|
Śatānanda
Śatānanda (fl. 1068–1099) was an Indian astronomer best known from his manual the ''Bhāsvatī'' (1099). Śatānanda is thought to have lived in Puri or Ujjain and drew from other texts including the Suryasiddhanta of Varahamihira. Śatānanda was the son of Sankara and Saraswati, born in Puri, Odisha. He may have served in the court of the Kesari dynasty. Some sources suggest he lived in Ujjain. His name literally means the "joy of hundreds" in Sanskrit and he used centesimal numbering in his astronomical manual ''Bhasvati'' published in 1099. The book has eight short chapters with 128 verses which include methods for preparing almanacs. He also includes methods for computing the longitudinal positions of the planets. Using 528 CE as a reference he computed the annual precession Precession is a change in the orientation of the rotational axis of a rotating body. In an appropriate reference frame it can be defined as a change in the first Euler angle, whereas the t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Floruit
''Floruit'' ( ; usually abbreviated fl. or occasionally flor.; from Latin for 'flourished') denotes a date or period during which a person was known to have been alive or active. In English, the unabbreviated word may also be used as a noun indicating the time when someone flourished. Etymology and use is the third-person singular perfect active indicative of the Latin verb ', ' "to bloom, flower, or flourish", from the noun ', ', "flower". Broadly, the term is employed in reference to the peak of activity for a person or movement. More specifically, it often is used in genealogy and historical writing when a person's birth or death dates are unknown, but some other evidence exists that indicates when they were alive. For example, if there are Will (law), wills Attestation clause, attested by John Jones in 1204 and 1229, as well as a record of his marriage in 1197, a record concerning him might be written as "John Jones (fl. 1197–1229)", even though Jones was born before ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian People
Indian people or Indians are the Indian nationality law, citizens and nationals of the India, Republic of India or people who trace their ancestry to India. While the demonym "Indian" applies to people originating from the present-day India, it was also used as the identifying term for people originating from what is now Bangladeshi diaspora, Bangladesh and Pakistani diaspora, Pakistan prior to the Partition of India in 1947. In 2022, the population of India stood at 1.4 billion people, of various Indian ethnic groups, ethnic groups. According to United Nations forecasts, India overtook China as the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, most populous country by the end of April 2023, containing 17.50 percent of the global population. In addition to the Indian population, the Non-resident Indian and Overseas Citizen of India, Indian overseas diaspora also boasts large numbers, particularly in former British Empire, British colonies due to the historical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astronomer
An astronomer is a scientist in the field of astronomy who focuses on a specific question or field outside the scope of Earth. Astronomers observe astronomical objects, such as stars, planets, natural satellite, moons, comets and galaxy, galaxies – in either observational astronomy, observational (by analyzing the data) or theoretical astronomy. Examples of topics or fields astronomers study include planetary science, Sun, solar astronomy, the Star formation, origin or stellar evolution, evolution of stars, or the galaxy formation and evolution, formation of galaxies. A related but distinct subject is physical cosmology, which studies the Universe as a whole. Types Astronomers typically fall under either of two main types: observational astronomy, observational and theoretical astronomy, theoretical. Observational astronomers make direct observations of Astronomical object, celestial objects and analyze the data. In contrast, theoretical astronomers create and investigate Con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Puri
Puri, also known as Jagannath Puri, () is a coastal city and a Nagar Palika, municipality in the state of Odisha in eastern India. It is the district headquarters of Puri district and is situated on the Bay of Bengal, south of the state capital of Bhubaneswar. It is home to the 12th-century Jagannath Temple (Puri), Jagannath Temple and is one of the original Char Dham pilgrimage sites for Hindus. Puri has been known by several names since ancient times and was locally known as "Sri Kshetra" and the Jagannath Temple, Puri, Jagannath temple is known as "Badadeula". Puri and the Jagannath Temple were invaded 18 times by Muslim rulers, from the 7th century AD until the early 19th century with the objective of looting the treasures of the temple. Odisha, including Puri and its temple, were part of British India from 1803 until India attained independence in August 1947. Even though princely states do not exist in India today, the heirs of the House of Gajapati still perform the r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ujjain
Ujjain (, , old name Avantika, ) or Ujjayinī is a city in Ujjain district of the Indian state of Madhya Pradesh. It is the fifth-largest city in Madhya Pradesh by population and is the administrative as well as religious centre of Ujjain district and Ujjain division. It is one of the Hindu pilgrimage centres of Sapta Puri famous for the ''Kumbh Mela'' (Simhastha) held there every 12 years. The ancient and world famous temple of Mahakaleshwar Jyotirlinga is located in the center of the city. The city has been one of the most prominent trade and political centres of the Indian Subcontinent from the time of the ancient Mahājanapadas until the British colonisation of India. An ancient city situated on the eastern bank of the Shipra River, Ujjain was the most prominent city on the Malwa plateau of central India for much of its history. It emerged as the political centre of central India around 600 BCE. It was the capital of the ancient Avanti kingdom, one of the sixteen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suryasiddhanta
The ''Surya Siddhanta'' (; ) is a Sanskrit treatise in Indian astronomy dated to 4th to 5th century,Menso Folkerts, Craig G. Fraser, Jeremy John Gray, John L. Berggren, Wilbur R. Knorr (2017)Mathematics Encyclopaedia Britannica, Quote: "(...) its Hindu inventors as discoverers of things more ingenious than those of the Greeks. Earlier, in the late 4th or early 5th century, the anonymous Hindu author of an astronomical handbook, the ''Surya Siddhanta'', had tabulated the sine function (...)" in fourteen chapters.Plofkerpp. 71–72 The ''Surya Siddhanta'' describes rules to calculate the motions of various planets and the moon relative to various constellations, diameters of various planets, and calculates the orbits of various astronomical bodies. The text is known from a palm-leaf manuscript, and several newer manuscripts. It was composed or revised probably c. 800 CE from an earlier text also called the ''Surya Siddhanta''. The ''Surya Siddhanta'' text is composed of verses mad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Odisha
Odisha (), formerly Orissa (List of renamed places in India, the official name until 2011), is a States and union territories of India, state located in East India, Eastern India. It is the List of states and union territories of India by area, eighth-largest state by area, and the List of states and union territories of India by population, eleventh-largest by population, with over 41 million inhabitants. The state also has the third-largest population of Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes, Scheduled Tribes in India. It neighbours the states of Jharkhand and West Bengal to the north, Chhattisgarh to the west, and Andhra Pradesh to the south. Odisha has a coastline of along the Bay of Bengal in the ''Indian Ocean''. The region is also known as Utka·∏∑a and is mentioned by this name in India's national anthem, Jana Gana Mana. The language of Odisha is Odia language, Odia, which is one of the Classical languages of India. The ancient kingdom of Kalinga (historical region), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kesari Dynasty
The Somavamshi (IAST: Somavaṃśī, "Lunar dynasty") or Keshari (IAST: Keśarī) dynasty ruled parts of present-day Odisha in eastern India between the 9th and the 12th centuries. Their capitals included Yayatinagara (modern Binka) and Abhinava-Yayatinagara (modern Jajpur). The Somavamshis may have been related to the Panduvamshis, who ruled the Dakshina Kosala region in central India. They were probably driven out from this region by the Kalachuris, following which they conquered the Kalinga and the Utkala regions in present-day Odisha, supplanting the Bhauma-Karas. The Somavamshis introduced a new style of art and architecture in Odisha, and their rule saw a remarkable shift from Buddhism to Hinduism in the region. The Somavamshi rule ended in the early 12th century, when the Eastern Ganga ruler Anantavarman Chodaganga captured their territories. Origin The Somavamshis may have been related to the Panduvamshis of Dakshina Kosala, whose rule in the Dakshina Kosa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; stem form ; nominal singular , ,) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in northwest South Asia after its predecessor languages had Trans-cultural diffusion, diffused there from the northwest in the late Bronze Age#South Asia, Bronze Age. Sanskrit is the sacred language of Hinduism, the language of classical Hindu philosophy, and of historical texts of Buddhism and Jainism. It was a lingua franca, link language in ancient and medieval South Asia, and upon transmission of Hindu and Buddhist culture to Southeast Asia, East Asia and Central Asia in the early medieval era, it became a language of religion and high culture, and of the political elites in some of these regions. As a result, Sanskrit had a lasting effect on the languages of South Asia, Southeast Asia and East Asia, especially in their formal and learned vocabularies. Sanskrit generally connotes several Indo-Aryan languages# ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
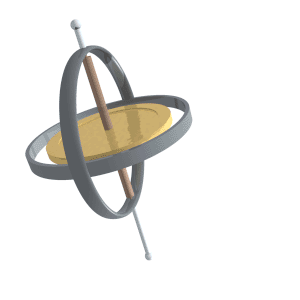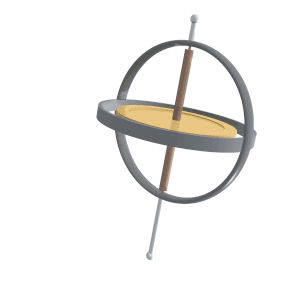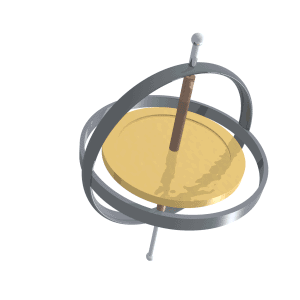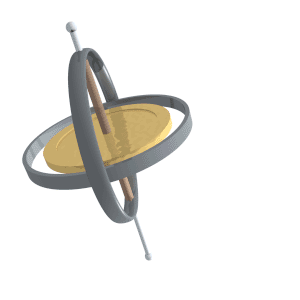
Precession
Precession is a change in the orientation of the rotational axis of a rotating body. In an appropriate reference frame it can be defined as a change in the first Euler angle, whereas the third Euler angle defines the rotation itself. In other words, if the axis of rotation of a body is itself rotating about a second axis, that body is said to be precessing about the second axis. A motion in which the second Euler angle changes is called '' nutation''. In physics, there are two types of precession: torque-free and torque-induced. In astronomy, ''precession'' refers to any of several slow changes in an astronomical body's rotational or orbital parameters. An important example is the steady change in the orientation of the axis of rotation of the Earth, known as the precession of the equinoxes. Torque-free or torque neglected Torque-free precession implies that no external moment (torque) is applied to the body. In torque-free precession, the angular momentum is a constant, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |