|
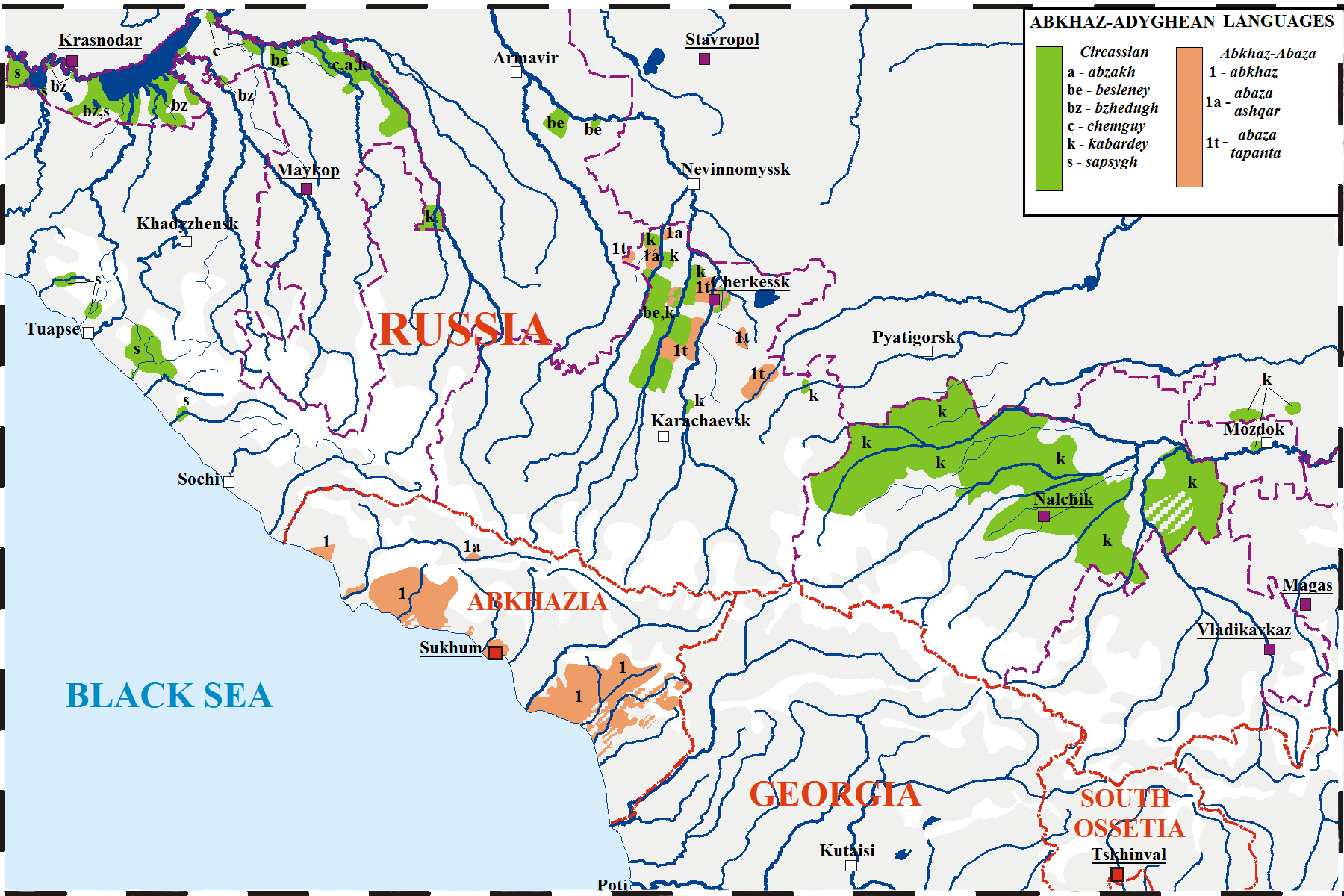
Abkhaz Language
Abkhaz, also known as Abkhazian, is a Northwest Caucasian languages, Northwest Caucasian language most closely related to Abaza language, Abaza. It is spoken mostly by the Abkhazians, Abkhaz people. It is one of the official languages of Abkhazia, where around 190,000 people speak it. Furthermore, it is spoken by thousands of members of the Abkhazian diaspora in Turkey, Georgia (country), Georgia's autonomous republic of Adjara, Syria, Jordan, and several Western countries. 27 October is the day of the Abkhazian language in Georgia (country), Georgia. Classification Abkhaz is a Northwest Caucasian languages, Northwest Caucasian language and is thus related to Adyghe language, Adyghe. The language of Abkhaz is especially close to Abaza language, Abaza, and they are sometimes considered dialects of the same language,''B. G. Hewitt Abkhaz 1979;'' page 1. Abazgi, of which the literary dialects of Abkhaz and Abaza are simply two ends of a dialect continuum. Grammatically, the two ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jiangshan Dialect
The Jiangshan dialect (江山話) is a Southern Wu dialect, closely related to that of Quzhou. It is spoken in Jiangshan, a city in Quzhou prefecture, China China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. With population of China, a population exceeding 1.4 billion, it is the list of countries by population (United Nations), second-most populous country after .... Phonology Initials Finals Tones The Jiangshan dialect is considered to have eight tones. However, since tone split from Middle Chinese, each character still depends on the voicing of the initial consonant. These constitute just three phonemic tones: ''pin, shang,'' and ''qu.'' (''Ru'' syllables are phonemically toneless, as their distinctiveness lies in a final glottal stop.) Wu Chinese {{St-lang-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adyghe Language
Adyghe ( or ; also known as West Circassian) is a Northwest Caucasian language spoken by the western subgroups of Circassians. It is spoken mainly in Russia, as well as in Turkey, Jordan, Syria, Iraq and Israel, where Circassians settled after the Circassian genocide (–1870) by the Russian Empire. It is closely related to the Kabardian language, Kabardian (East Circassian) language, though some reject the distinction between the two languages in favor of both being dialects of a unitary Circassian languages, Circassian language. The literary standard of Adyghe is based on its Temirgoy dialect. Adyghe and Russian language, Russian are the two official languages of the Adygea, Republic of Adygea in the Russian Federation. In Russia, there are around 128,000 speakers of Adyghe, almost all of them native speakers. In total, some 300,000 speak it worldwide. The largest Adyghe-speaking community is in Turkey, spoken by the diaspora from the Russo-Circassian War, Russian–Circassi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catalan Phonology
The Catalan phonology (or Valencian phonology) has a certain degree of dialectal variation. Although there are two standard varieties, one based on Central Catalan, Central Eastern dialect and another one based on South-Western or Valencian language, Valencian, this article deals with features of all or most dialects, as well as regional pronunciation differences. Catalan is characterized by final-obstruent devoicing, lenition, and voicing assimilation; a vowel system, set of 7 to 8 phoneme, phonemic vowels, vowel assimilation (phonology), assimilations (including vowel harmony), many phonetic diphthongs, and vowel reduction, whose precise details differ between dialects. Consonants : Phonetic notes: * , are Laminal consonant, laminal Denti-alveolar consonant, denti-alveolar , . After , they are laminal Alveolar consonant, alveolar , . * , are Velar consonant, velar but fronted to pre-velar position before front vowels. In some Majorcan dialects, the situation is revers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alveolopalatal Fricative
In phonetics, alveolo-palatal (alveolopalatal, ''alveo-palatal'' or ''alveopalatal'') consonants, sometimes synonymous with pre-palatal consonants, are intermediate in articulation between the coronal and dorsal consonants, or which have simultaneous alveolar and palatal articulation. In the official IPA chart, alveolo-palatals would appear between the retroflex and palatal consonants but for "lack of space".John Esling, 2010, "Phonetic Notation". In Hardcastle, Laver, & Gibbon, eds, ''The Handbook of Phonetic Sciences'', p 693 Ladefoged and Maddieson characterize the alveolo-palatals as palatalized postalveolars (and thus as palato-alveolars), articulated with the blade of the tongue behind the alveolar ridge and the body of the tongue raised toward the palate, whereas Esling describes them as advanced palatals (pre-palatals), the furthest front of the dorsal consonants, articulated with the body of the tongue approaching the alveolar ridge. These descriptions are essentiall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abkhaz Phonology
Abkhaz is a language of the Northwest Caucasian family which, like the other Northwest Caucasian languages, is very rich in consonants. Abkhaz has a large consonantal inventory that contrasts 58 consonants in the literary Abzhywa dialect, coupled with just two phonemic vowels (). Abkhaz has three major dialects: Abzhywa, Bzyp and Sadz, which differ mainly in phonology, with the lexical differences being due to contact with neighbouring languages. Consonants Below is the IPA phoneme chart of the consonant phonemes of Abkhaz: Phonemes preceded by an (*) are found in the Bzyp and Sadz dialects of Abkhaz, but not in Abzhywa; phonemes preceded by a (†) are unique to the Bzyp dialect. The total number of consonant phonemes in Abkhaz is, therefore, 58 in the Abzhywa dialect, 60 in the Sadz dialect, and 67 in Bzyp. The obstruents are characterised by a three-fold contrast between voiced, aspirated voiceless and glottalised forms; both the aspirated and glottalised forms are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sibilant Consonant
Sibilants (from 'hissing') are fricative and affricate consonants of higher amplitude and pitch, made by directing a stream of air with the tongue towards the teeth. Examples of sibilants are the consonants at the beginning of the English words ''sip'', ''zip'', ''ship'', and ''genre''. The symbols in the International Phonetic Alphabet used to denote the sibilant sounds in these words are, respectively, . Sibilants have a characteristically intense sound, which accounts for their paralinguistic use in getting one's attention (e.g. calling someone using "psst!" or quieting someone using "shhhh!"). Overview In the hissing sibilants and , the back of the tongue forms a narrow channel (is '' grooved'') to focus the stream of air more intensely, resulting in a high pitch. With the hushing sibilants (occasionally termed ''shibilants''), such as English , , , and , the tongue is flatter, and the resulting pitch lower. A broader category is stridents, which include more fricatives ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catalan Language
Catalan () is a Western Romance languages, Western Romance language and is the official language of Andorra, and the official language of three autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous communities in eastern Spain: Catalonia, the Balearic Islands and the Valencian Community, where it is called ''Valencian language, Valencian'' (). It has semi-official status in the Italy, Italian ''comune'' of Alghero, and it is spoken in the Pyrénées-Orientales department of France and in two further areas in eastern Spain: the La Franja, eastern strip of Aragon and the Carche area in the Region of Murcia. The Catalan-speaking territories are often called the or "Països Catalans". The language evolved from Vulgar Latin in the Middle Ages around the eastern Pyrenees. It became the language of the Principality of Catalonia and the kingdoms of kingdom of Valencia, Valencia and Kingdom of Majorca, Mallorca, being present throughout the Mediterranean. Replaced by Spanish as a language of gov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japanese Language
is the principal language of the Japonic languages, Japonic language family spoken by the Japanese people. It has around 123 million speakers, primarily in Japan, the only country where it is the national language, and within the Japanese diaspora worldwide. The Japonic family also includes the Ryukyuan languages and the variously classified Hachijō language. There have been many Classification of the Japonic languages, attempts to group the Japonic languages with other families such as Ainu languages, Ainu, Austronesian languages, Austronesian, Koreanic languages, Koreanic, and the now discredited Altaic languages, Altaic, but none of these proposals have gained any widespread acceptance. Little is known of the language's prehistory, or when it first appeared in Japan. Chinese documents from the 3rd century AD recorded a few Japanese words, but substantial Old Japanese texts did not appear until the 8th century. From the Heian period (794–1185), extensive waves of Sino-Ja ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taiwanese Hokkien
Taiwanese Hokkien ( , ), or simply Taiwanese, also known as Taigi ( zh, c=臺語, tl=Tâi-gí), Taiwanese Southern Min ( zh, c=臺灣閩南語, tl=Tâi-uân Bân-lâm-gí), Hoklo and Holo, is a variety of the Hokkien language spoken natively by more than 70 percent of the population of Taiwan. It is spoken by a significant portion of those Taiwanese people who are descended from Hoklo immigrants of Minnan region, southern Fujian. It is one of the national languages of Taiwan. Taiwanese is generally similar to Hokkien spoken in Amoy dialect, Amoy, Quanzhou dialect, Quanzhou, and Zhangzhou dialect, Zhangzhou, as well as dialectal forms used in Southeast Asia, such as Singaporean Hokkien, Penang Hokkien, Philippine Hokkien, Medan Hokkien, and Southern Peninsular Malaysian Hokkien. It is mutually intelligible with the Amoy and Zhangzhou varieties at the mouth of the Jiulong River in mainland China, and with Philippine Hokkien to the south in the Philippines, spoken altogether by a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pe̍h-ōe-jī
( ; , , ; POJ), also known as Church Romanization, is an orthography used to write variants of Hokkien Southern Min, particularly Taiwanese Hokkien, Taiwanese and Amoy dialect, Amoy Hokkien, and it is widely employed as one of the writing systems for Southern Min. During its peak, it had hundreds of thousands of readers. Developed by Western missionary, missionaries working among the Chinese emigration, Chinese diaspora in Southeast Asia in the 19th century and refined by missionaries working in Xiamen and Tainan, it uses a modified Latin alphabet and some diacritics to represent the spoken language. After initial success in Fujian, POJ became most widespread in Taiwan and, in the mid-20th century, there were over 100,000 people literate in POJ. A large amount of printed material, religious and secular, has been produced in the script, including Taiwan's first newspaper, the ''Taiwan Church News''. During Taiwan under Japanese rule, Japanese rule (1895–1945), the use of was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Romanization Of Japanese
The romanization of Japanese is the use of Latin script to write the Japanese language. This method of writing is sometimes referred to in Japanese as . Japanese is normally written in a combination of logographic characters borrowed from Chinese (kanji) and syllabic scripts (kana) that also ultimately derive from Chinese characters. There are several different romanization systems. The three main ones are Hepburn romanization, Kunrei-shiki romanization (ISO 3602) and Nihon-shiki romanization (ISO 3602 Strict). Variants of the Hepburn system are the most widely used. Romanized Japanese may be used in any context where Japanese text is targeted at non-Japanese speakers who cannot read kanji or kana, such as for names on street signs and passports and in dictionaries and textbooks for foreign learners of the language. It is also used to transliterate Japanese terms in text written in English (or other languages that use the Latin script) on topics related to Japan, such as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |