|
(E)-4-Hydroxy-3-methyl-but-2-enyl Pyrophosphate
(''E'')-4-Hydroxy-3-methyl-but-2-enyl pyrophosphate (HMBPP or HMB-PP) is an intermediate of the MEP pathway (non-mevalonate pathway) of isoprenoid biosynthesis. The enzyme HMB-PP synthase (GcpE, IspG) catalyzes the conversion of 2-''C''-methyl-D-erythritol 2,4-cyclodiphosphate (MEcPP) into HMB-PP. HMB-PP is then converted further to isopentenyl pyrophosphate (IPP) and dimethylallyl pyrophosphate (DMAPP) by HMB-PP reductase (LytB, IspH). HMB-PP is an essential metabolite in most pathogenic bacteria including '' Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' as well as in malaria parasites, but is absent from the human host. HMB-PP is the physiological activator (" phosphoantigen") for human Vγ9/Vδ2 T cells, the major γδ T cell population in peripheral blood. With a bioactivity of 0.1 nM it is 10,000-10,000,000 times more potent than any other natural compound, such as IPP or alkyl amines. HMB-PP functions in this capacity by binding the B30.2 domain of BTN3A1 Butyrophilin subfamily 3 mem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Non-mevalonate Pathway
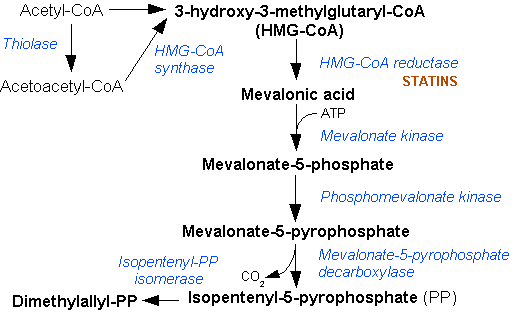
The non-mevalonate pathway—also appearing as the mevalonate-independent pathway and the 2-''C''-methyl-D-erythritol 4-phosphate/1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate (MEP/DOXP) pathway—is an alternative metabolic pathway for the biosynthesis of the isoprenoid precursors isopentenyl pyrophosphate (IPP) and dimethylallyl pyrophosphate (DMAPP). The currently preferred name for this pathway is the MEP pathway, since MEP is the first committed metabolite on the route to IPP. Isoprenoid precursor biosynthesis The classical mevalonate pathway (MVA pathway or HMG-CoA reductase pathway) is a metabolic pathway for the biosynthesis of isoprenoid precursors: IPP and DMAPP. The MVA pathway is present in most eukaryotes and some bacteria. IPP and DMAPP serve as the basis for the biosynthesis of isoprenoid (terpenoid) molecules used in processes as diverse as protein prenylation, cell membrane maintenance, the synthesis of hormones, protein anchoring and ''N''-glycosylation in all three domain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
4-hydroxy-3-methylbut-2-en-1-yl Diphosphate Synthase
In enzymology, a 4-hydroxy-3-methylbut-2-en-1-yl diphosphate synthase (HMB-PP synthase, IspG, ) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction :2-C-methyl-D-erythritol 2,4-cyclodiphosphate + protein-dithiol \rightleftharpoons (E)-4-hydroxy-3-methylbut-2-en-1-yl diphosphate + H2O + protein-disulfide The substrate of this enzyme is 2-C-methyl-D-erythritol 2,4-cyclodiphosphate (MEcPP) and the product is (E)-4-hydroxy-3-methylbut-2-en-1-yl diphosphate (HMB-PP). Electrons are donated by two reduced ferredoxin proteins per reaction. This enzyme participates in the MEP pathway (non-mevalonate pathway) of Isoprenoid precursor biosynthesis. Nomenclature This enzyme belongs to the family of oxidoreductases, specifically those acting on CH or CH2 groups with a disulfide as acceptor. The systematic name A systematic name is a name given in a systematic way to one unique group, organism, object or chemical substance, out of a specific population or collection. Systematic names are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2-C-Methyl-D-erythritol-2,4-cyclopyrophosphate
2-''C''-Methyl--erythritol-2,4-cyclopyrophosphate (MEcPP) (also ''2-C-Methyl--erythritol-2,4-cyclodiphosphate'') is an intermediate in the MEP pathway (non-mevalonate) of isoprenoid precursor biosynthesis. MEcPP is produced by MEcPP synthase (IspF) and is a substrate for HMB-PP synthase (IspG). Under conditions of oxidative stress, MEcPP accumulates in certain bacteria. MEcPP releases histone-like proteins from DNA, triggering nucleoid decondensation in ''Chlamydia trachomatis'' during the process of terminal differentiation. Abiotic stresses to plants, including wounding and excessive high-light exposure, lead to an increase in MEcPP accumulation in chloroplasts. Transported from the chloroplast to the plant cell nucleus Nucleus ( : nuclei) is a Latin word for the seed inside a fruit. It most often refers to: *Atomic nucleus, the very dense central region of an atom * Cell nucleus, a central organelle of a eukaryotic cell, containing most of the cell's DNA Nucl ..., MEcPP ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isopentenyl Pyrophosphate
Isopentenyl pyrophosphate (IPP, isopentenyl diphosphate, or IDP) is an isoprenoid precursor. IPP is an intermediate in the classical, HMG-CoA reductase pathway (commonly called the mevalonate pathway) and in the ''non-mevalonate'' MEP pathway of isoprenoid precursor biosynthesis. Isoprenoid precursors such as IPP, and its isomer DMAPP, are used by organisms in the biosynthesis of terpenes and terpenoids. Biosynthesis IPP is formed from acetyl-CoA via the mevalonate pathway (the "upstream" part), and then is isomerized to dimethylallyl pyrophosphate by the enzyme isopentenyl pyrophosphate isomerase. IPP can be synthesised via an alternative non-mevalonate pathway of isoprenoid precursor biosynthesis, the MEP pathway, where it is formed from (''E'')-4-hydroxy-3-methyl-but-2-enyl pyrophosphate (HMB-PP) by the enzyme HMB-PP reductase (LytB, IspH). The MEP pathway is present in many bacteria, apicomplexan protozoa such as malaria parasites, and in the plastids of higher plan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dimethylallyl Pyrophosphate
Dimethylallyl pyrophosphate (DMAPP; or alternatively, dimethylallyl diphosphate (DMADP); also isoprenyl pyrophosphate) is an isoprenoid precursor. It is a product of both the mevalonate pathway and the MEP pathway of isoprenoid precursor biosynthesis. It is an isomer of isopentenyl pyrophosphate (IPP) and exists in virtually all life forms. The enzyme isopentenyl pyrophosphate isomerase catalyzes isomerization between DMAPP and IPP. In the mevalonate pathway DMAPP is synthesised from mevalonic acid. In contrast, DMAPP is synthesised from HMBPP in the MEP pathway The non-mevalonate pathway—also appearing as the mevalonate-independent pathway and the 2-''C''-methyl-D-erythritol 4-phosphate/1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate (MEP/DOXP) pathway—is an alternative metabolic pathway for the biosynthesis of the is .... At present, it is believed that there is crossover between the two pathways in organisms that use both pathways to create terpenes and terpenoids, such as in plants ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
4-Hydroxy-3-methylbut-2-enyl Diphosphate Reductase
4-Hydroxy-3-methylbut-2-enyl diphosphate reductase (, ''isopentenyl-diphosphate:NADP+ oxidoreductase'', ''LytB'', ''(E)-4-hydroxy-3-methylbut-2-en-1-yl diphosphate reductase'', ''HMBPP reductase'', ''IspH'', ''LytB/IspH'') is an enzyme in the non-mevalonate pathway. It acts upon (E)-4-Hydroxy-3-methyl-but-2-enyl pyrophosphate (or "HMB-PP"). : (1) isopentenyl diphosphate + NAD(P)+ + H2O \rightleftharpoons (E)-4-hydroxy-3-methylbut-2-en-1-yl diphosphate + NAD(P)H + H+ : (2) dimethylallyl diphosphate + NAD(P)+ + H2O \rightleftharpoons (E)-4-hydroxy-3-methylbut-2-en-1-yl diphosphate + NAD(P)H + H+ 4-Hydroxy-3-methylbut-2-enyl diphosphate reductase is an iron-sulfur Sulfur (or sulphur in British English) is a chemical element with the symbol S and atomic number 16. It is abundant, multivalent and nonmetallic. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms form cyclic octatomic molecules with a chemical formul ... protein that contains either a Fe-4Sor a Fe-4Scluster. References ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mycobacterium Tuberculosis
''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (M. tb) is a species of pathogenic bacteria in the family Mycobacteriaceae and the causative agent of tuberculosis. First discovered in 1882 by Robert Koch, ''M. tuberculosis'' has an unusual, waxy coating on its cell surface primarily due to the presence of mycolic acid. This coating makes the cells impervious to Gram staining, and as a result, ''M. tuberculosis'' can appear weakly Gram-positive. Acid-fastness, Acid-fast stains such as Ziehl–Neelsen stain, Ziehl–Neelsen, or Fluorescence, fluorescent stains such as Auramine O, auramine are used instead to identify ''M. tuberculosis'' with a microscope. The physiology of ''M. tuberculosis'' is highly aerobic organism, aerobic and requires high levels of oxygen. Primarily a pathogen of the mammalian respiratory system, it infects the lungs. The most frequently used diagnostic methods for tuberculosis are the Mantoux test, tuberculin skin test, Acid-Fast Stain, acid-fast stain, Microbiological cultu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malaria
Malaria is a mosquito-borne infectious disease that affects humans and other animals. Malaria causes symptoms that typically include fever, tiredness, vomiting, and headaches. In severe cases, it can cause jaundice, seizures, coma, or death. Symptoms usually begin ten to fifteen days after being bitten by an infected mosquito. If not properly treated, people may have recurrences of the disease months later. In those who have recently survived an infection, reinfection usually causes milder symptoms. This partial resistance disappears over months to years if the person has no continuing exposure to malaria. Malaria is caused by single-celled microorganisms of the '' Plasmodium'' group. It is spread exclusively through bites of infected '' Anopheles'' mosquitoes. The mosquito bite introduces the parasites from the mosquito's saliva into a person's blood. The parasites travel to the liver where they mature and reproduce. Five species of ''Plasmodium'' can infect and be spr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphoantigen
Non-peptidic antigens are low-molecular-weight compounds that stimulate human Vγ9/Vδ2 T cells. The most potent activator for Vγ9/Vδ2 T cells is (''E'')-4-hydroxy-3-methyl-but-2-enyl pyrophosphate ( HMB-PP), a natural intermediate of the non-mevalonate pathway of isopentenyl pyrophosphate (IPP) biosynthesis. HMB-PP is an essential metabolite in most pathogenic bacteria including '' Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' as well as in malaria parasites, but is absent from the human host. IPP itself is structurally closely related to HMB-PP and ubiquitously present in all living cells (i.e., also in human cells), yet its potency ''in vitro'' is 10,000-fold reduced; whether IPP represents a physiological 'danger' signal of stressed or transformed cells is still unclear. Of pharmacological interest and with bioactivities comparable to that of IPP are synthetic aminobisphosphonates such as zoledronate (Zometa) that are widely used to treat osteoporosis and bone metastases, and act as V� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vg9/Vd2 T Cells
Gamma delta T cells (γδ T cells) are T cells that have a γδ T-cell receptor (TCR) on their surface. Most T cells are αβ (alpha beta) T cells with TCR composed of two glycoprotein chains called α (alpha) and β (beta) TCR chains. In contrast, γδ T cells have a TCR that is made up of one γ (gamma) chain and one δ (delta) chain. This group of T cells is usually less common than αβ T cells, but are at their highest abundance in the gut mucosa, within a population of lymphocytes known as intraepithelial lymphocytes (IELs). The antigenic molecules that activate gamma delta T cells are still largely unknown. However, γδ T cells are peculiar in that they do not seem to require antigen processing and major-histocompatibility-complex (MHC) presentation of peptide epitopes, although some recognize MHC class Ib molecules. γδ T cells are believed to have a prominent role in recognition of lipid antigens. They are of an invariant nature and may be triggered by alarm signals, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Non-peptidic Antigen
Non-peptidic antigens are low-molecular-weight compounds that stimulate human Vγ9/Vδ2 T cells. The most potent activator for Vγ9/Vδ2 T cells is (''E'')-4-hydroxy-3-methyl-but-2-enyl pyrophosphate ( HMB-PP), a natural intermediate of the non-mevalonate pathway of isopentenyl pyrophosphate (IPP) biosynthesis. HMB-PP is an essential metabolite in most pathogenic bacteria including '' Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' as well as in malaria parasites, but is absent from the human host. IPP itself is structurally closely related to HMB-PP and ubiquitously present in all living cells (i.e., also in human cells), yet its potency ''in vitro'' is 10,000-fold reduced; whether IPP represents a physiological 'danger' signal of stressed or transformed cells is still unclear. Of pharmacological interest and with bioactivities comparable to that of IPP are synthetic aminobisphosphonates such as zoledronate (Zometa) that are widely used to treat osteoporosis and bone metastases, and act as V� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |