|
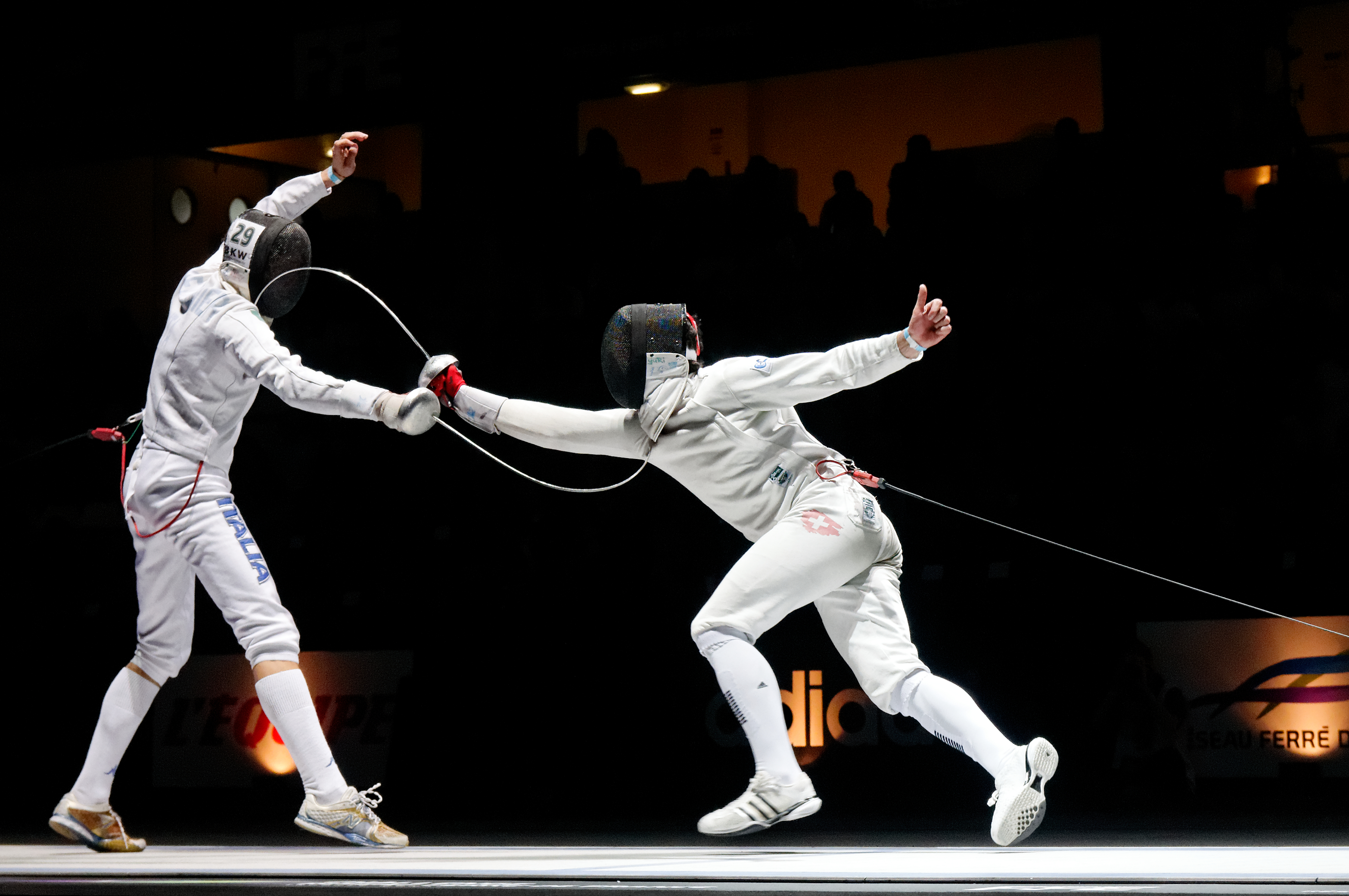
Épée (Fencing)
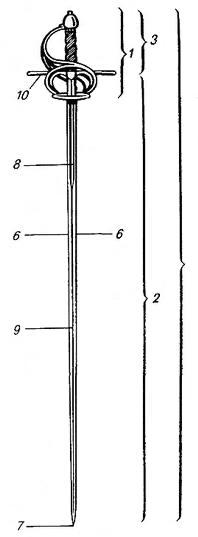
The (, ; ), also rendered as epee in English, is the largest and heaviest of the three weapons used in the sport of fencing. The modern derives from the 19th-century , a weapon which itself derives from the French small sword. This contains a detailed contempraneous description of the history and form of the sport. As a thrusting weapon, the is similar to a foil (contrasted with a sabre, which is designed for slashing). It has a stiffer blade than a foil. It is triangular in cross-section with a V-shaped groove called a fuller. The also has a larger bell guard designed to protect the user’s arm. In addition to the larger "bell" guard and blade, the weighs more than the foil and sabre which contributes to its reputation of being the slowest form of fencing. The techniques of use differ, as there are no rules regarding priority and a lack of right of way. Thus, immediate counterattacks are a common feature of fencing. The entire body is a valid target area. Overview Whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fencing Epee Valid Surfaces
Fencing is a combat sport that features sword fighting. It consists of three primary disciplines: foil, épée, and sabre (also spelled ''saber''), each with its own blade and set of rules. Most competitive fencers specialise in one of these disciplines. The modern sport gained prominence near the end of the 19th century, evolving from historical European swordsmanship. The Italian school altered the historical European martial art of classical fencing, and the French school later refined that system. Scoring points in a fencing competition is done by making contact with the opponent with one's sword. The 1904 Olympic Games featured a fourth discipline of fencing known as singlestick, but it was dropped after that year and is not a part of modern fencing. Competitive fencing was one of the first sports to be featured in the Olympics and, along with athletics, cycling, swimming, and gymnastics, has been featured in every modern Olympics. Competitive fencing Governing body ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Italy V Estonia Challenge International De Saint-Maur 2013 T142226
Italy, officially the Italian Republic, is a country in Southern and Western Europe. It consists of a peninsula that extends into the Mediterranean Sea, with the Alps on its northern land border, as well as nearly 800 islands, notably Sicily and Sardinia. Italy shares land borders with France to the west; Switzerland and Austria to the north; Slovenia to the east; and the two enclaves of Vatican City and San Marino. It is the tenth-largest country in Europe by area, covering , and the third-most populous member state of the European Union, with nearly 59 million inhabitants. Italy's capital and largest city is Rome; other major cities include Milan, Naples, Turin, Palermo, Bologna, Florence, Genoa, and Venice. The history of Italy goes back to numerous Italic peoples—notably including the ancient Romans, who conquered the Mediterranean world during the Roman Republic and ruled it for centuries during the Roman Empire. With the spread of Christianity, Rome became the sea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
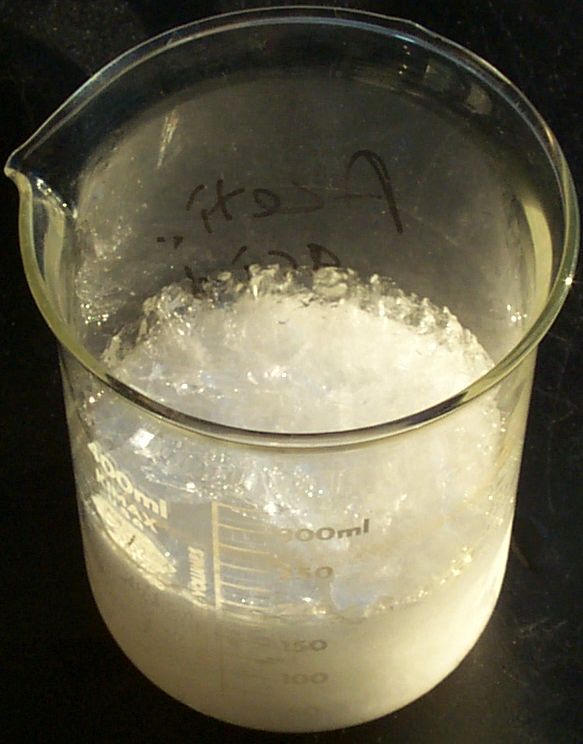
Acetic Acid
Acetic acid , systematically named ethanoic acid , is an acidic, colourless liquid and organic compound with the chemical formula (also written as , , or ). Vinegar is at least 4% acetic acid by volume, making acetic acid the main component of vinegar apart from water. Historically, vinegar was produced from the third century BC and was likely the first acid to be produced in large quantities. Acetic acid is the second simplest carboxylic acid (after formic acid). It is an important Reagent, chemical reagent and industrial chemical across various fields, used primarily in the production of cellulose acetate for photographic film, polyvinyl acetate for wood Adhesive, glue, and synthetic fibres and fabrics. In households, diluted acetic acid is often used in descaling agents. In the food industry, acetic acid is controlled by the E number, food additive code E260 as an acidity regulator and as a condiment. In biochemistry, the acetyl group, derived from acetic acid, is funda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duel
A duel is an arranged engagement in combat between two people with matched weapons. During the 17th and 18th centuries (and earlier), duels were mostly single combats fought with swords (the rapier and later the small sword), but beginning in the late 18th century in England, duels were more commonly fought using pistols. Fencing and shooting continued to coexist throughout the 19th century. The duel was based on a code of honor. Duels were fought not to kill the opponent but to gain "satisfaction", that is, to restore one's honor by demonstrating a willingness to risk one's life for it. As such, the tradition of dueling was reserved for the male members of nobility; however, in the modern era, it extended to those of the upper classes. On occasion, duels with swords or pistols were fought between women. Legislation against dueling dates back to the medieval period. The Fourth Council of the Lateran (1215) outlawed duels and civil legislation in the Holy Roman Empire agains ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rapier
A rapier () is a type of sword originally used in Spain (known as ' -) and Italy (known as '' spada da lato a striscia''). The name designates a sword with a straight, slender and sharply pointed two-edged long blade wielded in one hand. It was widely popular in Western Europe throughout the 16th and 17th centuries as a symbol of nobility or gentleman status. It is called because it was carried as an accessory to clothing, generally used for fashion and as a weapon for dueling, self-defense and as a military side arm. Its name is of Spanish origin and appears recorded for the first time in the '' Coplas de la panadera'', by Juan de Mena, written approximately between 1445 and 1450: As fencing spread throughout Western Europe, important sources for rapier fencing arose in Spain, known under the term ("dexterity"), in Italy and France. The French small sword or court sword of the 18th century was a direct continuation of this tradition of fencing. Rapier fencing form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dueling Sword
A duel is an arranged engagement in combat between two people with matched weapons. During the 17th and 18th centuries (and earlier), duels were mostly single combats fought with swords (the rapier and later the small sword), but beginning in the late 18th century in England, duels were more commonly fought using pistols. Fencing and shooting continued to coexist throughout the 19th century. The duel was based on a code of honor. Duels were fought not to kill the opponent but to gain "satisfaction", that is, to restore one's honor by demonstrating a willingness to risk one's life for it. As such, the tradition of dueling was reserved for the male members of nobility; however, in the modern era, it extended to those of the upper classes. On occasion, duels with swords or pistols were fought between women. Legislation against dueling dates back to the medieval period. The Fourth Council of the Lateran (1215) outlawed duels and civil legislation in the Holy Roman Empire against d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Civilian
A civilian is a person who is not a member of an armed force. It is war crime, illegal under the law of armed conflict to target civilians with military attacks, along with numerous other considerations for civilians during times of war. If a civilian engages in hostilities, they are an unlawful combatant and temporarily lose their protection from attack. It is slightly different from a non-combatant, because some non-combatants are not civilians (for example, people who are not in a military but support war effort or military operations, military chaplains, or military personnel who are serving with a neutral country). Civilians in the territories of a party to an armed conflict are entitled to certain privileges under the customary international law, customary laws of war and Treaty, international treaties such as the Fourth Geneva Convention. The privileges that they enjoy under international law depends on whether the conflict is an internal one (a civil war) or an internationa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spatha
The spatha was a type of straight and long sword, measuring between , with a handle length of between , in use in the territory of the Roman Empire during the 1st to 6th centuries AD. Later swords, from the 7th to 10th centuries, like the Viking swords, are recognizable derivatives and sometimes subsumed under the term ''spatha''. The Roman ''spatha'' was used in war and in gladiatorial fights. The ''spatha'' of literature appears in the Roman Empire in the 1st century AD as a weapon used by presumably Celtic auxiliaries and gradually became a standard heavy infantry weapon by the 3rd century AD, relegating the ''gladius'' to use as a light infantry weapon. The ''spatha'' apparently replaced the ''gladius'' in the front ranks, giving the infantry more reach when thrusting. While the infantry version had a long point, versions carried by the cavalry had a rounded tip that prevented accidental stabbing of the cavalryman's own foot or horse. Archaeologically many instances of the ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
épée
The (, ; ), also rendered as epee in English, is the largest and heaviest of the three weapons used in the sport of fencing. The modern derives from the 19th-century , a weapon which itself derives from the French small sword. This contains a detailed contempraneous description of the history and form of the sport. As a thrusting weapon, the is similar to a Foil (fencing), foil (contrasted with a Sabre (fencing), sabre, which is designed for slashing). It has a stiffer blade than a foil. It is triangular in cross-section with a V-shaped groove called a Fuller (weapon), fuller. The also has a larger bell guard designed to protect the user’s arm. In addition to the larger "bell" guard and blade, the weighs more than the foil and sabre which contributes to its reputation of being the slowest form of fencing. The techniques of use differ, as there are no rules regarding priority and a lack of right of way. Thus, immediate counterattacks are a common feature of fencing. The en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jacques Callot (1592-1635), Graveur
Jacques Callot (; – 1635) was a baroque printmaker and draftsman from the Duchy of Lorraine. He is an important person in the development of the old master print. He made more than 1,400 etchings that chronicled the life of his period, featuring soldiers, clowns, drunkards, Romani, beggars, as well as court life. He also etched many religious and military images, and many prints featured extensive landscapes in their background. Life and training Callot was born and died in Nancy, the capital of Lorraine, now in France. At the time, the Duchy of Lorraine was an independent state on the north-eastern border of France, southwestern border of Germany and overlapping the southern Netherlands. He came from an important family (his father was master of ceremonies at the court of the Duke), and he often describes himself as having noble status in the inscriptions to his prints. At the age of fifteen he was apprenticed to a goldsmith, but soon afterward travelled to Rome where he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Penn State University Press
The Penn State University Press, also known as The Pennsylvania State University Press, is a non-profit publisher of scholarly books and journals. Established in 1956, it is the independent publishing branch of the Pennsylvania State University and is a division of the Penn State University Library system. Penn State University Press publishes books and journals of interest to scholars and general audiences. As a part of a land-grant university with a mandate to serve the citizens of the commonwealth of Pennsylvania, it also specializes in works about Penn State University, Pennsylvania, and the mid-Atlantic region. The areas of scholarship the Press is best known for are art history, medieval studies, Latin American studies, rhetoric and communication, religious studies, and graphic medicine. The press produces about 80 books a year and over 60 journals. The Press employs 25 to 30 people, and has several internship programs for Penn State students interested in a publishing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shim (fencing)
Shim may refer to: * Shim (spacer), a thin and often tapered or wedged piece of material ** CPU shim, a spacer for a computer heat sink ** Shim (fencing), a device used in the sport fencing ** Shim (lock pick), a tool used to bypass padlocks * Shim (computing), an application compatibility workaround * Shim (magnetism), a device used to adjust the homogeneity of a magnetic field * Shim (band), an Australian hard rock band Microscopy * Second-harmonic imaging microscopy * Scanning helium ion microscope People * Shim (surname) * Sim (Korean surname), pronounced "shim" * Shim (musician) (born 1983), Israeli singer-songwriter and artist See also * * * Shimmer (other) * Shimon (other) Shimon () is the original Hebrew pronunciation of the names Simon (given name), Simon and Simeon. Among individuals, Shimon can refer to: Given names * Shimon Agranat (1906-1992), Israeli judge and President of the Israeli Supreme Court * Shimon Am ... * Sim (disambiguatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |