|
─░spir
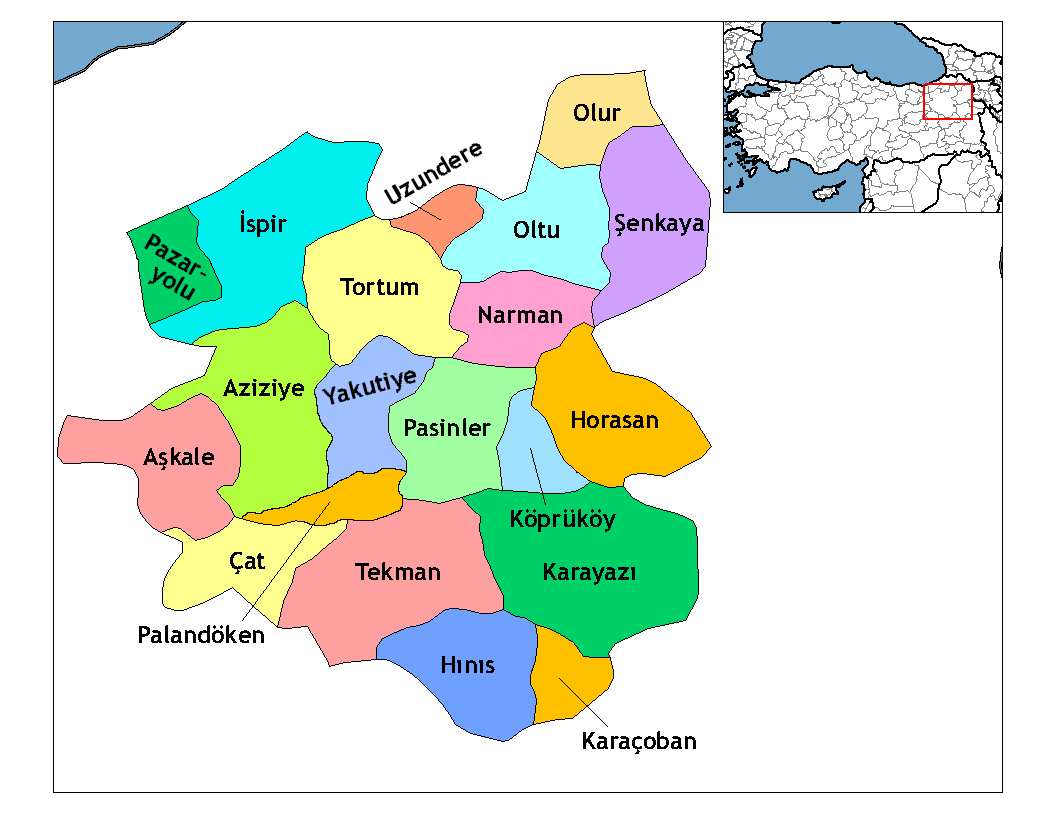
─░spir (, Sper; ka, ßāĪßā×ßāößāĀßāś, Speri) is a municipality and district of Erzurum Province, Turkey. Its area is 2,129 km2, and its population is 14,607 (2022). It is on the ├ćoruh River. The mayor is Ahmet Co┼¤kun ( MHP). History ─░spir is known from the 3rd millennium BC. The ancient kingdom of Hayasa-Azzi (2nd millennium BC), which was the forerunner of Armenian statehood, was located in the upper reaches of the rivers Euphrates and Chorokh, and included Sper. The name Sper is thought by some to be derived from Saspers, or Sasperi, the name Sper with a Georgian prefix of place Sa-, which evolved into the term Iberian. The Saspers were mentioned by Xenophon;T. A. Sinclair, "Eastern Turkey an Architectural and Archaeological Survey", Volume 2, 1989, p272 In the 4th-3rd centuries BC Sper was organized into a province of the Iberian Kingdom as noted by Strabo. Alexander the Great sent one of his generals Menon to conquer Sper, but Menon and his forces were def ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
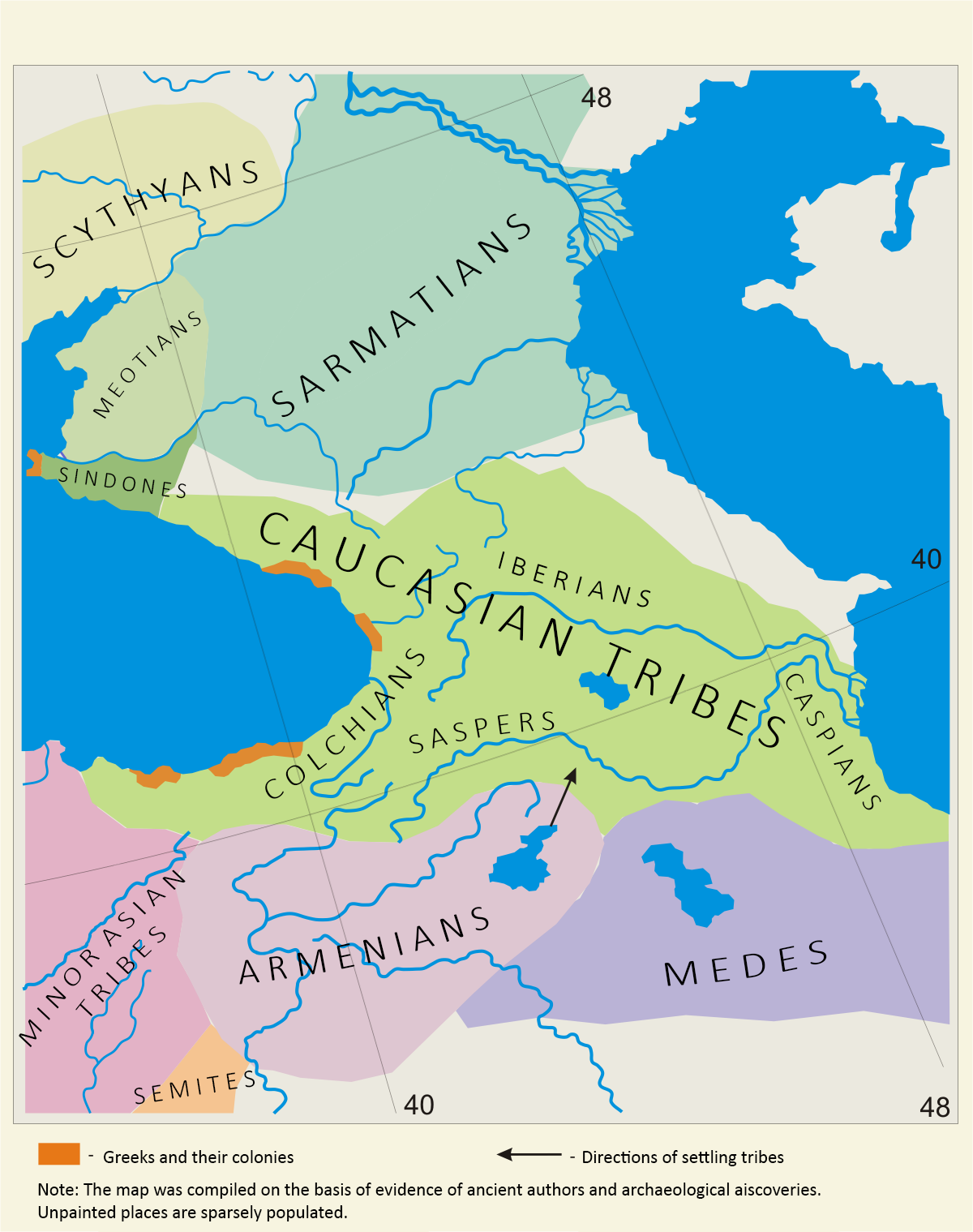
Saspeires
Saspeires (, ka, ßāĪßāÉßāĪßā×ßāößāĀßāößāæßāś, ''sasp'erebi'', other names include Saspers, Saspines, Sapinians, and Sapirians) are a people of uncertain origin mentioned by Herodotus. According to the most widespread theory, they are a Kartvelian peoples, Kartvelian tribe. The toponym of modern-day city ─░spir and ancient region of Speri (region), Speri is thought by some to be derived from their name. According to Rayfield, Diauehi is mentioned in the Greek records as Taochoi, but Herodotus in 450 BC refers to them as Sasperi. the name ─░spir, Sper with a Georgian prefix of place Sa-, which evolved into the term Kingdom of Iberia, Iberian. The Saspires were originally associated with the Caucasian Iberians and appear to have emerged from the Lesser Caucasus to the east. The Alarodians, Colchians, and Saspires were joined in one command, and all were dressed alike. The Colchians themselves, were not classified as belonging to any Satrapy. The Colchians, however, attended the army o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
├ćoruh River
The Chorokh ( ka, ßāŁßāØßāĀßāØßā«ßāś ''Ch'orokhi'' , , ''Chorokh'', , , ''Akampsis'') is a river that rises in the Mescit Mountains in north-eastern Turkey, flows through the cities of Bayburt, ─░spir, Yusufeli, and Artvin, along the Kelkit River, Kelkit-├ćoruh Fault, before flowing into Georgia (country), Georgia, where it reaches the Black Sea just south of Batumi and a few kilometers north of the Turkish-Georgian border. In Arrian's ''Periplus Ponti Euxini'', it is called the ''Acampsis'' (); Pliny the Elder, Pliny may have confused it with the ''Bathys''. Procopius writes that it was called Acampsis because it was impossible to force a way through it after it has entered the sea, since it discharges its stream with such force and swiftness, causing a great disturbance of the water before it, that it goes out for a very great distance into the sea and makes it impossible to coast along at that point. In English, it was formerly known as the Boas, the Churuk, or the Chorokh. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Districts Of Turkey
The Provinces of Turkey, 81 provinces of Turkey are divided into 973 districts (''il├¦eler''; sing. ''il├¦e''). In the Ottoman Empire and in the early Turkish Republic, the corresponding unit was the ''qadaa, kaza''. Most provinces bear the same name as their respective provincial capital (political), capital districts. However, many urban provinces, designated as greater municipalities, have a center consisting of multiple districts, such as the provincial capital of Ankara Province, Ankara province, Ankara, The City of Ankara, comprising nine separate districts. Additionally three provinces, Kocaeli, Sakarya, and Hatay have their capital district named differently from their province, as ─░zmit, Adapazar─▒, and Antakya respectively. A district may cover both rural and urban areas. In many provinces, one district of a province is designated the central district (''merkez il├¦e'') from which the district is administered. The central district is administered by an appointed pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erzurum Province
Erzurum Province () is a province and metropolitan municipality in the Eastern Anatolia Region of Turkey. Its area is 25,006 km2, and its population is 749,754 (2022). The capital of the province is the city of Erzurum. It is the fourth largest province in all of Turkey. It is bordered by the provinces of Kars and A─¤r─▒ to the east, Mu┼¤ and Bing├Čl to the south, Erzincan and Bayburt to the west, Rize and Artvin to the north and Ardahan to the northeast. The governor of the province is Mustafa ├ćift├¦i, appointed in August 2023. The province has a Turkish majority. Geography The surface area of the province of Erzurum is the fourth biggest in Turkey. The majority of the province is elevated. Most plateaus are about above sea level, and the mountainous regions beyond the plateaus are and higher. Depression plains are located between the mountains and plateaus. The southern mountain ranges include the Paland├Čken Mountains (highest peak B├╝y├╝k Ejder high) and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
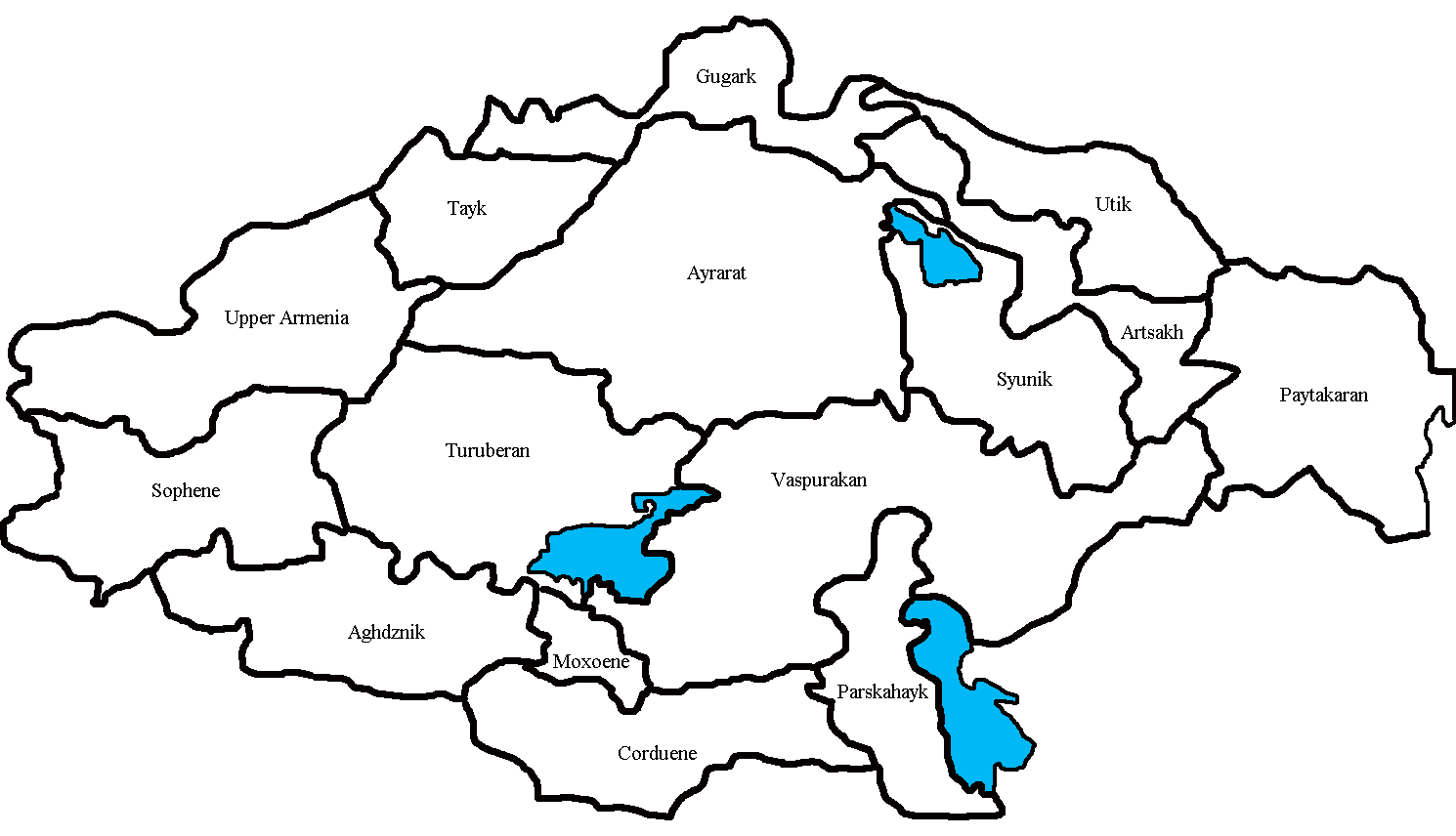
Tayk
Tayk () was a historical province of the Kingdom of Armenia, one of its 15 (worlds). Tayk consisted of 8 cantons: * Kogh * Berdats por * Partizats por * Tchakatk * Bokha * Vokaghe * Azordats por * Arsiats por In the 999 A.D., Tayk or Tao became part of the Georgian Bagrationi principality Tao-Klarjeti. The Tao province covered the contemporary Turkish districts of Yusufeli (Kiskim) in Artvin Province and Oltu, Olur (Tavusker), Tortum and ├ćaml─▒kaya (Hunut) to the north of ─░spir in Erzurum Province. To its southwest is found the ancient region of Sper. After World War I, Armenia and Georgia contested the region, with particular conflict over Oltik. As a result, in 1920, after the Russo-Turkish attacks Armenia lost the region of Oltik, which become a part of Turkey. Sources * Arutyunova-Fidanyan, Viada A., Some Aspects of the Military-Administrative Districts and Byzantine Administration in Armenia During the 11th Century, ''REArm'' 20, 1986-87: 309ŌĆō20. * Ga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Armenia (antiquity)
The Kingdom of Greater Armenia or simply Greater Armenia or Armenia Major ( '; ), sometimes referred to as the Armenian Empire under Tigranes the Great, Tigranes II, was an Armenians, Armenian kingdom in the Ancient Near East which existed from 331 BC to 428 AD. Its history is divided into the successive reigns of three Royal family, royal dynasties: Orontid dynasty, Orontid (331ŌĆō200 BC), Artaxiad dynasty, Artaxiad (189 BC12 AD), and Arsacid dynasty of Armenia, Arsacid (52ŌĆō428). The root of the kingdom lies in the Satrapy of Armenia of the Achaemenid Empire of Iran, which was formed from the territory of Urartu (860ŌĆō590 BC) after it was conquered by the Medes in 590 BC. The satrapy became a kingdom in 321 BC during the reign of the Orontid dynasty after the conquest of Persia by Alexander the Great, which was then incorporated as one of the Hellenistic period, Hellenistic kingdoms of the Seleucid Empire. Under the Seleucid Empire ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bagratuni Kingdom Of Armenia
Bagratid Armenia was an independent Armenian state established by Ashot I of the Bagratuni dynasty in the early 880s following nearly two centuries of foreign domination of Greater Armenia under Arab Umayyad and Abbasid rule. With each of the two contemporary powers in the regionŌĆöthe Abbasids and ByzantinesŌĆötoo preoccupied to concentrate their forces on subjugating the region, and with the dissipation of several of the Armenian '' nakharar'' noble families, Ashot succeeded in asserting himself as the leading figure of a movement to dislodge the Arabs from Armenia. Ashot's prestige rose as both Byzantine and Arab leadersŌĆöeager to maintain a buffer state near their frontiersŌĆöcourted him. The Abbasid Caliphate recognized Ashot as "prince of princes" in 862 and, later on, as king (in 884 or 885). The establishment of the Bagratuni kingdom later led to the founding of several other Armenian principalities and kingdoms: Taron, Vaspurakan, Kars, Khachen and Syunik. Duri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Upper Armenia
Upper Armenia ( ''Bardzr HaykŌĆś'') was the first province of the ancient kingdom of Armenia, located in present-day Turkey, roughly corresponding to the modern province of Erzincan, to the west of the Kura River. Within the borders of the kingdom, it was bounded by the regions of Sophene, Turuberan, Tayk, and Ayrarat. It was called Upper Armenia, as it was higher in elevation than the other provinces. The total area of Upper Armenia was . It consisted of 9 cantons: * Daranaghi * Aghyun * Mzur * Yekeghyats * Mananaghi * Derjan * Sper * Shaghagom * Karin History Upper Armenia was famous for its lakes, rivers (especially the Euphrates), gold mines and fields. In the 2nd millennium BC, Upper Armenia's western parts were conquered by Hittite Empire; from the 15th century BC, it was conquered by Hayasa-Azzi. From 189 BC, it became part of the Kingdom of Armenia. Upper Armenia was famous for its pagan temples. From 62 AD, it became part of the Arsacid dynasty of Armenia. As ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arab Caliphate
A caliphate ( ) is an institution or public office under the leadership of an Islamic steward with the title of caliph (; , ), a person considered a politicalŌĆōreligious successor to the Islamic prophet Muhammad and a leader of the entire Muslim world (''ummah''). Historically, the caliphates were polities based on Islam which developed into multi-ethnic trans-national empires. During the medieval period, three major caliphates succeeded each other: the Rashidun Caliphate (632ŌĆō661), the Umayyad Caliphate (661ŌĆō750), and the Abbasid Caliphate (750ŌĆō1517). In the fourth major caliphate, the Ottoman Caliphate, the rulers of the Ottoman Empire claimed caliphal authority from 1517 until the Ottoman caliphate was formally abolished as part of the 1924 secularisation of Turkey. An attempt to preserve the title was tried, with the Sharifian Caliphate, but this caliphate fell quickly after its conquest by the Sultanate of Nejd (present-day Saudi Arabia), leaving the claim in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seljuqs
The Seljuk dynasty, or Seljukids ( ; , ''Saljuqian'',) alternatively spelled as Saljuqids or Seljuk Turks, was an Oghuz Turkic, Sunni Muslim dynasty that gradually became Persianate and contributed to Turco-Persian culture. The founder of the Seljuk dynasty, Seljuk Beg, was a descendant of a royal Khazar chief Tuqaq who served as advisor to the King of the Khazars. in West Asia and Central Asia. The Seljuks established the Seljuk Empire (1037ŌĆō1194), the Sultanate of Kerm├ón (1041ŌĆō1186) and the Sultanate of Rum (1074ŌĆō1308), which stretched from Iran to Anatolia and were the prime targets of the First Crusade. Early history The Seljuks originated from the Kinik branch of the Oghuz Turks, who in the 8th century lived on the periphery of the Muslim world; north of the Caspian Sea and Aral Sea in their Oghuz Yabgu State in the Kazakh Steppe of Turkestan. During the 10th century, Oghuz had come into close contact with Muslim cities. When Seljuk, the leader of the Seljuk clan, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Armenia (Middle Ages)
Bagratid Armenia was an independent Armenian state established by Ashot I of the Bagratuni dynasty in the early 880s following nearly two centuries of foreign domination of Greater Armenia under Arab Umayyad and Abbasid rule. With each of the two contemporary powers in the regionŌĆöthe Abbasids and ByzantinesŌĆötoo preoccupied to concentrate their forces on subjugating the region, and with the dissipation of several of the Armenian '' nakharar'' noble families, Ashot succeeded in asserting himself as the leading figure of a movement to dislodge the Arabs from Armenia. Ashot's prestige rose as both Byzantine and Arab leadersŌĆöeager to maintain a buffer state near their frontiersŌĆöcourted him. The Abbasid Caliphate recognized Ashot as "prince of princes" in 862 and, later on, as king (in 884 or 885). The establishment of the Bagratuni kingdom later led to the founding of several other Armenian principalities and kingdoms: Taron, Vaspurakan, Kars, Khachen and Syunik. Duri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |