|
├ł Sempre Bello
├ł, ├© ( e-grave) is a letter of the Latin alphabet. In English, ''├©'' is formed with an addition of a grave accent onto the letter E and is sometimes used in the past tense or past participle forms of verbs in poetic texts to indicate that the final syllable should be pronounced separately. For example, ''bless├©d'' would indicate the pronunciation , as opposed to for the word ''blessed''. It also occurs in loanwords such as Italian ''caff├©''. In other languages * In Emilian, ├© is used to represent ø╦É e.g. ''l├©t'' ╔ø╦Ét"bed". * In French, it always represents a sound of letter ''e'' when this is at the end of a syllable. *''├ł'' (├©) is used in Indonesian dictionaries to represent which differs from plain ''e'' () and ''├®'' (). The same applies to Javanese and Sundanese. * ''├ł'' means "is" in modern Italian , e.g. ''il cane ├© piccolo'' meaning "the dog is small". It is derived from Latin ''─Ģst'' and is accented to distinguish it from the conjunction ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latin Script
The Latin script, also known as the Roman script, is a writing system based on the letters of the classical Latin alphabet, derived from a form of the Greek alphabet which was in use in the ancient Greek city of Cumae in Magna Graecia. The Greek alphabet was altered by the Etruscan civilization, Etruscans, and subsequently their alphabet was altered by the Ancient Romans. Several Latin-script alphabets exist, which differ in graphemes, collation and phonetic values from the classical Latin alphabet. The Latin script is the basis of the International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA), and the 26 most widespread letters are the letters contained in the ISO basic Latin alphabet, which are the same letters as the English alphabet. Latin script is the basis for the largest number of alphabets of any writing system and is the List of writing systems by adoption, most widely adopted writing system in the world. Latin script is used as the standard method of writing the languages of Western and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Romagnol Dialect
Romagnol ( or ; ) is a Romance language spoken in the historical region of Romagna, consisting mainly of the southeastern part of Emilia-Romagna, Italy. The name is derived from the Lombard name for the region, ''Romagna''. Romagnol is classified as endangered because older generations have "neglected to pass on the dialect as a native tongue to the next generation". Classification Romagnol belongs to the Gallo-Italic family alongside Piedmontese, Ligurian and Lombard, forming with Emilian and as one of the two branches of the Emilian-Romagnol linguistic continuum.Gregor, D. B. (1972). Romagnol Language and Literature. Stoughton Harrow: Oleander Press. Further groupings of variants of Romagnol have not been set yet and both speakers and authors tend to refer to their own town or the nearest major province cities. The variants of Romagnol form a dialect continuum with their neighbouring varieties, while the more distant dialects might be less mutually intelligible. Vari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ISO 8859-14
ISO/IEC 8859-14:1998, ''Information technology ŌĆö 8-bit single-byte coded graphic character sets ŌĆö Part 14: Latin alphabet No. 8 ( Celtic)'', is part of the ISO/IEC 8859 series of ASCII-based standard character encodings, first edition published in 1998. It is informally referred to as Latin-8 or ''Celtic''. It was designed to cover the Celtic languages, such as Irish, Manx, Scottish Gaelic, Welsh, Cornish, and Breton. ISO-8859-14 is the IANA preferred charset name for this standard when supplemented with the C0 and C1 control codes from ISO/IEC 6429. CeltScript made an extension for Windows called Extended Latin-8. Microsoft has assigned code page 28604 a.k.a. Windows-28604 to ISO-8859-14. FreeDOS assigned code page 58163 to ISO-8859-14. History ISO-8859-14 was originally proposed for the Sami languages. ISO 8859-12 was proposed for Celtic. Later, ISO 8859-12 was proposed for Devanagari, so the Celtic proposal was changed to ISO 8859-14. The Sami proposal was changed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ISO 8859-9
ISO/IEC 8859-9:1999, ''Information technology ŌĆö 8-bit single-byte coded graphic character sets ŌĆö Part 9: Latin alphabet No. 5'', is part of the ISO/IEC 8859 series of ASCII-based standard character encodings, first edition published in 1989. It is designated ECMA-128 by Ecma International and TS 5881 as a Turkish standard. It is informally referred to as Latin-5 or ''Turkish''. It was designed to cover the Turkish language (and the vast majority of users use it for that language, even though it can also be used for some other languages), designed as being of more use than the ISO/IEC 8859-3 encoding. It is identical to ISO/IEC 8859-1 except for the replacement of six Icelandic characters ( ├É├░, ├Ø├Į, ├×├Š) with characters unique to the Turkish alphabet ( ─×─¤, ─░, ─▒, ┼×┼¤). And the uppercase of i is ─░; the lowercase of I is ─▒. ISO-8859-9 is the IANA preferred charset name for this standard when supplemented with the C0 and C1 control codes from ISO/IEC 642 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ISO 8859-3
ISO/IEC 8859-3:1999, ''Information technology ŌĆö 8-bit single-byte coded graphic character sets ŌĆö Part 3: Latin alphabet No. 3'', is part of the ISO/IEC 8859 series of ASCII-based standard character encodings, first edition published in 1988. It is informally referred to as Latin-3 or ''South European''. It was designed to cover Turkish, Maltese and Esperanto, though the introduction of ISO/IEC 8859-9 superseded it for Turkish. The encoding was popular for users of Esperanto, but fell out of use as application support for Unicode became more common. ISO-8859-3 is the IANA preferred charset name for this standard when supplemented with the C0 and C1 control codes from ISO/IEC 6429. Microsoft has assigned code page 28593 a.k.a. Windows-28593 to ISO-8859-3 in Windows. IBM has assigned code page 913 ( CCSID 913) to ISO 8859-3. Codepage layout Differences from ISO-8859-1 ISO/IEC 8859-1:1998, ''Information technologyŌĆö8-bit computing, 8-bit single-byte coded graphic c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ISO 8859-1
ISO/IEC 8859-1:1998, ''Information technologyŌĆö 8-bit single-byte coded graphic character setsŌĆöPart 1: Latin alphabet No. 1'', is part of the ISO/IEC 8859 series of ASCII-based standard character encodings, first edition published in 1987. ISO/IEC 8859-1 encodes what it refers to as "Latin alphabet no. 1", consisting of 191 characters from the Latin script. This character-encoding scheme is used throughout the Americas, Western Europe, Oceania, and much of Africa. It is the basis for some popular 8-bit character sets and the first two blocks of characters in Unicode. , 1.1% of all web sites use . It is the most declared single-byte character encoding, but as Web browsers and the HTML5 standard interpret them as the superset Windows-1252, these documents may include characters from that set. Some countries or languages show a higher usage than the global average, in 2025 Brazil according to website use, use is at 2.9%, and in Germany at 2.3%. ISO-8859-1 was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ISO 8859
ISO/IEC 8859 is a joint International Organization for Standardization, ISO and International Electrotechnical Commission, IEC series of standards for 8-bit character encodings. The series of standards consists of numbered parts, such as ISO/IEC 8859-1, ISO/IEC 8859-2, etc. There are 15 parts, excluding the abandoned ISO/IEC 8859-12. The ISO working group maintaining this series of standards has been disbanded. ISO/IEC 8859 parts 1, 2, 3, and 4 were originally Ecma International standard ECMA-94. Introduction While the bit patterns of the 95 graphic character, printable ASCII characters are sufficient to exchange information in modern English language, English, most other languages that use Latin script, Latin alphabets need additional symbols not covered by ASCII. ISO/IEC 8859 sought to remedy this problem by utilizing the eighth bit in an 8-bit byte to allow positions for another 96 printable characters. Early encodings were limited to 7 bits because of restrictions of som ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
EBCDIC
Extended Binary Coded Decimal Interchange Code (EBCDIC; ) is an eight- bit character encoding used mainly on IBM mainframe and IBM midrange computer operating systems. It descended from the code used with punched cards and the corresponding six-bit binary-coded decimal code used with most of IBM's computer peripherals of the late 1950s and early 1960s. It is supported by various non-IBM platforms, such as Fujitsu-Siemens' BS2000/OSD, OS-IV, MSP, and MSP-EX, the SDS Sigma series, Unisys VS/9, Unisys MCP and ICL VME. History EBCDIC was devised in 1963 and 1964 by IBM and was announced with the release of the IBM System/360 line of mainframe computers. It is an eight-bit character encoding, developed separately from the seven-bit ASCII encoding scheme. It was created to extend the existing Binary-Coded Decimal (BCD) Interchange Code, or BCDIC, which itself was devised as an efficient means of encoding the two ''zone'' and ''number'' punches on punched cards into six ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
People's Republic Of China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. With population of China, a population exceeding 1.4 billion, it is the list of countries by population (United Nations), second-most populous country after India, representing 17.4% of the world population. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and Borders of China, borders fourteen countries by land across an area of nearly , making it the list of countries and dependencies by area, third-largest country by land area. The country is divided into 33 Province-level divisions of China, province-level divisions: 22 provinces of China, provinces, 5 autonomous regions of China, autonomous regions, 4 direct-administered municipalities of China, municipalities, and 2 semi-autonomous special administrative regions. Beijing is the country's capital, while Shanghai is List of cities in China by population, its most populous city by urban area and largest financial center. Considered one of six ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Administrative Divisions Of The People's Republic Of China
The administrative divisions of China have consisted of several levels since 1412, due to mainland China's large population and geographical area. In the People's Republic of China, the constitution provides for three levels of government. However in practice, there are five levels of local government; the provincial (province, autonomous region, municipality, and special administrative region), prefecture, county, township, and village. Since the 17th century, provincial boundaries in mainland China have remained largely static. Major changes since then have been the reorganization of provinces in the northeast after the establishment of the People's Republic of China in 1949 and the formation of autonomous regions, based on Soviet ethnic policies. The provinces serve an important cultural role in China, as people tend to identify with their native province. Levels The Constitution of the People's Republic of China provides for three levels: the provincial, the county l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
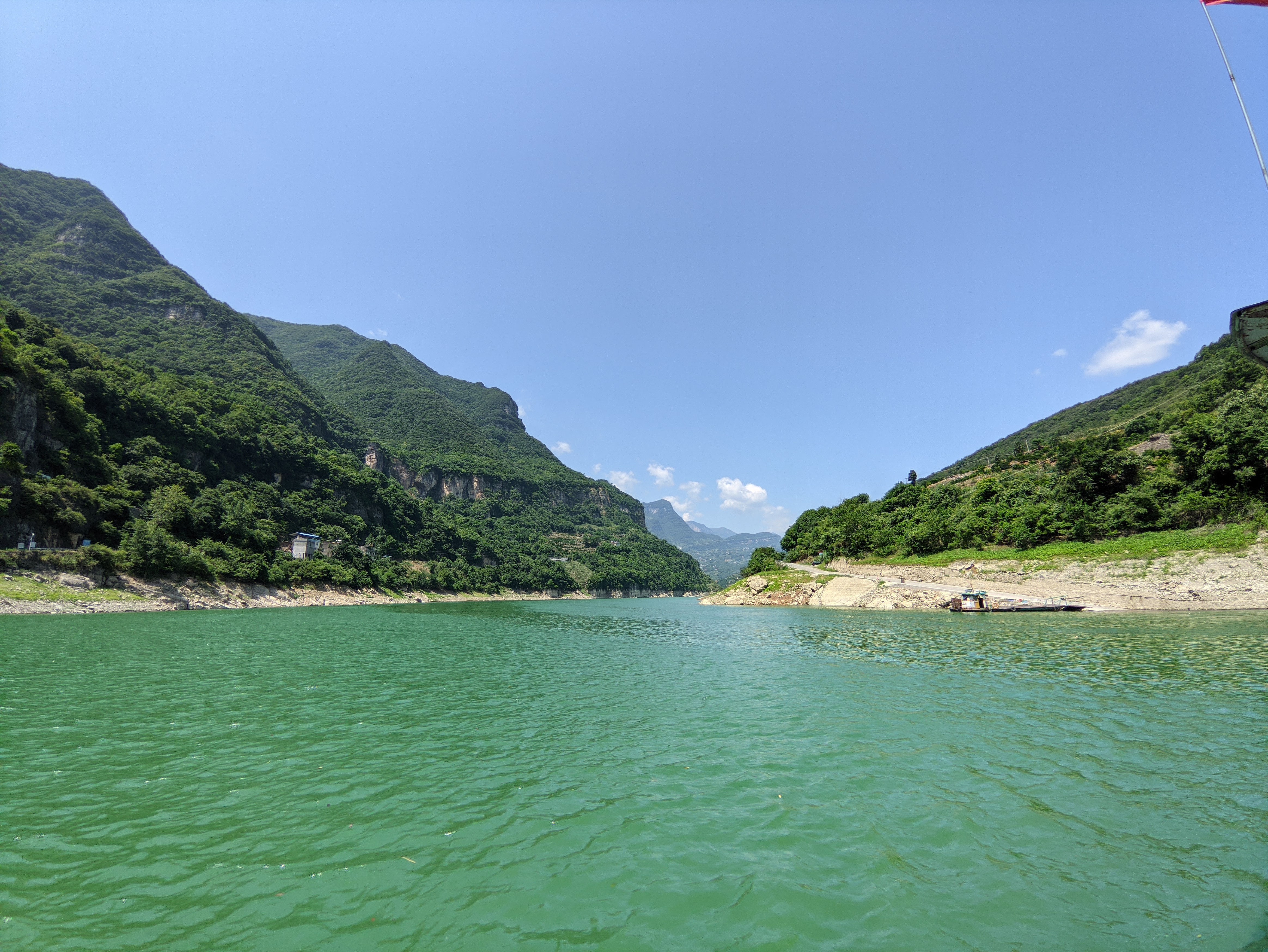
Hubei
Hubei is a province of China, province in Central China. It has the List of Chinese provincial-level divisions by GDP, seventh-largest economy among Chinese provinces, the second-largest within Central China, and the third-largest among inland provinces. Its provincial capital at Wuhan serves as a major political, cultural, and economic hub for the region. Hubei is associated with the historical state of E that existed during the Western Zhou dynasty (771 BCE). Its name means 'north of the lake', referring to Dongting Lake. It borders Henan to the north, Anhui and Jiangxi to the east, Hunan to the south, and Chongqing and Shaanxi to the west. The high-profile Three Gorges Dam is located at Yichang in the west of the province. History The Hubei region was home to sophisticated Neolithic cultures. By the Spring and Autumn period (770ŌĆō476 BC), the territory of today's Hubei formed part of the powerful Chu (state), State of Chu. Chu, nominally a tributary state of the Zh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Language
Chinese ( or ) is a group of languages spoken natively by the ethnic Han Chinese majority and List of ethnic groups in China, many minority ethnic groups in China, as well as by various communities of the Chinese diaspora. Approximately 1.39 billion people, or 17% of the global population, speak a variety of Chinese as their first language. Chinese languages form the Sinitic languages, Sinitic branch of the Sino-Tibetan language family. The spoken varieties of Chinese are usually considered by native speakers to be dialects of a single language. However, their lack of mutual intelligibility means they are sometimes considered to be separate languages in a Language family, family. Investigation of the historical relationships among the varieties of Chinese is ongoing. Currently, most classifications posit 7 to 13 main regional groups based on phonetic developments from Middle Chinese, of which the most spoken by far is Mandarin Chinese, Mandarin with 66%, or around 800&nb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |