Tycho Brahe on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Tycho Brahe ( ; born Tyge Ottesen Brahe; generally called Tycho (14 December 154624 October 1601) was a Danish
 On 11 November 1572, Tycho observed (from Herrevad Abbey) a very bright star, now numbered SN 1572, which had unexpectedly appeared in the constellation Cassiopeia. Because it had been maintained since
On 11 November 1572, Tycho observed (from Herrevad Abbey) a very bright star, now numbered SN 1572, which had unexpectedly appeared in the constellation Cassiopeia. Because it had been maintained since
 He observed the great comet that was visible in the Northern sky from November 1577 to January 1578. Within Lutheranism, it was commonly believed that celestial objects like comets were powerful portents, announcing the coming apocalypse, and in addition to Tycho's observations several Danish amateur astronomers observed the object and published prophesies of impending doom. He was able to determine that the comet's distance to Earth was much greater than the distance of the Moon, so that the comet could not have originated in the "earthly sphere", confirming his prior anti-Aristotelian conclusions about the fixed nature of the sky beyond the Moon. He also realized that the comet's
He observed the great comet that was visible in the Northern sky from November 1577 to January 1578. Within Lutheranism, it was commonly believed that celestial objects like comets were powerful portents, announcing the coming apocalypse, and in addition to Tycho's observations several Danish amateur astronomers observed the object and published prophesies of impending doom. He was able to determine that the comet's distance to Earth was much greater than the distance of the Moon, so that the comet could not have originated in the "earthly sphere", confirming his prior anti-Aristotelian conclusions about the fixed nature of the sky beyond the Moon. He also realized that the comet's
 In 1588, Tycho's royal benefactor died, and a volume of Tycho's great two-volume work ''Astronomiae Instauratae Progymnasmata'' (''Introduction to the New Astronomy'') was published. The first volume, devoted to the new star of 1572, was not ready, because the reduction of the observations of 1572–73 involved much research to correct the stars' positions for
In 1588, Tycho's royal benefactor died, and a volume of Tycho's great two-volume work ''Astronomiae Instauratae Progymnasmata'' (''Introduction to the New Astronomy'') was published. The first volume, devoted to the new star of 1572, was not ready, because the reduction of the observations of 1572–73 involved much research to correct the stars' positions for
burst bladder
prostatic hypertrophy, acute prostatitis, or
 Tycho's view of science was driven by his passion for accurate observations, and the quest for improved instruments of measurement drove his life's work. Tycho was the last major astronomer to work without the aid of a
Tycho's view of science was driven by his passion for accurate observations, and the quest for improved instruments of measurement drove his life's work. Tycho was the last major astronomer to work without the aid of a
 Although Tycho admired Copernicus and was the first to teach his theory in Denmark, he was unable to reconcile Copernican theory with the basic laws of Aristotelian physics, which he believed to be foundational. He was critical of the observational data that Copernicus built his theory on, which he correctly considered to be inaccurate. Instead, Tycho proposed a "geo-heliocentric" system in which the Sun and Moon orbited the Earth, while the other planets orbited the Sun. His system had many of the observational and computational advantages of Copernicus' system. It provided a safe position for those astronomers who were dissatisfied with older models, but reluctant to accept heliocentrism. It gained a following after 1616, when the Catholic Church declared the heliocentric model to be contrary to philosophy and Christian scripture, and only able to be discussed as a computational convenience. Tycho's system offered a major innovation in that it eliminated the idea of transparent rotating crystalline spheres to carry the planets in their orbits. Kepler and other Copernican astronomers, tried unsuccessfully to persuade Tycho to adopt the heliocentric model of the
Although Tycho admired Copernicus and was the first to teach his theory in Denmark, he was unable to reconcile Copernican theory with the basic laws of Aristotelian physics, which he believed to be foundational. He was critical of the observational data that Copernicus built his theory on, which he correctly considered to be inaccurate. Instead, Tycho proposed a "geo-heliocentric" system in which the Sun and Moon orbited the Earth, while the other planets orbited the Sun. His system had many of the observational and computational advantages of Copernicus' system. It provided a safe position for those astronomers who were dissatisfied with older models, but reluctant to accept heliocentrism. It gained a following after 1616, when the Catholic Church declared the heliocentric model to be contrary to philosophy and Christian scripture, and only able to be discussed as a computational convenience. Tycho's system offered a major innovation in that it eliminated the idea of transparent rotating crystalline spheres to carry the planets in their orbits. Kepler and other Copernican astronomers, tried unsuccessfully to persuade Tycho to adopt the heliocentric model of the
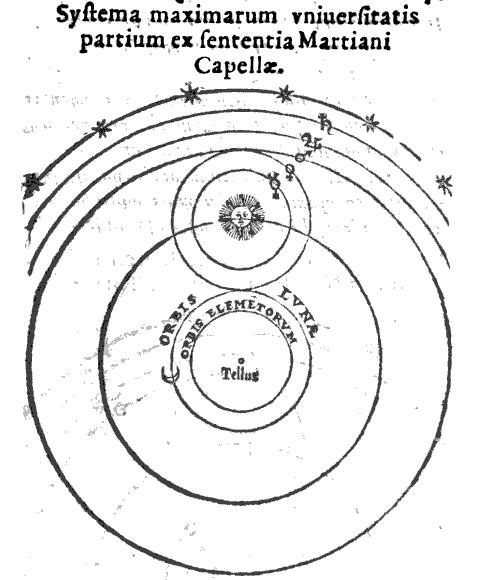 Galileo's 1610 telescopic discovery that Venus shows a full set of phases refuted the pure geocentric Ptolemaic model. After that it seems 17th-century astronomy mostly converted to geo-heliocentric planetary models that could explain these phases just as well as the heliocentric model could, but without the latter's disadvantage of the failure to detect any annual stellar parallax that Tycho and others regarded as refuting it. The three main geo-heliocentric models were the Tychonic, the Capellan with just Mercury and Venus orbiting the Sun such as favoured by
Galileo's 1610 telescopic discovery that Venus shows a full set of phases refuted the pure geocentric Ptolemaic model. After that it seems 17th-century astronomy mostly converted to geo-heliocentric planetary models that could explain these phases just as well as the heliocentric model could, but without the latter's disadvantage of the failure to detect any annual stellar parallax that Tycho and others regarded as refuting it. The three main geo-heliocentric models were the Tychonic, the Capellan with just Mercury and Venus orbiting the Sun such as favoured by  The ardent anti-heliocentric French astronomer Jean-Baptiste Morin devised a Tychonic planetary model with elliptical orbits published in 1650 in a simplified, Tychonic version of the ''Rudolphine Tables''. Another geocentric French astronomer, Jacques du Chevreul, rejected Tycho's observations including his description of the heavens and the theory that Mars was below the Sun. Some acceptance of the Tychonic system persisted through the 17th century and in places until the early 18th century; it was supported (after a 1633 decree about the Copernican controversy) by "a flood of pro-Tycho literature" of Jesuit origin. Among pro-Tycho Jesuits, Ignace Pardies declared in 1691 that it was still the commonly accepted system, and Francesco Blanchinus reiterated that as late as 1728. Persistence of the Tychonic system, especially in Catholic countries, has been attributed to its satisfaction of a need (relative to Catholic doctrine) for "a safe synthesis of ancient and modern". After 1670, even many Jesuit writers only thinly disguised their Copernicanism. But in Germany, the Netherlands, and England, the Tychonic system "vanished from the literature much earlier".
James Bradley's discovery of
The ardent anti-heliocentric French astronomer Jean-Baptiste Morin devised a Tychonic planetary model with elliptical orbits published in 1650 in a simplified, Tychonic version of the ''Rudolphine Tables''. Another geocentric French astronomer, Jacques du Chevreul, rejected Tycho's observations including his description of the heavens and the theory that Mars was below the Sun. Some acceptance of the Tychonic system persisted through the 17th century and in places until the early 18th century; it was supported (after a 1633 decree about the Copernican controversy) by "a flood of pro-Tycho literature" of Jesuit origin. Among pro-Tycho Jesuits, Ignace Pardies declared in 1691 that it was still the commonly accepted system, and Francesco Blanchinus reiterated that as late as 1728. Persistence of the Tychonic system, especially in Catholic countries, has been attributed to its satisfaction of a need (relative to Catholic doctrine) for "a safe synthesis of ancient and modern". After 1670, even many Jesuit writers only thinly disguised their Copernicanism. But in Germany, the Netherlands, and England, the Tychonic system "vanished from the literature much earlier".
James Bradley's discovery of
 The first biography of Tycho, which was also the first full-length biography of any scientist, was written by Gassendi in 1654. In 1779, Tycho de Hoffmann wrote of Tycho's life in his history of the Brahe family. In 1913, Dreyer published Tycho's collected works, facilitating further research. Early modern scholarship on Tycho tended to see the shortcomings of his astronomical model, painting him as a mysticist recalcitrant in accepting the Copernican revolution, and valuing mostly his observations that allowed Kepler to formulate his laws of planetary movement. Especially in Danish scholarship, Tycho was depicted as a mediocre scholar and a traitor to the nation—perhaps because of the important role in Danish historiography of Christian IV as a warrior king. In the second half of the 20th century, scholars began reevaluating his significance, and studies by Kristian Peder Moesgaard, Owen Gingerich, Robert Westman, Victor E. Thoren, and John R. Christianson focused on his contributions to science, and demonstrated that while he admired Copernicus he was simply unable to reconcile his basic theory of physics with the Copernican view. Christianson's work showed the influence of Tycho's Uraniborg as a training center for scientists who after studying with Tycho went on to make contributions in various scientific fields.
The first biography of Tycho, which was also the first full-length biography of any scientist, was written by Gassendi in 1654. In 1779, Tycho de Hoffmann wrote of Tycho's life in his history of the Brahe family. In 1913, Dreyer published Tycho's collected works, facilitating further research. Early modern scholarship on Tycho tended to see the shortcomings of his astronomical model, painting him as a mysticist recalcitrant in accepting the Copernican revolution, and valuing mostly his observations that allowed Kepler to formulate his laws of planetary movement. Especially in Danish scholarship, Tycho was depicted as a mediocre scholar and a traitor to the nation—perhaps because of the important role in Danish historiography of Christian IV as a warrior king. In the second half of the 20th century, scholars began reevaluating his significance, and studies by Kristian Peder Moesgaard, Owen Gingerich, Robert Westman, Victor E. Thoren, and John R. Christianson focused on his contributions to science, and demonstrated that while he admired Copernicus he was simply unable to reconcile his basic theory of physics with the Copernican view. Christianson's work showed the influence of Tycho's Uraniborg as a training center for scientists who after studying with Tycho went on to make contributions in various scientific fields.
 Tycho's discovery of the new star was the inspiration for
Tycho's discovery of the new star was the inspiration for
''De Mundi Aetherei Recentioribus Phaenomenis Liber Secundus''
(Uraniborg, 1588; Prague, 1603; Frankfurt, 1610)
''Tychonis Brahe Astronomiae Instauratae Progymnasmata''
(Prague, 1602/03; Frankfurt, 1610) *
Information about the opening of Brahe's tomb in 2010
from
The Noble Dane: Images of Tycho Brahe
', an exhibition by the Museum of the History of Science, Oxford in 2004
The Correspondence of Tycho Brahe
from the
''Astronomiae instauratae mechanica'', 1602 edition
from Lehigh University
archived
20 December 2022)
''Learned Tico Brahae, His Astronomicall Coniectur'', 1632
– full digital facsimile, Linda Hall Library
Coat-of-arms of Brahe
on the island of Ven (Sweden) {{DEFAULTSORT:Brahe, Tycho * 1546 births 1601 deaths 16th-century Danish astronomers 16th-century Latin-language writers 16th-century alchemists Christian astrologers Copernican Revolution Danish alchemists Danish astrologers Danish Lutherans Danish science writers Discoverers of supernovae Leipzig University alumni Philippists Danish scientific instrument makers University of Copenhagen alumni University of Rostock alumni
astronomer
An astronomer is a scientist in the field of astronomy who focuses their studies on a specific question or field outside the scope of Earth. They observe astronomical objects such as stars, planets, moons, comets and galaxies – in either ...
, known for his comprehensive astronomical observations, generally considered to be the most accurate of his time. He was known during his lifetime as an astronomer, astrologer
Astrology is a range of divinatory practices, recognized as pseudoscientific since the 18th century, that claim to discern information about human affairs and terrestrial events by studying the apparent positions of celestial objects. Di ...
, and alchemist
Alchemy (from Arabic: ''al-kīmiyā''; from Ancient Greek: χυμεία, ''khumeía'') is an ancient branch of natural philosophy, a philosophical and protoscientific tradition that was historically practiced in China, India, the Muslim ...
. He was the last major astronomer before the invention of the telescope
A telescope is a device used to observe distant objects by their emission, absorption, or reflection of electromagnetic radiation. Originally meaning only an optical instrument using lenses, curved mirrors, or a combination of both to obse ...
.
An heir to several noble families, Tycho was well-educated. He took an interest in astronomy and in the creation of more accurate instruments of measurement. He worked to combine what he saw as the geometrical
Geometry (; ) is, with arithmetic, one of the oldest branches of mathematics. It is concerned with properties of space such as the distance, shape, size, and relative position of figures. A mathematician who works in the field of geometry is c ...
benefits of Copernican heliocentrism with the philosophical benefits of the Ptolemaic system, and devised the Tychonic system, his own version of a model of the universe, with the Sun orbiting the Earth, and the planets as orbiting the Sun. In ''De nova stella'' (1573), he refuted the Aristotelian belief in an unchanging celestial realm. His measurements indicated that "new stars" (''stellae nova
A nova (plural novae or novas) is a transient astronomical event that causes the sudden appearance of a bright, apparently "new" star (hence the name "nova", which is Latin for "new") that slowly fades over weeks or months. Causes of the dramat ...
e'', now called ''supernova
A supernova is a powerful and luminous explosion of a star. It has the plural form supernovae or supernovas, and is abbreviated SN or SNe. This transient astronomical event occurs during the last evolutionary stages of a massive star or whe ...
e'') moved beyond the Moon, and he was able to show that comets were not atmospheric phenomena, as was previously thought.
King Frederick II granted Tycho an estate on the island of Hven and the money to build Uraniborg
Uraniborg ( da, Uranienborg, sv, Uraniborg) was a Danish astronomical observatory and alchemy laboratory established and operated by Tycho Brahe. It was built on Hven, an island in the Øresund between Zealand and Scania, Sweden, whic ...
, the first large observatory
An observatory is a location used for observing terrestrial, marine, or celestial events. Astronomy, climatology/meteorology, geophysical, oceanography and volcanology are examples of disciplines for which observatories have been constructed. ...
in Christian Europe. He later worked underground at Stjerneborg, where he realised that his instruments in Uraniborg were not sufficiently steady. He treated the island residents as if he were an autocrat, who unsuccessfully sued him over their treatment. In 1597, he was forced by the new king, Christian IV, to leave Denmark. He was invited to Prague, where he became the official imperial astronomer, and built an observatory at Benátky nad Jizerou
Benátky nad Jizerou (; german: Benatek) is a town in Mladá Boleslav District in the Central Bohemian Region of the Czech Republic. It has about 7,400 inhabitants. The historic town centre is well preserved and is protected by law as an urban ...
. Prior to his death in 1601, he was assisted for a year by Johannes Kepler
Johannes Kepler (; ; 27 December 1571 – 15 November 1630) was a German astronomer, mathematician, astrologer, natural philosopher and writer on music. He is a key figure in the 17th-century Scientific Revolution, best known for his laws ...
, who went on to use Tycho's data to develop his own three laws of planetary motion.
Life
Family
Tycho Brahe was born as heir to several of Denmark's most influential noble families and in addition to his immediate ancestry with theBrahe
Brahe (originally ''Bragde'') is the name of two closely related Scanian noble families who were influential in both Danish and Swedish history.
Danish family
The first member of the family using the name Brahe is speculated to have been Verner ...
and the Bille families, he also counted the Rud, Trolle, Ulfstand
Ulfstand was a Danish, mostly Scanian, noble family, known since the 14th century and extinct in the male line in 1637. It was possibly descended from a German noble family, and took the name Ulfstand when King Frederick decreed that the nobility ...
, and Rosenkrantz families among his ancestors. Both of his grandfathers and all of his great-grandfathers had served as members of the Danish king's Privy Council
A privy council is a body that advises the head of state of a state, typically, but not always, in the context of a monarchic government. The word "privy" means "private" or "secret"; thus, a privy council was originally a committee of the mo ...
. His paternal grandfather and namesake, Thyge Brahe, was the lord of Tosterup Castle
Tosterup Castle ( sv, Tosterups slott) is a castle in Tomelilla Municipality, Scania, in southern Sweden. It is situated approximately north-east of Ystad.
Owners
List of owners of Tosterup Castle:
*Early 1300s – Axel Eskildsen Mule
*1300s ...
in Scania and died in battle during the 1523 Siege of Malmö during the Lutheran Reformation Wars. His maternal grandfather, Claus Bille, lord to Bohus Castle and a second cousin of Swedish king Gustav Vasa, participated in the Stockholm Bloodbath on the side of the Danish king against the Swedish nobles. Tycho's father, Otte Brahe
Otte Brahe (; 2 October 1518 – 9 May 1571) was a Danish (Scanian) nobleman and statesman, who served on the privy council ( Rigsraad, "Council of the Realm"). He was married to Beate Clausdatter Bille and was the father of astronomers Tycho a ...
, a royal Privy Councilor (like his own father), married Beate Bille, a powerful figure at the Danish court holding several royal land titles. Tycho's parents are buried under the floor of the church of Kågeröd
Kågeröd is a locality situated in Svalöv Municipality, Skåne County, Sweden with 1,446 inhabitants in 2010.
The permanent motor circuit Ring Knutstorp
Ring Knutstorp is a motor racing circuit in Kågeröd, Sweden. The circuit was built ...
, four kilometres east of Knutstorp Castle.
Early years
Tycho was born on 14 December 1546, at his family's ancestral seat at Knutstorp (Danish: ''Knudstrup borg''; Swedish: ''Knutstorps borg''), about north ofSvalöv
Svalöv () is a locality and the seat of Svalöv Municipality
Svalöv Municipality (''Svalövs kommun'') is a municipality in Skåne County in southern Sweden. Its seat is located in the town Svalöv.
The local government reform of 1952 grouped ...
in then Danish Scania
Scania, also known by its native name of Skåne (, ), is the southernmost of the historical provinces (''landskap'') of Sweden. Located in the south tip of the geographical region of Götaland, the province is roughly conterminous with Skån ...
. He was the oldest of 12 siblings, 8 of whom lived to adulthood, including Steen Brahe and Sophia Brahe. His twin brother died before being baptized
Baptism (from grc-x-koine, βάπτισμα, váptisma) is a form of ritual purification—a characteristic of many religions throughout time and geography. In Christianity, it is a Christian sacrament of initiation and adoption, almost i ...
. Tycho later wrote an ode in Latin to his dead twin, which was printed in 1572 as his first published work. An epitaph
An epitaph (; ) is a short text honoring a deceased person. Strictly speaking, it refers to text that is inscribed on a tombstone or plaque, but it may also be used in a figurative sense. Some epitaphs are specified by the person themselves be ...
, originally from Knutstorp, but now on a plaque near the church door, shows the whole family, including Tycho as a boy.
When he was only two years old Tycho was taken away to be raised by his uncle Jørgen Thygesen Brahe and his wife Inger Oxe Inger Johansdatter Oxe (c. 1526 - 1591) was a Danish noblewoman and court official. She was Hofmesterinde to the Danish Queen Sophie of Mecklenburg-Güstrow.
She was the sister to Peder Oxe Steward of the Realm, daughter of Johan Johansen Oxe and ...
(sister to Peder Oxe, Steward of the Realm) who were childless. It is unclear why Otte Brahe reached this arrangement with his brother, but Tycho was the only one of his siblings not to be raised by his mother at Knutstorp. Instead, Tycho was raised at Jørgen Brahe's estate at Tosterup and at Tranekær on the island of Langeland, and later at Næsbyhoved Castle near Odense, and later again at the Castle of Nykøbing on the island of Falster
Falster () is an island in south-eastern Denmark with an area of and 43,398 inhabitants as of 1 January 2010.
. Tycho later wrote that Jørgen Brahe "raised me and generously provided for me during his life until my eighteenth year; he always treated me as his own son and made me his heir".
From ages 6 to 12, Tycho attended Latin school, probably in Nykøbing. At age 12, on 19 April 1559, Tycho began studies at the University of Copenhagen
The University of Copenhagen ( da, Københavns Universitet, KU) is a prestigious public university, public research university in Copenhagen, Copenhagen, Denmark. Founded in 1479, the University of Copenhagen is the second-oldest university in ...
. There, following his uncle's wishes, he studied law, but also studied a variety of other subjects and became interested in astronomy
Astronomy () is a natural science that studies celestial objects and phenomena. It uses mathematics, physics, and chemistry in order to explain their origin and evolution. Objects of interest include planets, moons, stars, nebulae, g ...
. At the university, Aristotle
Aristotle (; grc-gre, Ἀριστοτέλης ''Aristotélēs'', ; 384–322 BC) was a Greek philosopher and polymath during the Classical period in Ancient Greece. Taught by Plato, he was the founder of the Peripatetic school of ...
was a staple of scientific theory, and Tycho likely received a thorough training in Aristotelian physics and cosmology. He experienced the solar eclipse of 21 August 1560, and was greatly impressed by the fact that it had been predicted, although the prediction based on current observational data was a day off. He realized that more accurate observations would be the key to making more exact predictions. He purchased an ephemeris
In astronomy and celestial navigation, an ephemeris (pl. ephemerides; ) is a book with tables that gives the trajectory of naturally occurring astronomical objects as well as artificial satellites in the sky, i.e., the position (and possibly ...
and books on astronomy, including Johannes de Sacrobosco's '' De sphaera mundi'', Petrus Apianus's ''Cosmographia seu descriptio totius orbis'' and Regiomontanus's ''De triangulis omnimodis''.
Jørgen Thygesen Brahe, however, wanted Tycho to educate himself in order to become a civil servant, and sent him on a study tour of Europe in early 1562. 15-year old Tycho was given as mentor the 19-year-old Anders Sørensen Vedel, whom he eventually talked into allowing the pursuit of astronomy during the tour. Vedel and his pupil left Copenhagen in February 1562. On 24 March, they arrived in Leipzig
Leipzig ( , ; Upper Saxon: ) is the most populous city in the German state of Saxony. Leipzig's population of 605,407 inhabitants (1.1 million in the larger urban zone) as of 2021 places the city as Germany's eighth most populous, as ...
, where they matriculated at the Lutheran Leipzig University. In 1563, he observed a close conjunction of the planets Jupiter
Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the largest in the Solar System. It is a gas giant with a mass more than two and a half times that of all the other planets in the Solar System combined, but slightly less than one-thousand ...
and Saturn
Saturn is the sixth planet from the Sun and the second-largest in the Solar System, after Jupiter. It is a gas giant with an average radius of about nine and a half times that of Earth. It has only one-eighth the average density of Earth; h ...
, and noticed that the Copernican and Ptolemaic tables used to predict the conjunction were inaccurate. This led him to realise that progress in astronomy required systematic, rigorous observation, night after night, using the most accurate instruments obtainable. He began maintaining detailed journals of all his astronomical observations. In this period, he combined the study of astronomy with astrology
Astrology is a range of divinatory practices, recognized as pseudoscientific since the 18th century, that claim to discern information about human affairs and terrestrial events by studying the apparent positions of celestial objects. Di ...
, laying down horoscopes for different famous personalities.
When Tycho and Vedel returned from Leipzig in 1565, Denmark was at war with Sweden, and as vice-admiral of the Danish fleet, Jørgen Brahe had become a national hero for having participated in the sinking of the Swedish warship ''Mars'' during the First battle of Öland (1564). Shortly after Tycho's arrival in Denmark, Jørgen Brahe was defeated in the action of 4 June 1565, and shortly afterwards died of a fever. Stories have it that he contracted pneumonia after a night of drinking with the Danish King Frederick II when the king fell into the water in a Copenhagen canal and Brahe jumped in after him. Brahe's possessions passed on to his wife Inger Oxe, who considered Tycho with special fondness.
Tycho's nose
In 1566, Tycho left to study at theUniversity of Rostock
The University of Rostock (german: link=no, Universität Rostock) is a public university located in Rostock, Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Germany. Founded in 1419, it is the third-oldest university in Germany. It is the oldest university in continen ...
. Here, he studied with professors of medicine at the university's famous medical school and became interested in medical alchemy
Alchemy (from Arabic: ''al-kīmiyā''; from Ancient Greek: χυμεία, ''khumeía'') is an ancient branch of natural philosophy, a philosophical and protoscientific tradition that was historically practiced in China, India, the Muslim wo ...
and herbal medicine
Herbal medicine (also herbalism) is the study of pharmacognosy and the use of medicinal plants, which are a basis of traditional medicine. With worldwide research into pharmacology, some herbal medicines have been translated into modern remedie ...
. On 29 December 1566 at the age of 20, Tycho lost part of his nose in a sword duel
A duel is an arranged engagement in combat between two people, with matched weapons, in accordance with agreed-upon rules.
During the 17th and 18th centuries (and earlier), duels were mostly single combats fought with swords (the rapier and ...
with a fellow Danish nobleman, his third cousin Manderup Parsberg
Manderup Parsberg (24 December 1546 – 11 November 1625) was a Danish nobleman and politician who was member of the Royal Privy Council to King Christian IV of Denmark.
Student life
As a student at the University of Rostock, he participated in a ...
. The two had drunkenly quarreled over who was the superior mathematician at an engagement party at the home of Professor Lucas Bachmeister on 10 December. Coming nearly to quarrel again with his cousin on 29 December, they ended up resolving their feud with a duel in the dark. Though the two were later reconciled, the duel resulted in Tycho losing the bridge of his nose and gaining a broad scar across his forehead. He received the best possible care at the university and wore a prosthetic nose for the rest of his life. It was kept in place with paste or glue and said to be made of silver and gold. In November 2012, Danish and Czech researchers reported that the prosthetic was actually made of brass
Brass is an alloy of copper (Cu) and zinc (Zn), in proportions which can be varied to achieve different mechanical, electrical, and chemical properties. It is a substitutional alloy: atoms of the two constituents may replace each other wi ...
after chemically analyzing a small bone sample from the nose from the body exhumed in 2010. The prosthetics made of gold and silver were mostly worn for special occasions, rather than everyday wear.
Science and life on Uraniborg
In April 1567, Tycho returned home from his travels, with a firm intention of becoming an astrologer. Although he had been expected to go into politics and the law, like most of his kinsmen, and although Denmark was still at war with Sweden, his family supported his decision to dedicate himself to the sciences. His father wanted him to take up law, but Tycho was allowed to travel to Rostock and then toAugsburg
Augsburg (; bar , Augschburg , links=https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Swabian_German , label=Swabian German, , ) is a city in Swabia, Bavaria, Germany, around west of Bavarian capital Munich. It is a university town and regional seat of the ' ...
(where he built a great quadrant), Basel
, french: link=no, Bâlois(e), it, Basilese
, neighboring_municipalities= Allschwil (BL), Hégenheim (FR-68), Binningen (BL), Birsfelden (BL), Bottmingen (BL), Huningue (FR-68), Münchenstein (BL), Muttenz (BL), Reinach (BL), Riehen (B ...
, and Freiburg. In 1568, he was appointed a canon at the Cathedral of Roskilde, a largely honorary position that would allow him to focus on his studies. At the end of 1570, he was informed of his father's ill health, so he returned to Knutstorp Castle, where his father died on 9 May 1571. The war was over, and the Danish lords soon returned to prosperity. Soon, another uncle, Steen Bille, helped him build an observatory and alchemical laboratory at Herrevad Abbey. Tycho was acknowledged by King Frederick II who proposed to him that an observatory be built to better study the night sky. After accepting this proposal, the location for the Uraniborg's construction took place at a remote island called Hven in the Sont near Copenhagen, the earliest large observatory in Christian Europe.
Marriage to Kirsten Jørgensdatter
Towards the end of 1571, Tycho fell in love with Kirsten, daughter of Jørgen Hansen, theLutheran
Lutheranism is one of the largest branches of Protestantism, identifying primarily with the theology of Martin Luther, the 16th-century German monk and reformer whose efforts to reform the theology and practice of the Catholic Church launched ...
minister in Knudstrup. As she was a commoner
A commoner, also known as the ''common man'', ''commoners'', the ''common people'' or the ''masses'', was in earlier use an ordinary person in a community or nation who did not have any significant social status, especially a member of neither ...
, Tycho never formally married her, since if he did he would lose his noble privileges. However, Danish law permitted morganatic marriage, which meant that a nobleman and a common woman could live together openly as husband and wife for three years, and their alliance then became a legally binding marriage. However, each would maintain their social status, and any children they had together would be considered commoners, with no rights to titles, landholdings, coat of arms, or even their father's noble name. While King Frederick respected Tycho's choice of wife, himself having been unable to marry the woman he loved, many of Tycho's family members disagreed, and many churchmen would continue to hold the lack of a divinely sanctioned marriage against him. Kirsten Jørgensdatter gave birth to their first daughter, Kirstine (named after Tycho's late sister) on 12October 1573. Kirstine died from the plague in 1576, and Tycho wrote a heartfelt elegy for her tombstone. In 1574, they moved to Copenhagen where their daughter Magdalene was born, and later the family followed him into exile. Kirsten and Tycho lived together for almost thirty years until Tycho's death. Together, they had eight children, six of whom lived to adulthood.
1572 supernova
 On 11 November 1572, Tycho observed (from Herrevad Abbey) a very bright star, now numbered SN 1572, which had unexpectedly appeared in the constellation Cassiopeia. Because it had been maintained since
On 11 November 1572, Tycho observed (from Herrevad Abbey) a very bright star, now numbered SN 1572, which had unexpectedly appeared in the constellation Cassiopeia. Because it had been maintained since antiquity
Antiquity or Antiquities may refer to:
Historical objects or periods Artifacts
*Antiquities, objects or artifacts surviving from ancient cultures
Eras
Any period before the European Middle Ages (5th to 15th centuries) but still within the histo ...
that the world beyond the Moon's orbit was eternally unchangeable (celestial immutability was a fundamental axiom of the Aristotelian world-view), other observers held that the phenomenon was something in the terrestrial sphere below the Moon. However, Tycho observed that the object showed no daily parallax
Parallax is a displacement or difference in the apparent position of an object viewed along two different lines of sight and is measured by the angle or semi-angle of inclination between those two lines. Due to foreshortening, nearby object ...
against the background of the fixed stars. This implied that it was at least farther away than the Moon and those planets that do show such parallax. He also found that the object did not change its position relative to the fixed stars over several months, as all planets did in their periodic orbital motions, even the outer planets, for which no daily parallax was detectable. This suggested that it was not even a planet, but a fixed star in the stellar sphere beyond all the planets. In 1573, he published a small book ''De nova stella'', thereby coining the term nova
A nova (plural novae or novas) is a transient astronomical event that causes the sudden appearance of a bright, apparently "new" star (hence the name "nova", which is Latin for "new") that slowly fades over weeks or months. Causes of the dramat ...
for a "new" star (we now classify this star as a supernova
A supernova is a powerful and luminous explosion of a star. It has the plural form supernovae or supernovas, and is abbreviated SN or SNe. This transient astronomical event occurs during the last evolutionary stages of a massive star or whe ...
and know that it is 7,500 light-year
A light-year, alternatively spelled light year, is a large unit of length used to express astronomical distance, astronomical distances and is equivalent to about 9.46 Orders of magnitude (numbers)#1012, trillion kilometers (), or 5.88 ...
s from Earth). This discovery was decisive for his choice of astronomy as a profession. Tycho was strongly critical of those who dismissed the implications of the astronomical appearance, writing in the preface to ''De nova stella'': "''O crassa ingenia. O caecos coeli spectatores''" ("Oh thick wits. Oh blind watchers of the sky"). The publication of his discovery made him a well-known name among scientists in Europe.
Lord of Hven
Tycho continued with his detailed observations, often assisted by his first assistant and student, his younger sister Sophie. In 1574, Tycho published the observations made in 1572 from his first observatory at Herrevad Abbey. He then started lecturing on astronomy, but gave it up and left Denmark in spring 1575 to tour abroad. He first visited William IV, Landgrave of Hesse-Kassel's observatory at Kassel, then went on to Frankfurt, Basel, and Venice, where he acted as an agent for the Danish king, contacting artisans and craftsmen whom the king wanted to work on his new palace at Elsinore. Upon his return, the King wished to repay Tycho's service by offering him a position worthy of his family; he offered him a choice of lordships of militarily and economically important estates, such as the castles of Hammershus or Helsingborg. But Tycho was reluctant to take up a position as a lord of the realm, preferring to focus on his science. He wrote to his friend Johannes Pratensis, "I did not want to take possession of any of the castles our benevolent king so graciously offered me. I am displeased with society here, customary forms and the whole rubbish". Tycho secretly began to plan to move to Basel, wishing to participate in the burgeoning academic and scientific life there. But the King heard of Tycho's plans, and desiring to keep the distinguished scientist, in 1576 he offered Tycho the island of Hven inØresund
Øresund or Öresund (, ; da, Øresund ; sv, Öresund ), commonly known in English as the Sound, is a strait which forms the Danish–Swedish border, separating Zealand (Denmark) from Scania (Sweden). The strait has a length of ; its width ...
and funding to set up an observatory.
Until then, Hven had been property directly under the Crown, and the 50 families on the island considered themselves to be freeholding farmers, but with Tycho's appointment as Feudal Lord of Hven, this changed. Tycho took control of agricultural planning, requiring the peasants to cultivate twice as much as they had done before, and he also exacted corvée labor from the peasants for the construction of his new castle. The peasants complained about Tycho's excessive taxation and took him to court. The court established Tycho's right to levy taxes and labor, and the result was a contract detailing the mutual obligations of lord and peasants on the island.
Tycho envisioned his castle Uraniborg
Uraniborg ( da, Uranienborg, sv, Uraniborg) was a Danish astronomical observatory and alchemy laboratory established and operated by Tycho Brahe. It was built on Hven, an island in the Øresund between Zealand and Scania, Sweden, whic ...
as a temple dedicated to the muse
In ancient Greek religion and mythology, the Muses ( grc, Μοῦσαι, Moûsai, el, Μούσες, Múses) are the inspirational goddesses of literature, science, and the arts. They were considered the source of the knowledge embodied in ...
s of arts and sciences, rather than as a military fortress; indeed, it was named after Urania
Urania ( ; grc, , Ouranía; modern Greek shortened name ''Ránia''; meaning "heavenly" or "of heaven") was, in Greek mythology, the muse of astronomy, and in later times, of Christian poetry. Urania is the goddess of astronomy and stars, ...
, the muse of astronomy. Construction began in 1576 (with a laboratory for his alchemical experiments in the cellar). Uraniborg was inspired by the Venetian architect Andrea Palladio
Andrea Palladio ( ; ; 30 November 1508 – 19 August 1580) was an Italian Renaissance architect active in the Venetian Republic. Palladio, influenced by Roman and Greek architecture, primarily Vitruvius, is widely considered to be one of ...
, and was one of the first buildings in northern Europe to show influence from Italian renaissance architecture.
When he realized that the towers of Uraniborg were not adequate as observatories because of the instruments' exposure to the elements and the movement of the building, he constructed an underground observatory close to Uraniborg called Stjerneborg (Star Castle) in 1584. This consisted of several hemispherical crypts which contained the great equatorial armillary, large azimuth quadrant, zodiacal armillary, largest azimuth quadrant of steel and the trigonal sextant.
The basement of Uraniborg included an alchemical laboratory with 16 furnaces for conducting distillations and other chemical experiments. Unusually for the time, Tycho established Uraniborg as a research centre, where almost 100 students and artisans worked from 1576 to 1597. Uraniborg also contained a printing press and a paper mill, both among the first in Scandinavia, enabling Tycho to publish his own manuscripts, on locally made paper with his own watermark
A watermark is an identifying image or pattern in paper that appears as various shades of lightness/darkness when viewed by transmitted light (or when viewed by reflected light, atop a dark background), caused by thickness or density variations ...
. He created a system of ponds and canals to run the wheels of the paper mill. Over the years he worked on Uraniborg, Tycho was assisted by a number of students and protegés, many of whom went on to their own careers in astronomy: among them were Christian Sørensen Longomontanus
Christians () are people who follow or adhere to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. The words ''Christ'' and ''Christian'' derive from the Koine Greek title ''Christós'' (Χρ� ...
, later one of the main proponents of the Tychonic model and Tycho's replacement as royal Danish astronomer; Peder Flemløse; Elias Olsen Morsing; and Cort Aslakssøn. Tycho's instrument-maker Hans Crol also formed part of the scientific community on the island.
 He observed the great comet that was visible in the Northern sky from November 1577 to January 1578. Within Lutheranism, it was commonly believed that celestial objects like comets were powerful portents, announcing the coming apocalypse, and in addition to Tycho's observations several Danish amateur astronomers observed the object and published prophesies of impending doom. He was able to determine that the comet's distance to Earth was much greater than the distance of the Moon, so that the comet could not have originated in the "earthly sphere", confirming his prior anti-Aristotelian conclusions about the fixed nature of the sky beyond the Moon. He also realized that the comet's
He observed the great comet that was visible in the Northern sky from November 1577 to January 1578. Within Lutheranism, it was commonly believed that celestial objects like comets were powerful portents, announcing the coming apocalypse, and in addition to Tycho's observations several Danish amateur astronomers observed the object and published prophesies of impending doom. He was able to determine that the comet's distance to Earth was much greater than the distance of the Moon, so that the comet could not have originated in the "earthly sphere", confirming his prior anti-Aristotelian conclusions about the fixed nature of the sky beyond the Moon. He also realized that the comet's tail
The tail is the section at the rear end of certain kinds of animals’ bodies; in general, the term refers to a distinct, flexible appendage to the torso. It is the part of the body that corresponds roughly to the sacrum and coccyx in mammal ...
was always pointing away from the Sun. He calculated its diameter, mass, and the length of its tail, and speculated about the material it was made of. At this point, he had not yet broken with Copernican heliocentrism, and observing the comet inspired him to try to develop an alternative Copernican model in which the Earth was immobile. The second half of his manuscript about the comet dealt with the astrological and apocalyptic aspects of the comet, and he rejected the prophesies of his competitors; instead, making his own predictions of dire political events in the near future. Among his predictions was bloodshed in Moscow and the imminent fall of Ivan the Terrible
Ivan IV Vasilyevich (russian: Ива́н Васи́льевич; 25 August 1530 – ), commonly known in English as Ivan the Terrible, was the grand prince of Moscow from 1533 to 1547 and the first Tsar of all Russia from 1547 to 1584.
Iva ...
by 1583.
The support that Tycho received from the Crown was substantial, amounting to 1% of the annual total revenue at one point in the 1580s. Tycho often held large social gatherings in his castle. Pierre Gassendi
Pierre Gassendi (; also Pierre Gassend, Petrus Gassendi; 22 January 1592 – 24 October 1655) was a French philosopher, Catholic priest, astronomer, and mathematician. While he held a church position in south-east France, he also spent much t ...
wrote that Tycho also had a tame elk (moose) and that his mentor the Landgrave
Landgrave (german: Landgraf, nl, landgraaf, sv, lantgreve, french: landgrave; la, comes magnus, ', ', ', ', ') was a noble title used in the Holy Roman Empire, and later on in its former territories. The German titles of ', ' (" margrave") ...
Wilhelm of Hesse-Kassel
The Landgraviate of Hesse-Kassel (german: Landgrafschaft Hessen-Kassel), spelled Hesse-Cassel during its entire existence, was a state in the Holy Roman Empire that was directly subject to the Emperor. The state was created in 1567 when the L ...
(Hesse-Cassel) asked whether there was an animal faster than a deer. Tycho replied that there was none, but he could send his tame elk. When Wilhelm replied he would accept one in exchange for a horse, Tycho replied with the sad news that the elk had just died on a visit to entertain a nobleman at Landskrona
Landskrona (old da, Landskrone) is a town in Scania, Sweden. Located on the shores of the Öresund, it occupies a natural port, which has lent the town at first military and subsequent commercial significance. Ferries operate from Landskrona ...
. Apparently, during dinner, the elk had drunk a lot of beer, fallen down the stairs, and died. Among the many noble visitors to Hven was James VI of Scotland
James VI and I (James Charles Stuart; 19 June 1566 – 27 March 1625) was King of Scotland as James VI from 24 July 1567 and King of England and Ireland as James I from the union of the Scottish and English crowns on 24 March 1603 until ...
, who married the Danish princess Anne. After his visit to Hven in 1590, he wrote a poem comparing Tycho with Apollon and Phaethon
Phaethon (; grc, Φαέθων, Phaéthōn, ), also spelled Phaëthon, was the son of the Oceanid Clymene and the sun-god Helios in Greek mythology.
According to most authors, Phaethon is the son of Helios, and out of desire to have his paren ...
.
As part of Tycho's duties to the Crown in exchange for his estate, he fulfilled the functions of a royal astrologer. At the beginning of each year, he had to present an Almanac to the court, predicting the influence of the stars on the political and economic prospects of the year. And at the birth of each prince, he prepared their horoscopes, predicting their fates. He also worked as a cartographer with his former tutor Anders Sørensen Vedel on mapping out all of the Danish realm. An ally of the king and friendly with Queen Sophie (both his mother Beate Bille and adoptive mother Inger Oxe had been her court maids), he secured a promise from the King that ownership of Hven and Uraniborg would pass to his heirs.
Publications, correspondence and scientific disputes
 In 1588, Tycho's royal benefactor died, and a volume of Tycho's great two-volume work ''Astronomiae Instauratae Progymnasmata'' (''Introduction to the New Astronomy'') was published. The first volume, devoted to the new star of 1572, was not ready, because the reduction of the observations of 1572–73 involved much research to correct the stars' positions for
In 1588, Tycho's royal benefactor died, and a volume of Tycho's great two-volume work ''Astronomiae Instauratae Progymnasmata'' (''Introduction to the New Astronomy'') was published. The first volume, devoted to the new star of 1572, was not ready, because the reduction of the observations of 1572–73 involved much research to correct the stars' positions for refraction
In physics, refraction is the redirection of a wave as it passes from one medium to another. The redirection can be caused by the wave's change in speed or by a change in the medium. Refraction of light is the most commonly observed phenomen ...
, precession, the motion of the Sun etc., and was not completed in Tycho's lifetime (it was published in Prague in 1602/03), but the second volume, titled ''De Mundi Aetherei Recentioribus Phaenomenis Liber Secundus'' (''Second Book About Recent Phenomena in the Celestial World'') and devoted to the comet of 1577, was printed at Uraniborg and some copies were issued in 1588. Besides the comet observations, it included an account of Tycho's system of the world. The third volume was intended to treat the comets of 1580 and following years in a similar manner, but it was never published, nor even written, though a great deal of material about the comet of 1585 was put together and first published in 1845 with the observations of this comet.
While at Uraniborg, Tycho maintained correspondence with scientists and astronomers across Europe. He inquired about other astronomers' observations and shared his own technological advances to help them achieve more accurate observations. Thus, his correspondence was crucial to his research. Often, correspondence was not just private communication between scholars, but also a way to disseminate results and arguments and to build progress and scientific consensus. Through correspondence, Tycho was involved in several personal disputes with critics of his theories. Prominent among them were John Craig, a Scottish physician who was a strong believer in the authority of the Aristotelian worldview, and Nicolaus Reimers Baer, known as Ursus, an astronomer at the Imperial court in Prague, whom Tycho accused of having plagiarized his cosmological model. Craig refused to accept Tycho's conclusion that the comet of 1577 had to be located within the aetherial sphere rather than within the atmosphere of Earth. Craig tried to contradict Tycho by using his own observations of the comet, and by questioning his methodology. Tycho published an ''apologia'' (a defense) of his conclusions, in which he provided additional arguments, as well as condemning Craig's ideas in strong language for being incompetent. Another dispute concerned the mathematician Paul Wittich, who, after staying on Hven in 1580, taught Count Wilhelm of Kassel and his astronomer Christoph Rothmann to build copies of Tycho's instruments without permission from Tycho. In turn, Craig, who had studied with Wittich, accused Tycho of minimizing Wittich's role in developing some of the trigonometric methods used by Tycho. In his dealings with these disputes, Tycho made sure to leverage his support in the scientific community, by publishing and disseminating his own answers and arguments.
Exile and later years
When Frederick died in 1588, his son and heir Christian IV was only 11 years old. A regency council was appointed to rule for the young prince-elect until his coronation in 1596. The head of the council (Steward of the Realm) was Christoffer Valkendorff, who disliked Tycho after a conflict between them, and hence Tycho's influence at the Danish court steadily declined. Feeling that his legacy on Hven was in peril, he approached the Dowager Queen Sophie and asked her to affirm in writing her late husband's promise to endow Hven to Tycho's heirs. Nonetheless, he realized that the young king was more interested in war than in science, and was of no mind to keep his father's promise. King Christian IV followed a policy of curbing the power of the nobility by confiscating their estates to minimize their income bases, by accusing nobles of misusing their offices and of heresies against the Lutheran church. Tycho, who was known to sympathize with the Philippists (followers ofPhilip Melanchthon
Philip Melanchthon. (born Philipp Schwartzerdt; 16 February 1497 – 19 April 1560) was a German Lutheran reformer, collaborator with Martin Luther, the first systematic theologian of the Protestant Reformation, intellectual leader of the L ...
), was among the nobles who fell out of grace with the new king. The king's unfavorable disposition towards Tycho was likely also a result of efforts by several of his enemies at court to turn the king against him. Tycho's enemies included, in addition to Valkendorff, the king's doctor Peter Severinus, who also had personal gripes with Tycho, and several gnesio-Lutheran Bishops who suspected Tycho of heresy—a suspicion motivated by his known Philippist sympathies, his pursuits in medicine and alchemy (both of which he practiced without the church's approval) and his prohibiting the local priest on Hven to include the exorcism in the baptismal ritual. Among the accusations raised against Tycho were his failure to adequately maintain the royal chapel at Roskilde, and his harshness and exploitation of the Hven peasantry.
Tycho became even more inclined to leave when a mob of commoners, possibly incited by his enemies at court, rioted in front of his house in Copenhagen. Tycho left Hven in 1597, bringing some of his instruments with him to Copenhagen, and entrusting others to a caretaker on the island. Shortly before leaving, he completed his star catalogue giving the positions of 1,000 stars. After some unsuccessful attempts at influencing the king to let him return; including showcasing his instruments on the wall of the city, he finally acquiesced to exile, but he wrote his most famous poem ''Elegy to Dania'' in which he chided Denmark for not appreciating his genius. The instruments he had used in Uraniborg and Stjerneborg were depicted and described in detail in his star catalogue
A star catalogue is an astronomical catalogue that lists stars. In astronomy, many stars are referred to simply by catalogue numbers. There are a great many different star catalogues which have been produced for different purposes over the years ...
'' Astronomiae instauratae mechanica'' or ''Instruments for the restoration of astronomy'', first published in 1598. The King sent two envoys to Hven to describe the instruments left behind by Tycho. Unversed in astronomy, the envoys reported to the king that the large mechanical contraptions such as his large quadrant and sextant were "useless and even harmful".
From 1597 to 1598, he spent a year at the castle of his friend Heinrich Rantzau in Wandesburg outside Hamburg
Hamburg (, ; nds, label=Hamburg German, Low Saxon, Hamborg ), officially the Free and Hanseatic City of Hamburg (german: Freie und Hansestadt Hamburg; nds, label=Low Saxon, Friee un Hansestadt Hamborg),. is the List of cities in Germany by popul ...
, and then they moved for a while to Wittenberg
Wittenberg ( , ; Low Saxon: ''Wittenbarg''; meaning ''White Mountain''; officially Lutherstadt Wittenberg (''Luther City Wittenberg'')), is the fourth largest town in Saxony-Anhalt, Germany. Wittenberg is situated on the River Elbe, north of ...
, where they stayed in the former home of Philip Melanchthon.
In 1599, he obtained the sponsorship of Rudolf II, Holy Roman Emperor
Rudolf II (18 July 1552 – 20 January 1612) was Holy Roman Emperor (1576–1612), King of Hungary and Croatia (as Rudolf I, 1572–1608), King of Bohemia (1575–1608/1611) and Archduke of Austria (1576–1608). He was a member of the H ...
and moved to Prague, as Imperial Court Astronomer. Tycho built a new observatory in a castle in Benátky nad Jizerou
Benátky nad Jizerou (; german: Benatek) is a town in Mladá Boleslav District in the Central Bohemian Region of the Czech Republic. It has about 7,400 inhabitants. The historic town centre is well preserved and is protected by law as an urban ...
, 50 km from Prague, and worked there for one year. The emperor then brought him back to Prague, where he stayed until his death. At the imperial court even Tycho's wife and children were treated like nobility, which they had never been at the Danish court.
Tycho received financial support from several nobles in addition to the emperor, including Oldrich Desiderius Pruskowsky von Pruskow, to whom he dedicated his famous ''Mechanica''. In return for their support, Tycho's duties included preparing astrological charts and predictions for his patrons at events such as births, weather forecasting
Weather forecasting is the application of science and technology to predict the conditions of the atmosphere for a given location and time. People have attempted to predict the weather informally for millennia and formally since the 19th cen ...
, and astrological interpretations of significant astronomical events, such as the supernova of 1572 (sometimes called Tycho's supernova) and the Great Comet of 1577.
Relationship with Kepler
In Prague, Tycho worked closely with Kepler, his assistant. Kepler was a convinced Copernican, and considered Tycho's model to be mistaken, and derived from simple "inversion" of the Sun's and Earth's positions in the Copernican model. Together, the two worked on a new star catalogue based on his own accurate positions—this catalogue became the ''Rudolphine Tables
The ''Rudolphine Tables'' ( la, Tabulae Rudolphinae) consist of a star catalogue and planetary tables published by Johannes Kepler in 1627, using observational data collected by Tycho Brahe (1546–1601). The tables are named in memory of Rudolf ...
''. Also at the court in Prague was the mathematician Nicolaus Reimers (Ursus), with whom Tycho had previously corresponded, and who, like Tycho, had developed a geo-heliocentric planetary model, which Tycho considered to have been plagiarized from his own. Kepler had previously spoken highly of Ursus, but now found himself in the problematic position of being employed by Tycho and having to defend his employer against Ursus' accusations, even though he disagreed with both of their planetary models. In 1600, he finished the tract ''Apologia pro Tychone contra Ursum'' (defense of Tycho against Ursus). Kepler had great respect for Tycho's methods and the accuracy of his observations and considered him to be the new Hipparchus
Hipparchus (; el, Ἵππαρχος, ''Hipparkhos''; BC) was a Greek astronomer, geographer, and mathematician. He is considered the founder of trigonometry, but is most famous for his incidental discovery of the precession of the e ...
, who would provide the foundation for a restoration of the science of astronomy.
Illness, death, and investigations
Tycho suddenly contracted a bladder or kidney ailment after attending a banquet in Prague, and died eleven days later, on 24 October 1601, at the age of 54. According to Kepler's first-hand account, Tycho had refused to leave the banquet to relieve himself because it would have been a breach of etiquette. After he returned home, he was no longer able to urinate, except eventually in very small quantities and with excruciating pain. The night before he died, he suffered from adelirium
Delirium (also known as acute confusional state) is an organically caused decline from a previous baseline of mental function that develops over a short period of time, typically hours to days. Delirium is a syndrome encompassing disturbances ...
during which he was frequently heard to exclaim that he hoped he would not seem to have lived in vain. Before dying, he urged Kepler to finish the ''Rudolphine Tables'' and expressed the hope that he would do so by adopting Tycho's own planetary system, rather than that of the polymath
A polymath ( el, πολυμαθής, , "having learned much"; la, homo universalis, "universal human") is an individual whose knowledge spans a substantial number of subjects, known to draw on complex bodies of knowledge to solve specific pro ...
Nicolaus Copernicus
Nicolaus Copernicus (; pl, Mikołaj Kopernik; gml, Niklas Koppernigk, german: Nikolaus Kopernikus; 19 February 1473 – 24 May 1543) was a Renaissance polymath, active as a mathematician, astronomer, and Catholic canon, who formulat ...
. It was reported that Tycho had written his own epitaph, "He lived like a sage and died like a fool." A contemporary physician attributed his death to a kidney stone, but no kidney stones were found during an autopsy
An autopsy (post-mortem examination, obduction, necropsy, or autopsia cadaverum) is a surgical procedure that consists of a thorough examination of a corpse by dissection to determine the cause, mode, and manner of death or to evaluate any d ...
performed after his body was exhumed in 1901, and modern medical assessment is that his death was more likely caused by either burst bladder
prostatic hypertrophy, acute prostatitis, or
prostate cancer
Prostate cancer is cancer of the prostate. Prostate cancer is the second most common cancerous tumor worldwide and is the fifth leading cause of cancer-related mortality among men. The prostate is a gland in the male reproductive system that su ...
, which lead to urinary retention, overflow incontinence, and uremia
Uremia is the term for high levels of urea in the blood. Urea is one of the primary components of urine. It can be defined as an excess of amino acid and protein metabolism end products, such as urea and creatinine, in the blood that would be no ...
.
Investigations in the 1990s suggested that Tycho may not have died from urinary problems, but instead from mercury poisoning
Mercury poisoning is a type of metal poisoning due to exposure to mercury. Symptoms depend upon the type, dose, method, and duration of exposure. They may include muscle weakness, poor coordination, numbness in the hands and feet, skin rashes ...
. It was speculated that he had been intentionally poisoned. The two main suspects were his assistant, Johannes Kepler, whose motives would be to gain access to Tycho's laboratory and chemicals, and his cousin, Erik Brahe, at the order of friend-turned-enemy Christian IV, because of rumors that Tycho had had an affair with Christian's mother.
In February 2010, the Prague city authorities approved a request by Danish scientists to exhume the remains, and in November 2010 a group of Czech and Danish scientists from Aarhus University
Aarhus University ( da, Aarhus Universitet, abbreviated AU) is a public research university with its main campus located in Aarhus, Denmark. It is the second largest and second oldest university in Denmark. The university is part of the Coimbra Gr ...
collected bone, hair and clothing samples for analysis. The scientists, led by Dr Jens Vellev, analyzed Tycho's beard hair once again. The team reported in November 2012 that not only was there not enough mercury present to substantiate murder, but that there were no lethal levels of any poisons present. The team's conclusion was that "it is impossible that Tycho Brahe could have been murdered". The findings were confirmed by scientists from the University of Rostock, who examined a sample of Tycho's beard hairs that had been taken in 1901. Although traces of mercury were found, these were present only in the outer scales. Therefore, mercury poisoning as the cause of death was ruled out, while the study suggests that the accumulation of mercury may have come from the "precipitation of mercury dust from the air during ycho'slong-term alchemistic activities".
Tycho is buried in the Church of Our Lady before Týn, in Old Town Square
Old Town Square ( cs, Staroměstské náměstí or colloquially ) is a historic square in the Old Town quarter of Prague, the capital of the Czech Republic. It is located between Wenceslas Square and Charles Bridge.
Buildings
The square ...
near the Prague Astronomical Clock.
Career: observing the heavens
Observational astronomy
 Tycho's view of science was driven by his passion for accurate observations, and the quest for improved instruments of measurement drove his life's work. Tycho was the last major astronomer to work without the aid of a
Tycho's view of science was driven by his passion for accurate observations, and the quest for improved instruments of measurement drove his life's work. Tycho was the last major astronomer to work without the aid of a telescope
A telescope is a device used to observe distant objects by their emission, absorption, or reflection of electromagnetic radiation. Originally meaning only an optical instrument using lenses, curved mirrors, or a combination of both to obse ...
, soon to be turned skyward by Galileo Galilei
Galileo di Vincenzo Bonaiuti de' Galilei (15 February 1564 – 8 January 1642) was an Italian astronomer, physicist and engineer, sometimes described as a polymath. Commonly referred to as Galileo, his name was pronounced (, ). He ...
and others. Given the limitations of the naked eye for making accurate observations, he devoted many of his efforts to improving the accuracy of the existing types of instrument—the sextant
A sextant is a doubly reflecting navigation instrument that measures the angular distance between two visible objects. The primary use of a sextant is to measure the angle between an astronomical object and the horizon for the purposes of ce ...
and the quadrant. He designed larger versions of these instruments, which allowed him to achieve much higher accuracy. Because of the accuracy of his instruments, he quickly realized the influence of wind and the movement of buildings, and instead opted to mount his instruments underground directly on the bedrock.
Tycho's observations of stellar and planet
A planet is a large, rounded astronomical body that is neither a star nor its remnant. The best available theory of planet formation is the nebular hypothesis, which posits that an interstellar cloud collapses out of a nebula to create a you ...
ary positions were noteworthy both for their accuracy and quantity. With an accuracy approaching one arcminute, his celestial positions were much more accurate than those of any predecessor or contemporary—about five times as accurate as the observations of Wilhelm of Hesse. asserts of Tycho's Star Catalog D, "In it, Tycho achieved, on a mass scale, a precision far beyond that of earlier catalogers. Cat D represents an unprecedented confluence of skills: instrumental, observational, & computational—all of which combined to enable Tycho to place most of his hundreds of recorded stars to an accuracy of ordermag 1'!"
He aspired to a level of accuracy in his estimated positions of celestial bodies of being consistently within an arcminute of their real celestial locations, and also claimed to have achieved this level. But, in fact, many of the stellar positions in his star catalogues were less accurate than that. The median errors for the stellar positions in his final published catalog were about 1.5', indicating that only half of the entries were more accurate than that, with an overall mean error in each coordinate of around 2'. Although the stellar observations as recorded in his observational logs were more accurate, varying from 32.3" to 48.8" for different instruments, systematic errors of as much as 3' were introduced into some of the stellar positions Tycho published in his star catalog—due, for instance, to his application of an erroneous ancient value of parallax and his neglect of polestar refraction. Incorrect transcription in the final published star catalogue, by scribes in Tycho's employ, was the source of even larger errors, sometimes by many degrees.
Celestial objects observed near the horizon and above appear with a greater altitude
Altitude or height (also sometimes known as depth) is a distance measurement, usually in the vertical or "up" direction, between a reference datum and a point or object. The exact definition and reference datum varies according to the context ...
than the real one, due to atmospheric refraction
In physics, refraction is the redirection of a wave as it passes from one medium to another. The redirection can be caused by the wave's change in speed or by a change in the medium. Refraction of light is the most commonly observed phenomen ...
, and one of Tycho's most important innovations was that he worked out and published the very first tables for the systematic correction of this possible source of error. But, as advanced as they were, they attributed no refraction whatever above 45° altitude for solar refraction, and none for starlight above 20° altitude.
To perform the huge number of multiplications needed to produce much of his astronomical data, Tycho relied heavily on the then-new technique of '' prosthaphaeresis'', an algorithm for approximating products based on trigonometric identities that predated logarithms.
Instruments
Much of Tycho's observations and discoveries were done with the aid of various instruments, many of which he himself made. The process that went into creating and refining his devices was haphazard at first, but were critical in the advancement of his observations. He pioneered an early example while he was a student in Leipzig. While he was gazing at the stars he realized that he needed a better way to write down not just his observations but also the angles and descriptions as well. So, he pioneered the use of the observational. In this notebook, he made his observations and asked himself questions to try and answer later on. Tycho also made sketches of what he saw as well from comets to the motions of planets. His astronomical instrument innovation continued after his schooling. When he gained access to his inheritance, he went straight to work creating brand new instruments to replace the ones he used as a student. Tycho created a quadrant that was thirty-nine centimeters in diameter and added a new type of sight to it called a ''pinnacidia'', or light cutters as it is translated. This brand-new sight meant that the old pinhole style sight was rendered obsolete. When the sights of the pinnacidia were aligned in the correct manner the object that it is lined up with it will look exactly the same from both ends. This instrument was kept still on a heavy duty base and adjusted via a brass plumb line and thumb screws, all of which helped give Tycho Brahe more accurate measurements of the heavens. There were times that the instruments Tycho made were for a specific purpose or an event that he was witness to. Such was the case in 1577 when he first started construction of what would be called Uraniborg. In that year a comet was spotted moving across the sky. During this period of time Tycho made many observations, and one of the instruments that he used to make his observations was called a brass azimuthal quadrant. At sixty-five centimeters in radius it was a large instrument built either in 1576 or 1577, just in time for Tycho to use it to observe the path and distance of the 1577 comet. This instrument helped him to accurately track the comet's path as it crossed the orbits of the solar system. A great many more instruments were constructed at Tycho Brahe's new manor on Hven called Uraniborg. It was a combination of a home, observatories and laboratory where he made some of his discoveries along with many of his instruments. Several of these instruments were very large, such as a steel azimuth quadrant equipped with a brass arc that was six feet (or 194 centimeters) in diameter. This and other instruments were placed in the two observatories attached to the manor.The Tychonic cosmological model
Solar System
The Solar System Capitalization of the name varies. The International Astronomical Union, the authoritative body regarding astronomical nomenclature, specifies capitalizing the names of all individual astronomical objects but uses mixed "Solar ...
. To Tycho, the idea of a moving Earth was "in violation not only of all physical truth but also of the authority of Holy Scripture, which ought to be paramount."
Tycho held that the Earth was too sluggish and massive to be continuously in motion. According to the accepted Aristotelian physics of the time, the heavens (whose motions and cycles were continuous and unending) were made of aether, a substance not found on Earth that caused objects to move in a circle. By contrast, objects on Earth seem to have motion only when moved, and the natural state of objects on its surface was rest. Tycho said the Earth was an inert body, not readily moved. He acknowledged that the rising and setting of the Sun and stars could be explained by a rotating Earth, as Copernicus had said, still:
such a fast motion could not belong to the earth, a body very heavy and dense and opaque, but rather belongs to the sky itself whose form and subtle and constant matter are better suited to a perpetual motion, however fast.Tycho believed that, if the Earth did orbit the Sun, there should be an observable
stellar parallax
Stellar parallax is the apparent shift of position of any nearby star (or other object) against the background of distant objects, and a basis for determining (through trigonometry) the distance of the object. Created by the different orbital p ...
every six months (the stars' positions would change thanks to Earth's changing position). The lack of any stellar was explained by the Copernican theory as being due to the stars' enormous distances from Earth. Tycho noted and attempted to measure the apparent relative sizes of the stars in the sky. He used geometry
Geometry (; ) is, with arithmetic, one of the oldest branches of mathematics. It is concerned with properties of space such as the distance, shape, size, and relative position of figures. A mathematician who works in the field of geometry is c ...
to show that the distance to the stars in the Copernican system would have to be 700 times greater than the distance from the Sun to Saturn, and to be seen the stars at these distances, they would have to be gigantic—at least as big as the orbit of the Earth, and of course vastly larger than the Sun. Tycho said:
Deduce these things geometrically if you like, and you will see how many absurdities (not to mention others) accompany this assumption f the motion of the earthby inference.Copernicans offered a religious response to Tycho's geometry: titanic, distant stars might seem unreasonable, but they were not, for the Creator could make his creations that large if He wanted. In fact, Rothmann responded to this argument of Tycho's by saying:
at is so absurd about n average starhaving size equal to the whole rbit of the Earth What of this is contrary to divine will, or is impossible by divine Nature, or is inadmissible by infinite Nature? These things must be entirely demonstrated by you, if you will wish to infer from here anything of the absurd. These things that vulgar sorts see as absurd at first glance are not easily charged with absurdity, for in fact divine Sapience and Majesty is far greater than they understand. Grant the vastness of the Universe and the sizes of the stars to be as great as you like—these will still bear no proportion to the infinite Creator. It reckons that the greater the king, so much greater and larger the palace befitting his majesty. So how great a palace do you reckon is fitting to GOD?Religion played a role in Tycho's geocentrism also—he cited the authority of scripture in portraying the Earth as being at rest. He rarely used Biblical arguments alone (to him they were a secondary objection to the idea of Earth's motion) and over time he came to focus on scientific arguments, but he did take Biblical arguments seriously. Tycho's 1587 geo-heliocentric model differed from those of other geo-heliocentric astronomers, such as Wittich,
Reimarus Ursus
Nicolaus Reimers Baer (2 February 1551 – 16 October 1600), also ''Reimarus Ursus'', ''Nicolaus Reimers Bär'' or ''Nicolaus Reymers Baer'', was an astronomer and imperial mathematician to Emperor Rudolf II. Due to his family's background, ...
, Helisaeus Roeslin
Helisaeus Roeslin or Helisäus Röslin (17 January 1545 – 14 August 1616) was a German physician and astrologer who adopted a geoheliocentric model of the universe. He was one of five observers who concluded that the Great Comet of 1577 was loc ...
and David Origanus
David Origanus or David Tost (9 July 1558 – 11 July 1628/29) was a German astronomer and professor for Greek language and Mathematics at the Viadrina University in Frankfurt (Oder), where he had also studied.
Tost was born in Glatz (Klads ...
, in that the orbits of Mars and the Sun intersected. This was because Tycho had come to believe the distance of Mars from the Earth at opposition (that is, when Mars is on the opposite side of the sky from the Sun) was less than that of the Sun from the Earth. Tycho believed this because he came to believe Mars had a greater daily parallax than the Sun. But, in 1584, in a letter to a fellow astronomer, Brucaeus, he had claimed that Mars had been further than the Sun at the opposition of 1582, because he had observed that Mars had little or no daily parallax. He said he had therefore rejected Copernicus's model because it predicted Mars would be at only two-thirds the distance of the Sun. But, he apparently later changed his mind to the opinion that Mars at opposition was indeed nearer the Earth than the Sun was, but apparently without any valid observational evidence in any discernible Martian parallax. Such intersecting Martian and solar orbits meant that there could be no solid rotating celestial spheres, because they could not possibly interpenetrate. Arguably, this conclusion was independently supported by the conclusion that the comet of 1577 was superlunary, because it showed less daily parallax than the Moon and thus must pass through any celestial spheres in its transit.
Lunar theory
Tycho's distinctive contributions tolunar theory Lunar theory attempts to account for the motions of the Moon. There are many small variations (or perturbations) in the Moon's motion, and many attempts have been made to account for them. After centuries of being problematic, lunar motion can now ...
include his discovery of the variation of the Moon's longitude. This represents the largest inequality of longitude after the equation of the center
In two-body, Keplerian orbital mechanics, the equation of the center is the angular difference between the actual position of a body in its elliptical orbit and the position it would occupy if its motion were uniform, in a circular orbit of the ...
and the evection. He also discovered librations in the inclination of the plane of the lunar orbit, relative to the ecliptic (which is not a constant of about 5° as had been believed before him, but fluctuates through a range of over a quarter of a degree), and accompanying oscillations in the longitude of the lunar node
A lunar node is either of the two orbital nodes of the Moon, that is, the two points at which the orbit of the Moon intersects the ecliptic. The ''ascending'' (or ''north'') node is where the Moon moves into the northern ecliptic hemisphere ...
. These represent perturbations in the Moon's ecliptic latitude. Tycho's lunar theory doubled the number of distinct lunar inequalities, relative to those anciently known, and reduced the discrepancies of lunar theory to about a fifth of their previous amounts. It was published posthumously by Kepler
Johannes Kepler (; ; 27 December 1571 – 15 November 1630) was a German astronomer, mathematician, astrologer, natural philosopher and writer on music. He is a key figure in the 17th-century Scientific Revolution, best known for his laws o ...
in 1602, and Kepler's own derivative form appears in Kepler's ''Rudolphine Tables'' of 1627.
Subsequent developments in astronomy
Kepler used Tycho's records of the motion of Mars to deduce laws of planetary motion, enabling calculation of astronomical tables with unprecedented accuracy (the ''Rudolphine Tables'') and providing powerful support for aheliocentric
Heliocentrism (also known as the Heliocentric model) is the astronomical model in which the Earth and planets revolve around the Sun at the center of the universe. Historically, heliocentrism was opposed to geocentrism, which placed the Earth ...
model of the Solar System.
Francis Bacon
Francis Bacon, 1st Viscount St Alban (; 22 January 1561 – 9 April 1626), also known as Lord Verulam, was an English philosopher and statesman who served as Attorney General and Lord Chancellor of England. Bacon led the advancement of both ...
, for example, and the extended Capellan model of Riccioli
Giovanni Battista Riccioli, SJ (17 April 1598 – 25 June 1671) was an Italian astronomer and a Catholic priest in the Jesuit order. He is known, among other things, for his experiments with pendulums and with falling bodies, for his discussion ...
with Mars also orbiting the Sun whilst Saturn and Jupiter orbit the fixed Earth. But the Tychonic model was probably the most popular, albeit probably in what was known as 'the semi-Tychonic' version with a daily rotating Earth. This model was advocated by Tycho's ex-assistant and disciple Longomontanus in his 1622 ''Astronomia Danica'' that was the intended completion of Tycho's planetary model with his observational data, and which was regarded as the canonical statement of the complete Tychonic planetary system. Longomontanus' work was published in several editions and used by many subsequent astronomers, and through him the Tychonic system was adopted by astronomers as far away as China.
 The ardent anti-heliocentric French astronomer Jean-Baptiste Morin devised a Tychonic planetary model with elliptical orbits published in 1650 in a simplified, Tychonic version of the ''Rudolphine Tables''. Another geocentric French astronomer, Jacques du Chevreul, rejected Tycho's observations including his description of the heavens and the theory that Mars was below the Sun. Some acceptance of the Tychonic system persisted through the 17th century and in places until the early 18th century; it was supported (after a 1633 decree about the Copernican controversy) by "a flood of pro-Tycho literature" of Jesuit origin. Among pro-Tycho Jesuits, Ignace Pardies declared in 1691 that it was still the commonly accepted system, and Francesco Blanchinus reiterated that as late as 1728. Persistence of the Tychonic system, especially in Catholic countries, has been attributed to its satisfaction of a need (relative to Catholic doctrine) for "a safe synthesis of ancient and modern". After 1670, even many Jesuit writers only thinly disguised their Copernicanism. But in Germany, the Netherlands, and England, the Tychonic system "vanished from the literature much earlier".
James Bradley's discovery of
The ardent anti-heliocentric French astronomer Jean-Baptiste Morin devised a Tychonic planetary model with elliptical orbits published in 1650 in a simplified, Tychonic version of the ''Rudolphine Tables''. Another geocentric French astronomer, Jacques du Chevreul, rejected Tycho's observations including his description of the heavens and the theory that Mars was below the Sun. Some acceptance of the Tychonic system persisted through the 17th century and in places until the early 18th century; it was supported (after a 1633 decree about the Copernican controversy) by "a flood of pro-Tycho literature" of Jesuit origin. Among pro-Tycho Jesuits, Ignace Pardies declared in 1691 that it was still the commonly accepted system, and Francesco Blanchinus reiterated that as late as 1728. Persistence of the Tychonic system, especially in Catholic countries, has been attributed to its satisfaction of a need (relative to Catholic doctrine) for "a safe synthesis of ancient and modern". After 1670, even many Jesuit writers only thinly disguised their Copernicanism. But in Germany, the Netherlands, and England, the Tychonic system "vanished from the literature much earlier".
James Bradley's discovery of stellar aberration
In astronomy, aberration (also referred to as astronomical aberration, stellar aberration, or velocity aberration) is a phenomenon which produces an apparent motion of celestial objects about their true positions, dependent on the velocity of t ...
, published in 1729, eventually gave direct evidence excluding the possibility of all forms of geocentrism including Tycho's. Stellar aberration could only be satisfactorily explained on the basis that the Earth is in annual orbit around the Sun, with an orbital velocity that combines with the finite speed of the light coming from an observed star or planet, to affect the apparent direction of the body observed.
Work in medicine, alchemy and astrology
Tycho worked in medicine and alchemy. He was influenced by the Swiss physicianParacelsus
Paracelsus (; ; 1493 – 24 September 1541), born Theophrastus von Hohenheim (full name Philippus Aureolus Theophrastus Bombastus von Hohenheim), was a Swiss physician, alchemist, lay theologian, and philosopher of the German Renaissance.
He ...
, who considered the human body to be directly affected by celestial bodies.. Tycho used Paracelsus's ideas to connect empiricism and natural science, and religion and astrology. Using his herbal garden
The traditional kitchen garden, vegetable garden, also known as a potager (from the French ) or in Scotland a kailyaird, is a space separate from the rest of the residential garden – the ornamental plants and lawn areas. It is used for g ...
at Uraniborg, Tycho produced recipes for herbal medicines, and used them to treat fever and plague; his herbal medicines were in use until the end of the 19th century.
The expression '' Tycho Brahe days'' referred to "unlucky days" that were featured in almanacs from the 1700s onwards, but which have no direct connection to Tycho or his work. Whether because Tycho realized that astrology was not an empirical science, or because he feared religious repercussions, he did not publicise his own astrological work. For example, two of his more astrological treatises, one on weather predictions and an almanac, were published in the names of his assistants, in spite of the fact that he worked on them personally. Some scholars have argued that he lost faith in horoscope astrology over the course of his career, and others that he simply changed his public communication on the topic as he realized that connections with astrology could influence the reception of his empirical astronomical work.
Legacy
Biographies
 The first biography of Tycho, which was also the first full-length biography of any scientist, was written by Gassendi in 1654. In 1779, Tycho de Hoffmann wrote of Tycho's life in his history of the Brahe family. In 1913, Dreyer published Tycho's collected works, facilitating further research. Early modern scholarship on Tycho tended to see the shortcomings of his astronomical model, painting him as a mysticist recalcitrant in accepting the Copernican revolution, and valuing mostly his observations that allowed Kepler to formulate his laws of planetary movement. Especially in Danish scholarship, Tycho was depicted as a mediocre scholar and a traitor to the nation—perhaps because of the important role in Danish historiography of Christian IV as a warrior king. In the second half of the 20th century, scholars began reevaluating his significance, and studies by Kristian Peder Moesgaard, Owen Gingerich, Robert Westman, Victor E. Thoren, and John R. Christianson focused on his contributions to science, and demonstrated that while he admired Copernicus he was simply unable to reconcile his basic theory of physics with the Copernican view. Christianson's work showed the influence of Tycho's Uraniborg as a training center for scientists who after studying with Tycho went on to make contributions in various scientific fields.
The first biography of Tycho, which was also the first full-length biography of any scientist, was written by Gassendi in 1654. In 1779, Tycho de Hoffmann wrote of Tycho's life in his history of the Brahe family. In 1913, Dreyer published Tycho's collected works, facilitating further research. Early modern scholarship on Tycho tended to see the shortcomings of his astronomical model, painting him as a mysticist recalcitrant in accepting the Copernican revolution, and valuing mostly his observations that allowed Kepler to formulate his laws of planetary movement. Especially in Danish scholarship, Tycho was depicted as a mediocre scholar and a traitor to the nation—perhaps because of the important role in Danish historiography of Christian IV as a warrior king. In the second half of the 20th century, scholars began reevaluating his significance, and studies by Kristian Peder Moesgaard, Owen Gingerich, Robert Westman, Victor E. Thoren, and John R. Christianson focused on his contributions to science, and demonstrated that while he admired Copernicus he was simply unable to reconcile his basic theory of physics with the Copernican view. Christianson's work showed the influence of Tycho's Uraniborg as a training center for scientists who after studying with Tycho went on to make contributions in various scientific fields.
Scientific legacy
Although Tycho's planetary model was soon discredited, his astronomical observations were an essential contribution to thescientific revolution
The Scientific Revolution was a series of events that marked the emergence of modern science during the early modern period, when developments in mathematics, physics, astronomy, biology (including human anatomy) and chemistry transforme ...
. The traditional view of Tycho is that he was primarily an empiricist who set new standards for precise and objective measurements. This appraisal originated in Gassendi's 1654 biography, ''Tychonis Brahe, equitis Dani, astronomorum coryphaei, vita''. It was furthered by Dreyer's biography in 1890, which was long the most influential work on Tycho. According to historian of science Helge Kragh, this assessment grew out of Gassendi's opposition to Aristotelianism and Cartesianism, and fails to account for the diversity of Tycho's activities.
The Tycho Brahe Prize
The Tycho Brahe Prize is awarded by the European Astronomical Society. Inaugurated in 2008, the prize is awarded annually in recognition of the pioneering development or exploitation of European astronomical instrumentation, or major discoveries ...
, inaugurated in 2008, is awarded annually by the European Astronomical Society in recognition of the pioneering development or exploitation of European astronomical instrumentation, or major discoveries based largely on such instruments.
Cultural legacy
 Tycho's discovery of the new star was the inspiration for
Tycho's discovery of the new star was the inspiration for Edgar Allan Poe
Edgar Allan Poe (; Edgar Poe; January 19, 1809 – October 7, 1849) was an American writer, poet, editor, and literary critic. Poe is best known for his poetry and short stories, particularly his tales of mystery and the macabre. He is wid ...
's poem "Al Aaraaf
"Al Aaraaf" is an early poem by American writer Edgar Allan Poe, first published in 1829. It tells of the afterlife in a place called Al Aaraaf, inspired by A'raf as described in the Quran. At 422 lines, it is Poe's longest poem.
"Al Aaraaf", w ...
". In 1998, ''Sky & Telescope
''Sky & Telescope'' (''S&T'') is a monthly American magazine covering all aspects of amateur astronomy, including the following:
*current events in astronomy and space exploration;
*events in the amateur astronomy community;
*reviews of astronomic ...
'' magazine published an article by Donald Olson, Marilynn S. Olson and Russell L. Doescher arguing, in part, that Tycho's supernova was also the same "star that's westward from the pole" in Shakespeare's ''Hamlet
''The Tragedy of Hamlet, Prince of Denmark'', often shortened to ''Hamlet'' (), is a tragedy written by William Shakespeare sometime between 1599 and 1601. It is Shakespeare's longest play, with 29,551 words. Set in Denmark, the play depicts ...
''.
Tycho is directly referenced in Sarah Williams' poem The Old Astronomer: "Reach me down my Tycho Brahé,—I would know him when we meet". Though, the poem's oft quoted line comes later: "Though my soul may set in darkness, it will rise in perfect light; / I have loved the stars too truly to be fearful of the night." Alfred Noyes also wrote a long biographical poem in honor of Brahe.
The lunar crater Tycho is named in his honour, as is the crater Tycho Brahe on Mars and the minor planet 1677 Tycho Brahe
1677 Tycho Brahe, provisional designation , is a stony Marian asteroid from the central region of the asteroid belt, approximately in diameter. It was discovered on 6 September 1940, by Finnish astronomer Yrjö Väisälä at Turku Observatory i ...
in the asteroid belt. The bright supernova, SN 1572, is also known as Tycho's Nova
SN 1572 ('' Tycho's Supernova'', ''Tycho's Nova''), or B Cassiopeiae (B Cas), was a supernova of Type Ia in the constellation Cassiopeia, one of eight supernovae visible to the naked eye in historical records. It appeared in early November 1572 ...
and the Tycho Brahe Planetarium in Copenhagen is also named after him,Lutz D. Schmadel. ''Dictionary of Minor Planet Names''. Springer Science + Business Media. p. 96. as is the palm genus ''Brahea
''Brahea'' is a genus of palms in the family Arecaceae. They are commonly referred to as hesper palms and are endemic to Mexico and Central America.Govaerts, R. & Dransfield, J. (2005). World Checklist of Palms: 1-223. The Board of Trustees of ...
''.
Brahe Rock in Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean, it contains the geographic South Pole. Antarctica is the fifth-largest cont ...
is named after Tycho Brahe.
Notes
Works (selection)
''De Mundi Aetherei Recentioribus Phaenomenis Liber Secundus''
(Uraniborg, 1588; Prague, 1603; Frankfurt, 1610)
''Tychonis Brahe Astronomiae Instauratae Progymnasmata''
(Prague, 1602/03; Frankfurt, 1610) *
See also
* December 1573 lunar eclipse * History of trigonometryReferences
Sources
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *Further reading
* * *External links
*Information about the opening of Brahe's tomb in 2010
from
Aarhus University
Aarhus University ( da, Aarhus Universitet, abbreviated AU) is a public research university with its main campus located in Aarhus, Denmark. It is the second largest and second oldest university in Denmark. The university is part of the Coimbra Gr ...
* The Noble Dane: Images of Tycho Brahe
', an exhibition by the Museum of the History of Science, Oxford in 2004
The Correspondence of Tycho Brahe
from the
Bodlean Library
The Bodleian Library () is the main research library of the University of Oxford, and is one of the oldest libraries in Europe. It derives its name from its founder, Sir Thomas Bodley. With over 13 million printed items, it is the second- ...
's Early Modern Letters Online website
''Astronomiae instauratae mechanica'', 1602 edition
from Lehigh University
archived
20 December 2022)
''Learned Tico Brahae, His Astronomicall Coniectur'', 1632
– full digital facsimile, Linda Hall Library
Coat-of-arms of Brahe
on the island of Ven (Sweden) {{DEFAULTSORT:Brahe, Tycho * 1546 births 1601 deaths 16th-century Danish astronomers 16th-century Latin-language writers 16th-century alchemists Christian astrologers Copernican Revolution Danish alchemists Danish astrologers Danish Lutherans Danish science writers Discoverers of supernovae Leipzig University alumni Philippists Danish scientific instrument makers University of Copenhagen alumni University of Rostock alumni