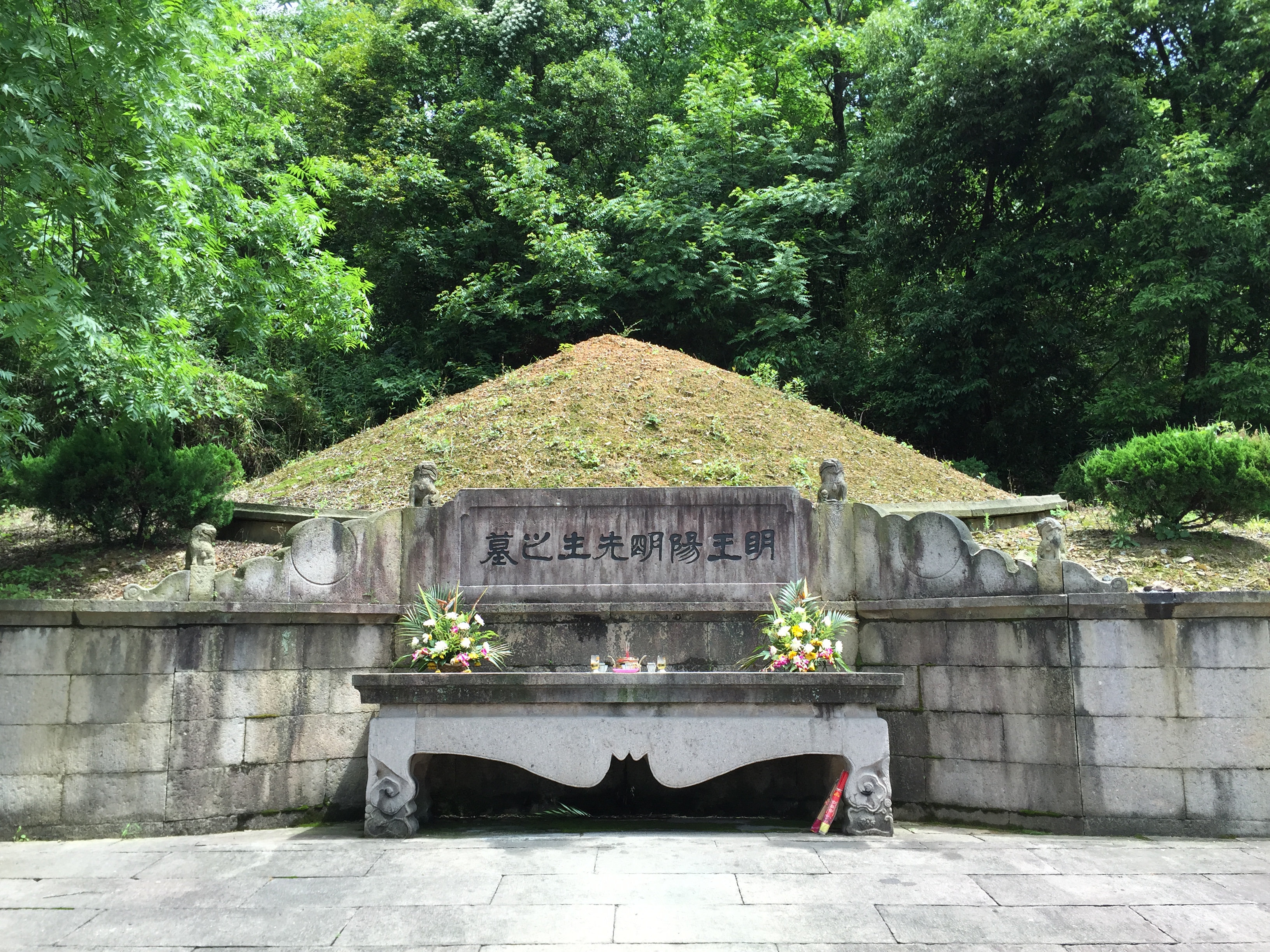
Wang Yangming
Wang Shouren (, 26 October 1472 – 9 January 1529), courtesy name Bo'an (), art name Yangmingzi (), usually referred to as Wang Yangming (), was a Chinese statesman, general, and Neo-Confucian philosopher during the Ming dynasty. After Zhu Xi, he is commonly regarded as the most important Neo-Confucian thinker, for his interpretations of Confucianism that denied the rationalist dualism of the orthodox philosophy of Zhu Xi. Wang and Lu Xiangshan are regarded as the founders as the Lu–Wang school, or the School of the Mind. In China, Japan, and Western countries, he is known by his honorific name rather than his private name. Life and times Wang was born in Yuyao, Zhejiang Province, to a scholarly family with a tradition of bureaucratic service. His father, Wang Hua, was first (''Zhuangyuan'', з‹Ђе…ѓ) in the Imperial Examination of 1481, and rose to become the vice-minister of the Ministry of Rites, but was later demoted and subsequently expelled from government ser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
17th-century Chinese Philosophers
The 17th century lasted from January 1, 1601 (represented by the Roman numerals MDCI), to December 31, 1700 (MDCC). It falls into the early modern period of Europe and in that continent (whose impact on the world was increasing) was characterized by the Baroque cultural movement, the latter part of the Spanish Golden Age, the Dutch Golden Age, the French ''Grand SiГЁcle'' dominated by Louis XIV, the Scientific Revolution, the world's first public company and megacorporation known as the Dutch East India Company, and according to some historians, the General Crisis. From the mid-17th century, European politics were increasingly dominated by the Kingdom of France of Louis XIV, where royal power was solidified domestically in the civil war of the Fronde. The semi-feudal territorial French nobility was weakened and subjugated to the power of an absolute monarchy through the reinvention of the Palace of Versailles from a hunting lodge to a gilded prison, in which a greatly expanded r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1695 Deaths
Events January–March * January 7 (December 28, 1694 O.S.) – The United Kingdom's last joint monarchy, the reign of husband-and-wife King William III and Queen Mary II comes to an end with the death of Queen Mary, at the age of 32. Princess Mary had been installed as the monarch along with her husband and cousin, Willem Hendrik von Oranje, Stadtholder of the Dutch Republic, in 1689 after King James II was deposed by Willem during the "Glorious Revolution". * January 14 (January 4 O.S.) – The Royal Navy warship HMS ''Nonsuch'' is captured near England's Isles of Scilly by the 48-gun French privateer ''Le Francois''. ''Nonsuch'' is then sold to the French Navy and renamed ''Le Sans Pareil''. * January 24 – Milan's Court Theater is destroyed in a fire. * January 27 – A flotilla of six Royal Navy warships under the command of Commodore James Killegrew aboard HMS ''Plymouth'' captures two French warships, the ''Content'' and the ''Trident'', the day after th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1610 Births
Some have suggested that 1610 may mark the beginning of the Anthropocene, or the 'Age of Man', marking a fundamental change in the relationship between humans and the Earth system, but earlier starting dates (ca. 1000 C.E.) have received broader consensus, based on high resolution pollution records that show the massive impact of human activity on the atmosphere. Events January–March * January 6 – ''Nossa Senhora da GraГ§a'' incident: A Portuguese carrack sinks near Nagasaki, after fighting Japanese samurai for four nights. * January 7 – Galileo Galilei first observes the four Galilean moons of Jupiter: Ganymede, Callisto, Europa and Io, but is unable to distinguish the latter two until the following day. * February 24 – English courtier Thomas Roe sets out on an expedition to The Guianas and Amazon River. * March 13 – Galileo Galilei's treatise on astronomy, ''Sidereus Nuncius'', the first printed scientific record of observations thro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yuan Dynasty
The Yuan dynasty ( ; zh, c=е…ѓжњќ, p=YuГЎnchГЎo), officially the Great Yuan (; Mongolian language, Mongolian: , , literally 'Great Yuan State'), was a Mongol-led imperial dynasty of China and a successor state to the Mongol Empire after Division of the Mongol Empire, its division. It was established by Kublai (Emperor Shizu or Setsen Khan), the fifth khagan-emperor of the Mongol Empire from the Borjigin clan, and lasted from 1271 to 1368. In Chinese history, the Yuan dynasty followed the Song dynasty and preceded the Ming dynasty. Although Genghis Khan's enthronement as Khagan in 1206 was described in Chinese language, Chinese as the Han Chinese, Han-style title of Emperor of China, Emperor and the Mongol Empire had ruled territories including modern-day northern China for decades, it was not until 1271 that Kublai Khan officially proclaimed the dynasty in the traditional Han style, and the conquest was not complete until 1279 when the Southern Song dynasty was defeated in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Song Dynasty
The Song dynasty ( ) was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 960 to 1279. The dynasty was founded by Emperor Taizu of Song, who usurped the throne of the Later Zhou dynasty and went on to conquer the rest of the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period#Ten Kingdoms, Ten Kingdoms, ending the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period. The Song frequently came into conflict with the contemporaneous Liao dynasty, Liao, Western Xia and Jin dynasty (1115–1234), Jin dynasties in northern China. After retreating to southern China following attacks by the Jin dynasty, the Song was eventually conquered by the Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The History of the Song dynasty, dynasty's history is divided into two periods: during the Northern Song (; 960–1127), the capital was in the northern city of Bianjing (now Kaifeng) and the dynasty controlled most of what is now East China. The #Southern Song, 1127–1279, Southern Song (; 1127–1279) comprise the period following ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Historiography
Historiography is the study of the methods used by historians in developing history as an academic discipline. By extension, the term ":wikt:historiography, historiography" is any body of historical work on a particular subject. The historiography of a specific topic covers how historians have studied that topic by using particular sources, techniques of research, and theoretical approaches to the interpretation of documentary sources. Scholars discuss historiography by topic—such as the historiography of the United Kingdom, of historiography of World War II, WWII, of the Pre-Columbian era, pre-Columbian Americas, of early historiography of early Islam, Islam, and of Chinese historiography, China—and different approaches to the work and the genres of history, such as political history and social history. Beginning in the nineteenth century, the development of academic history produced a great corpus of historiographic literature. The extent to which historians are influence ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Philosophy
Chinese philosophy (Simplified Chinese characters, simplified Chinese: дёе›Ѕе“Іе¦; Traditional Chinese characters, traditional Chinese: дёењ‹е“Іеё) refers to the philosophical traditions that originated and developed within the historical and cultural context of China. It encompasses systematic reflections on issues such as existence, knowledge, ethics, and politics. Evolving over more than two millennia, Chinese philosophy includes classical traditions such as Confucianism, Taoism, Daoism, and Buddhism, as well as modern responses to Western philosophical currents. As a cultural form of philosophy, it addresses universal philosophical concerns while also reflecting the specific historical and social conditions of China. The historical development of Chinese philosophy began during the Spring and Autumn period, Spring and Autumn and Warring States period, Warring States periods, a time known as the "Hundred Schools of Thought". Major schools such as Confucianism, Taoism, Da ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imperial Examination
The imperial examination was a civil service examination system in History of China#Imperial China, Imperial China administered for the purpose of selecting candidates for the Civil service#China, state bureaucracy. The concept of choosing bureaucrats by merit rather than by birth started Imperial examination in Chinese mythology, early in Chinese history, but using written examinations as a tool of selection started in earnest during the Sui dynasty (581–618), then into the Tang dynasty (618–907). The system became dominant during the Song dynasty (960–1279) and lasted for almost a millennium until its abolition during the late Qing reforms, late Qing dynasty reforms in 1905. The key sponsors for abolition were Yuan Shikai, Yin Chang and Zhang Zhidong. Aspects of the imperial examination still exist for entry into the civil service of both China and Taiwan. The exams served to ensure a common knowledge of writing, Chinese classics, and literary style among state officials. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wanli Emperor
The Wanli Emperor (4 September 1563 – 18 August 1620), also known by his temple name as the Emperor Shenzong of Ming, personal name Zhu Yijun, art name Yuzhai, was the 14th List of emperors of the Ming dynasty, emperor of the Ming dynasty, reigning from 1572 to 1620. He succeeded his father, the Longqing Emperor. His reign of 48 years was the longest among all the Ming dynasty emperors. The Wanli Emperor ascended the throne at the age of nine. During the first ten years of his reign, the young emperor was assisted and effectively led by Grand Secretary Zhang Juzheng, a skilled administrator. With the support of the emperor's mother, Empress Dowager Xiaoding, Lady Li, and the imperial eunuchs led by Feng Bao, the country experienced economic and military prosperity, reaching a level of power not seen since the early 15th century. The emperor held great respect and appreciation for Zhang Juzheng. However, as time passed, various factions within the government openly opposed Zhang, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |