|
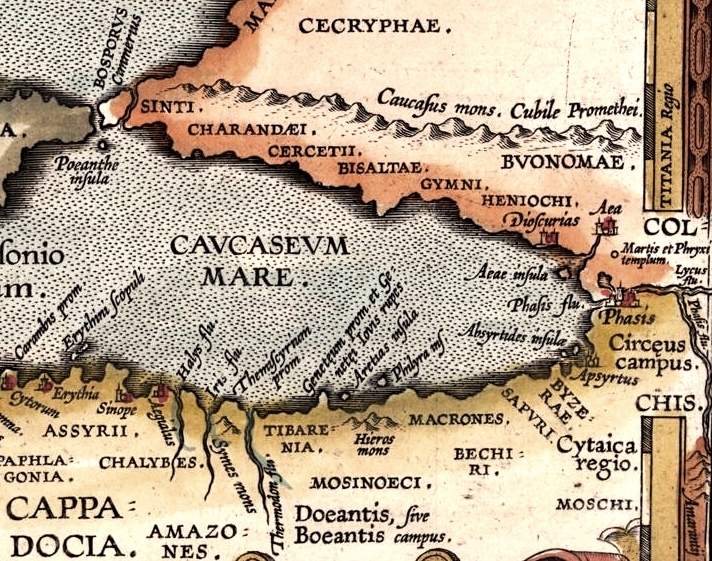
√áarŇüamba Plain
The √áarŇüamba Plain, the ancient Themiscyra Plain (; ''Themiskyra''), is a plain on the Black Sea coast of Turkey, formed largely of the delta of the YeŇüilńĪrmak river (ancient Iris), but also traversed by the much smaller Terme (ancient Thermodon) river. It is the largest delta plain on the Black Sea coast of Turkey. It lies within the districts of Tekkek√∂y, √áarŇüamba, Terme, and SalńĪpazarńĪ on the eastern part of the province of Samsun.Harun ReŇüit Bańüci, "YeŇüiŐálirmak Deltasi‚Äônda (√áarŇüamba/Samsun) Dońüal Ortam ńįnsan ńįliŐáŇükiŐáleriŐá Ve Dońüal √áevre Planlamasi", doctoral thesis, Ondokuz MayńĪs University (Samsun), October 2017 The town of Tekkek√∂y lies on the west end of the plain. √áarŇüamba lies in the middle, and is traversed by the YeŇüilńĪrmak. Terme (the ancient Themiscyra), on the east, is traversed by the Terme, as is SalńĪpazarńĪ in the south. The ancient plain has been described as:a rich and beautiful district, ever verdant... hatsuppl edfood ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kephale (Byzantine Empire)
In the late Byzantine Empire, the term ''kephale'' () was used to denote local and provincial governors. It entered use in the second half of the 13th century, and was derived from the colloquial language. Consequently, it never became an established title or rank of the Byzantine imperial hierarchy, but remained a descriptive term.. In essence, the ''kephalńď'' replaced the Komnenian-era '' doux'' as the civil and military governor of a territorial administrative unit, known as a ''katepanikion'' (őļőĪŌĄőĶŌÄőĪőĹőĮőļőĻőŅőĹ, ''katepan√≠kion''),Not to be confused with the very different katepanates of the 10th-11th centuries. but also termed a ''kephalatikion'' (őļőĶŌÜőĪőĽőĪŌĄőĮőļőĻőŅőĹ, ''kephalat√≠kion''). In size, these provinces were small compared to the earlier '' themata'', and could range from a few villages surrounding the ''kephales seat (a ''kastron'', "fortress"), to an entire island. This arrangement was also adopted by the Second Bulgarian Empire (as , ''kefaliya'') an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naturalis Historia
The ''Natural History'' () is a Latin work by Pliny the Elder. The largest single work to have survived from the Roman Empire to the modern day, the ''Natural History'' compiles information gleaned from other ancient authors. Despite the work's title, its subject area is not limited to what is today understood by natural history; Pliny himself defines his scope as "the natural world, or life". It is encyclopedic in scope, but its structure is not like that of a modern encyclopedia. It is the only work by Pliny to have survived, and the last that he published. He published the first 10 books in AD 77, but had not made a final revision of the remainder at the time of Pliny the Elder#Death, his death during the Eruption of Mount Vesuvius in 79 AD, AD 79 eruption of Vesuvius. The rest was published posthumously by Pliny's nephew, Pliny the Younger. The work is divided into 37 books, organised into 10 volumes. These cover topics including astronomy, mathematics, geography, ethn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pliny The Elder
Gaius Plinius Secundus (AD 23/24 79), known in English as Pliny the Elder ( ), was a Roman Empire, Roman author, Natural history, naturalist, and naval and army commander of the early Roman Empire, and a friend of the Roman emperor, emperor Vespasian. He wrote the encyclopedic (''Natural History''), a comprehensive thirty-seven-volume work covering a vast array of topics on human knowledge and the natural world, which became an editorial model for encyclopedias. He spent most of his spare time studying, writing, and investigating natural and geographic phenomena in the field. Among Pliny's greatest works was the twenty-volume ''Bella Germaniae'' ("The History of the German Wars"), which is Lost literary work, no longer extant. ''Bella Germaniae'', which began where Aufidius Bassus' ''Libri Belli Germanici'' ("The War with the Germans") left off, was used as a source by other prominent Roman historians, including Plutarch, Tacitus, and Suetonius. Tacitus may have used ''Bella Ger ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apollonius Of Rhodes
Apollonius of Rhodes ( ''ApollŠĻďnios Rh√≥dios''; ; fl. first half of 3rd century BC) was an ancient Greek literature, ancient Greek author, best known for the ''Argonautica'', an epic poem about Jason and the Argonauts and their quest for the Golden Fleece. The poem is one of the few extant examples of the epic genre and it was both innovative and influential, providing Ptolemaic Egypt with a "cultural mnemonic" or national "archive of images", and offering the Latin poets Virgil and Gaius Valerius Flaccus a model for their own epics. His other poems, which survive only in small fragments, concerned the beginnings or foundations of cities, such as Alexandria and Cnidus places of interest to the Ptolemies, whom he served as a scholar and librarian at the Library of Alexandria. A literary dispute with Callimachus, another Alexandrian librarian/poet, is a topic much discussed by modern scholars since it is thought to give some insight into their poetry, although there is very little ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bibliotheca (Pseudo-Apollodorus)
The ''Bibliotheca'' (Ancient Greek: ), is a compendium of Greek mythology, Greek myths and heroic legends, genealogical tables and histories arranged in three books, generally dated to the first or second century AD. The work is commonly described as having been written by Apollodorus (or sometimes Pseudo-Apollodorus), a result of its false attribution to the 2nd-century BC scholar Apollodorus of Athens. Overview The ''Bibliotheca'' of Pseudo-Apollodorus is a comprehensive collection of myths, genealogies and histories that presents a continuous history of Greek mythology from the earliest gods and the origin of the world to the death of Odysseus.. The narratives are organized by genealogy, chronology and geography in summaries of myth. The myths are sourced from a wide number of sources like early epic, early Hellenistic poets, and mythographical summaries of tales. Homer and Hesiod are the most frequently named along with other poets.Kenens, Ulrike. 2011. "The Sources of Ps.-A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aeschylus
Aeschylus (, ; ; /524 ‚Äď /455 BC) was an ancient Greece, ancient Greek Greek tragedy, tragedian often described as the father of tragedy. Academic knowledge of the genre begins with his work, and understanding of earlier Greek tragedy is largely based on inferences made from reading his surviving plays. According to Aristotle, he expanded the number of characters in the theatre and allowed conflict among them. Formerly, characters interacted only with the Greek chorus, chorus.The remnant of a commemorative inscription, dated to the 3rd century BC, lists four, possibly eight, dramatic poets (probably including Choerilus, Phrynichus, and Pratinas) who had won Dionysia#Known winners of the City Dionysia, tragic victories at the Dionysia before Aeschylus had. Thespis was traditionally regarded the inventor of tragedy. According to another tradition, tragedy was established in Athens in the late 530s BC, but that may simply reflect an absence of records. Major innovations in dramatic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
√únye
√únye (''Oin√≤e'', őüŠľįőĹŌĆő∑ in ancient Greek) is a municipality and district of Ordu Province, Turkey. Its area is 569 km2, and its population is 132,432 (2022). It is on the Black Sea coast, 76 km west of the city of Ordu. Geography √únye has a little port, in a bay on one of the flatter areas of the Black Sea coast. Agriculture is the basis of the local economy, in particular hazelnut growing, hazelnut trading and hazelnut processing. The town is very quiet in late-July and August when most people are in the countryside for the hazelnut harvest. The town of √únye provides high schools, higher education and other services to the surrounding countryside, and other industry includes a large cement factory, flour mills, local handicrafts and the port. The town has grown in recent decades, acquiring the multi-storey concrete blocks spreading along the coast, typical of so many Turkish towns. There are cafes and internet cafes popular with students. The cuisine includes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chalybia
The Chalybes (; ; ka, ŠÉģŠÉźŠÉöŠÉėŠÉĎŠÉĒŠÉĎŠÉė, Khalibebi) and Chaldoi (; ) were peoples mentioned by classical authors as living in Pontus and Cappadocia in northern Anatolia during Classical Antiquity. Their territory was known as Chaldia, extending from the Halys River to Pharnakeia and Trabzon in the east and as far south as eastern Anatolia. According to Apollonius of Rhodes, the Chalybes were Scythians. The Chaldoi, Chalybes, '' Mossynoikoi'', and ''Tibareni'', are counted among the first ironsmith nations by classical authors. , the tribe's name in Ancient Greek, means "tempered iron, steel", a term that passed into Latin as , "steel". Sayce derived the Greek name from Hittite , "land of Halys River". More than an identifiable people or tribe, "Chalybes" was a generic Greek term for "peoples of the Black Sea coast who trade in iron" or "a group of specialised metalworkers". The main sources for the history of the Chaldoi are accounts from classical authors, including ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PerŇüembe
PerŇüembe (originated from Persian word meaning "Thursday"), also Heneti ( Laz and ka, ŠÉįŠÉĒŠÉúŠÉĒŠÉóŠÉė) and formerly Vona (), is a municipality and district of Ordu Province, Turkey. Its area is 217 km2, and its population is 30,101 (2022). The town lies on the Black Sea coast at an elevation of . Legend and history PerŇüembe is on the Vona Peninsula on the Black Sea coast and is held to be the point where the legendary Jason and the Argonauts were forced to land during their struggle with the storms and currents of the Black Sea. For a long time Vona was part of the Roman Empire and its successors the Byzantine Empire and Empire of Trebizond. This era ended in 1461 when Trebizond was overturned by Sultan Mehmet II and Vona was brought into the Ottoman Empire, although there was a Turkish (Chepni Tribes) community in the town before this date. By 1520 the port of Vona was a predominantly Muslim town. Composition There are 54 neighbourhoods A neighbourhood (Com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Çam Burnu
√áam (pronounced ''Cham'') may refer to: People * Gizem √áam (born 1991), Turkish swimmer * Serdar √áam (born 1966), Turkish bureaucrat * Sibel √áam (born 1990), Turkish Paralympian powerlifter Places * √áam, Kuk√ęs, a village in the municipality of Kuk√ęs, Albania * √áam, Akyurt, a neighbourhood in Ankara Province, Turkey See also * Cham (other) * Cam (other) {{Disambiguation, surname ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |