|
öÝ-Isopropylmalate Synthase
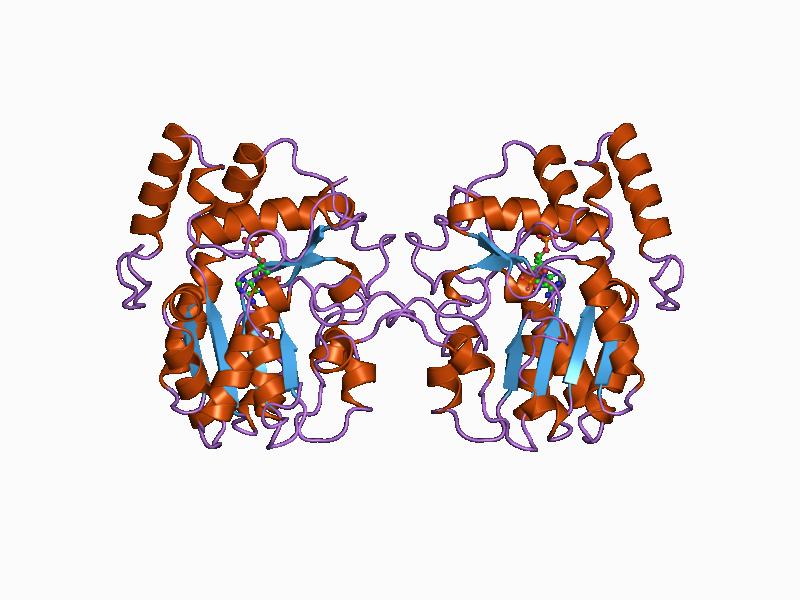
In enzymology, a 2-isopropylmalate synthase () is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction :acetyl-CoA + 3-methyl-2-oxobutanoate + H2O \rightleftharpoons (2S)-2-isopropylmalate + CoA The three substrates of this enzyme are acetyl-CoA, 3-methyl-2-oxobutanoate, and H2O, and its products are (2S)-2-isopropylmalate and CoA. The enzyme belongs to the family of transferases, specifically those acyltransferases that convert acyl groups into alkyl groups on transfer. The systematic name of this enzyme class is ''acetyl-CoA:3-methyl-2-oxobutanoate C-acetyltransferase (thioester-hydrolysing, carboxymethyl-forming)''. Other names in common use include ''3-carboxy-3-hydroxy-4-methylpentanoate 3-methyl-2-oxobutanoate-lyase'', ''(CoA-acetylating)'', ''alpha-isopropylmalate synthetase'', ''alpha-isopropylmalate synthase'', ''alpha-isopropylmalic synthetase'', ''isopropylmalate synthase'', and ''isopropylmalate synthetase''. This enzyme participates in biosynthesis of L-leucine and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzymology
An enzyme () is a protein that acts as a biological catalyst by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as product (chemistry), products. Almost all metabolism, metabolic processes in the cell (biology), cell need enzyme catalysis in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. Metabolic pathways depend upon enzymes to catalyze individual steps. The study of enzymes is called ''enzymology'' and the field of pseudoenzyme, pseudoenzyme analysis recognizes that during evolution, some enzymes have lost the ability to carry out biological catalysis, which is often reflected in their amino acid sequences and unusual 'pseudocatalytic' properties. Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Other biocatalysts include Ribozyme, catalytic RNA molecules, also called ribozymes. They are sometimes descr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transferase
In biochemistry, a transferase is any one of a class of enzymes that catalyse the transfer of specific functional groups (e.g. a methyl or glycosyl group) from one molecule (called the donor) to another (called the acceptor). They are involved in hundreds of different biochemical pathways throughout biology, and are integral to some of life's most important processes. Transferases are involved in myriad reactions in the cell. Three examples of these reactions are the activity of coenzyme A (CoA) transferase, which transfers thiol esters, the action of N-acetyltransferase, which is part of the pathway that metabolizes tryptophan, and the regulation of pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH), which converts pyruvate to acetyl CoA. Transferases are also utilized during translation. In this case, an amino acid chain is the functional group transferred by a peptidyl transferase. The transfer involves the removal of the growing amino acid chain from the tRNA molecule in the A-site of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
EC 2
EC or ec may refer to: Arts and entertainment * EC Comics, an American publisher of comic books * '' Electric Circus'', a Canadian television program * Eric Clapton Stratocaster, signature model guitars by Fender Businesses and organisations Government * Environment and Climate Change Canada, a Canadian federal government department * European Commission, the executive body of the European Union * European Council, the European Union institution comprising the college of heads of state of government * European Communities, one of the three pillars of the EU * European Community, a significant component of the European Union from 1993 to 2009, renamed European Economic Community Transportation * EuroCity, a train service of the European inter-city rail network * EasyJet Europe (IATA code: EC) * Avialeasing (former IATA code: EC), a cargo airline * East Coast (train operating company), a train operating company in the UK * EC, the aircraft registration prefix for Spain Educ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Data Bank
The Protein Data Bank (PDB) is a database for the three-dimensional structural data of large biological molecules such as proteins and nucleic acids, which is overseen by the Worldwide Protein Data Bank (wwPDB). This structural data is obtained and deposited by biologists and biochemists worldwide through the use of experimental methodologies such as X-ray crystallography, Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins, NMR spectroscopy, and, increasingly, cryo-electron microscopy. All submitted data are reviewed by expert Biocuration, biocurators and, once approved, are made freely available on the Internet under the CC0 Public Domain Dedication. Global access to the data is provided by the websites of the wwPDB member organizations (PDBe, PDBj, RCSB PDB, and BMRB). The PDB is a key in areas of structural biology, such as structural genomics. Most major scientific journals and some funding agencies now require scientists to submit their structure data to the PDB. Many other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tertiary Structure
Protein tertiary structure is the three-dimensional shape of a protein. The tertiary structure will have a single polypeptide chain "backbone" with one or more protein secondary structures, the protein domains. Amino acid side chains and the backbone may interact and bond in a number of ways. The interactions and bonds of side chains within a particular protein determine its tertiary structure. The protein tertiary structure is defined by its atomic coordinates. These coordinates may refer either to a protein domain or to the entire tertiary structure. A number of these structures may bind to each other, forming a quaternary structure. History The science of the tertiary structure of proteins has progressed from one of hypothesis to one of detailed definition. Although Emil Fischer had suggested proteins were made of polypeptide chains and amino acid side chains, it was Dorothy Maud Wrinch who incorporated geometry into the prediction of protein structures. Wrinch demon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mycobacterium Tuberculosis
''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (M. tb), also known as Koch's bacillus, is a species of pathogenic bacteria in the family Mycobacteriaceae and the causative agent of tuberculosis. First discovered in 1882 by Robert Koch, ''M. tuberculosis'' has an unusual, waxy coating on its cell surface primarily due to the presence of mycolic acid. This coating makes the cells impervious to Gram staining, and as a result, ''M. tuberculosis'' can appear weakly Gram-positive. Acid-fastness, Acid-fast stains such as ZiehlãNeelsen stain, ZiehlãNeelsen, or Fluorescence, fluorescent stains such as Auramine O, auramine are used instead to identify ''M. tuberculosis'' with a microscope. The physiology of ''M. tuberculosis'' is highly aerobic organism, aerobic and requires high levels of oxygen. Primarily a pathogen of the mammalian respiratory system, it infects the lungs. The most frequently used diagnostic methods for tuberculosis are the Mantoux test, tuberculin skin test, Acid-Fast Stain, aci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyruvate Metabolism
Pyruvic acid (CH3COCOOH) is the simplest of the alpha-keto acids, with a carboxylic acid and a ketone functional group. Pyruvate, the conjugate base, CH3COCOOã, is an intermediate in several metabolic pathways throughout the cell. Pyruvic acid can be made from glucose through glycolysis, converted back to carbohydrates (such as glucose) via gluconeogenesis, or converted to fatty acids through a reaction with acetyl-CoA. It can also be used to construct the amino acid alanine and can be converted into ethanol or lactic acid via fermentation. Pyruvic acid supplies energy to cells through the citric acid cycle (also known as the Krebs cycle) when oxygen is present (aerobic respiration), and alternatively ferments to produce lactate when oxygen is lacking. Chemistry In 1834, Thûˋophile-Jules Pelouze distilled tartaric acid and isolated glutaric acid and another unknown organic acid. JûÑns Jacob Berzelius characterized this other acid the following year and named pyruvic acid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leucine
Leucine (symbol Leu or L) is an essential amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. Leucine is an öÝ-amino acid, meaning it contains an öÝ-amino group (which is in the protonated ãNH3+ form under biological conditions), an öÝ-Carboxylic acid, carboxylic acid group (which is in the deprotonated ãCOOã form under biological conditions), and a side chain Isobutyl, isobutyl group, making it a Chemical polarity, non-polar Aliphatic compound, aliphatic amino acid. It is Essential amino acid, essential in humans, meaning the body cannot synthesize it; it must be obtained from the diet. Human dietary sources are foods that contain protein, such as meats, dairy products, soy products, and beans and other legumes. It is genetic code, encoded by the codons UUA, UUG, CUU, CUC, CUA, and CUG. Leucine is named after the Greek language, Greek word for "white": ''ö£öçü ö¤üü'' (''leukû°s'', "white"), after its common appearance as a white powder, a property it shares with many ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Enzymes
Enzymes are listed here by their classification in the International Union of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology's Enzyme Commission (EC) numbering system: :Oxidoreductases (EC 1) ( Oxidoreductase) * Dehydrogenase * Luciferase * DMSO reductase :EC 1.1 (act on the CH-OH group of donors) * :EC 1.1.1 (with NAD+ or NADP+ as acceptor) ** Alcohol dehydrogenase (NAD) ** Alcohol dehydrogenase (NADP) ** Homoserine dehydrogenase ** Aminopropanol oxidoreductase ** Diacetyl reductase ** Glycerol dehydrogenase ** Propanediol-phosphate dehydrogenase ** glycerol-3-phoshitiendopene dehydrogenase (NAD+) ** D-xylulose reductase ** L-xylulose reductase ** Lactate dehydrogenase ** Malate dehydrogenase ** Isocitrate dehydrogenase ** HMG-CoA reductase * :EC 1.1.2 (with a cytochrome as acceptor) * :EC 1.1.3 (with oxygen as acceptor) ** Glucose oxidase ** L-gulonolactone oxidase ** Thiamine oxidase ** Xanthine oxidase * EC 1.1.4 (with a disulfide as accep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acyltransferases
Acyltransferase is a type of transferase enzyme that acts upon acyl groups. Examples include: * Glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferases * Glyceronephosphate O-acyltransferase * Lecithin-cholesterol acyltransferase *Long-chain-alcohol O-fatty-acyltransferase See also * Acetyltransferase An acetyltransferase (also referred to as a transacetylase) is any of a class of transferase enzymes that transfers an acetyl group in a reaction called acetylation. In biological organisms, post-translational modification of a protein via acetyl ... External links * Transferases EC 2.3 {{2.3-enzyme-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coenzyme A
Coenzyme A (CoA, SHCoA, CoASH) is a coenzyme, notable for its role in the Fatty acid metabolism#Synthesis, synthesis and Fatty acid metabolism#.CE.B2-Oxidation, oxidation of fatty acids, and the oxidation of pyruvic acid, pyruvate in the citric acid cycle. All genomes sequenced to date encode enzymes that use coenzyme A as a Substrate (chemistry), substrate, and around 4% of cellular enzymes use it (or a thioester) as a substrate. In humans, CoA biosynthesis requires cysteine, pantothenic acid, pantothenate (vitamin B5), and adenosine triphosphate (ATP). In acetyl-CoA, its acetyl form, coenzyme A is a highly versatile molecule, serving metabolic functions in both the Anabolism, anabolic and Catabolism, catabolic pathways. Acetyl-CoA is utilised in the post-translational regulation and allosteric regulation of pyruvate dehydrogenase and carboxylase to maintain and support the partition of Pyruvic acid, pyruvate synthesis and degradation. Discovery of structure Coenzyme A was ident ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzyme
An enzyme () is a protein that acts as a biological catalyst by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as product (chemistry), products. Almost all metabolism, metabolic processes in the cell (biology), cell need enzyme catalysis in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. Metabolic pathways depend upon enzymes to catalyze individual steps. The study of enzymes is called ''enzymology'' and the field of pseudoenzyme, pseudoenzyme analysis recognizes that during evolution, some enzymes have lost the ability to carry out biological catalysis, which is often reflected in their amino acid sequences and unusual 'pseudocatalytic' properties. Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Other biocatalysts include Ribozyme, catalytic RNA molecules, also called ribozymes. They are sometimes descr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |