|
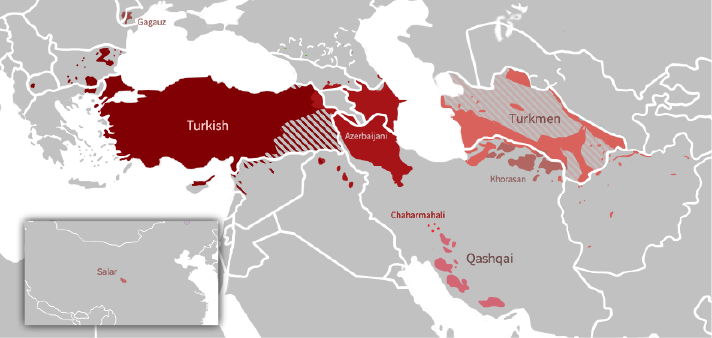
Turkmen Language
Turkmen (, , , or , , , ) is a Turkic language of the Oghuz branch spoken by the Turkmens of Central Asia. It has an estimated 4.7 million native speakers in Turkmenistan (where it is the official language), and a further 359,000 speakers in northeastern Iran and 1.2 million people in northwestern Afghanistan, where it has no official status. Turkmen is also spoken to lesser varying degrees in Turkmen communities of Uzbekistan and Tajikistan and by diaspora communities, primarily in Turkey and Russia. Turkmen is a member of the Oghuz branch of the Turkic languages. It is closely related to Azerbaijani, Gagauz, Qashqai, and Turkish, sharing varying degrees of mutual intelligibility with each of those languages. However, the closest relative of Turkmen is considered Khorasani Turkic, spoken in northeastern regions of Iran and with which it shares the eastern subbranch of Oghuz languages, as well as Khorazm, the Oghuz dialect of Uzbek spoken mainly in Khorezm along the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Czech Orthography
Czech orthography is a system of rules for proper formal writing (orthography) in Czech. The earliest form of separate Latin script specifically designed to suit Czech was devised by Czech theologian and church reformist Jan Hus, the namesake of the Hussite movement, in one of his seminal works, '' De orthographia bohemica'' (''On Bohemian orthography''). The modern Czech orthographic system is diacritic, having evolved from an earlier system which used many digraphs (although one digraph has been kept - ''ch''). The caron (known as ''h├Ī─Źek'' in Czech) is added to standard Latin letters to express sounds which are foreign to Latin. The acute accent is used for long vowels. The Czech orthography is considered the model for many other Balto-Slavic languages using the Latin alphabet; Slovak orthography being its direct revised descendant, while the Croatian Gaj's Latin alphabet and its Slovene and Serbian descendant system are largely based on it. The Baltic languages, such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Slovak Orthography
The first Slovak orthography was proposed and created by the Slovak Catholic priest Anton Bernol├Īk (1762ŌĆō1813) in his ''Dissertatio philologico-critica de litteris Slavorum'', used in the six-volume ''Slovak-Czech-Latin-German-Hungarian Dictionary'' (1825ŌĆō1927) and used primarily by Slovak Catholics. The standard orthography of the Slovak language is immediately based on the standard developed by ─Įudov├Łt ┼Āt├║r in 1844 and reformed by Martin Hattala in 1851 with the agreement of ┼Āt├║r. The then-current (1840s) form of the central Slovak dialect was chosen as the standard. After Hattala's reform, the standardized orthography remained mostly unchanged. Alphabet The Slovak alphabet is an extension of the Latin alphabet with 46 letters including four diacritics (╦ć( m├żk─Źe┼ł), ┬┤(acute accent), ┬©( diaeresis/umlaut), ╦å(circumflex)), which makes it the longest Slavic and European alphabet. In IPA transcriptions of Slovak, are often written with , i.e. as if they were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Czech Alphabet
Czech orthography is a system of rules for proper formal writing (orthography) in Czech language, Czech. The earliest form of separate Latin script specifically designed to suit Czech was devised by Czech theologian and church reformist Jan Hus, the namesake of the Hussite movement, in one of his seminal works, ''De orthographia bohemica'' (''On Bohemian orthography''). The modern Czech orthographic system is diacritic, having evolved from an earlier system which used many Digraph (orthography), digraphs (although one digraph has been kept - ''ch''). The caron (known as ''h├Ī─Źek'' in Czech) is added to standard Latin letters to express sounds which are foreign to Latin language, Latin. The acute accent is used for long vowels. The Czech orthography is considered the model for many other Balto-Slavic languages using the Latin alphabet; Slovak orthography, Slovak orthography being its direct revised descendant, while the Croatian Gaj's Latin alphabet and its Slovene alphabet, Slov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |