|
иҚүеұҘ
Zori (), also rendered as zЕҚri (, ), are thonged Japanese sandals made of rice straw, cloth, lacquered wood, leather, rubber, orвҖ”most commonly and informallyвҖ”synthetic materials. They are a slip-on descendant of the tied-on sandal. Similar in form, modern flip-flops became popular in the United States, Australia and New Zealand when soldiers returning from World War II brought Japanese zori with them. Use Like many Japanese sandals, zori are easily slipped on and off, which is important in Japan, where shoes are removed and put back on when Genkan, entering and leaving a house, and where tying shoelaces would be impractical when wearing kimono, traditional clothing. The traditional forms of zori are seen when worn with other traditional clothing. Modern forms are fairly common, however, with casual Western wear, especially in summer. While geta (footwear), geta are now mostly worn with the informal , traditional zori are often worn with the more formal kimono. In rain, z ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waraji
() are light tie-on sandals, made from ropemaking fibers (usually straw), that were the standard footwear of the common people in Japan. Use resemble other forms of traditional Japanese footwear, such as zori and geta, with a few key differences. They were historically the simplest form of outdoor footwear (sandals of any type were not worn indoors). , due to their cheap and rustic nature, are considered to be a very informal type of footwear, and are not worn with formal kimono. They are typically worn with socks, and are woven so that the wearer's toes generally protrude slightly over the edge of the shoe. were once common footwear in Japan. There are records of in the Heian period (794вҖ“1185 CE), with the possibility of having existed before this time. In the Edo period (1603вҖ“1867 CE), geta were worn in cities, but anyone making a long journey wore . (sponsored article) They were also worn for energetic or prolonged labour. Their light weight and grip were va ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wicker
Wicker is a method of weaving used to make products such as furniture and baskets, as well as a descriptor to classify such products. It is the oldest furniture making method known to history, dating as far back as . Wicker was first documented in ancient Egypt, then having been made from pliable plant material, but in modern times it is made from any pliable, easily woven material. The word ''wicker'' or "wisker" is believed to be of Scandinavian origin: , which means "to fold" in Swedish. Wicker is traditionally made of material of plant origin, such as willow, rattan, reed (plant), reed, and bamboo, though the term also applies to products woven from synthetic fibers. Wicker is light yet sturdy, making it suitable for items that will be moved often like porch and patio furniture. ''Rushwork'' and ''wickerwork'' are terms used in England. A typical braiding pattern is called ''Wiener Geflecht'', Viennese braiding, as it was invented in 18th century Vienna and later most promine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elastomer
An elastomer is a polymer with viscoelasticity (i.e. both viscosity and elasticity) and with weak intermolecular forces, generally low Young's modulus (E) and high failure strain compared with other materials. The term, a portmanteau of ''elastic polymer'', is often used interchangeably with ''rubber'', although the latter is preferred when referring to vulcanisates. Each of the monomers which link to form the polymer is usually a compound of several elements among carbon, hydrogen, oxygen and silicon. Elastomers are amorphous polymers maintained above their glass transition temperature, so that considerable molecular reconformation is feasible without breaking of covalent bonds. Rubber-like solids with elastic properties are called elastomers. Polymer chains are held together in these materials by relatively weak intermolecular bonds, which permit the polymers to stretch in response to macroscopic stresses. Elastomers are usually thermosets (requiring vulcanization ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
EVA Foam
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA), also known as poly(ethylene-vinyl acetate) (PEVA), is a copolymer of ethylene and vinyl acetate. The weight percent of vinyl acetate usually varies from 10 to 50%, with the remainder being ethylene. There are three different types of EVA copolymer, which differ in the vinyl acetate (VA) content and the way the materials are used. The EVA copolymer which is based on a low proportion of VA (approximately up to 4%) may be referred to as vinyl acetate modified polyethylene. It is a copolymer and is processed as a thermoplastic material вҖ“ just like low-density polyethylene. It has some of the properties of a low-density polyethylene but increased gloss (useful for film), softness and flexibility. The material is generally considered non-toxic. The EVA copolymer which is based on a medium proportion of VA (approximately 4 to 30%) is referred to as thermoplastic ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymer and is a thermoplastic elastomer material. It is not vulcan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PVC Clothing
PVC clothing is shiny clothing made from the plastic polyvinyl chloride (PVC). PVC plastic is often called "vinyl" and this type of clothing is commonly known as vinyl clothing. PVC is sometimes confused with the similarly shiny patent leather. The terms "PVC", "vinyl" and "PU" tend to be used interchangeably by retailers for clothing made from shiny plastic-coated fabrics. These fabrics usually consist of a backing woven from polyester fibers with a surface coating of shiny plastic. The plastic layer itself is typically a blend of PVC and polyurethane (PU), with 100% PVC producing a stiff fabric with a glossy shine and 100% PU producing a stretchy fabric with a silky shine (see PU laminate). A manufacturer's label may say, for example, 67% polyester, 33% polyurethane for a fabric that contains no PVC; or 80% polyvinyl chloride, 20% polyurethane with mention of the polyester backing omitted. PVC clothing is a highly resistant material and waterproof. PVC can be produced in brigh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skiamorph
A skeuomorph (also spelled skiamorph, ) is a derivative object that retains ornamental design cues (attributes) from structures that were necessary in the original. Skeuomorphs are typically used to make something new feel familiar in an effort to speed understanding and acclimation. They employ elements that, while essential to the original object, serve no pragmatic purpose in the new system, except for identification. Examples include pottery embellished with imitation rivets reminiscent of similar pots made of metal and a software calendar that imitates the appearance of binding on a paper desk calendar. Definition and purpose The term ''skeuomorph'' is compounded from the Greek ''skeuos'' (ПғОәОөбҝҰОҝПӮ), meaning "container or tool", and ''morphбё—'' (ОјОҝПҒПҶО®), meaning "shape". It has been applied to material objects since 1890. With the advent of graphical computer systems in the 1980s, skeuomorph is used to characterize the many "old fashioned" icons utilized in graphi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
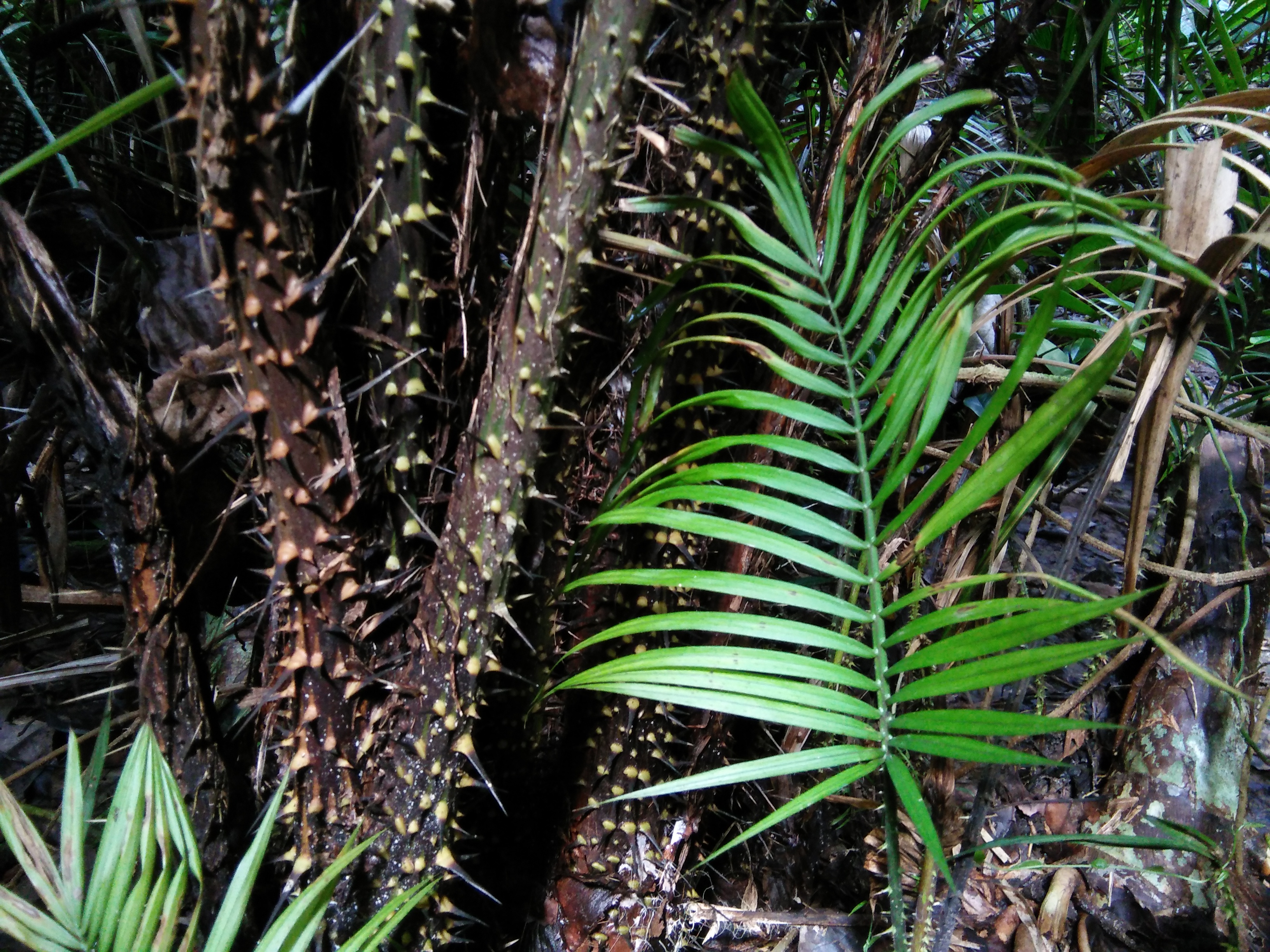
Rattan
Rattan, also spelled ratan (from Malay language, Malay: ''rotan''), is the name for roughly 600 species of Old World climbing palms belonging to subfamily Calamoideae. The greatest diversity of rattan palm species and genera are in the closed-Canopy (biology), canopy Old-growth forest, old-growth tropical forests of Southeast Asia, though they can also be found in other parts of tropical Asia and Africa. Most rattan palms are ecologically considered lianas due to their climbing habits, unlike other palm species. A few species also have tree-like or shrub-like habits. Around 20% of rattan palm species are economically important and are traditionally used in Southeast Asia in producing wickerwork furniture, baskets, Walking stick, canes, woven mats, Rope, cordage, and other handicrafts. Rattan canes are one of the world's most valuable non-timber forest products. Some species of rattan also have edible scaly fruit and heart of palm. Despite increasing attempts in the last 30 y ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raffia
Raffia palms are members of the genus ''Raphia''. The Malagasy language, Malagasy name is derived from ' "to squeeze #Raffia wine, juice". The genus contains about twenty species of Arecaceae, palms native to tropical regions of Africa, and especially Madagascar, with one species (''Raphia taedigera, R. taedigera'') also occurring in Central America, Central and South America. ''R. taedigera'' is the source of raffia fibers, which are the Leaf#Veins, veins of the leaves, and this species produces a fruit called "brazilia pods", "uxi nuts" or "uxi pods". They grow up to tall and are remarkable for their Leaf#Divisions of the blade, compound pinnate leaf, leaves, the longest in the plant kingdom; leaves of ''R. regalis'' up to long and wide are known. The plants are monocarpic, meaning that they flower once and then die after the seeds are mature. Some species have individual stems which die after fruiting, but have a root system which remains alive and sends up new stems which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |