|
Turkic Languages
The Turkic languages are a language family of more than 35 documented languages, spoken by the Turkic peoples of Eurasia from Eastern Europe and Southern Europe to Central Asia, East Asia, North Asia (Siberia), and West Asia. The Turkic languages originated in a region of East Asia spanning from Mongolia to Northwest China, where Proto-Turkic language, Proto-Turkic is thought to have been spoken, from where they Turkic migration, expanded to Central Asia and farther west during the first millennium. They are characterized as a dialect continuum. Turkic languages are spoken by some 200 million people. The Turkic language with the greatest number of speakers is Turkish language, Turkish, spoken mainly in Anatolia and the Balkans; its native speakers account for about 38% of all Turkic speakers, followed by Uzbek language, Uzbek. Characteristic features such as vowel harmony, agglutination, subject-object-verb order, and lack of grammatical gender, are almost universal within the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swedish Language
Swedish ( ) is a North Germanic languages, North Germanic language from the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family, spoken predominantly in Sweden and parts of Finland. It has at least 10 million native speakers, making it the Germanic_languages#Statistics, fourth most spoken Germanic language, and the first among its type in the Nordic countries overall. Swedish, like the other North Germanic languages, Nordic languages, is a descendant of Old Norse, the common language of the Germanic peoples living in Scandinavia during the Viking Age. It is largely mutually intelligible with Norwegian language, Norwegian and Danish language, Danish, although the degree of mutual intelligibility is dependent on the dialect and accent of the speaker. Standard Swedish, spoken by most Swedes, is the national language that evolved from the Central Swedish dialects in the 19th century, and was well established by the beginning of the 20th century. While distinct regional Variety ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hungarian Alphabet
The Hungarian alphabet (, ) is an extension of the Latin alphabet used for writing the Hungarian language. The alphabet is based on the Latin alphabet, with several added variations of letters, consisting 44 letters. Over the 26 letters of the ISO basic Latin alphabet it has five letters with an acute accent, two letters with an umlaut, two letters with a double acute accent, eight letters made up of two characters, and one letter made up of three characters. In some other languages, characters with diacritical marks would be considered variations of the base letter, however in Hungarian, these characters are considered letters in their own right. One sometimes speaks of the ''smaller'' (or basic) and ''greater'' (or ''extended'') Hungarian alphabets, differing by the inclusion or exclusion of the letters ''Q'', ''W'', ''X'', ''Y'', which can only be found in family names, and in foreign words. (As for Y, however, it exists as part of four digraphs.) As an auxiliary letter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uralic Languages
The Uralic languages ( ), sometimes called the Uralian languages ( ), are spoken predominantly in Europe and North Asia. The Uralic languages with the most native speakers are Hungarian, Finnish, and Estonian. Other languages with speakers above 100,000 are Erzya, Moksha, Mari, Udmurt and Komi spoken in the European parts of the Russian Federation. Still smaller minority languages are Sámi languages of the northern Fennoscandia; other members of the Finnic languages, ranging from Livonian in northern Latvia to Karelian in northwesternmost Russia; the Samoyedic languages and the others of members of the Ugric languages, Mansi and Khanty spoken in Western Siberia. The name ''Uralic'' derives from the family's purported "original homeland" (''Urheimat'') hypothesized to have been somewhere in the vicinity of the Ural Mountains, and was first proposed by Julius Klaproth in ''Asia Polyglotta'' (1823). Finno-Ugric is sometimes used as a synonym for Uralic but more accu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Language
German (, ) is a West Germanic language in the Indo-European language family, mainly spoken in Western Europe, Western and Central Europe. It is the majority and Official language, official (or co-official) language in Germany, Austria, Switzerland, and Liechtenstein. It is also an official language of Luxembourg, German-speaking Community of Belgium, Belgium and the Italian autonomous province of South Tyrol, as well as a recognized national language in Namibia. There are also notable German-speaking communities in other parts of Europe, including: Poland (Upper Silesia), the Czech Republic (North Bohemia), Denmark (South Jutland County, North Schleswig), Slovakia (Krahule), Germans of Romania, Romania, Hungary (Sopron), and France (European Collectivity of Alsace, Alsace). Overseas, sizeable communities of German-speakers are found in the Americas. German is one of the global language system, major languages of the world, with nearly 80 million native speakers and over 130 mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Azeri Alphabet
The Azerbaijani alphabet (, , ) has three versions which includes the Arabic, Latin, and Cyrillic alphabets. North Azerbaijani, the official language of Republic of Azerbaijan, is written in a modified Latin alphabet. After the fall of Soviet Union this superseded previous versions based on Cyrillic and Arabic scripts. South Azerbaijani, the language spoken in Iran’s Azerbaijan region, is written in a modified Arabic script since Safavid Empire. Azerbaijanis of Dagestan still use the Cyrillic script. Azerbaijani Latin alphabet The Azerbaijani Latin alphabet consists of 32 letters. History From the nineteenth century there were efforts by some intellectuals like Mirza Fatali Akhundov and Mammad agha Shahtakhtinski to replace the Arabic script and create a Latin alphabet for Azerbaijani. In 1922, a Latin alphabet was created by Soviet Union sponsored ''Yeni türk əlifba komitəsi'' (New Turkic Alphabet Committee; ) in Baku which hoped that the new alphabet would d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Umlaut (diacritic)
Umlaut () is a name for the Two dots (diacritic), two dots diacritical mark () as used to indicate in writing (as part of the letters , , and ) the result of the historical sound shift due to which former back vowels are now pronounced as front vowels (for example , , and as , , and ). (The term Germanic umlaut is also used for the underlying historical sound shift process.) In its contemporary printed form, the mark consists of two dots placed over the letter to represent the changed vowel sound. (In some Romance and other languages, the diaeresis (diacritic), diaeresis diacritic has the same appearance but a different function.) German origin and current usage (literally "changed sound") is the German name of the sound shift phenomenon also known as ''i-mutation''. In German, this term is also used for the corresponding letters ä, ö, and ü (and the diphthong äu) and the sounds that these letters represent. In German, the combination of a letter with the diacritical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germanic Languages
The Germanic languages are a branch of the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family spoken natively by a population of about 515 million people mainly in Europe, North America, Oceania, and Southern Africa. The most widely spoken Germanic language, English language, English, is also the world's most List of languages by total number of speakers, widely spoken language with an estimated 2 billion speakers. All Germanic languages are derived from Proto-Germanic language, Proto-Germanic, spoken in Iron Age Scandinavia, History of Germany#Iron Age, Iron Age Northern Germany and along the North Sea and Baltic coasts. The West Germanic languages include the three most widely spoken Germanic languages: English language, English with around 360–400 million native speakers; German language, German, with over 100 million native speakers; and Dutch language, Dutch, with 24 million native speakers. Other West Germanic languages include Afrikaans, an offshoot of Dutch origi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
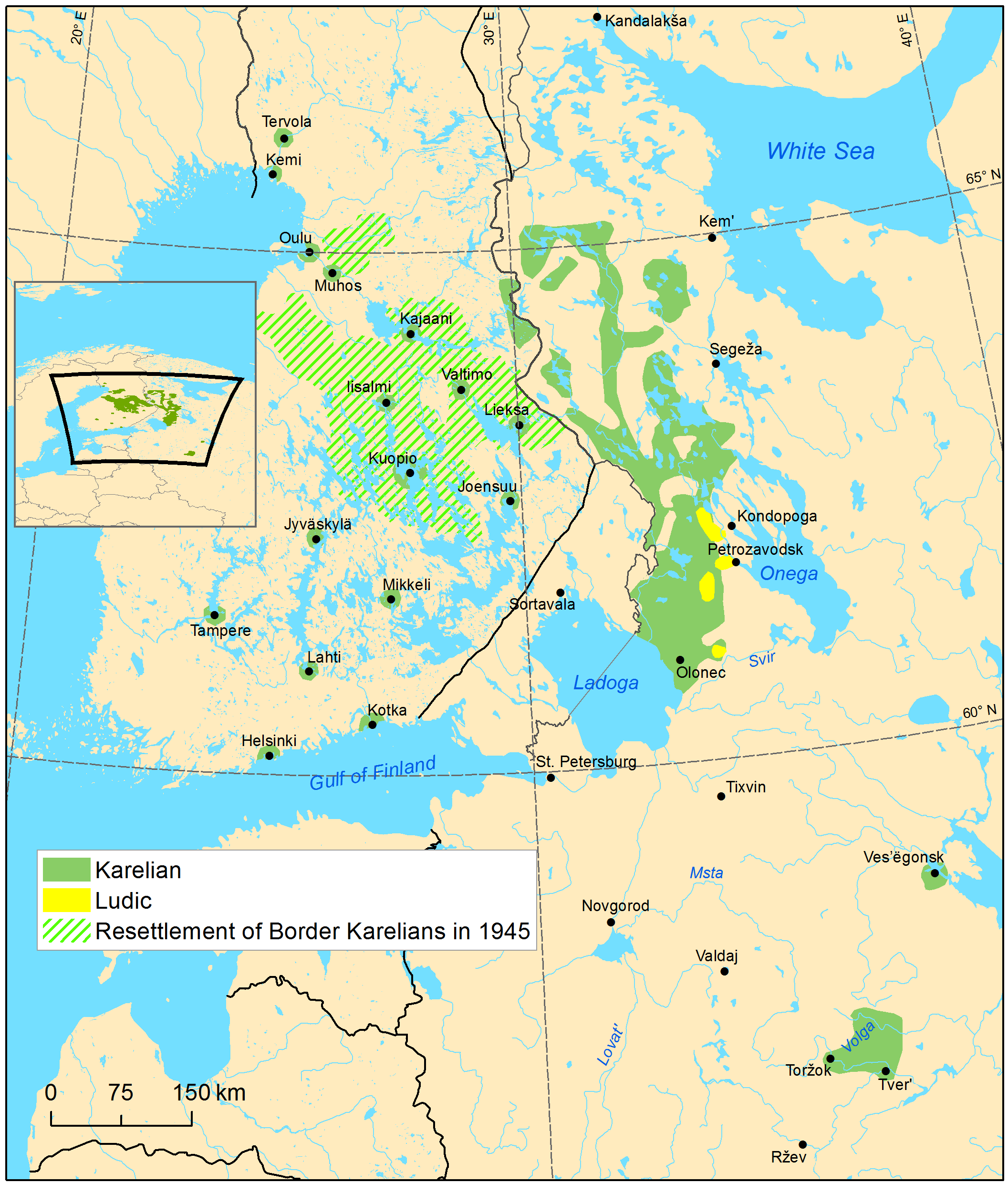
Karelian Language
Karelian (; ; ; ) is a Finnic language spoken mainly by the Karelians, Karelian people in the Russian Republic of Karelia. Linguistically, Karelian is closely related to the Finnish language, Finnish dialects spoken in eastern Finland, and some Finnish linguists have even classified Karelian as a dialect of Finnish, but nowadays it is widely considered a separate language. Karelian is not to be confused with the South Karelian dialects, Southeastern dialects of Finnish, sometimes referred to as ("Karelian dialects") in Finland. In the Russian 2020–2021 census, around 9,000 people spoke Karelian natively, but around 14,000 said they were able to speak the language. There are around 11,000 speakers of Karelian in Finland, and around 30,000 people in Finland have at least some knowledge of Karelian. The Karelian language is a group of two supradialects. The two supradialects are Karelian Proper language, Karelian Proper (which comprises Northern Karelian dialect, Northern Kareli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Veps Language
Veps, also known as Vepsian (, or ), is an endangered Finnic languages, Finnic language from the Uralic languages, Uralic language family, that is spoken by Vepsians. The language is written in the Latin script, and is closely related to Finnish language, Finnish and Karelian language, Karelian. According to Soviet Union, Soviet statistics, 12,500 people were self-designated ethnic Veps at the end of 1989. There were 5,900 self-designated ethnic Veps in 2010, and around 3,600 native speakers. According to the location of the people, the language is divided into three main dialects: Northern Veps (at Lake Onega to the south of Petrozavodsk, to the north of the river Svir River, Svir, including the former Veps National Volost), Central Veps (in the east of the Leningrad Oblast and northwest of the Vologda Oblast), and Southern Veps (in the Leningrad Oblast). The Northern dialect seems the most distinct of the three; however, it is still mutually intelligible for speakers of the oth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Finnish Alphabet
Finnish orthography is based on the Latin script, and uses an alphabet derived from the Swedish alphabet, officially comprising twenty-nine letters but also including two additional letters found in some loanwords. The Finnish orthography strives to represent all morphemes phonologically and, roughly speaking, the sound value of each letter tends to correspond with its value in the International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA) – although some discrepancies do exist. Alphabet The following table describes how each letter in the Finnish alphabet () is spelled and pronounced separately. If the name of a consonant begins with a vowel (usually ), it can be pronounced and spelled either as a monosyllabic or bisyllabic word. In practice, the names of the letters are rarely spelled, as people usually just type the (uppercase or lowercase) glyph when they want to refer to a particular letter. The pronunciation instructions enclosed in slashes are broad transcriptions based on the IPA sy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uyghur Language
Uyghur or Uighur (; , , or , , ), formerly known as Turki or Eastern Turki, is a Turkic languages, Turkic language with 8 to 13 million speakers (), spoken primarily by the Uyghur people in the Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region of Western China. Apart from Xinjiang, significant communities of Uyghur speakers are also located in Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, and Uzbekistan, and various other countries. Uyghur is an official language of the Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region; it is widely used in both social and official spheres, as well as in print, television, and radio. Other Ethnic minorities in China, ethnic minorities in Xinjiang also use Uyghur as a Lingua franca, common language. Uyghur belongs to the Karluk languages, Karluk branch of the Turkic languages, Turkic language family, which includes languages such as Uzbek language, Uzbek. Like many other Turkic languages, Uyghur displays vowel harmony and agglutination, lacks noun classes or grammatical gender, and is a Branchi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |