|
'Umar Ibn Hafs Al-Muhallabi
Umar ibn Hafs Hazarmard () (d. November 27, 771) was a member of the Muhallabid family who served as a provincial governor for the Abbasid Caliphate during the reigns of Abu al-'Abbas (r. 749–754) al-Mansur (r. 754–775). His appointment to Ifriqiya in 768 marked the beginning of nearly three decades of Muhallabid rule there, but he was unable to maintain order in the province and was killed during a major Kharijite rebellion. Career 'Umar was a supporter of the Abbasid Revolution and fought during the Siege of Wasit. Following the Abbasid victory against the Umayyads, he was appointed to a number of governorships. Under Abu al-'Abbas he was governor of al-Basrah until 750 and was subsequently appointed to al-Bahrayn. Following the ascension of al-Mansur, he was appointed twice more to al-Basrah, from 755 to 757 and from 759 to 760. In 760 'Umar was appointed to al-Sind, which was under the control of 'Uyaynah ibn Musa al-Tamimi. When the latter refused to relinquish h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muhallabid
The Muhallabids () or the Muhallabid dynasty were an Arab family who became prominent in the middle Umayyad Caliphate and reached its greatest eminence during the early Abbasids, when members of the family ruled Basra and Ifriqiya. The founders of the family's fortunes were al-Muhallab ibn Abi Sufra (c. 632 – 702) and his son Yazid ibn al-Muhallab (672–720), governor of Khurasan and Iraq, who led an unsuccessful anti-Umayyad rebellion in Basra in 720. Despite his defeat and death, the family remained influential in their power base of Basra, and at the time of the Abbasid Revolution they rose up in their support. Despite the support of some Muhallabids to the abortive Alid revolt of Muhammad al-Nafs al-Zakiyya, the new Abbasid regime rewarded their support with governorships at Basra and the Ahwaz, but most prominently in Ifriqiya, where the family ruled in uninterrupted succession from 768 to 795. Ifriqiya under their rule enjoyed a period of prosperity, above all agriculture ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Habib Ibn Habib Al-Muhallabi
Habib (; ; also romanized as Habeeb) is an Arabic masculine given name, occasional surname, and honorific, with the meaning "beloved" or "my love", or "darling". It also forms the famous Arabic word ''"Habibi"'' which is used to refer to a friend or a significant other in the aspect of love or admiration''.'' The name is popular throughout the Muslim World, though particularly in the Middle East and Africa. In other countries, especially in the Hadhramaut region of Yemen and Southeast Asian countries such as Brunei, Singapore, Indonesia and Malaysia, it is an honorific to address a Muslim scholar of ''Sayyid'' descent and where it is one of the names of the Islamic prophet Muhammad – حبيب الله '' Habib Allah'' (Habibullah/ Habiballah) - "Most Beloved of Allah (God)". The name, as is the case with other Arabic names, is not only confined to Muslims. Notable examples of Christian individuals named Habib include Habib the Deacon, Gabriel Habib and the Philosopher Habib ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
771 Deaths
__NOTOC__ The year 771 ( DCCLXXI) was a common year starting on Tuesday of the Julian calendar. The denomination 771 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Europe * December 4 – King Carloman I, youngest son of Pepin III ("the Short"), dies (of a severe nosebleed, according to one source)"Cathwulf, Kingship, and the Royal Abbey of Saint-Denis", by Joanna Story, ''Speculum'' at the Villa of Samoussy, leaving his brother Charlemagne sole ruler of the now reunified Frankish Kingdom. Gerberga, the widow of Carloman, flees with her two sons to the court of King Desiderius of the Lombards, at Pavia. * Charlemagne repudiates his Lombard wife Desiderata, daughter of Desiderius, after one year of marriage. He marries the 13-year-old Swabian girl Hildegard, who will bear him nine children. Desiderius, furious at Charlemagne, plans a punitive cam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hisham Ibn 'Amr Al-Taghlibi
Hisham ibn Abd al-Malik ibn Marwan (; 6 February 743) was the tenth Umayyad caliph, ruling from 724 until his death in 743. Early life Hisham was born in Damascus, the administrative capital of the Umayyad Caliphate, in AH 72 (691–692 CE). His father was the Umayyad caliph Abd al-Malik (). His mother, A'isha, was a daughter of Hisham ibn Isma'il of the Banu Makhzum, a prominent family of the Quraysh, and Abd al-Malik's longtime governor of the Islamic holy cities of Mecca and Medina. According to the history of al-Tabari (d. 923), Hisham was given the '' kunya'' (patronymic) of Abu al-Walid. There is little information about Hisham's early life. He was too young to play any political or military role during his father's reign. He supposedly led the Hajj pilgrimage to Mecca once during his brother al-Walid I's reign () and while there, met a respected descendant of Caliph Ali (), Zayn al-Abidin. Hisham is credited by al-Tabari for leading an expedition against the Byzantines ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Caliphal Governors Of Sind
Sind (, Urdu & ) was an administrative division of the Umayyad Caliphate and later of the Abbasid Caliphate in post-classical India, from around 711 CE with the Umayyad conquest of Sindh by the Arab military commander Muhammad ibn al-Qasim, to around 854 CE with the emergence of the independent dynasties of the Habbarid Emirate in Sindh proper and the Emirate of Multan in Punjab. The "Governor of Sind" () was an official who administered the caliphal province over what are now Sindh, southern Punjab and Makran (Balochistan) in Pakistan. The governor was the chief Muslim official in the province and was responsible for maintaining security in the region. As the leader of the provincial military, he was also in charge of carrying out campaigns against the non-Muslim kingdoms of India. Governors appointed to the region were selected either directly by the caliph or by an authorized subordinate, and remained in office until they either died or were dismissed. Geography Sind wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tunis
Tunis (, ') is the capital city, capital and largest city of Tunisia. The greater metropolitan area of Tunis, often referred to as "Grand Tunis", has about 2,700,000 inhabitants. , it is the third-largest city in the Maghreb region (after Casablanca and Algiers) and the List of largest cities in the Arab world, eleventh-largest in the Arab world. Situated on the Gulf of Tunis, behind the Lake of Tunis and the port of La Goulette (Ḥalq il-Wād), the city extends along the coastal plain and the hills that surround it. At its core lies the Medina of Tunis, Medina, a World Heritage Site. East of the Medina, through the Sea Gate (also known as the ''Bab el Bhar'' and the ''Porte de France''), begins the modern part of the city called "Ville Nouvelle", traversed by the grand Avenue Habib Bourguiba (often referred to by media and travel guides as "the Tunisian Champs-Élysées"), where the colonial-era buildings provide a clear contrast to smaller, older structures. Further east by th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rustamids
The Rustamid dynasty () (or ''Rustumids'', ''Rostemids'') was an Ibadi dynasty of Persian origin which ruled a state that was centered in present-day Algeria. The dynasty governed as a Muslim theocracy for a century and a half from its capital Tahert (present day Tagdemt) until the Ismaili Fatimid Caliphate defeated it. Rustamid authority extended over what is now central and western Algeria, parts of southern Tunisia, and the Jebel Nafusa and Fezzan regions in Libya as far as Zawila. History The Ibāḍī movement reached North Africa by 719, when the missionary Salma ibn Sa'd was sent from the Ibādī ''jama'a'' of Basra to Kairouan. By 740, their efforts had converted the major Berber tribes of Huwara around Tripoli, in the Nafusa Mountains and at Zenata in western Tripolitania. In 757 (140 AH), a group of four Basra-educated missionaries including ʻAbd ar-Rahmān ibn Rustam proclaimed an Ibāḍī imamate in Tripolitania, starting an abortive state led by Abu l-Kha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abu Qurra
Abu Qurra () a member of the Sufrite tribe Banu Ifran of Tlemcen, was the founder of the indigenous Berber Muslim movement with Kharijite tendencies in North Africa after the overthrow of the Umayyad dynasty. Between 767 and 776, Abu Qurra organised an army of more than 350,000 riders in the north of Africa. He was the first head of state of the Berber Muslim Maghreb. Ibn Khaldun Ibn Khaldun (27 May 1332 – 17 March 1406, 732–808 Hijri year, AH) was an Arabs, Arab Islamic scholar, historian, philosopher and sociologist. He is widely acknowledged to be one of the greatest social scientists of the Middle Ages, and cons ... described him in his book ''Kitab El Ibar''. Abu Qurra is known as the founder of Tlemcen during his reign on the Sufri kingdom (776-778). References 8th-century Berber people Berber monarchs Berber Muslims Kharijites Ifranid dynasty 8th-century monarchs in Africa {{Algeria-bio-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sufri
The Sufris ( ''aṣ-Ṣufriyya'') were Khariji Muslims in the seventh and eighth centuries. They established the Midrarid state at Sijilmassa, now in Morocco. In Tlemcen, Algeria, the Banu Ifran were Sufri Berbers who opposed rule by the Umayyad, Abbasid and Fatimid Caliphates, most notably under resistance movements led by Abu Qurra (8th century) and Abu Yazid. The Khawarij were divided into separate groups such as the Sufri, Azariqa, Bayhasiyya, Ajardi, Najdat, and Ibadi. The Sufri and Ibadi sects are considered the most moderate of the Kharijite groups due to their refusal to shed the blood of those who disagree with them. Of all the Kharijite sects, only the Ibadi Ibadism (, ) is a school of Islam concentrated in Oman established from within the Kharijites. The followers of the Ibadi sect are known as the Ibadis or, as they call themselves, The People of Truth and Integrity (). Ibadism emerged around 6 ... sect continues to exist today. According to an Ibadi webs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
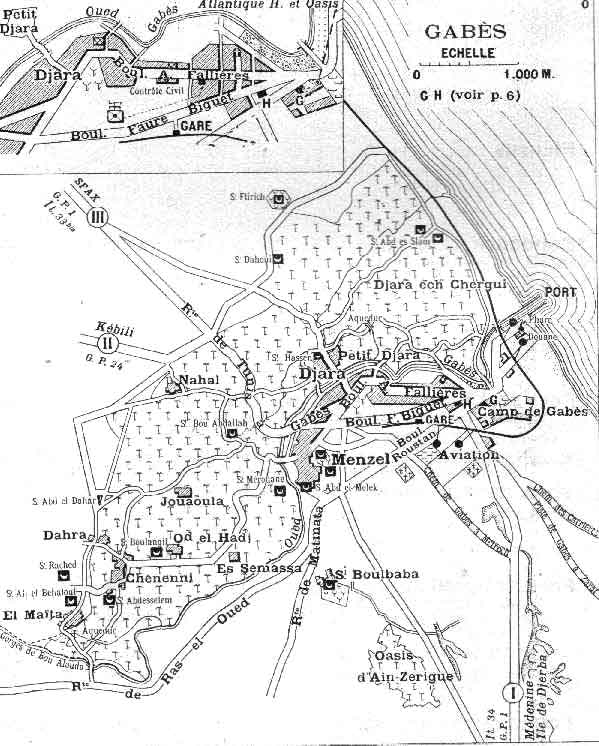
Gabès
Gabès (, ; ), also spelled Cabès, Cabes, and Kabes, is the capital of the Gabès Governorate in Tunisia. Situated on the coast of the Gulf of Gabès, the city has a population of 167,863, making it the 6th largest city in Tunisia. Located 327 km southeast of Tunis and 113 km from Sfax, Gabès lies at the delta of the Wadi Qabis, which originates 10 kilometers upstream at Ras El Oued, Algeria, Ras al-Oued and serves as its primary water source. Historically, the town was a Ancient Carthage, Carthaginian settlement known as Tacapae before falling under Roman Empire, Roman control. It was later ruined during the 7th-century Arab invasion but was recovered by Sidi Boulbaba, a revered companion of the Muhammad, Prophet Muhammad and a patron of the town. Although it experienced decline under the Ottoman Empire, Ottomans, Gabès saw significant growth under French rule from 1881 to 1955, with the development of key infrastructure, including a railway, road network, and port. During ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abu Hatim Ya'qub Ibn Habib Al-Ibadi
Abu or ABU may refer to: Aviation * Airman Battle Uniform, a utility uniform of the United States Air Force * IATA airport code for A. A. Bere Tallo Airport in Atambua, Province of East Nusa Tenggara, Indonesia People * Abu (Arabic term), a kunya when written in the construct state * Ab (Semitic), a common part of Arabic-derived names, meaning "father of" in Arabic * Abu al-Faraj (other) * Abu Baker Asvat, a murdered South African activist and medical doctor * Abu Ibrahim (other) * Abu Mohammed (other) * Abu Salim (other) *Abdul-Malik Abu (born 1995), American basketball player in the Israeli Premier Basketball League * Raneo Abu, Filipino politician Places * Abu (volcano), a volcano on the island of Honshū in Japan * Abu, Yamaguchi, a town in Japan * Ahmadu Bello University, a university located in Zaria, Nigeria * Atlantic Baptist University, a Christian university located in Moncton, New Brunswick, Canada * Elephantine, Egypt, known as Abu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |