|
├ēnna Mac Murchada
├ēnna Mac Murchada, or Enna Mac Murchada, also known as ├ēnna mac Donnchada, and ├ēnna mac Donnchada mic Murchada, was a twelfth-century ruler of U├Ł Chennselaig, Leinster, and Dublin. ├ēnna was a member of the Meic Murchada, a branch of the U├Ł Chennselaig dynasty that came to power in Leinster in the person of his paternal great-grandfather. ├ēnna himself gained power following the death of his cousin Diarmait mac ├ēnna. Throughout much of his reign, ├ēnna acknowledged the overlordship of Toirdelbach Ua Conchobair, King of Connacht, although he participated in a failed revolt against the latter in 1124 before making amends. When ├ēnna died in 1126, Toirdelbach successfully took advantage of the resulting power vacuum. Background ├ēnna was a son of Donnchad mac Murchada, King of Leinster. Donnchad had two other sons: one slain in 1115, ├ō Corr├Īin (1971) p. 20. and another named Diarmait. The men were members of the U├Ł Chennselaig. In the 1040s, the family seized posses ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Murchad Mac Diarmata
Murchad mac Diarmata (English: Murrough MacDermot) (died 1070) was a late eleventh-century ruler of the kingdoms of Leinster, Dublin, and the Isles. He was a member of the U├Ł Chennselaig, and a son of Diarmait mac M├Īel na mB├│, King of Leinster (died 1072). Murchad had three sons: Domnall (died 1075), Donnchad (died 1115), and ├ēnna. He is the eponymous founder of the Meic Murchada, a branch of the U├Ł Chennselaig who adopted the surname ''Mac Murchada'' (MacMurrough, MacMorrow, Morrow). Murchad led an army into the Kingdom of Meath in July 1069 "where he burned territories and churches", he was however badly wounded by Feichin, a defender. It was probably these injuries, or complications, that led to Murchad's death in 1070. He was then buried in ├üth Cliath, near what is now Dublin. Murchad's death in the ''Annals of the Four Masters The ''Annals of the Kingdom of Ireland'' () or the ''Annals of the Four Masters'' () are chronicles of Middle Ages, medieval Iris ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High King Of Ireland
High King of Ireland ( ) was a royal title in Gaelic Ireland held by those who had, or who are claimed to have had, lordship over all of Ireland. The title was held by historical kings and was later sometimes assigned anachronously or to legendary figures. Medieval and early modern Irish literature portrays an almost unbroken line of High Kings, ruling from the Hill of Tara over a hierarchy of lesser kings, stretching back thousands of years. Modern historians believe this scheme was crafted in the 8th century from the various genealogical traditions of powerful dynasties, and intended to justify their status by projecting it far into the past.D├Īibh├Ł ├ō Cr├│in├Łn, "Ireland, 400ŌĆō800", in D├Īibh├Ł ├ō Cr├│in├Łn (ed.), ''A New History of Ireland 1: Prehistoric and Early Ireland'', Oxford University Press, 2005, pp. 182ŌĆō234. John T. Koch explains: "Although the kingship of Tara was a special kingship whose occupants had aspirations towards supremacy among the kings of Irela ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cousin
A cousin is a relative who is the child of a parent's sibling; this is more specifically referred to as a first cousin. A parent of a first cousin is an aunt or uncle. More generally, in the kinship system used in the English-speaking world, cousins are in a type of relationship in which the two cousins are two or more generations away from their most recent common ancestor. In this usage, "degrees" and "removals" are used to specify the relationship more precisely. "Degree" measures how distant the relationship is from the most recent common ancestor(s), starting with one for first cousins and increasing with every subsequent generation. If the cousins do not come from the same generation, "removal" expresses the difference in generations between the two cousins. When no removal is not specified, no removal is assumed. Various governmental entities have established systems for legal use that can precisely specify kinship with common ancestors any number of generations i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conchobar Ua Conchobair
Conchobar Ua Conchobair (Anglicised as Conor O'Conor), served as t├Īnaiste of Connacht, fl. 1126ŌĆō1144. Background Conchobar was one of over twenty sons sired by Tairrdelbach Ua Conchobair, and his first chosen heir. King of Dublin ''1126. An army was led by Toirdhealbhach Ua Conchobhair, and he gave the kingdom of Ath-cliath and Leinster to his own son, Conchobhar; he afterwards proceeded to the South, and defeated Cormac Mac Carthaigh, and burned his camp at Sliabh-an-Caithligh.'' King of Mide Following Tairrdelbach's kidnapping of the king of Mide in 1143, ''"the kingdom of Meath was given by Toirdhealbhach to his own son, Conchobhar."'' However, the strategy backfired as the annals for 1144 record: ''Conchobhar, son of Toirdhealbhach Ua Conchobhair, heir apparent to the monarchy of Ireland, was killed at Bealach Muine-na-Siride, by Ua Dubhlaich, lord of Feara-Tulach, for he considered him as a stranger in sovereignty over the men of Meath. Toirdhealbhach Ua Conchobhai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Book Of Leinster
The Book of Leinster ( , LL) is a medieval Irish manuscript compiled and now kept in Trinity College Dublin. It was formerly known as the ''Lebor na Nuachongb├Īla'' ("Book of Nuachongb├Īil"), a monastic site known today as Oughaval. In 2023, Trinity College started an extensive restoration project to make the manuscript available for public viewing. Fragments of the book, such as the ''Martyrology of Tallaght'', are in the collection of University College Dublin. Date and provenance The manuscript is a composite work and more than one hand appears to have been responsible for its production. The principal compiler and scribe was probably ├üed Ua Crimthainn,Hellmuth, "''Lebor Laignech''", pp. 1125-6. who was abbot of the monastery of T├Łr-D├Ī-Glas on the Shannon, now Terryglass (County Tipperary), and the last abbot of that house for whom we have any record. Internal evidence from the manuscript itself bears witness to ├üed's involvement. His signature can be read on f. 32 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
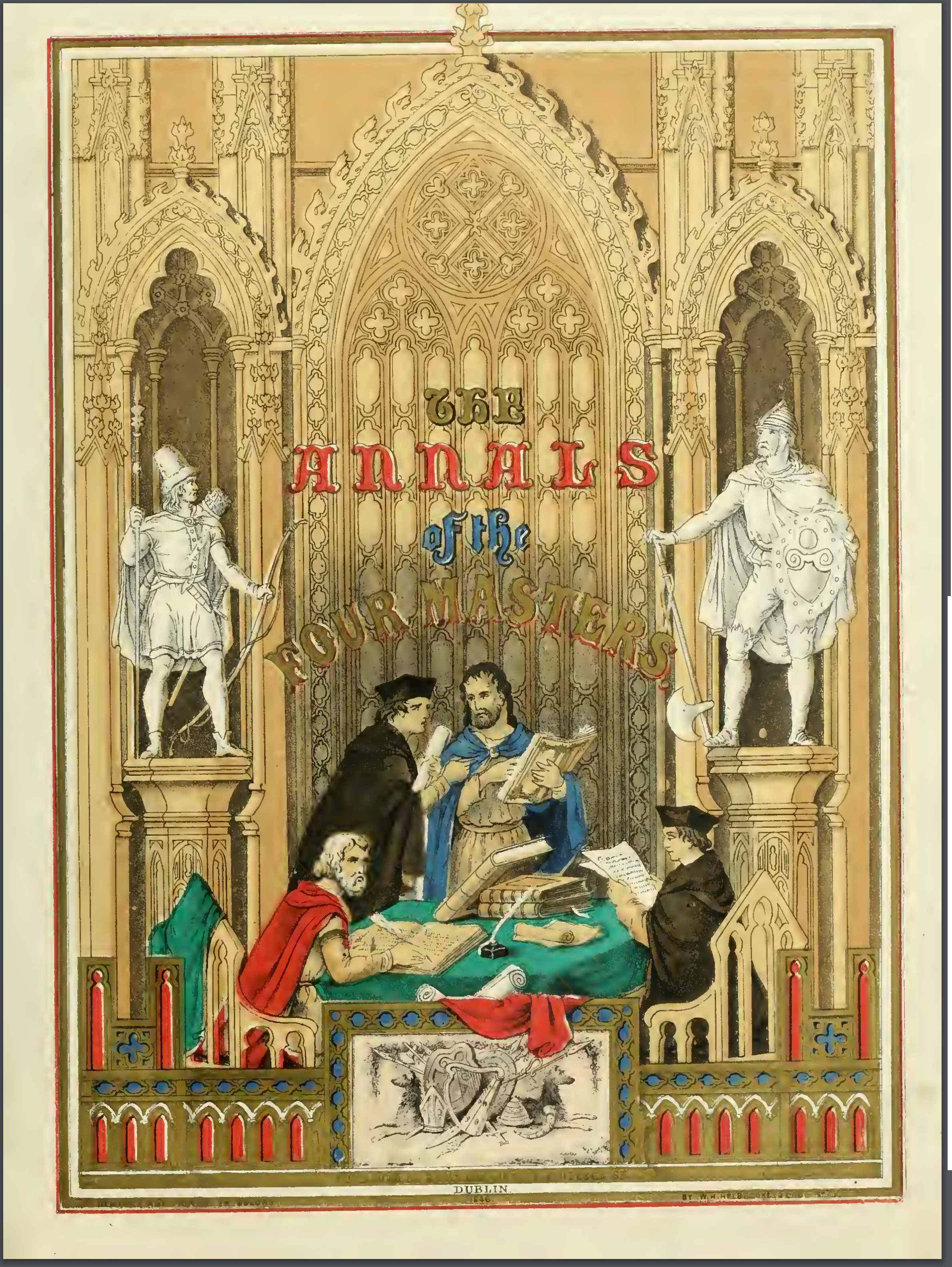
Annals Of The Four Masters
The ''Annals of the Kingdom of Ireland'' () or the ''Annals of the Four Masters'' () are chronicles of Middle Ages, medieval Irish history. The entries span from the Genesis flood narrative, Deluge, dated as 2,242 Anno Mundi, years after creation to AD 1616. Publication delay Due to the criticisms by 17th-century Irish historian Tuileagna ├ō Maol Chonaire, the text was not published in the lifetimes of any of the participants. Text The annals are mainly a compilation of earlier annals, although there is some original work. They were compiled between 1632 and 1636, allegedly in a cottage beside the ruins of Donegal Abbey, just outside Donegal (town), Donegal Town. At this time, however, the Franciscans had a house of refuge by the River Drowes in County Leitrim, just outside Ballyshannon, and it was here, according to others, that the ''Annals'' were compiled. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christ Church Cathedral, Dublin
Christ Church Cathedral, more formally The Cathedral of the Holy Trinity (Irish: ''Ardeaglais Theampall Chr├Łost''), is the cathedral of the Diocese of Dublin and Glendalough, United Dioceses of Dublin and Glendalough and the cathedral of the ecclesiastical province of the Province of Dublin (Church of Ireland), United Provinces of Dublin and Cashel in the (Anglican) Church of Ireland. It is situated in Dublin, Republic of Ireland, Ireland, and is the elder of the capital city's two Middle Ages, medieval cathedrals, the other being St Patrick's Cathedral, Dublin, St Patrick's Cathedral. The cathedral was founded in the early 11th century under the Viking king Sitric Silkenbeard. It was rebuilt in stone in the late 12th century under the Norman potentate Richard de Clare, 2nd Earl of Pembroke, Strongbow, and considerably enlarged in the early 13th century, using Somerset stones and craftsmen. A partial collapse in the 16th century left it in poor shape and the building was extens ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annals Of Tigernach
The ''Annals of Tigernach'' (Abbreviation, abbr. AT, ) are chronicles probably originating in Clonmacnoise, Ireland. The language is a mixture of Latin language, Latin and Old Irish, Old and Middle Irish. Many of the pre-historic entries come from the 12th-century MS, Rawlinson B 502.Hughes, ''Early Christian Ireland: Introduction to the Sources'', pp. 99-162. However, the real importance of the chronicle is for the period 489ŌĆō766, 973ŌĆō1003 and 1018ŌĆō1178. These three fragments survive from the 14th-century MS Rawlinson B 488. The coverage of the period 766 to 973 is lost, but is thought to survive in abbreviated form in the ''Chronicon Scotorum, Chronicon Scottorum'' (abbr. CT). The latter is defective for the period 718 to 804, but as much of its content is derived from the hypothetical ''The Chronicle of Ireland, Chronicle of Ireland'' (itself partly derived from the ''Iona Chronicle''), of which the ''Annals of Ulster'' (abbr. AU) and ''Annals of Inisfallen'' (abbr. AI) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cormac Mac C├Īrthaigh
Cormac Mac C├Īrthaigh (died 1138) was a Gaelic Irish ruler who was King of Munster. A member of the Mac C├Īrthaigh clan of the E├│ganacht Chaisil, he was the final king of the unified Kingdom of Munster before the realm was divided into the Kingdom of Desmond and Kingdom of Thomond in the aftermath of the Treaty of Glanmire. Origins Since the 10th century, the kingship of Munster had been held by the D├Īl gCais at the expense of the original dynasty, the E├│ganachta. In 1983, Henry Alan Jefferies stated: Since the days of Ceallach├Īn (ŌĆĀ 954), their fortunes had gone into grave and seemingly endless decline. Not only did they lose the kingship of Munster to Brian Boru, but by the 1070s Brian's descendants had wrested possession of Cashel itself from them. The dispossessed remnant of the E├│ghanacht of Cashel migrated westwards and by the reign of Muiredach son of C├Īrthach, they may have occupied some location in the Emly-Duhallow district. Certainly the early expansion of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Banshenchas
''An Banshenchas'' (literally "the woman lore") is a medieval text which collects brief descriptions of prominent women in Irish legend and history into a poetic narrative. Unlike much of early Irish literature, ''An Banshenchas'' may be attributed to a specific author and date. The introduction of the poem states that Gilla Mo Dutu ├Üa Caiside, of Ard Brec├Īin in Meath, composed it in 1147. Content ''An Banshenchas'' is framed in a historical context and starts with Eve and other biblical women, moves to the legendary women of Irish mythology such as ├ēta├Łn and Emer, then completes with later-day characters who are almost certainly historical, including a few women of the Hiberno-Norse aristocracy. The references to each of the characters within are short; a few lines at most. For example, in regard to some early biblical figures: Adam, Seth, pious Sili and Cain were the four first men who propagated multitudes. Eve, Olla, Pib and Pithib (women of power in the etern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annals Of Ulster
The ''Annals of Ulster'' () are annals of History of Ireland, medieval Ireland. The entries span the years from 431 AD to 1540 AD. The entries up to 1489 AD were compiled in the late 15th century by the scribe Ruaidhr├Ł ├ō Luin├Łn, under his patron Cathal ├ōg Mac Maghnusa, on the island of ''Senadh-Mic-Maghnusa'', also known as ''Senad'' or Ballymacmanus Island (now known as Belle Isle, where Belle Isle Castle is located), near Lisbellaw, on Lough Erne in the kingdom of ''Fir Manach'' (Fermanagh). Later entries (up to AD 1540) were added by others. Entries up to the mid-6th century are retrospective, drawing on earlier annalistic and historical texts, while later entries were contemporary, based on recollection and oral history. Thomas Charles-Edwards, T. M. Charles-Edwards has claimed that the main source for its records of the first millennium A.D. is a now-lost Armagh continuation of the ''Chronicle of Ireland''. The Annals used the Irish language, with some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |