
Terumah, Terumoh, Terimuh, or Trumah (—
Hebrew
Hebrew (; ; ) is a Northwest Semitic language of the Afroasiatic language family. Historically, it is one of the spoken languages of the Israelites and their longest-surviving descendants, the Jews and Samaritans. It was largely preserved ...
for "gift" or "offering," the twelfth
word
A word is a basic element of language that carries an objective or practical meaning, can be used on its own, and is uninterruptible. Despite the fact that language speakers often have an intuitive grasp of what a word is, there is no conse ...
and first distinctive word in the parashah) is the nineteenth
weekly Torah portion
It is a custom among religious Jewish communities for a weekly Torah portion to be read during Jewish prayer services on Monday, Thursday, and Saturday. The full name, ''Parashat HaShavua'' ( he, פָּרָשַׁת הַשָּׁבוּעַ), is p ...
(, ''parashah'') in the annual
Jewish
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
cycle of
Torah reading
Torah reading (; ') is a Jewish religious tradition that involves the public reading of a set of passages from a Torah scroll. The term often refers to the entire ceremony of removing the scroll (or scrolls) from the Torah ark, chanting th ...
and the seventh in the
Book of Exodus
The Book of Exodus (from grc, Ἔξοδος, translit=Éxodos; he, שְׁמוֹת ''Šəmōṯ'', "Names") is the second book of the Bible. It narrates the story of the Exodus, in which the Israelites leave slavery in Biblical Egypt through ...
. The parashah tells of
God's
In monotheistic thought, God is usually viewed as the supreme being, creator, and principal object of faith. Swinburne, R.G. "God" in Honderich, Ted. (ed)''The Oxford Companion to Philosophy'', Oxford University Press, 1995. God is typically ...
instructions to make the
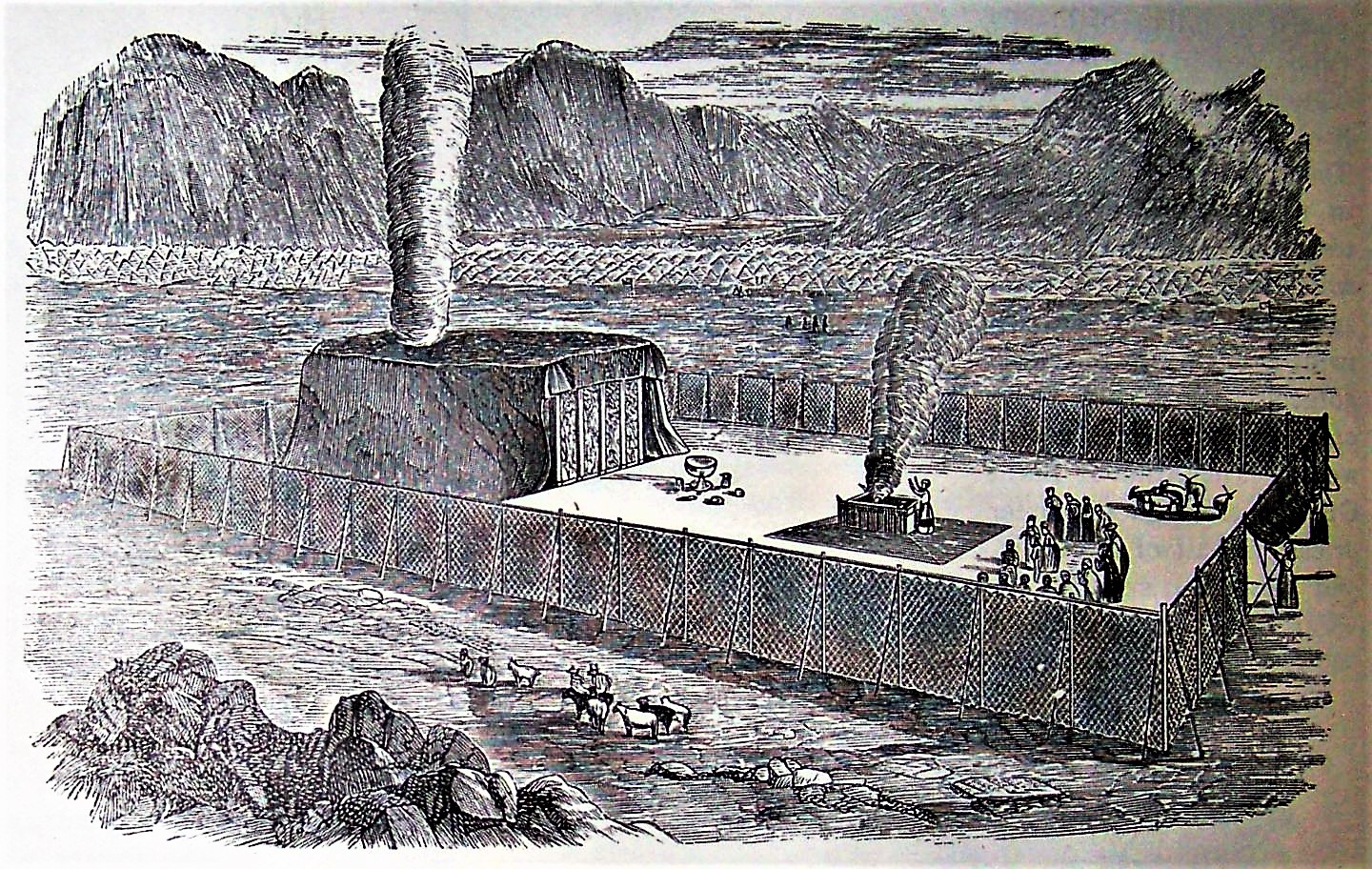
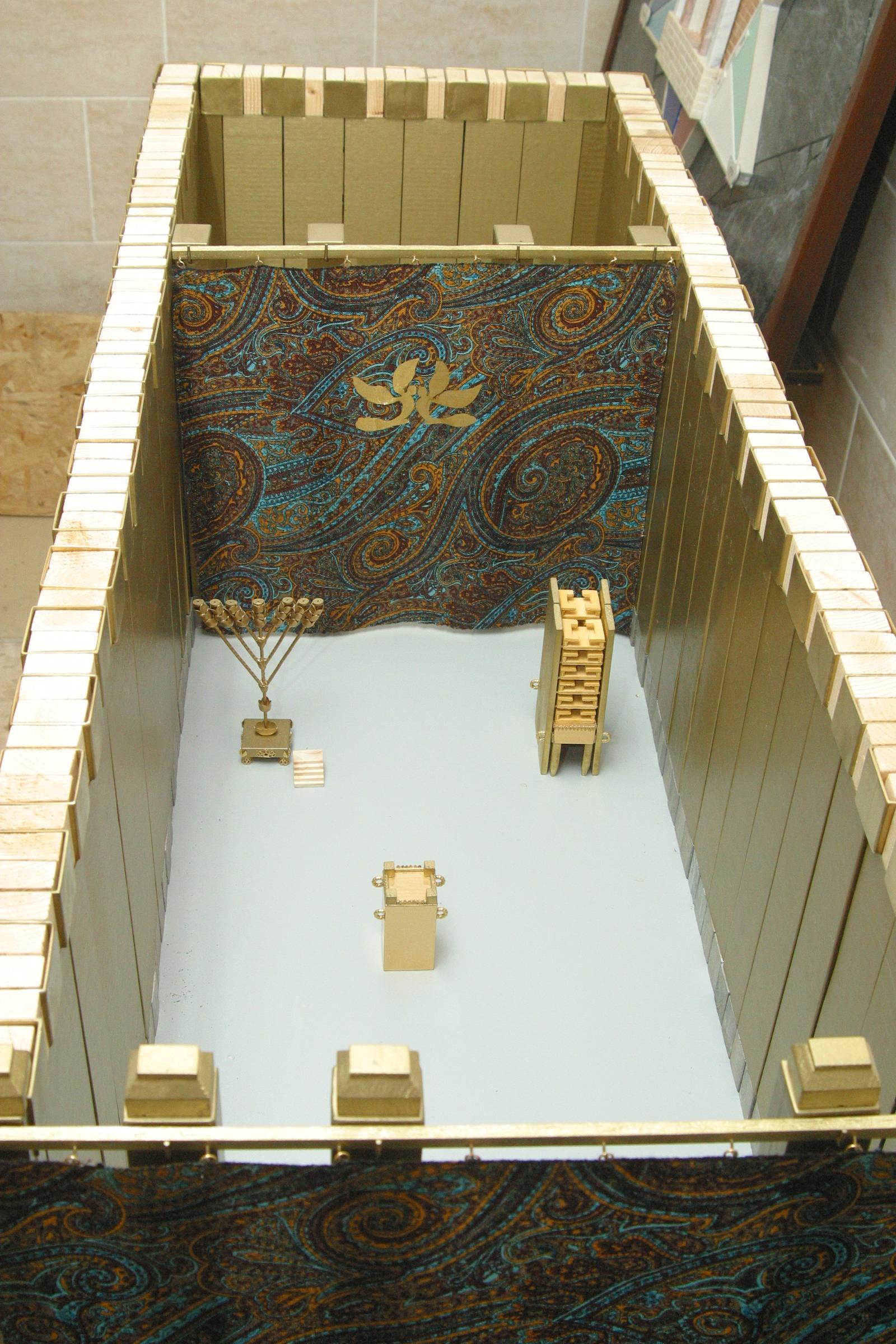
Tabernacle
According to the Hebrew Bible, the tabernacle ( he, מִשְׁכַּן, mīškān, residence, dwelling place), also known as the Tent of the Congregation ( he, link=no, אֹהֶל מוֹעֵד, ’ōhel mō‘ēḏ, also Tent of Meeting, etc.), ...
and its furnishings. The parashah constitutes . It is made up of 4,692 Hebrew letters, 1,145 Hebrew words, 96
verses, and 155 lines in a Torah Scroll (''
Sefer Torah
A ( he, סֵפֶר תּוֹרָה; "Book of Torah"; plural: ) or Torah scroll is a handwritten copy of the Torah, meaning the five books of Moses (the first books of the Hebrew Bible). The Torah scroll is mainly used in the ritual of To ...
'').
Jew
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""T ...
s in the
Diaspora
A diaspora ( ) is a population that is scattered across regions which are separate from its geographic place of origin. Historically, the word was used first in reference to the dispersion of Greeks in the Hellenic world, and later Jews after ...
read it the nineteenth
Sabbath
In Abrahamic religions, the Sabbath () or Shabbat (from Hebrew ) is a day set aside for rest and worship. According to the Book of Exodus, the Sabbath is a day of rest on the seventh day, commanded by God to be kept as a holy day of rest, as ...
after
Simchat Torah
Simchat Torah or Simhat Torah (, lit., "Rejoicing with/of the Torah", Ashkenazi: ''Simchas Torah'') is a Jewish holiday that celebrates and marks the conclusion of the annual cycle of public Torah readings, and the beginning of a new cycle. Simch ...
, generally in February and rarely in early March.
Readings
In traditional Sabbath Torah reading, the parashah is divided into seven readings, or , ''
aliyot''.

First reading—Exodus 25:1–16
In the first reading, God instructed
Moses
Moses hbo, מֹשֶׁה, Mōše; also known as Moshe or Moshe Rabbeinu ( Mishnaic Hebrew: מֹשֶׁה רַבֵּינוּ, ); syr, ܡܘܫܐ, Mūše; ar, موسى, Mūsā; grc, Mωϋσῆς, Mōÿsēs () is considered the most important pr ...
to tell all
Israelite
The Israelites (; , , ) were a group of Semitic-speaking tribes in the ancient Near East who, during the Iron Age, inhabited a part of Canaan.
The earliest recorded evidence of a people by the name of Israel appears in the Merneptah Stel ...
s whose heart so moved them to bring gifts of
gold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au (from la, aurum) and atomic number 79. This makes it one of the higher atomic number elements that occur naturally. It is a bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile ...
,
silver
Silver is a chemical element with the symbol Ag (from the Latin ', derived from the Proto-Indo-European ''h₂erǵ'': "shiny" or "white") and atomic number 47. A soft, white, lustrous transition metal, it exhibits the highest electrical ...
,
copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu (from la, cuprum) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pink ...
, colored
yarn
Yarn is a long continuous length of interlocked fibres, used in sewing, crocheting, knitting, weaving, embroidery, ropemaking, and the production of textiles. Thread is a type of yarn intended for sewing by hand or machine. Modern manu ...
s, fine
linen
Linen () is a textile made from the fibers of the flax plant.
Linen is very strong, absorbent, and dries faster than cotton. Because of these properties, linen is comfortable to wear in hot weather and is valued for use in garments. It also ...
,
goats' hair, tanned
ram
Ram, ram, or RAM may refer to:
Animals
* A male sheep
* Ram cichlid, a freshwater tropical fish
People
* Ram (given name)
* Ram (surname)
* Ram (director) (Ramsubramaniam), an Indian Tamil film director
* RAM (musician) (born 1974), Dutch
* ...
skins,
acacia
''Acacia'', commonly known as the wattles or acacias, is a large genus of shrubs and trees in the subfamily Mimosoideae of the pea family Fabaceae. Initially, it comprised a group of plant species native to Africa and Australasia. The genus nam ...
wood, oil, spices,
lapis lazuli
Lapis lazuli (; ), or lapis for short, is a deep-blue metamorphic rock used as a semi-precious stone that has been prized since antiquity for its intense color.
As early as the 7th millennium BC, lapis lazuli was mined in the Sar-i Sang mine ...
, and other fine stones to make a sanctuary—the Tabernacle (''Mishkan'', )—and its furnishings, so that God could dwell among them.
[.] God instructed them to make the
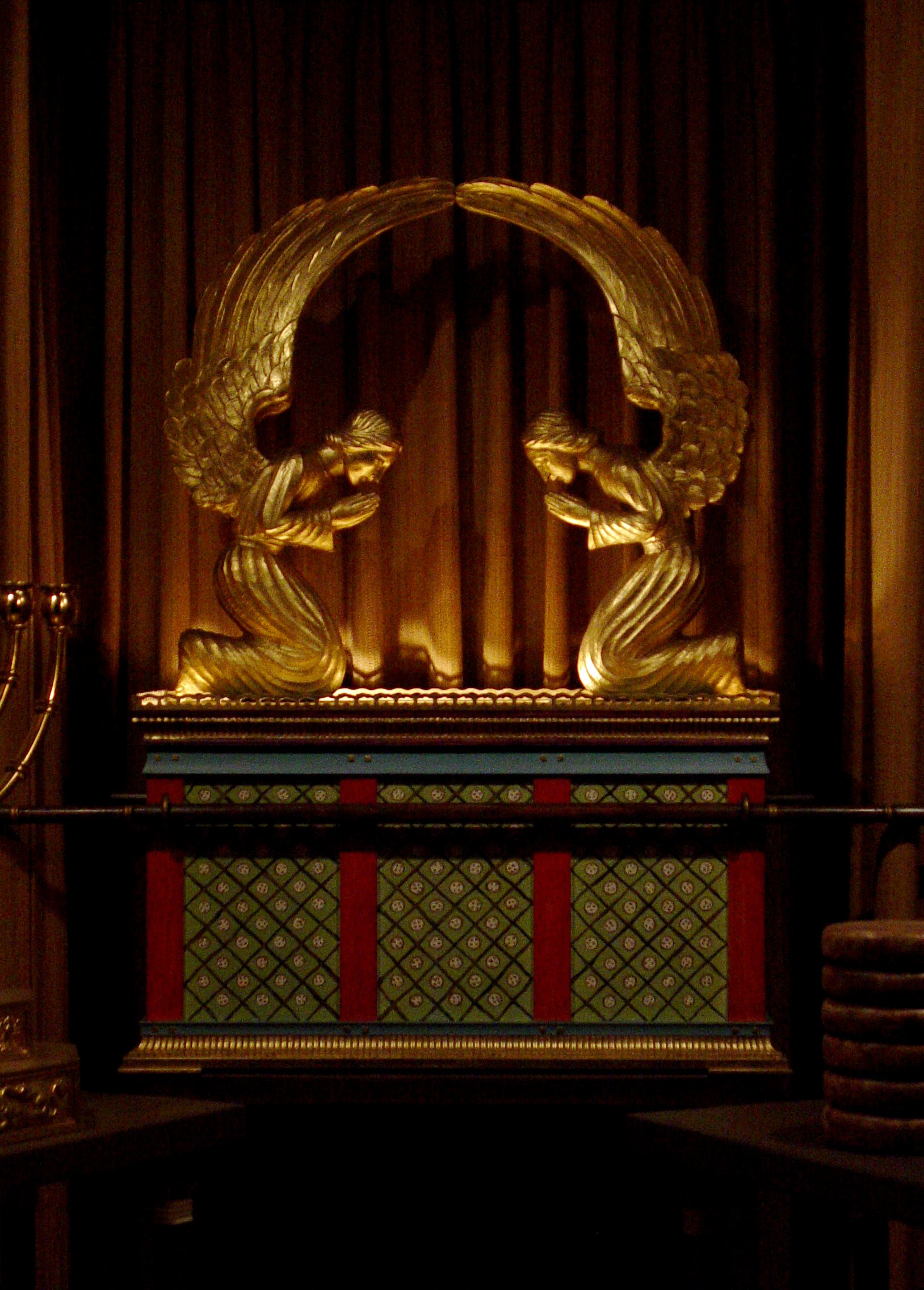
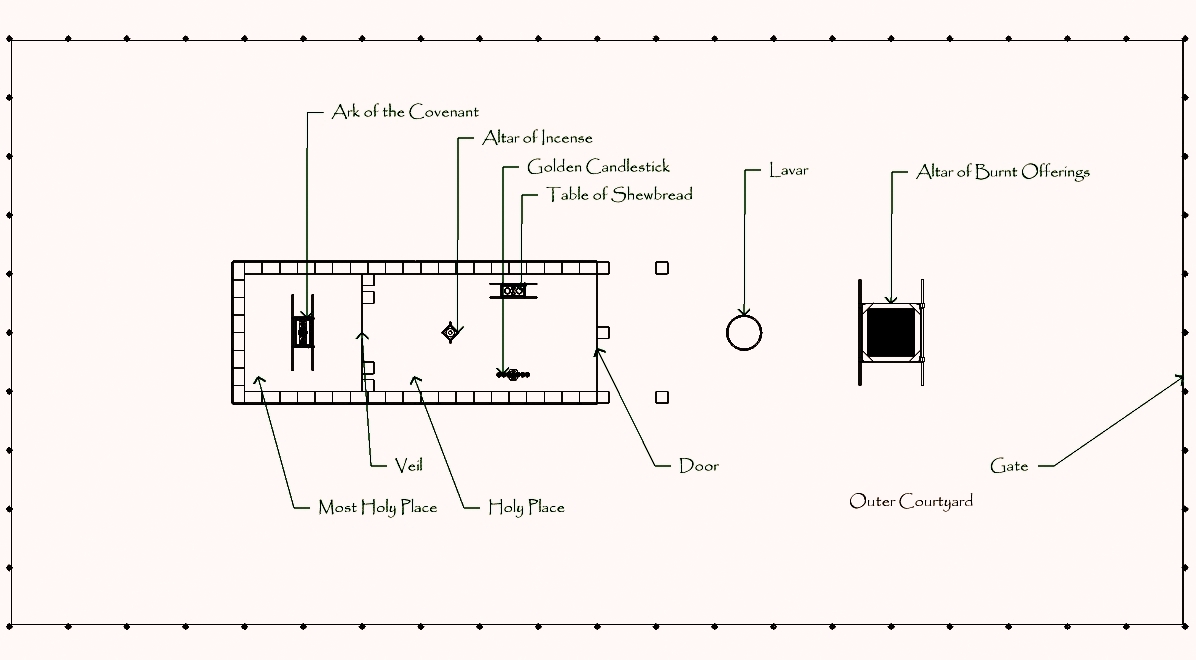
Ark of the Covenant
The Ark of the Covenant,; Ge'ez: also known as the Ark of the Testimony or the Ark of God, is an alleged artifact believed to be the most sacred relic of the Israelites, which is described as a wooden chest, covered in pure gold, with an ...
of acacia wood overlaid with gold in which to deposit the tablets setting forth God's commandments.
Second reading—Exodus 25:17–30
In the second reading, God told them to make two
cherub
A cherub (; plural cherubim; he, כְּרוּב ''kərūḇ'', pl. ''kərūḇīm'', likely borrowed from a derived form of akk, 𒅗𒊏𒁍 ''karabu'' "to bless" such as ''karibu'', "one who blesses", a name for the lamassu) is one of the ...
im of gold to be for the ark's cover over the
mercy seat. God promised to impart commandments to Moses from between the two cherubim above the cover of the Ark.
God instructed them to make a table of acacia wood overlaid with gold, on which to set the bread of display or
showbread
Showbread ( he, לחם הפנים ''Leḥem haPānīm'', literally: "Bread of the Faces"), in the King James Version: shewbread, in a biblical or Jewish context, refers to the cakes or loaves of bread which were always present, on a specially-d ...
.

Third reading—Exodus 25:31–26:14
In the third reading, God instructed them to make a six-branched, seven-lamped lampstand—
menorah—of pure gold. God instructed them to make the Tabernacle of ten curtains of fine twisted linen, of blue, purple, and crimson yarns, with a design of cherubim worked into them. God instructed them to make 11 cloths of goats' hair for a tent over the Tabernacle, and coverings of tanned ram skins and ''tachash'' skins ().
Fourth reading—Exodus 26:15–30
In the fourth reading, God instructed them to make boards of acacia wood and overlay the boards with gold for the Tabernacle.
Fifth reading—Exodus 26:31–37
In the fifth reading, God instructed them to make a curtain of blue, purple, and crimson yarns, and fine twisted linen, with a design of cherubim, to serve as a partition obscuring the
Holy of Holies
The Holy of Holies (Hebrew: ''Qōḏeš haqQŏḏāšīm'' or ''Kodesh HaKodashim''; also הַדְּבִיר ''haDəḇīr'', 'the Sanctuary') is a term in the Hebrew Bible that refers to the inner sanctuary of the Tabernacle, where God's pres ...
. God instructed them to place the Ark, the table, and the lampstand in the Tabernacle. God instructed them to make a screen for the entrance of the Tent, of colored yarns, and fine twisted linen, done in embroidery and supported by five posts of acacia wood overlaid with gold.
Sixth reading—Exodus 27:1–8
In the sixth reading, God instructed them to make the altar of acacia wood overlaid with copper.
Seventh reading—Exodus 27:9–19
In the seventh reading, God instructed them to make the enclosure of the Tabernacle from fine twisted linen.
Readings according to the triennial cycle
Jews who read the Torah according to the
triennial cycle
The Triennial cycle of Torah reading may refer to either
* The historical practice in ancient Israel by which the entire Torah was read in serial fashion over a three-year period, or
* The practice adopted by many Reform, Conservative, Reconstruct ...
of Torah reading read the parashah according to the following schedule:
Inner-biblical interpretation
The parashah has parallels or is discussed in these Biblical sources:
This is the pattern of instruction and construction of the Tabernacle and its furnishings:

The
Priestly story of the Tabernacle in echoes the Priestly story of creation in . As the creation story unfolds in seven days, the instructions about the Tabernacle unfold in seven speeches. In both creation and Tabernacle accounts, the text notes the completion of the task. In both creation and Tabernacle, the work done is seen to be good. In both creation and Tabernacle, when the work is finished, God takes an action in acknowledgement. In both creation and Tabernacle, when the work is finished, a blessing is invoked. And in both creation and Tabernacle, God declares something "holy."
Jeffrey Tigay noted
[Jeffrey H. Tigay, "Exodus," in Adele Berlin and Marc Brettler, editors, ''Jewish Study Bible: 2nd Edition'', page 157.] that the lampstand held seven candles, Aaron wore seven sacral vestments, the account of the building of the Tabernacle alludes to the creation account, and the Tabernacle was completed on New Year's Day. And
Carol Meyers noted that and list seven kinds of substances—metals, yarn, skins, wood, oil, spices, and gemstones—signifying the totality of supplies.
[Carol Meyers, "Exodus," in ]Michael D. Coogan
Michael D. Coogan is lecturer on Hebrew Bible/Old Testament at Harvard Divinity School, Director of Publications for the Harvard Semitic Museum, editor-in-chief of Oxford Biblical Studies Online, and professor emeritus of religious studies at Stone ...
, Marc Z. Brettler, Carol A. Newsom, and Pheme Perkins Pheme Perkins (born 1945 in Louisville, Kentucky) is a Professor of Theology at Boston College, where she has been teaching since 1972. She is a nationally recognized expert on the Greco-Roman cultural setting of early Christianity, as well as the P ...
, editors, ''The New Oxford Annotated Bible'' (New York: Oxford University Press, Revised 4th Edition 2010), page 117. Martin Buber
Martin Buber ( he, מרטין בובר; german: Martin Buber; yi, מארטין בובער; February 8, 1878 –
June 13, 1965) was an Austrian Jewish and Israeli philosopher best known for his philosophy of dialogue, a form of existentialism ...
and others noted that the language used to describe the building of the Tabernacle parallels that used in the story of creation:

The Tabernacle also exhibited similarities with Mount Sinai. Both Mount Sinai and the Tabernacle had three separate areas with increasing levels of exclusivity—one for the people generally, one for the anointed class, and one for only the single representative of the people; the tablets of the law a cloud; and God's presence. And God spoke to Moses at both Mount Sinai and the Tabernacle. But in contrast to Mount Sinai, with the Tabernacle God's presence was constant; God's presence was in their midst, no longer distant; and God's presence was no longer rooted to a fixed place.
God's request for "willing" gifts in is echoed in the accounts of gifts given "willingly" in
1 Chronicles
The Book of Chronicles ( he, דִּבְרֵי־הַיָּמִים ) is a book in the Hebrew Bible, found as two books (1–2 Chronicles) in the Christian Old Testament. Chronicles is the final book of the Hebrew Bible, concluding the third sect ...
in the time of
David
David (; , "beloved one") (traditional spelling), , ''Dāwūd''; grc-koi, Δαυΐδ, Dauíd; la, Davidus, David; gez , ዳዊት, ''Dawit''; xcl, Դաւիթ, ''Dawitʿ''; cu, Давíдъ, ''Davidŭ''; possibly meaning "beloved one". w ...
and in for the
Second Temple
The Second Temple (, , ), later known as Herod's Temple, was the reconstructed Temple in Jerusalem between and 70 CE. It replaced Solomon's Temple, which had been built at the same location in the United Kingdom of Israel before being inherited ...
.
In early nonrabbinic interpretation
The parashah is discussed in these early nonrabbinic sources:
Josephus
Flavius Josephus (; grc-gre, Ἰώσηπος, ; 37 – 100) was a first-century Romano-Jewish historian and military leader, best known for '' The Jewish War'', who was born in Jerusalem—then part of Roman Judea—to a father of priestly ...
interpreted the Tabernacle and its furnishings to represent the universe. He saw the Tabernacle's two parts accessible to the
priests
A priest is a religious leader authorized to perform the sacred rituals of a religion, especially as a mediatory agent between humans and one or more deities. They also have the authority or power to administer religious rites; in particu ...
(the Holy and the Courtyard) to denote the land and the sea, the third division set aside for God (the Holy of Holies) to represent heaven, inaccessible to people. He saw the 12 loaves to denote the year divided into months. He saw the Menorah divided into 70 parts, representing the 70 divisions of the planets, and the seven lamps on the Menorah to refer to the course of the seven planets (then known). He saw the veils, composed of four things, to declare the four elements: the fine linen signified the earth, because the flax grows out of the earth; the purple signified the sea, because purple was dyed by the blood of shellfish from the sea; the blue signified the air; and the scarlet signified fire.

Philo
Philo of Alexandria (; grc, Φίλων, Phílōn; he, יְדִידְיָה, Yəḏīḏyāh (Jedediah); ), also called Philo Judaeus, was a Hellenistic Jewish philosopher who lived in Alexandria, in the Roman province of Egypt.
Philo's de ...
taught that the two cherubim in represented God's two primary powers—(1) God's beneficent power, in accordance with which God made the world, and in respect of which God is called "God," and (2) God's chastening power, according to which God rules and governs what God has created, and in respect of which God is called "Lord." Philo read to teach that God's two powers were divided in the middle by God standing above them both. And reports that God would speak to the Israelites from between the two cherubim to show that the two powers are equal, God's beneficent and chastising powers being divided by the same Word.
In classical rabbinic interpretation
The parashah is discussed in these
rabbi
A rabbi () is a spiritual leader or religious teacher in Judaism. One becomes a rabbi by being ordained by another rabbi – known as '' semikha'' – following a course of study of Jewish history and texts such as the Talmud. The basic form o ...
nic sources from the era of the
Mishnah
The Mishnah or the Mishna (; he, מִשְׁנָה, "study by repetition", from the verb ''shanah'' , or "to study and review", also "secondary") is the first major written collection of the Jewish oral traditions which is known as the Oral Tor ...
and the
Talmud
The Talmud (; he, , Talmūḏ) is the central text of Rabbinic Judaism and the primary source of Jewish religious law ('' halakha'') and Jewish theology. Until the advent of modernity, in nearly all Jewish communities, the Talmud was the ce ...
:

Exodus chapter 25
A
Midrash
''Midrash'' (;["midrash"]
''Random House Webster's Unabridged Dictionary''. he, מִדְרָשׁ; ...
read to say "that they take Me as an offering" and thus to tell how God gave the Torah to Israel and said to them: "You are taking Me."
Reading God's words in , "accept gifts for Me from ''every person'' whose heart so moves him," the
Mekhilta of Rabbi Simeon deduced that each and every Israelite was so rich from having stripped the Egyptians (as reported in ) that each Israelite had the wherewithal to erect the Tent of Meeting, with all its vessels, all of its golden hooks, boards, wooden bars, columns, and pedestals.
A Midrash taught that calls for offerings of gold, silver, and brass for the construction of the Tabernacle, because gold symbolizes
Babylon
''Bābili(m)''
* sux, 𒆍𒀭𒊏𒆠
* arc, 𐡁𐡁𐡋 ''Bāḇel''
* syc, ܒܒܠ ''Bāḇel''
* grc-gre, Βαβυλών ''Babylṓn''
* he, בָּבֶל ''Bāvel''
* peo, 𐎲𐎠𐎲𐎡𐎽𐎢 ''Bābiru''
* elx, 𒀸𒁀𒉿𒇷 ''Babi ...
, of which says, "As for that image, its head was of fine gold"; silver symbolizes the
Medes
The Medes ( Old Persian: ; Akkadian: , ; Ancient Greek: ; Latin: ) were an ancient Iranian people who spoke the Median language and who inhabited an area known as Media between western and northern Iran. Around the 11th century BC, ...
, of which says, "Its breast and its arms were of silver"; and brass refers to
Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders wi ...
, of which says, "Its belly and thighs were of brass." But the Bible makes no mention of iron in the construction either of the Tabernacle or of the
Temple in Jerusalem
The Temple in Jerusalem, or alternatively the Holy Temple (; , ), refers to the two now-destroyed religious structures that served as the central places of worship for Israelites and Jews on the modern-day Temple Mount in the Old City of Jeru ...
, because iron symbolizes
Rome
, established_title = Founded
, established_date = 753 BC
, founder = King Romulus ( legendary)
, image_map = Map of comune of Rome (metropolitan city of Capital Rome, region Lazio, Italy).svg
, map_caption ...
, which destroyed the Temple.
The Rabbis taught in a
Baraita
''Baraita'' ( Aramaic: "external" or "outside"; pl. ''Barayata'' or ''Baraitot''; also Baraitha, Beraita; Ashkenazi: Beraisa) designates a tradition in the Jewish oral law not incorporated in the Mishnah. ''Baraita'' thus refers to teachings ...
that the turquoise wool (''techeilet'', ) listed in came from an animal called a ''chilazon'' that resembled the sea in color and a fish in shape, that appeared once every 70 years, and whose blood was used to dye the expensive blue thread.
But what fabric did the blue of dye? The school of Rabbi Ishmael taught that all unspecified garments mentioned in the Torah are of wool or linen.
Rabbi Elai said in the name of Rabbi
Simeon ben Lakish
Shim‘on ben Lakish ( he, שמעון בן לקיש; arc, שמעון בר לקיש ''Shim‘on bar Lakish'' or ''bar Lakisha''), better known by his nickname Reish Lakish (c. 200 — c. 275), was an amora who lived in the Roman province of Judae ...
(Resh Lakish) that
Rabbi Meir
Rabbi Meir ( he, רַבִּי מֵאִיר) was a Jewish sage who lived in the time of the Mishnah. He was considered one of the greatest of the Tannaim of the fourth generation (139-163). He is the third most frequently mentioned sage in the Mis ...
used to maintain that the , ''techashim'' (sometimes translated "sealskins" or "dolphin skins") listed in came from an animal called a ''tachash'' that lived in the time of Moses. It was a separate species, and the Sages could not decide whether it was a wild beast or a domestic animal. It had one horn on its forehead, and it came to Moses providentially just for the occasion. Moses made the Tabernacle's covering, and then the ''tachash'' disappeared. The
Gemara
The Gemara (also transliterated Gemarah, or in Yiddish Gemo(r)re; from Aramaic , from the Semitic root ג-מ-ר ''gamar'', to finish or complete) is the component of the Talmud comprising rabbinical analysis of and commentary on the Mishnah ...
taught that the ''tachash'' was multicolored.
The
Tosefta
The Tosefta ( Jewish Babylonian Aramaic: תוספתא "supplement, addition") is a compilation of the Jewish oral law from the late 2nd century, the period of the Mishnah.
Overview
In many ways, the Tosefta acts as a supplement to the Mishnah ( ...
deduced from (and the principle that the law prohibits doing on the Sabbath all that was done to build the Tabernacle) that one who tans hides on the Sabbath violates the commandment to keep the Sabbath.
The Tosefta taught that invalidity of either the onyx stones or the stones to be set described in invalidated the other.
[Tosefta Menachot 6:11, in, e.g., Jacob Neusner, translator, ''Tosefta'', volume 2, pages 1430–31.]
The Tosefta taught that provided the commandment that said that Moses fulfilled.
A Midrash explained with a parable God's instruction to build a Tabernacle. A king had only one daughter, who married another king. When the son-in-law king wished to return to his country and take his wife with him, the father king told him that he could neither part with his daughter nor tell her husband not to take her, as she was now his wife. The father king thus asked the son-in-law king the favor that wherever the son-in-law king would go to live, he would have a chamber ready for the father king to dwell with them, for he could not bear to leave his daughter. Thus, God told Israel that God had given Israel a Torah from which God could not part, and yet God also could not tell Israel not to take the Torah. Thus, God asked the Israelites to make for God a house wherein God might sojourn wherever the Israelites went, and thus says, "And let them make Me a sanctuary, that I may dwell among them."
Rabbi
Eleazar ben Azariah
Eleazar ben Azariah ( he, אלעזר בן עזריה) was a 1st-century CE Jewish tanna, i.e. Mishnaic sage. He was of the second generation and a junior contemporary of Gamaliel II, Eliezer b. Hyrcanus, Joshua b. Hananiah, and Akiva.
Bio ...
taught that the words of , "And let them make Me a sanctuary, that I may dwell among them," demonstrate that so great is labor that God's Presence did not dwell among the Israelites until they had performed the labor of making the sanctuary.
The
Mekhilta of Rabbi Ishmael
The Mekhilta of Rabbi Ishmael ( arc, מְכִילְתָּא דְּרַבִּי יִשְׁמָעֵאל IPA /məˈχiltɑ/, "a collection of rules of interpretation") is midrash halakha to the Book of Exodus. The Jewish Babylonian Aramaic title ' ...
asked why in God commanded, "Let them make Me a sanctuary that I may dwell among them," when in , God said, "The heaven is My throne, and the earth is My footstool; where is the house that you may build for Me?" The Mekhilta of Rabbi Ishmael taught that the purport of the commandment was simply to enable the Israelites to receive a reward for fulfilling it.
The Babylonian Talmud related a story about God's desire for the Tabernacle. Rabbi
Judah ha-Nasi
Judah ha-Nasi ( he, יְהוּדָה הַנָּשִׂיא, ''Yəhūḏā hanNāsīʾ''; Yehudah HaNasi or Judah the Prince) or Judah I, was a second-century rabbi (a tanna of the fifth generation) and chief redactor and editor of the ''Mis ...
arranged for his son to marry a daughter of the household of Rabbi Yosei ben Zimra. The two Rabbis agreed that they would support the groom for twelve years to go to study in the study hall. It was assumed that he would first go to study and then get married. But when the groom saw the bride to be, he asked that they shorten the delay to just six years. When he saw her again, he said that he wanted to marry her immediately and then go to study. He was then ashamed to see his father, as he thought Rabbi Judah would reprimand him for his impatience. His father placated him and told him that he had his Maker's perception, meaning that he acted the same way as God did. For initially, the words of , "You bring them and plant them in the mountain of Your inheritance, the place that You, O Lord, have made for You to dwell in," indicated that God’s original intention was to build a Temple for the Jewish people after they had entered the Land of Israel. But then in , God directed, "And let them make Me a Sanctuary, that I may dwell among them," that is, even while they were still in the desert, indicating that due to their closeness to God, the Israelites enjoyed greater affection from God and God therefore advanced what would originally have come later.
Abba Ḥanan in the name of Rabbi Elazar noted that says, "And make you an ark of wood," indicating that it should be from your own property, while says, "And they shall make an ark of acacia wood," meaning from the Jewish people. The Gemara resolved this apparent contradiction by teaching that refers to a time when the Jewish people did God's will, and they are credited with building the Ark of the Covenant. , however, refers to a time when the Jewish people do not do God's will, and making the Ark is attributed to Moses alone. Thus, when Israel acts according to the Torah, they are accounted as makers of the Ark, but when they do not, the Ark is seen as the product of Moses alone.

A Midrash taught that everything God created in heaven has a replica on earth. And the Midrash taught that many things in the Tabernacle reflected things in heaven. Thus reports that there are cherubim in heaven, saying, "O Lord of hosts, the God of Israel, Who sits between the cherubim." While below on earth, directs the Israelites to fashion two cherubim of gold to spread their wings to cover the Ark. Of heaven,
Psalm
The Book of Psalms ( or ; he, תְּהִלִּים, , lit. "praises"), also known as the Psalms, or the Psalter, is the first book of the ("Writings"), the third section of the Tanakh, and a book of the Old Testament. The title is derived f ...
reports that God "stretches out the heavens like a curtain." While of earth, directs the Israelites to create "ten curtains" for the Tabernacle. Of heaven, reports, "Above
odstood the seraphim." While on earth, directs the Israelites to "make the boards for the Tabernacle of acacia-wood, standing up." (Thus, the standing boards of acacia wood correspond to the standing seraphim.) Of heaven, reports God's command, "Let there be a firmament in the midst of the waters, and let it divide the waters from the waters." While on earth, directs the Israelites that "the veil shall divide between the holy place and the most holy." Of heaven, reports, "And the light dwells with
od" While on earth, directs, "That they bring to you pure olive-oil beaten for the light." (Thus, since all that is above is also below, God dwells on earth just as God dwells in heaven.) And what is more, the Midrash taught that God holds the things below on earth dearer than those above, for as reports, God left the things in heaven to descend to dwell among those below, saying, "And let them make Me a sanctuary, that I may dwell among them."
The Mekhilta of Rabbi Ishmael taught that sets forth laws of Sabbath observance where it does because in God directed, "And let them make Me a sanctuary," and one might have understood that they could build the sanctuary both on weekdays and the Sabbath. The Mekhilta of Rabbi Ishmael taught that God's direction in to "make Me a sanctuary" applied on all days other than the Sabbath. The Mekhilta of Rabbi Ishmael posited that one might argue that since the Temple service occurs even on the Sabbath, then perhaps the preparation for the service, without which the priests could not perform the service, could occur even on the Sabbath. One might conclude that if the horn of the altar broke off or a knife became defective, one might repair them on the Sabbath. teaches, however, that even such work must be done only on weekdays, and not on the Sabbath.

Rabbi Simeon son of Rabbi Ishmael interpreted the term "the Tabernacle of the testimony" in to mean that the Tabernacle was God's testimony to the whole world that God had forgiven Israel for having made the
Golden Calf
According to the Bible, the golden calf (עֵגֶל הַזָּהָב '' ‘ēgel hazzāhāv'') was an idol (a cult image) made by the Israelites when Moses went up to Mount Sinai. In Hebrew, the incident is known as ''ḥēṭə’ hā‘ēgel'' ...
. Rabbi Isaac explained with a parable. A king took a wife whom he dearly loved. He became angry with her and left her, and her neighbors taunted her, saying that he would not return. Then the king sent her a message asking her to prepare the king's palace and make the beds therein, for he was coming back to her on such-and-such a day. On that day, the king returned to her and became reconciled to her, entering her chamber and eating and drinking with her. Her neighbors at first did not believe it, but when they smelled the fragrant spices, they knew that the king had returned. Similarly, God loved Israel, bringing the Israelites to Mount Sinai, and giving them the Torah, but after only 40 days, they sinned with the Golden Calf. The heathen nations then said that God would not be reconciled with the Israelites. But when Moses pleaded for mercy on their behalf, God forgave them, as reports, "And the Lord said: ‘I have pardoned according to your word.'" Moses then told God that even though he personally was quite satisfied that God had forgiven Israel, he asked that God might announce that fact to the nations. God replied that God would cause God's
Shechinah
Shekhinah, also spelled Shechinah ( Hebrew: שְׁכִינָה ''Šəḵīnā'', Tiberian: ''Šăḵīnā'') is the English transliteration of a Hebrew word meaning "dwelling" or "settling" and denotes the presence of God, as it were, in a pla ...
to dwell in their midst, and thus says, "And let them make Me a sanctuary, that I may dwell among them." And by that sign, God intended that all nations might know that God had forgiven the Israelites. And thus calls it "the Tabernacle of the testimony," because the Tabernacle was a testimony that God had pardoned the Israelites' sins.

A Midrash told that when God told Moses to make a tabernacle for God (in ), Moses questioned how God could command Moses make a tabernacle for God, if God's Glory fills heaven and earth. And Moses saw prophetically that
Solomon
Solomon (; , ),, ; ar, سُلَيْمَان, ', , ; el, Σολομών, ; la, Salomon also called Jedidiah (Hebrew language, Hebrew: , Modern Hebrew, Modern: , Tiberian Hebrew, Tiberian: ''Yăḏīḏăyāh'', "beloved of Yahweh, Yah"), ...
would one day build a Temple, much larger than the Tabernacle, and yet (in
1 Kings
The Book of Kings (, '' Sēfer Məlāḵīm'') is a book in the Hebrew Bible, found as two books (1–2 Kings) in the Old Testament of the Christian Bible. It concludes the Deuteronomistic history, a history of Israel also including the book ...
) Solomon would say to God, "But will God in truth dwell on the earth? Behold, heaven and the heaven of heavens cannot contain You; how much less this house that I have built!" God replied that God does not think as humans think. Twenty boards on the north, twenty on the south, and eight in the west can suffice. God could even confine God's Shechinah within one square
cubit
The cubit is an ancient unit of length based on the distance from the elbow to the tip of the middle finger. It was primarily associated with the Sumerians, Egyptians, and Israelites. The term ''cubit'' is found in the Bible regarding ...
.
Rav Assi of Hozna'ah deduced from the words, "And it came to pass in the first month of the second year, on the first day of the month," in that the Tabernacle was erected on the first of
Nisan
Nisan (or Nissan; he, נִיסָן, Standard ''Nīsan'', Tiberian ''Nīsān''; from akk, 𒊬𒊒𒄀 ''Nisanu'') in the Babylonian and Hebrew calendars is the month of the barley ripening and first month of spring. The name of the month i ...
. With reference to this, a
Tanna taught that the first of Nisan took ten crowns of distinction by virtue of the ten momentous events that occurred on that day. The first of Nisan was: (1) the first day of the Creation, (2) the first day of the princes' offerings, (3) the first day for the priesthood to make the sacrificial offerings, (4) the first day for public sacrifice, (5) the first day for the descent of fire from Heaven, (6) the first for the priests' eating of sacred food in the sacred area, (7) the first for the dwelling of the Shechinah in Israel, (8) the first for the
Priestly Blessing
The Priestly Blessing or priestly benediction, ( he, ברכת כהנים; translit. ''birkat kohanim''), also known in rabbinic literature as raising of the hands (Hebrew ''nesiat kapayim'') or rising to the platform (Hebrew ''aliyah ledukhan'') ...
of Israel, (9) the first for the prohibition of the
high place
"High place", or "high places", (Hebrew במה ''bamah'' and plural במות ''bamot'' or ''bamoth'') in a biblical context always means "place(s) of worship". This rendering has etymological justification, as appears from the poetical use of the ...
s, and (10) the first of the months of the year.
A Baraita further compared the day that the Israelites dedicated the Tabernacle with the day that God created the universe. Reading the words of , "And it came to pass on the eighth day," the Baraita taught that on that day (when the Israelites dedicated the Tabernacle) there was joy before God as on the day when God created heaven and earth. For says, "And it came to pass (, ''va-yehi'') on the eighth day," and says, "And there was (, ''va-yehi'') one day." And Rav Judah taught in the name of Rav that God endowed the Tabernacle's craftsman Bezalel with the same attribute that God used in creating the universe. Rav Judah said in the name of Rav that Bezalel knew how to combine the letters by which God created the heavens and earth. For says (about Bezalel), "And He has filled him with the spirit of God, in wisdom and in understanding, and in knowledge," and says (about creation), "The Lord by wisdom founded the earth; by understanding He established the heavens," and says, "By His knowledge the depths were broken up."
The Gemara deduced from , "And let them make Me a sanctuary, that I may dwell among them," that the Tabernacle was called "Sanctuary." And the Gemara deduced that the Sanctuary (that is, the Temple in Jerusalem) was called "Tabernacle" from , "And I will set my Tabernacle among you" (as this was said after the Israelites had already erected the Tabernacle in the wilderness). Thus the Gemara concluded that Scripture calls the Tabernacle "Sanctuary" and the Sanctuary (that is, the Temple) "Tabernacle," and one may thus draw analogies between the two.
Reading , "According to all that I show you, the pattern of the Tabernacle . . . even so shall you make it," Rav
Shimi bar Hiyya deduced that just as the Tabernacle required the consent of Moses, so additions to the Temple or the City of Jerusalem required the consent of the Sanhedrin (the heir to the authority of Moses). (The phrase, "so shall you make it," is superfluous, because already said, "Let them make Me a sanctuary." So Rav Shimi read the superfluous phrase to imply that whatever was done for the Tabernacle in the wilderness should be done for any future Temple or Temple city, as well.)
Interpreting the words, "And ''they'' shall make an Ark," in , Rabbi Judah ben Rabbi Shalom taught that God said that all should come and occupy themselves with the Ark so that they all might merit the Torah.
Rabbi Simeon taught that there are three crowns—the crown of Torah, the crown of priesthood, and the crown of royalty; but the crown of a good name surpasses them all. The table is the crown of kingship, of which says, "And make thereto a crown of gold round about." The altar is the crown of priesthood, of which says, "And you shall make unto it a crown of gold round about." And the Ark is the crown of the Torah, of which says, "And you shall make upon it a crown of gold round about." The word for "crown" (''zer'', ) can also be read as ''zar'' (stranger), to teach that if a person has merit, it becomes like a crown, but if a person does not have merit, then it becomes alien to that person. Of the other furnishings, Scripture says, "And ''you'' shall make," whereas of the Ark, says, "And ''they'' shall make," to teach that the crown of the Torah stands above all; when a person acquires the Torah, it is as though that person has acquired all the rest.

Once when Rabbi
Hanina
Rav Hanina (or Hananiah, sometimes spelled: Hananyah; he, רב חנינא or ) was second and third generation Amora Sage of the Land of Israel.
Biography
He was a student of Rabbi Yannai and R. Yochanan bar Nafcha.
He was the scion of a fa ...
went out to the country, some villagers noted an apparent contradiction between two verses. says: "And the house which King Solomon built for the Lord, the length thereof was 60 cubits, and the breadth thereof 20 cubits, and the height thereof 30 cubits." And says: "And before the Sanctuary which was 20 cubits in length, and 20 cubits in breadth, and 20 cubits in the height thereof." Rabbi Hanina replied that accounts for the space from the edge of the Cherubim upwards. The Gemara deduced that thus teaches that the 10 cubits of space below (from the floor to the top of the Cherubim) was like the 20 cubits of space above (the Cherubim) in that neither space served any material purpose. (Both spaces were devoid of any structure.) This supports Rabbi Levi (or others say
Rabbi Johanan), who said it is a tradition passed down from our fathers that the place of the Ark and the Cherubim is not included in the measured space (and miraculously they occupied none of the space of the Sanctuary). So, as well, it was taught in a Baraita that the Ark that Moses made had a free space of 10 cubits on every side (and miraculously occupied none of the space of the Holy of Holies in the Tabernacle).
Ravina said in the name of
Samuel
Samuel ''Šəmūʾēl'', Tiberian: ''Šămūʾēl''; ar, شموئيل or صموئيل '; el, Σαμουήλ ''Samouḗl''; la, Samūēl is a figure who, in the narratives of the Hebrew Bible, plays a key role in the transition from the bib ...
that the Cherubim made by Solomon stood by a miracle (and took up no space), for says, "And five cubits was the one wing of the cherub, and five cubits the other wing of the cherub; from the uttermost part of the one wing unto the uttermost part of the other were ten cubits." (The two Cherubim would thus have filled up the entire 20 cubits of the Sanctuary.) As the Sanctuary thus left no room for their bodies to stand, the Gemara inferred that they stood by a miracle.
Abaye
Abaye ( he, אַבַּיֵי) was a rabbi of the Jewish Talmud who lived in Babylonia, known as an amora of the fourth generation. He was born about the close of the third century, and died 337 CE.
Biography
His father, Kaylil, was the brother ...
demurred that they might have been standing with their bodies under their wings like hens (whose wings touch each other on their backs, leaving their entire bodies covered by their wings).
Rava demurred that perhaps they did not stand opposite each another (and thus their wings overlapped). Rav
Aha bar Jacob
Rav Aha bar Jacob (or R. Aha bar Ya'akov; he, רבי אחא בר יעקב) was an Babylonian rabbi of the third and fourth generations of Amoraim.
He was one of the disciples of Rav Huna. He was also one of the prominent Jewish leaders of Papu ...
demurred that they might have stood diagonally.
Rav Huna the son of Rav Joshua demurred that the house might have been wider above than below.
Rav Papa
Rav Pappa ( he, רַב פַּפָּא) (c. 300 – died 375) was a Babylonian rabbi, of the fifth generation of amoraim.
Biography
He was a student of Rava and Abaye. After the death of his teachers he founded a school at Naresh, a city near ...
demurred that their wings might have been bent.
Rav Ashi
Rav Ashi ( he, רב אשי) ("Rabbi Ashi") (352–427) was a Babylonian Jewish rabbi, of the sixth generation of amoraim. He reestablished the Academy at Sura and was the first editor of the Babylonian Talmud.
Biography
According to a trad ...
demurred that their wings might have overlapped each other.

Noting that says, "You shall overlay it with pure gold, within and without," Rava interpreted that any scholar whose inside is not like the outside is no scholar. (A scholar thus should have the same golden character inside and out.)
The Mishnah described how on
Yom Kippur
Yom Kippur (; he, יוֹם כִּפּוּר, , , ) is the holiest day in Judaism and Samaritanism. It occurs annually on the 10th of Tishrei, the first month of the Hebrew calendar. Primarily centered on atonement and repentance, the day' ...
the
High Priest
The term "high priest" usually refers either to an individual who holds the office of ruler-priest, or to one who is the head of a religious caste.
Ancient Egypt
In ancient Egypt, a high priest was the chief priest of any of the many gods rev ...
(, ''Kohen Gadol'') would place a fire pan between the two bars of the Ark of the Covenant described in .

Rabbi
Abbahu
Rabbi Abbahu ( he, אבהו) was a Jew and Talmudist of the Talmudic Academies in Syria Palaestina from about 279-320 and is counted a member of the third generation of Amoraim. He is sometimes cited as Rabbi Abbahu of Kisrin (Caesarea).
Biogra ...
taught that a cherub (as in ) had a face like a child (''keravya''), for in Babylonia they called a child ''ravya''. Rav Papa asked Abaye that if this is so, then there is a difficulty interpreting , which says of
Ezekiel
Ezekiel (; he, יְחֶזְקֵאל ''Yəḥezqēʾl'' ; in the Septuagint written in grc-koi, Ἰεζεκιήλ ) is the central protagonist of the Book of Ezekiel in the Hebrew Bible.
In Judaism, Christianity, and Islam, Ezekiel is ac ...
's vision, "the first face was the face of the cherub, and the second face was the face of a man, and the third the face of a lion, and the fourth the face of an eagle." Would not the face of the cherub and the face of a man be the same? The Gemara answered that one was a big face, and the other was a small face.

Rabbi Johanan and
Rabbi Eleazar differed on how the Cherubim stood. One said that they faced each other, and the other said they faced inward (toward the door). The Gemara asked how one could reconcile the view that they faced each other with , which says, "And their faces were inward." The Gemara explained that they faced each other (in a sign of affection, symbolizing the relationship between God and the people) when Israel obeyed God's will of God; they faced inward (away from each other, symbolizing God's unrequited love for Israel) when Israel did not obey God's will. The Gemara asked how one could reconcile the view that they faced inward with , which says, "With their faces one to another." The Gemara explained that they were slightly turned sideways (partly facing each other and partly facing inward). As it was taught in a Baraita,
Onkelos
Onkelos ( he, אֻנְקְלוֹס ''ʾunqəlōs''), possibly identical to Aquila of Sinope, was a Roman national who converted to Judaism in Tannaic times ( 35–120 CE). He is considered to be the author of the Targum Onkelos ( 110 C ...
the proselyte said that the Cherubim were formed like children (as some read ) and their faces were turned sideways, like those of a student who takes leave of the student's master (turning sideways for some distance before turning the student's back completely on the master).
Rav Kattina said that whenever the Israelites came up to the Temple on a
Festival
A festival is an event ordinarily celebrated by a community and centering on some characteristic aspect or aspects of that community and its religion or cultures. It is often marked as a local or national holiday, mela, or eid. A festival c ...
, the priests would pull back the curtain and show them the Cherubim, whose bodies were intertwined with one another (in an embrace). And the priests would tell the people that they were as beloved by God as the love between a man and a woman. Rav Aha bar Jacob explained that the
Second Temple
The Second Temple (, , ), later known as Herod's Temple, was the reconstructed Temple in Jerusalem between and 70 CE. It replaced Solomon's Temple, which had been built at the same location in the United Kingdom of Israel before being inherited ...
contained painted Cherubim, as says: "And he (Solomon) carved all the walls of the house round about with carved figures of Cherubim and palm-trees and open flowers, within and without," and says, "he overlaid them with gold fitted upon the graven work." And says: "According to the space of each, with ''loyot'' (, ‘wreaths round about')." Rabbah son of
Rav Shilah said that "according to the space of each with ''loyot''" means "even as a man embracing his companion." ("''Loyot''" is connected with the root signifying "attach.") Resh Lakish taught that when the Romans entered the Temple (during its destruction) and saw the Cherubim whose bodies were intertwined with one another, they carried them out and mocked the Israelites, saying that a people whose blessings and curses God supposedly fulfilled occupied themselves with such (sensuous) things. And immediately the Romans debased them, as says: "All that honored her, despised her, because they have seen her nakedness."

Rabbi Meir and
Rabbi Judah differed over what the "testimony" was that God directed Moses to place in the Ark in . Rabbi Meir taught that the Ark contained the stone tablets and a Torah scroll. Rabbi Judah, however, taught that the Ark contained only the stone tablets, with the Torah scroll placed outside. Reading , Rabbi Meir noted that the Ark was 2½ cubits long, and as a standard cubit equals 6 handbreadths, the Ark was thus 15 handbreadths long. Rabbi Meir calculated that the tablets were 6 handbreadths long, 6 wide, and 3 thick, and were placed next to each other in the Ark. Thus the tablets accounted for 12 handbreadths, leaving 3 handbreadths unaccounted for. Rabbi Meir subtracted 1 handbreadth for the two sides of the Ark (½ handbreadth for each side), leaving 2 handbreadths for the Torah scroll. Rabbi Meir deduced that a scroll was in the Ark from the words of , "There was nothing in the Ark save the two tablets of stone that Moses put there." As the words "nothing" and "save" create a limitation followed by a limitation, Rabbi Meir followed the rule of Scriptural construction that a limitation on a limitation implies the opposite—here the presence of something not mentioned—the Torah scroll. Rabbi Judah, however, taught that the cubit of the Ark equaled only 5 handbreadths, meaning that the Ark was 12½ handbreadths long. The tablets (each 6 handbreadths wide) were deposited next to each other in the Ark, accounting for 12 handbreadths. There was thus left half a handbreadth, for which the two sides of the Ark accounted. Accounting next for width of the Ark, Rabbi Judah calculated that the tablets took up 6 handbreadths and the sides of the Ark accounted for ½ handbreadth, leaving 1 handbreadth. There Rabbi Judah taught were deposited the silver columns mentioned in
Song of Songs ,, "King Solomon made himself a palanquin of the wood of Lebanon, he made the pillars thereof of silver." At the side of the Ark was placed the coffer that the
Philistines
The Philistines ( he, פְּלִשְׁתִּים, Pəlīštīm; Koine Greek ( LXX): Φυλιστιείμ, romanized: ''Phulistieím'') were an ancient people who lived on the south coast of Canaan from the 12th century BC until 604 BC, whe ...
sent as a present, as reported in
1 Samuel
The Book of Samuel (, ''Sefer Shmuel'') is a book in the Hebrew Bible, found as two books (1–2 Samuel) in the Old Testament. The book is part of the narrative history of Ancient Israel called the Deuteronomistic history, a series of books ( Jo ...
, where the Philistine king said, "And put the jewels of gold which you return him for a guilt offering in a coffer by the side thereof, and send it away that it may go." And on this coffer was placed the Torah scroll, as says, "Take this book of the law, and put it by the side of the Ark of the Covenant of the Lord," demonstrating that the scroll was placed by the side of the Ark and not in it. Rabbi Judah interpreted the double limitation of , "nothing in the Ark save," to imply that the Ark also contained the fragments of the first tablets that Moses broke. The Gemara further explained that according to Rabbi Judah's theory, before the Philistine coffer came, the Torah scroll was placed on a ledge projecting from the Ark. Rabbi
Joshua ben Levi
Joshua ben Levi (Yehoshua ben Levi) was an amora, a scholar of the Talmud, who lived in the Land of Israel in the first half of the third century. He lived and taught in the city of Lod. He was an elder contemporary of Johanan bar Nappaha an ...
taught his children to be careful to respect an elderly scholar who has forgotten his learning through no fault of his own, for it was said that both the whole tablets and the fragments of the tablets that Moses broke were placed in the Ark.

Rabbi Hanina noted that for all the vessels that Moses made, the Torah gave the measurements of their length, breadth, and height (in for the altar, for the table, and for the incense altar). But for the Ark-cover, gave its length and breadth, but not its height. Rabbi Hanina taught that one can deduce the Ark-cover's height from the smallest of the vessel features, the border of the table, concerning which says, "And you shall make for it a border of a handbreadth round about." Just as the height of the table's border was a handbreadth, so was it also for the Ark-cover.
Rav Huna
Rav Huna (Hebrew: רב הונא) was a Jewish Talmudist and Exilarch who lived in Babylonia, known as an amora of the second generation and head of the Academy of Sura; he was born about 216 (212 according to Gratz) and died in 296-297 (608 of ...
taught that the height of the Ark-cover may be deduced from , which refers to "the ''face'' of the ark-cover," and a "face" cannot be smaller than a handbreadth. Rav Aha bar Jacob taught a tradition that the face of the cherubim was not less than a handbreadth, and Rav Huna also made his deduction about the Ark-cover's height from the parallel.
The Mishnah described details of the table envisioned in .
Rabbi Jose
Jose ben Halafta or Yose ben Halafta (or Yose ben Halpetha) (Hebrew: רבי יוסי בן חלפתא; IPA: /ʁa'bi 'josi ben xa'lafta/) was a tanna of the fourth generation (2nd century CE). He is the fifth-most-frequently mentioned sage in the M ...
differed with the Mishnah to teach that the handbreadth-high frame described in , not props, held the showbread in place, but they interpreted the table's rim to exist only at the feet of the table, not at its surface.
The Mishnah taught that one who stole one of the sacred vessels (''kisvot'') described in and was struck down by zealots on the spot.

Ben Zoma
Simeon ben Zoma, also known as Simon ben Zoma, Shimon ben Zoma or simply Ben Zoma (), was a tanna of the 1st and 2nd centuries CE. His name is used without the title "Rabbi" because, like Ben Azzai, he died at a young age, remaining in the grade ...
interpreted to teach that the showbread had to have faces. And the Tosefta interpreted to teach that the table did not remain overnight without bread.
The Rabbis considered what one needed to do to fulfill the commandment of to set the bread of display before God "continually" (, ''tamid'')—and the implications of that for the commandment of that "this book of the law shall not depart out of your mouth, but you shall meditate therein day and night." Rabbi Jose taught that even if they took the old bread of display away in the morning and placed the new bread on the table only in the evening, they had honored the commandment to set the bread "continually." Rabbi Ammi analogized from this teaching of Rabbi Jose that people who learn only one chapter of Torah in the morning and one chapter in the evening have nonetheless fulfilled the precept of that "this book of the law shall not depart out of your mouth, but you shall meditate therein day and night." Rabbi Johanan said in the name of Rabbi Simeon ben Yohai that even people who read just the ''
Shema
''Shema Yisrael'' (''Shema Israel'' or ''Sh'ma Yisrael''; he , שְׁמַע יִשְׂרָאֵל ''Šəmaʿ Yīsrāʾēl'', "Hear, O Israel") is a Jewish prayer (known as the Shema) that serves as a centerpiece of the morning and evening Jewis ...
'' () morning and evening thereby fulfill the precept of . Rabbi Johanan taught that it is forbidden, however, to teach this to people who through ignorance are careless in the observance of the laws (as it might deter them from further Torah study). But Rava taught that it is meritorious to say it in their presence (as they might think that if merely reciting the ''Shema'' twice daily earns reward, how great would the reward be for devoting more time to Torah study).
The Rabbis taught in a Baraita that throughout the 40 years that
Simeon the Just
Simeon the Righteous or Simeon the Just ( he, שִׁמְעוֹן הַצַדִּיק ''Šīməʿōn haṢadīq'') was a Jewish High Priest during the Second Temple period. He is also referred to in the Mishnah, where he is described as one of the la ...
served as High Priest, a blessing was bestowed upon the showbread. Every priest who obtained a piece of the showbread as big as an olive ate it and became sated. Some would eat less and leave some uneaten. After the time of Simeon the Just, a curse was sent upon the showbread, so that every priest received a piece as small as a bean. The pious priests withdrew their hands from it, while gluttonous priests took and devoured it. Once a gluttonous priest grabbed his portion as well as that of his fellow, and thereafter they called him "grasper" until his dying day.

The Mishnah taught that the absence of one of the seven branches of the menorah mandated in invalidated the others and the absence of one of the seven lamps of the menorah invalidated the others. The Gemara explained that this is so because uses the expression "shall be" in this connection. Similarly, the Tosefta taught that invalidity of any of the cups, knops, or flowers of the menorah described in invalidated the others.
Issi ben Judah
Issi ben Judah ( he, איסי בן יהודה, "''Issi ben Yehuda''") was a Tanna of the late 2nd century and early 3rd century. He is often identified with ''R. Yosi Ish Hakfar HaBavli'' (Pirkei Avot 4:26), ''Yosef HaBavli'', ''Issi Ha-babli'', a ...
listed the words "like almond blossoms" in among five passages in the Torah whose grammatical structures are unclear. Issi ben Judah taught that it is unclear whether "like almond blossoms" refers to the cups mentioned before or the knobs and flowers mentioned after.
Rabbi Hiyya
Hiyya, or Hiyya the Great, (ca. 180–230 CE) (Hebrew: רבי חייא, or רבי חייא הגדול) was a Jewish sage in the Land of Israel during the transitional generation between the Tannaic and Amoraic eras (1st Amora generation). Activ ...
bar Abba said in the name of Rabbi Johanan that the angel
Gabriel
In Abrahamic religions (Judaism, Christianity and Islam), Gabriel (); Greek: grc, Γαβριήλ, translit=Gabriḗl, label=none; Latin: ''Gabriel''; Coptic: cop, Ⲅⲁⲃⲣⲓⲏⲗ, translit=Gabriêl, label=none; Amharic: am, ገብ� ...
put on something like an artisan's apron and demonstrated to Moses the work of the menorah, for says, "And this was the work of the menorah" (the term "this" implying that something was held up as a pattern or model to illustrate the instructions).

Rabbi Abin compared the instruction of to a handsome king who instructed a servant to fashion a bust exactly like him. The servant exclaimed that he could not possibly make a likeness exactly like the king. But the king replied that the servant would paint it with his materials, but the king would appear in his own glory. Thus, when in God told Moses "see that you make them after their pattern," Moses complained that he was not God that he should be able to make one exactly like the pattern. God replied that Moses should follow the pattern of blue, purple, and scarlet that he saw above. The "acacia-wood, standing up" of would reflect the Seraphim who stand above, and Rabbi Hiyya bar Abba said that the gold clasps of would reflect the glittering stars in heaven. Thus God told Moses that if he would make below a replica of that which was above, God would cause God's Shechinah to dwell among the people.

Exodus chapter 26
instructed the Israelites to make the Tabernacle curtains out of "fine twined linen" (, ''sheish''). The Rabbis taught in a Baraita that whenever the Torah instructed the Israelites to make things with "fine twined linen" (, ''sheish''), they used threads composed of six (, ''sheish'') strands woven into each thread.
Noting that with regard to the curtains in the Tabernacle, calls it "the work of the skillful designer," while calls it "the work of the embroiderer," Rabbi Eleazar read the two verses together. Rabbi Eleazar taught that the embroiderers embroidered over the design that the designers had drawn. Alternatively, a Baraita taught in the name of Rabbi Nehemiah that the embroiderer's work was needlework that was visible on only one face of the cloth, while the designer's work was woven work that appeared on both faces of the cloth.
Rabban Yochanan ben Zakai, Johanan ben Zakai interpreted the word "Lebanon" in to refer to the Temple in Jerusalem and "that goodly mountain" to refer to the Temple Mount. A Midrash employed this understanding of "Lebanon" as the Temple to explain the role of gold in the world. Rabbi
Simeon ben Lakish
Shim‘on ben Lakish ( he, שמעון בן לקיש; arc, שמעון בר לקיש ''Shim‘on bar Lakish'' or ''bar Lakisha''), better known by his nickname Reish Lakish (c. 200 — c. 275), was an amora who lived in the Roman province of Judae ...
taught that the world did not deserve to have the use of gold. But God created gold for the sake of the Tabernacle (for example, in ) and the Temple. The Midrash deduced this from the use of the word "good" in both , where it says, "the gold of that land is good," and , where it says, "that goodly hill-country, and Lebanon," concluding that the gold of the land was created for that which is good, the Temple.
Rav Ashi taught that one could derive from the term , ''ashtei-esreih'', or "eleven," in that one who adds to God's word actually subtracts from it. Were one to subtract the first letter of the term, it would yield , ''shtei-esreih'', or "twelve," so adding that letter reduces its meaning.
The Rabbis taught in a Baraita that the Tabernacle's lower curtains were made of blue wool, purple wool, crimson wool, and fine linen, while the upper curtains that made the tent spread were made of goats' hair. And they taught that the upper curtains required greater skill than the lower, for says of the lower ones, "And all the women that were wise-hearted did spin with their hands," while says of the upper ones, "And all the women whose heart stirred them up in wisdom spun the goats." It was taught in Rabbi Nehemiah's name that the hair was washed on the goats and spun while still on the goats.
Rav Adda bar Ahavah said that the ''tachash'' skins mentioned in came from an animal that lived in the days of Moses. The Gemara interpreted Rabbi Nehemiah to say that its skin had many colors.
Rabbi Haninah taught that the world was unworthy to have Cedrus libani, cedar trees, but God created them for the sake of the Tabernacle (for example, in the acacia-wood of ) and the Temple, as says, "The trees of the Lord have their fill, the cedars of Lebanon, which He has planted," once again interpreting Lebanon to mean the Temple. Rabbi Samuel ben Nahman in the name of Rabbi Jonathan taught that there are 24 kinds of cedars, of which seven are especially fine, as says, "I will plant in the wilderness the cedar, the acacia-tree, and the myrtle, and the oil-tree; I will set in the desert the cypress, the plane-tree, and the larch together." God foresaw that the Tabernacle would be made of these trees, as says, "Wherein the birds make their nests," and "birds" refers to those birds that the priests offered. And when says, "As for the stork (, ''hasidah''), the fir-trees are her house," the , ''hasidah'' (stork) refers to the High Priest, of whom says, "Urim and Thummim, Your Thummim and Your Urim be with Your holy one (, ''hasidekha'')."
Another Midrash explained that in , God chose acacia-wood—the wood of a tree that does not bear fruit—to build the Tabernacle to set an example for all time that people should not build houses with the wood of fruit-producing trees.
The Gemara deduced from the report in of the length of the boards that both the Tabernacle and the altar were ten cubits (about 15 feet) high.

In , Moses foretold that "A prophet will the Lord your God raise up for you . . . ''like me''," and Rabbi Johanan thus taught that prophets would have to be, like Moses, strong, wealthy, wise, and meek. Strong, for says of Moses, "he spread the tent over the tabernacle," and a Master taught that Moses himself spread it, and reports, "Ten cubits shall be the length of a board." Similarly, the strength of Moses can be derived from , in which Moses reports, "And I took the two tablets, and cast them out of my two hands, and broke them," and it was taught that the tablets were six handbreadths in length, six in breadth, and three in thickness. Wealthy, as reports God's instruction to Moses, "Carve yourself two tablets of stone," and the Rabbis interpreted the verse to teach that the chips would belong to Moses. Wise, for Abba Arika, Rav and Samuel both said that 50 gates of understanding were created in the world, and all but one were given to Moses, for said of Moses, "You have made him a little lower than God." Meek, for reports, "Now the man Moses was very meek."
Rabbi Samuel ben Nahman used the description of the side (, ''zela'') of the tabernacle in to help interpret the creation of woman. Rabbi Jeremiah ben Leazar taught that when God created Adam, God created him a hermaphrodite—two bodies, male and female, joined together—for says, "male and female created He them . . . and called their name Adam." Rabbi Samuel ben Nahman taught that when God created Adam, God created Adam double-faced. Then God split Adam and made Adam of two backs, one back on this side and one back on the other side. An objection was raised that says, "And He took one of his ribs" (implying that God created Eve separately from Adam). Rabbi Samuel ben Nahman replied that the word read as "rib"—, ''mi-zalotav''—actually means one of Adam's sides, just as one reads in , "And for the second side (, ''zela'') of the tabernacle."

Rabbi Levi read , regarding "the middle bar in the midst of the boards, which shall pass through from end to end," calculated that the beam must have been 32 cubits in length, and asked where the Israelites would find such a beam in the desert. Rabbi Levi deduced that the Israelites had stored up the cedar to construct the Tabernacle since the days of Jacob. Thus reports, "And every man, with whom ''was found'' acacia-wood," not "with whom ''would be found'' acacia-wood." Rabbi Levi taught that the Israelites cut the trees down in Magdala of the Dyers near Tiberias and brought them with them to Ancient Egypt, Egypt, and no knot or crack was found in them.
The Mishnah described two veils that separated the Holy Place from the Most Holy Place in the Second Temple, but Rabbi Jose said that there was only a single veil, as described in in connection with the Tabernacle.

Exodus chapter 27
Rabbi Judah maintained that the altar was wider than Rabbi Jose thought it was, whereas Rabbi Jose maintained that the altar was taller than Rabbi Judah thought it was. Rabbi Jose said that one should read literally the words of , "five cubits long, and five cubits broad." But Rabbi Judah noted that uses the word "square" (, ''ravua''), just as uses the word "square" (, ''ravua''). Rabbi Judah argued that just as in , the dimension was measured from the center (so that the dimension described only one quadrant of the total), so the dimensions of should be measured from the center (and thus, according to Rabbi Judah, the altar was 10 cubits on each side.) The Gemara explained that we know that this is how to understand because says, "And the hearth shall be 12 cubits long by 12 cubits broad, square," and continues, "to the four sides thereof," teaching that the measurement was taken from the middle (interpreting "to" as intimating that from a particular point, there were 12 cubits in all directions, hence from the center). Rabbi Jose, however, reasoned that a common use of the word "square" applied to the height of the altar. Rabbi Judah said that one should read literally the words of , "And the height thereof shall be three cubits." But Rabbi Jose noted that uses the word "square" (, ''ravua''), just as uses the word "square" (, ''ravua'', referring to the inner altar). Rabbi Jose argued that just as in the altar's height was twice its length, so too in , the height was to be read as twice its length (and thus the altar was 10 cubits high). Rabbi Judah questioned Rabbi Jose's conclusion, for if priests stood on the altar to perform the service 10 cubits above the ground, the people would see them from outside the courtyard. Rabbi Jose replied to Rabbi Judah that states, "And the hangings of the court, and the screen for the door of the gate of the court, which is by the Tabernacle and by the altar round about," teaching that just as the Tabernacle was 10 cubits high, so was the altar 10 cubits high; and says, "The hangings for the one side were fifteen cubits" (teaching that the walls of the courtyard were 15 cubits high). The Gemara explained that according to Rabbi Jose's reading, the words of , "And the height five cubits," meant from the upper edge of the altar to the top of the hangings. And according to Rabbi Jose, the words of , "and the height thereof shall be three cubits," meant that there were three cubits from the edge of the terrace (on the side of the altar) to the top of the altar. Rabbi Judah, however, granted that the priest could be seen outside the Tabernacle, but argued that the sacrifice in his hands could not be seen.
A Midrash taught that the altar was overlaid with copper (, ''nechosheit''), as instructs, to atone for the Israelites' brazen forehead (, ''meitzach ha-nechosheit''), as says, "Your neck is an iron sinew, and your forehead brazen (, ''nechushah'')."
Rabbi Jose noted that even though reported that the Tabernacle's courtyard was just 100 cubits by 50 cubits (about 150 feet by 75 feet), a little space held a lot, as implied that the space miraculously held the entire Israelite people.
A Midrash taught that the length of the courtyard reported in at 100 cubits added to the length of the Tabernacle—30 cubits—to total 130 cubits. And the Midrash taught that this number was alluded to when (as reports) the prince of the Tribe of Simeon brought an offering of "one silver dish, the weight of which was 130 shekels." The Midrash taught that the dish was in allusion to the court that encompassed the Tabernacle as the sea encompasses the world.
The Gemara, however, cited Abaye's as the plain meaning of the words, "The length of the court shall be 100 cubits, and the breadth 50 everywhere," in . Abaye taught that the Israelites erected the Tabernacle 50 cubits from the entrance to the courtyard, so that there might be a space of 50 cubits in front of the Tabernacle and a space of 20 cubits on every other side of the Tabernacle.
A Midrash taught that God considers studying the sanctuary's structure as equivalent to rebuilding it.
In medieval Jewish interpretation
The parashah is discussed in these Middle Ages, medieval Jewish sources:

Exodus chapter 25
Maimonides taught that God told the Israelites to build to a Sanctuary in and instituted the practice of sacrifices generally as transitional steps to wean the Israelites off of the worship of the times and move them toward prayer as the primary means of worship. Maimonides noted that in nature, God created animals that develop gradually. For example, when a mammal is born, it is extremely tender, and cannot eat dry food, so God provided breasts that yield milk to feed the young animal, until it can eat dry food. Similarly, Maimonides taught, God instituted many laws as temporary measures, as it would have been impossible for the Israelites suddenly to discontinue everything to which they had become accustomed. So God sent Moses to make the Israelites (in the words of ) "a kingdom of priests and a holy nation." But the general custom of worship in those days was sacrificing animals in temples that contained idols. So God did not command the Israelites to give up those manners of service, but allowed them to continue. God transferred to God's service what had formerly served as a worship of idols, and commanded the Israelites to serve God in the same manner—namely, to build to a Sanctuary (), to erect the altar to God's name (), to offer sacrifices to God (), to bow down to God, and to burn incense before God. God forbad doing any of these things to any other being and selected priests for the service in the Temple in . By this Divine plan, God blotted out the traces of idolatry, and established the great principle of the Existence and Unity of God. But the sacrificial service, Maimonides taught, was not the primary object of God's commandments about sacrifice; rather, supplications, prayers, and similar kinds of worship are nearer to the primary object. Thus God limited sacrifice to only one Temple (see ) and the priesthood to only the members of a particular family. These restrictions, Maimonides taught, served to limit sacrificial worship, and kept it within such bounds that God did not feel it necessary to abolish sacrificial service altogether. But in the Divine plan, prayer and supplication can be offered everywhere and by every person, as can be the wearing of ''tzitzit'' () and ''tefillin'' (
16 and similar kinds of service.
Maimonides taught that the belief in the existence of angels was connected with the belief in the existence of God, and the belief in God and angels led to the belief in prophecy and the Law. To support this understanding, God commanded the Israelites to make over the Ark the form of two angels. Maimonides taught that there was not a single cherub so that the people would not be misled to mistake it for God's image or to assume that the angel was a deity. By making two cherubim and declaring (in ) "the Lord is our God, the Lord is One," Moses proclaimed the theory of the existence of a number of angels and that they were not deities.
In modern interpretation
The parashah is discussed in these modern sources:

Exodus chapters 25–27
Franz Rosenzweig argued that the building of the Tabernacle was the Torah's goal and pinnacle: In Egyptian slavery, the Israelites had made buildings for the pharaohs, now they were privileged to labor for God's sake, thus confirming their freedom.

Umberto Cassuto argued that the purpose of the Tabernacle (literally, "Dwelling") in was to serve as a tangible symbol of God's presence among the Israelites, who were about to journey away from Mount Sinai, the site of the theophany where they had witnessed the revelation of God. As long as they were encamped at Sinai, they were conscious of God's nearness, but once they set out on their journey, the link would seem broken without the symbol in their midst.
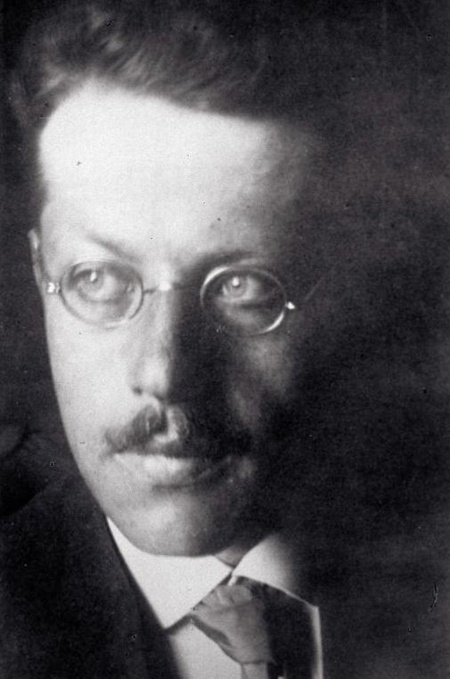
Terence E. Fretheim, Terence Fretheim argued that represent a climax in both Israel's and God's journeys, signaling a change in God's presence with Israel: (1) God's occasional appearance on the mountain or at the traveling tent (in ) became the ongoing presence of God with Israel; (2) God's distance from the people changed from the remote mountaintop to the center of the camp; and (3) God's dwelling was no longer a fixed place but portable, on the move with God's people.
Robert Alter reported the strong scholarly consensus that is the work of the Priestly source (P), reflecting P's special fascination with the details of cultic paraphernalia. Alter argued that the Biblical editors chose to introduce this block of material when Moses had disappeared into the cloud on the mountaintop to offer a reassuring antithesis to the people's fearful distance from the fiery Divine presence and the closeness of Moses to God. The architectural plan for the Tabernacle promised that God would come down from above to dwell among God's people within the Tabernacle's secure sanctum. As well, the Divinely-endorsed donations contrast with the transgressive donations that enable the Golden Calf in .
Meyers argued that although a modest tent shrine, perhaps reflected in the term "tent of meeting" (, ''ohel moed'') in , would have been possible, the elaborate and costly structure of likely in part reflected the actual Jerusalem Temple. Like Mount Sinai (in ) and the Jerusalem Temple, the Tabernacle had three zones of sanctity. Thus unlike religious edifices today, which are places for people to enter and worship, the Tabernacle was like temples and shrines in the ancient world, which were considered earthly residences for deities (see ), off-limits for most humans—costly, well-furnished structures befitting their divine occupants.
[
Tigay reported that scholars debate whether the Tabernacle actually existed. Some believe that describes some form of the First Temple in Jerusalem, historically retrojected into the period of the wanderings to give it legitimacy. Others note parallels to aspects of the Tabernacle's architecture in second millennium Egypt and Mari, Syria, and among Arabs, Arab tribes, and suggest that (at least in broad strokes) the Tabernacle reflected a recollection of a sanctuary that may have antedated the Israelites' settlement in Canaan.][
]
Exodus chapter 25
Tigay noted that lists metals and lists fabrics in descending order of quality, and the material of which an item was made depended on its proximity to the Holy of Holies.[ Nahum M. Sarna, Nahum Sarna observed that iron is notably absent, either on account of its great rarity at the time or because its use for more efficient weapons of death made it incompatible with the spiritual ends that the Tabernacle served.
Citing an Akkadian term that indicates a yellow or orange dye, Alter argued that the word , ''techashim'' in is more plausibly translated as "ocher-dyed skins" than "dolphin skins" or "dugong skins." Alter argued that the yellow or orange coloring would be in keeping with the brilliantly dyed stuff in . Richard Elliott Friedman wrote that no one knows what the term means, noting that it has been translated to be dolphin skins, badger skins, goatskins, and skins of a particular color. Friedman wrote that it is a cognate of an Arabic word for dolphin, but, since it does not occur in the list of animals that are forbidden or permitted for food in , it may not refer to a particular species of animal at all. Friedman concluded that it may just mean tanned skins or leather.
Sharon Sobel observed that when God stated in , “Let them make me a sanctuary,” the word “them” referred to both men and women. In , beginning the parallel description of the Tabernacle's construction that corresponds to the instructions given in Parashat Terumah, Moses explicitly brought together all the community of Israel, including both men and women, as confirmed by , “men and women, all whose hearts moved them, all who would make an offering”; , “all the skilled women spun with their own hands and brought what they had spun . . . ; and all the women who excelled in that skill spun the goats’ hair”; and , “thus the Israelites, all the men and women whose hearts moved them to bring anything for the work that the Lord, through Moses, had commanded to be done, brought it as a freewill offering to the Lord.” Sobel concluded that the Torah text thus tells us that it is necessary for the entire community, including both men and women, to be involved to bring God's presence into their midst. Similarly, Meyers noted that both women and men provided the materials to which and refer, as an]
29
make clear, including fabrics made and donated by women craftspersons (as indicated in ).
Sarna noted that speaks of God dwelling not "in it," that is, in the Tabernacle, but "among them," that is, among the Israelites. Sarna observed that the verb "to dwell" is not the common Hebrew ''y-sh-v'' but the rarer ''sh-k-n'', which conveys the idea of temporary lodging in a tent as in the nomadic lifestyle. Sarna concluded that the Tabernacle was not God's abode, as were similar pagan structures. Rather, Sarna argued, the Tabernacle made perceptible and tangible the conception of God's immanence, that is, of the indwelling of the Divine Presence in the Israelite camp.
Meyers suggested that the word "pattern" in referred to the heavenly abode after which the earthly abode was to be modeled. Bruce Wells reported, however, that scholars debate the meaning of the word "pattern." One possibility is that the item God showed Moses represented God's dwelling place in the heavens. The other possibility is that refers simply to a scale model of the structure that God commanded Moses to build. Wells noted that several ancient Near Eastern texts support this second option, referring to instances where gods revealed models of or plans for religious objects to those responsible for building them. In one Middle Babylonian document, a clay model of the statue of the god Shamash was miraculously discovered near the Euphrates, which showed long-missing information about how the statue was to look and what clothing was to adorn it, allowing the Babylonian king to then make a new statue.
Alter wrote that the instruction of to place the stone tablets of the Ten Commandments in the Tabernacle reflected a common ancient Near Eastern practice of placing documents of solemn contracts within sacred precincts.[Robert Alter. ''The Five Books of Moses: A Translation with Commentary'', page 462.]
Alter wrote that the term "cherubim" (, ''keruvim'') in is derived from a root that suggests hybrid or composite and perhaps also "steed," and refers to fearsome winged beasts like the Egyptian sphinx that figure in poetry as God's celestial steeds.[
] Baruch Spinoza asserted that a perusal of Scripture shows that all God's revelations to the prophets were made through words or appearances, or a combination of the two, and these words and appearances were either real, when external to the mind of the prophet who heard or saw them, or imaginary, when the imagination of the prophet was in a state that led the prophet distinctly to suppose that the prophet heard or saw them. Spinoza read , where God says, "And there I will meet with you and I will commune with you from the mercy seat that is between the Cherubim," to report that God revealed to Moses the laws that God wished to transmit to the Israelites with a real voice. Spinoza argued that God must necessarily have employed some sort of real voice, for Moses found God ready to commune with him at any time. And Spinoza argued that this, where God proclaimed the law, was the only instance of a real voice.
Baruch Spinoza asserted that a perusal of Scripture shows that all God's revelations to the prophets were made through words or appearances, or a combination of the two, and these words and appearances were either real, when external to the mind of the prophet who heard or saw them, or imaginary, when the imagination of the prophet was in a state that led the prophet distinctly to suppose that the prophet heard or saw them. Spinoza read , where God says, "And there I will meet with you and I will commune with you from the mercy seat that is between the Cherubim," to report that God revealed to Moses the laws that God wished to transmit to the Israelites with a real voice. Spinoza argued that God must necessarily have employed some sort of real voice, for Moses found God ready to commune with him at any time. And Spinoza argued that this, where God proclaimed the law, was the only instance of a real voice.
 Noting the botanical terms (branches, calyxes, almond blossoms, petals) in the description of the lampstand in , Meyers suggested that the lampstand represented a sacred tree and perhaps God as source of fertility.
Gunther Plaut traced the history of the menorah, reporting that, as depicted on the Arch of Titus, the Roman army took the menorah to Rome as war booty. After that, Jews carried on the intent of the commandment in to light the menorah by keeping a separate light, a ''ner tamid'', in the synagogue. Originally Jews set the ''ner tamid'' opposite the ark on the synagogue's western wall, but then moved it to a niche by the side of the ark and later to a lamp suspended above the ark. Plaut reported that the ''ner tamid'' has come to symbolize God's presence, a spiritual light emanating as if from the Temple.
Noting the botanical terms (branches, calyxes, almond blossoms, petals) in the description of the lampstand in , Meyers suggested that the lampstand represented a sacred tree and perhaps God as source of fertility.
Gunther Plaut traced the history of the menorah, reporting that, as depicted on the Arch of Titus, the Roman army took the menorah to Rome as war booty. After that, Jews carried on the intent of the commandment in to light the menorah by keeping a separate light, a ''ner tamid'', in the synagogue. Originally Jews set the ''ner tamid'' opposite the ark on the synagogue's western wall, but then moved it to a niche by the side of the ark and later to a lamp suspended above the ark. Plaut reported that the ''ner tamid'' has come to symbolize God's presence, a spiritual light emanating as if from the Temple.
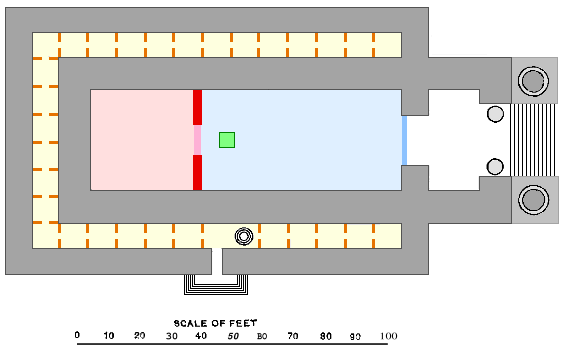
Exodus chapter 26
Friedman observed that the cubit-and-a-half width of each board used to construct the Tabernacle described in is strange, as he presumed that ancient Israelites carried a one-cubit-long measuring string. Friedman asked why the Israelites would design a structure with one-and-a-half-cubit components instead of one-cubit or two-cubit. Friedman explained the unusual one-and-a-half cubit width by positing that the extra half cubit was for overlapping with the adjacent board. Friedman reported that architects whom he consulted said that such an overlapping arrangement would have advantages of stability and ventilation. Based on this arrangement, Friedman suggested that the Tabernacle was 20 cubits long and 6 to 8 cubits wide and that the Tabernacle would thus have been just the size to fit under the outstretched wings between the two cherubim that describes inside of the Holy of Holies in Solomon's Temple. Friedman concluded from this that the author of the Priestly source thought to have written this material must have lived before Nebuchadnezzar II destroyed Solomon's Temple in 587 BCE.
Mark S. Smith, Mark Smith saw in the word for these boards, , ''kerashim'', a connection to the dwelling place of the Ancient Canaanite religion, Canaanite god El (deity), El, called ''krsh'', for "tabernacle" or "pavilion." Smith cited this as one of several reasons that he concluded that the Israelite God , YHVH, and El were identified at an early stage.
Commandments
According to Maimonides and Sefer ha-Chinuch, there are 2 positive and 1 negative Mitzvah, commandments in the parashah:
*To build a Sanctuary
*Not to remove the staves from the Ark of the Covenant
*To make the showbread

Liturgy
God's Presence in a throne between cherubim in is reflected in , which is in turn one of the six Psalms recited at the beginning of the Kabbalat Shabbat Jewish services, prayer service.
The kindled lights of the Menorah of played a key role in Hanukkah and are thus in turn noted in the Hanukkah insertion to the ''Modim'' section of the ''Amidah'' prayer in each of the three prayer services.
Weekly maqam
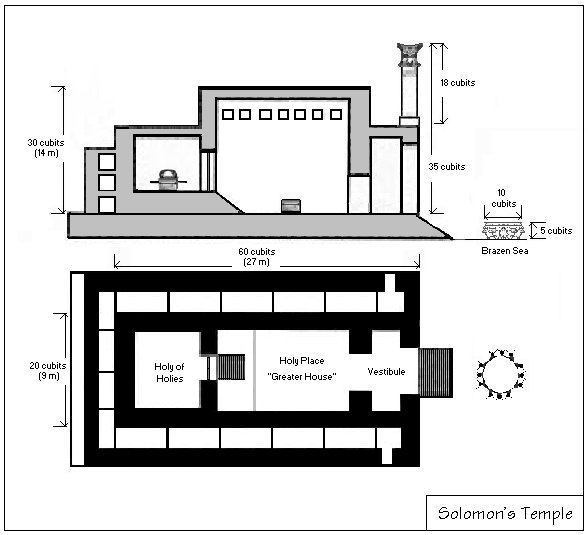 In the Weekly Maqam, Sephardi Jews each week base the songs of the services on the content of that week's parashah. For Parashat Terumah, Sephardi Jews apply Maqam Hoseni, the maqam that expresses beauty, as it is the parashah where the beauty of the Tabernacle and its utensils are elaborated.
In the Weekly Maqam, Sephardi Jews each week base the songs of the services on the content of that week's parashah. For Parashat Terumah, Sephardi Jews apply Maqam Hoseni, the maqam that expresses beauty, as it is the parashah where the beauty of the Tabernacle and its utensils are elaborated.
Haftarah
The haftarah for the parashah is .

Summary
God gave King Solomon wisdom, and Solomon made a peace treaty with King Hiram I of Tyre, Lebanon, Tyre. Solomon directed his tax collector Adoniram to draft 30,000 men and send them to Lebanon in shifts of 10,000, with one month in Lebanon and two months at home. Solomon also had 70,000 men who bore burdens, 80,000 men who hewed stone in the mountains, and 3,300 chief officers who supervised the work. Solomon ordered great and costly stones cut to lay the foundation of the Temple in Jerusalem, and Solomon's builders, Hiram's builders, and the Byblos, Gebalites fashioned them and prepared the timber and the stones to build the Temple.
 Solomon began to build the Temple in the 480th year after the Israelites came out of Egypt, in the fourth year of his reign, in the month Iyar, Ziv. The Temple measured 60 cubits long, 20 cubits wide, and 30 cubits high, and had a portico 20 cubits long and 10 cubits deep. Its windows were broad within and narrow without. Along the Temple's wall all around were side-structures and side-chambers, with the lowest story of the side-structure 5 cubits broad, the middle 6 cubits broad, and the third story 7 cubits broad, and recesses ringed the outside wall. The Temple was built from stone made ready at the quarry, and no hammer, ax, or other iron tool was heard at the building site. The door for the lowest story of side-chambers was on the right side of the Temple, and winding stairs went into the middle story and out into the third. So Solomon built the Temple and finished it with planks of cedar over beams, with all the Temple resting on cedar timbers.
Solomon began to build the Temple in the 480th year after the Israelites came out of Egypt, in the fourth year of his reign, in the month Iyar, Ziv. The Temple measured 60 cubits long, 20 cubits wide, and 30 cubits high, and had a portico 20 cubits long and 10 cubits deep. Its windows were broad within and narrow without. Along the Temple's wall all around were side-structures and side-chambers, with the lowest story of the side-structure 5 cubits broad, the middle 6 cubits broad, and the third story 7 cubits broad, and recesses ringed the outside wall. The Temple was built from stone made ready at the quarry, and no hammer, ax, or other iron tool was heard at the building site. The door for the lowest story of side-chambers was on the right side of the Temple, and winding stairs went into the middle story and out into the third. So Solomon built the Temple and finished it with planks of cedar over beams, with all the Temple resting on cedar timbers.
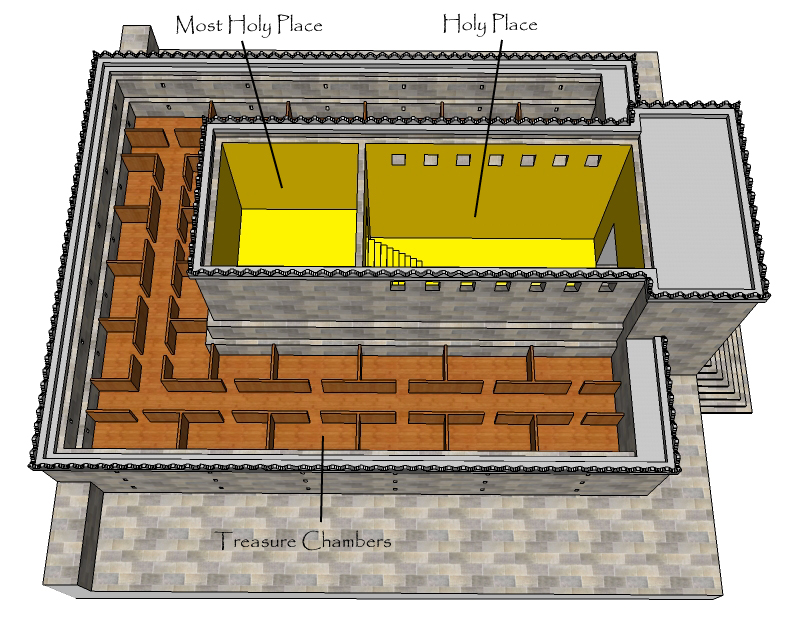 And the word of the Lord came to Solomon, saying: "As for this house that you are building, if you will walk in My statutes, and execute My ordinances, and keep all My commandments, then I will establish My word with you that I spoke to David your father and I will dwell therein among the children of Israel, and will not forsake My people Israel."
And the word of the Lord came to Solomon, saying: "As for this house that you are building, if you will walk in My statutes, and execute My ordinances, and keep all My commandments, then I will establish My word with you that I spoke to David your father and I will dwell therein among the children of Israel, and will not forsake My people Israel."
Connection to the Parashah
Both the parashah and the haftarah describe a great Jewish leader's marshalling of resources to build a dwelling place for God, the parashah in Moses' collection of gifts to build the Tabernacle,Temple in Jerusalem
The Temple in Jerusalem, or alternatively the Holy Temple (; , ), refers to the two now-destroyed religious structures that served as the central places of worship for Israelites and Jews on the modern-day Temple Mount in the Old City of Jeru ...
. Both the parashah and the haftarah describe conditions for a structure where God could dwell (''ve-shakhanti'') among (''be-tokh'') the Israelites.[; .]
On Shabbat Zachor
When the parashah coincides with the Special Shabbat, special Sabbath Shabbat Zachor (as it does in 2021), the haftarah is .[
]
On Shabbat Rosh Chodesh
When the parashah coincides with the special Sabbath Shabbat Rosh Chodesh (as it does in 2025), the haftarah is .[
]
Notes
Further reading
The parashah has parallels or is discussed in these sources:
Biblical
* (cherubim).
* (cherubim); (cherubim).
* (cherubim); (cherubim);
11
(Tabernacle, courts); (dwelling); (courts); (court); (ark).
Early nonrabbinic
*1 Maccabees]
4:47–59
(rededication of the Temple).
*Philo
Philo of Alexandria (; grc, Φίλων, Phílōn; he, יְדִידְיָה, Yəḏīḏyāh (Jedediah); ), also called Philo Judaeus, was a Hellenistic Jewish philosopher who lived in Alexandria, in the Roman province of Egypt.
Philo's de ...
''Allegorical Interpretation''
3:33:102
23:113; 34:166; 46:218
2:8; 17:89; 21:114; 30:168
19:101
35:190. Alexandria, Egypt, early 1st Century C.E. In, e.g., ''The Works of Philo: Complete and Unabridged, New Updated Edition''. Translated by Charles Duke Yonge, pages 62, 285, 290, 294, 304, 312, 314, 319, 330, 357. Peabody, Massachusetts: Hendrickson Publishers, 1993.
*Josephus
Flavius Josephus (; grc-gre, Ἰώσηπος, ; 37 – 100) was a first-century Romano-Jewish historian and military leader, best known for '' The Jewish War'', who was born in Jerusalem—then part of Roman Judea—to a father of priestly ...
, ''Antiquities of the Jews'
3:6:1
Circa 93–94. In, e.g., ''The Works of Josephus: Complete and Unabridged, New Updated Edition''. Translated by William Whiston, pages 85–86, 90. Peabody, Massachusetts: Hendrickson Publishers, 1987.
Classical rabbinic
*Mishnah
The Mishnah or the Mishna (; he, מִשְׁנָה, "study by repetition", from the verb ''shanah'' , or "to study and review", also "secondary") is the first major written collection of the Jewish oral traditions which is known as the Oral Tor ...
Yoma 5:1Sanhedrin 9:6Avot 4:13Menachot 11:4–7
Land of Israel, circa 200 C.E. In, e.g., ''The Mishnah: A New Translation''. Translated by Jacob Neusner, pages 272, 604, 757–58. New Haven: Yale University Press, 1988.
*Tosefta
The Tosefta ( Jewish Babylonian Aramaic: תוספתא "supplement, addition") is a compilation of the Jewish oral law from the late 2nd century, the period of the Mishnah.
Overview
In many ways, the Tosefta acts as a supplement to the Mishnah ( ...
: Shabbat 8:23; Eruvin 4:9; Shekalim 3:13–14; Kippurim (Yoma) 2:12; Sanhedrin 4:8; Menachot 6:11, 7:7, 11:6, 12. Land of Israel, circa 250 C.E. In, e.g., ''The Tosefta: Translated from the Hebrew, with a New Introduction''. Translated by Jacob Neusner, volume 1, pages 384, 444, 535–36, 553; volume 2, pages 1159, 1431, 1434–35, 1457, 1458–59. Peabody, Massachusetts: Hendrickson Publishers, 2002.
*Jerusalem Talmud: Terumot 1a–b; Shabbat 5b, 20b, 63a, 85a, 94a; Shekalim 2b, 44a–45a, 47b–48a, 59a–b; Yoma 2a, 4a, 31b; Sukkah 3a–b; Megillah 12b; Sotah 39b–40a; Sanhedrin 10a; Shevuot 13b; Avodah Zarah 14b; Horayot 18b. Tiberias, Land of Israel, circa 400 CE. In, e.g., ''Talmud Yerushalmi''. Edited by Chaim Malinowitz, Yisroel Simcha Schorr, and Mordechai Marcus, volumes 7, 13–15, 20–22, 26, 37, 44, 46–47, 49. Brooklyn: Mesorah Publications, 2008–2020. And in, e.g., ''The Jerusalem Talmud: A Translation and Commentary''. Edited by Jacob Neusner and translated by Jacob Neusner, Tzvee Zahavy, B. Barry Levy, and Edward Goldman (professor), Edward Goldman. Peabody, Massachusetts: Hendrickson Publishers, 2009.
*Genesis Rabbah]
3:95:78:116:217:6
66:2; 80:6; 91:9; 94:4. Land of Israel, 5th Century. In, e.g., ''Midrash Rabbah: Genesis''. Translated by Harry Freedman (rabbi), Harry Freedman and Maurice Simon, volume 1, pages 26, 38, 54, 125, 137; volume 2, pages 601, 739, 845, 871. London: Soncino Press, 1939.
 *Midrash Tanhuma Terumah. 5th–10th centuries. In, e.g., ''The Metsudah Midrash Tanchuma: Shemos II.'' Translated and annotated by Avrohom Davis; edited by Yaakov Y.H. Pupko, volume 4 (Shemos volume 2), pages 101–44. Monsey, New York: Eastern Book Press, 2004.
*Babylonian
*Midrash Tanhuma Terumah. 5th–10th centuries. In, e.g., ''The Metsudah Midrash Tanchuma: Shemos II.'' Translated and annotated by Avrohom Davis; edited by Yaakov Y.H. Pupko, volume 4 (Shemos volume 2), pages 101–44. Monsey, New York: Eastern Book Press, 2004.
*Babylonian Talmud
The Talmud (; he, , Talmūḏ) is the central text of Rabbinic Judaism and the primary source of Jewish religious law ('' halakha'') and Jewish theology. Until the advent of modernity, in nearly all Jewish communities, the Talmud was the ce ...
Berakhot 8b30a55aShabbat 28a48a91a92a98b133bEruvin 2a–b4a–b23b58aPesachim 76bYoma 3b33b38a39a–b51b–52b54a–b71b72bSukkah 4b–5b7b45b49a50bRosh Hashanah 31aMegillah 10bChagigah 13b26bYevamot 4b81bKetubot 62b106aNedarim 38aBava Kamma 110bBava Batra 12b14a–b67a98b–99aSanhedrin 7a16b22a29a39a81bMakkot 15a22aShevuot 14b–15a16bAvodah Zarah 9b23b–24bZevachim 53a59b–60a62a–b82b85b96a119bMenachot 27b–29a42b44a88b96a97a98a–b99bChullin 133bBekhorot 44aTemurah 31bNiddah 26b
Sasanian Empire, 6th Century. In, e.g., ''Talmud Bavli''. Edited by Yisroel Simcha Schorr, Chaim Malinowitz, and Mordechai Marcus, 72 volumes. Brooklyn: Mesorah Publications, 2006.
Medieval
 *Bede. ''Of the Tabernacle and Its Vessels, and of the Priestly Vestments''. Monkwearmouth, England, 720s. In ''Bede: On the Tabernacle''. Translated with notes and introduction by Arthur G. Holder. Liverpool: Liverpool University Press, 1994.
*Exodus Rabbah 33:1–35:6. 10th Century. In, e.g., ''Midrash Rabbah: Exodus''. Translated by Simon M. Lehrman, volume 3, pages 414–35. London: Soncino Press, 1939.
*Solomon ibn Gabirol. ''A Crown for the King''
*Bede. ''Of the Tabernacle and Its Vessels, and of the Priestly Vestments''. Monkwearmouth, England, 720s. In ''Bede: On the Tabernacle''. Translated with notes and introduction by Arthur G. Holder. Liverpool: Liverpool University Press, 1994.
*Exodus Rabbah 33:1–35:6. 10th Century. In, e.g., ''Midrash Rabbah: Exodus''. Translated by Simon M. Lehrman, volume 3, pages 414–35. London: Soncino Press, 1939.
*Solomon ibn Gabirol. ''A Crown for the King''
31:378
Spain, 11th Century. Translated by David R. Slavitt, pages 50–51. New York: Oxford University Press, 1998.
 *Rashi. ''Commentary''
*Rashi. ''Commentary''
Exodus 25–27
Troyes, France, late 11th Century. In, e.g., Rashi. ''The Torah: With Rashi's Commentary Translated, Annotated, and Elucidated''. Translated and annotated by Yisrael Isser Zvi Herczeg, volume 2, pages 319–73. Brooklyn: Mesorah Publications, 1994.
*Rashbam. ''Commentary on the Torah''. Troyes, early 12th century. In, e.g., ''Rashbam's Commentary on Exodus: An Annotated Translation''. Edited and translated by Martin I. Lockshin, pages 303–51. Atlanta: Scholars Press, 1997.
*Yehuda Halevi, Judah Halevi. ''Kuzari''. s:Kitab al Khazari/Part Three, 3:23. Toledo, Spain, 1130–1140. In, e.g., Jehuda Halevi. ''Kuzari: An Argument for the Faith of Israel.'' Introduction by Henry Slonimsky, page 162. New York: Schocken, 1964.
*Abraham ibn Ezra. ''Commentary on the Torah''. France, 1153. In, e.g., ''Ibn Ezra's Commentary on the Pentateuch: Exodus (Shemot)''. Translated and annotated by H. Norman Strickman and Arthur M. Silver, volume 2, pages 531–83. New York: Menorah Publishing Company, 1996.
 *Maimonides. ''The Guide for the Perplexed'', part 1, chapters s:The Guide for the Perplexed (Friedlander)/Part I#CHAPTER III, 3, s:The Guide for the Perplexed (Friedlander)/Part I#CHAPTER VI, 6, s:The Guide for the Perplexed (Friedlander)/Part I#CHAPTER XXXVIII, 38; part 2, chapters s:Page:Guideforperplexed.djvu/284, 30, s:Page:Guideforperplexed.djvu/313, 45; part 3, chapter s:Page:Guideforperplexed.djvu/426, 45. Cairo, Egypt, 1190. In, e.g., Moses Maimonides. ''The Guide for the Perplexed''. Translated by Michael Friedländer, pages 16, 19, 53, 216, 245, 356. New York: Dover Publications, 1956.
*Hezekiah ben Manoah. ''Hizkuni''. France, circa 1240. In, e.g., Chizkiyahu ben Manoach. ''Chizkuni: Torah Commentary''. Translated and annotated by Eliyahu Munk, volume 2, pages 575–94. Jerusalem: Ktav Publishers, 2013.
*Nahmanides, Nachmanides. ''Commentary on the Torah''. Jerusalem, circa 1270. In, e.g., ''Ramban (Nachmanides): Commentary on the Torah.'' Translated by Charles B. Chavel, volume 2, pages 434–70. New York: Shilo Publishing House, 1973.
*Maimonides. ''The Guide for the Perplexed'', part 1, chapters s:The Guide for the Perplexed (Friedlander)/Part I#CHAPTER III, 3, s:The Guide for the Perplexed (Friedlander)/Part I#CHAPTER VI, 6, s:The Guide for the Perplexed (Friedlander)/Part I#CHAPTER XXXVIII, 38; part 2, chapters s:Page:Guideforperplexed.djvu/284, 30, s:Page:Guideforperplexed.djvu/313, 45; part 3, chapter s:Page:Guideforperplexed.djvu/426, 45. Cairo, Egypt, 1190. In, e.g., Moses Maimonides. ''The Guide for the Perplexed''. Translated by Michael Friedländer, pages 16, 19, 53, 216, 245, 356. New York: Dover Publications, 1956.
*Hezekiah ben Manoah. ''Hizkuni''. France, circa 1240. In, e.g., Chizkiyahu ben Manoach. ''Chizkuni: Torah Commentary''. Translated and annotated by Eliyahu Munk, volume 2, pages 575–94. Jerusalem: Ktav Publishers, 2013.
*Nahmanides, Nachmanides. ''Commentary on the Torah''. Jerusalem, circa 1270. In, e.g., ''Ramban (Nachmanides): Commentary on the Torah.'' Translated by Charles B. Chavel, volume 2, pages 434–70. New York: Shilo Publishing House, 1973.
 *Zohar 1:31a, 74a, 130a, 217a, 224a; 2:14b, 55a, 63a, 76a, 89b, 126a–43a, 154b, 157b, 159a, 162b, 169a, 171a, 176a, 195a, 221a, 233b, 235b, 241a; 3:4b, 126a, 192a. Spain, late 13th Century. In, e.g., ''The Zohar''. Translated by Harry Sperling and Maurice Simon. 5 volumes. London: Soncino Press, 1934.
*Bahya ben Asher. ''Commentary on the Torah''. Spain, early 14th century. In, e.g., ''Midrash Rabbeinu Bachya: Torah Commentary by Rabbi Bachya ben Asher''. Translated and annotated by Eliyahu Munk, volume 4, pages 1217–75. Jerusalem: Lambda Publishers, 2003.
*Jacob ben Asher (Baal Ha-Turim). ''Commentary on the Torah''. Early 14th century. In, e.g., ''Baal Haturim Chumash: Shemos/Exodus''. Translated by Eliyahu Touger; edited and annotated by Avie Gold, volume 2, pages 813–43. Brooklyn: Mesorah Publications, 2000.
*Isaac ben Moses Arama. ''Akedat Yizhak (The Binding of Isaac)''. Late 15th century. In, e.g., Yitzchak Arama. ''Akeydat Yitzchak: Commentary of Rabbi Yitzchak Arama on the Torah''. Translated and condensed by Eliyahu Munk, volume 1, pages 458–71. New York, Lambda Publishers, 2001.
*Zohar 1:31a, 74a, 130a, 217a, 224a; 2:14b, 55a, 63a, 76a, 89b, 126a–43a, 154b, 157b, 159a, 162b, 169a, 171a, 176a, 195a, 221a, 233b, 235b, 241a; 3:4b, 126a, 192a. Spain, late 13th Century. In, e.g., ''The Zohar''. Translated by Harry Sperling and Maurice Simon. 5 volumes. London: Soncino Press, 1934.
*Bahya ben Asher. ''Commentary on the Torah''. Spain, early 14th century. In, e.g., ''Midrash Rabbeinu Bachya: Torah Commentary by Rabbi Bachya ben Asher''. Translated and annotated by Eliyahu Munk, volume 4, pages 1217–75. Jerusalem: Lambda Publishers, 2003.
*Jacob ben Asher (Baal Ha-Turim). ''Commentary on the Torah''. Early 14th century. In, e.g., ''Baal Haturim Chumash: Shemos/Exodus''. Translated by Eliyahu Touger; edited and annotated by Avie Gold, volume 2, pages 813–43. Brooklyn: Mesorah Publications, 2000.
*Isaac ben Moses Arama. ''Akedat Yizhak (The Binding of Isaac)''. Late 15th century. In, e.g., Yitzchak Arama. ''Akeydat Yitzchak: Commentary of Rabbi Yitzchak Arama on the Torah''. Translated and condensed by Eliyahu Munk, volume 1, pages 458–71. New York, Lambda Publishers, 2001.
Modern
*Isaac Abravanel. ''Commentary on the Torah''. Italy, between 1492–1509. In, e.g., ''Abarbanel: Selected Commentaries on the Torah: Volume 2: Shemos/Exodus''. Translated and annotated by Israel Lazar, pages 294–328. Brooklyn: CreateSpace, 2015.
*Abraham Saba. ''Ẓeror ha-Mor (Bundle of Myrrh)''. Fes, Fez, Morocco, circa 1500. In, e.g., ''Tzror Hamor: Torah Commentary by Rabbi Avraham Sabba''. Translated and annotated by Eliyahu Munk, volume 3, pages 1101–22. Jerusalem, Lambda Publishers, 2008.
*Obadiah ben Jacob Sforno. ''Commentary on the Torah''. Venice, 1567. In, e.g., ''Sforno: Commentary on the Torah''. Translation and explanatory notes by Raphael Pelcovitz, pages 418–31. Brooklyn: Mesorah Publications, 1997.
*Moshe Alshich. ''Commentary on the Torah''. Safed, circa 1593. In, e.g., Moshe Alshich. ''Midrash of Rabbi Moshe Alshich on the Torah''. Translated and annotated by Eliyahu Munk, volume 2, pages 537–50. New York, Lambda Publishers, 2000.
*Shlomo Ephraim Luntschitz. ''Kli Yakar''. Lublin, 1602. In, e.g., ''Kli Yakar: Shemos''. Translated by Elihu Levine, volume 2, pages 164–224. Southfield, Michigan: Targum Press/Feldheim Publishers, 2007.
 *Avraham Yehoshua Heschel. ''Commentaries on the Torah''. Kraków, Cracow, Poland, mid 17th century. Compiled as ''Chanukat HaTorah''. Edited by Chanoch Henoch Erzohn. Piotrków Trybunalski, Piotrkow, Poland, 1900. In Avraham Yehoshua Heschel. ''Chanukas HaTorah: Mystical Insights of Rav Avraham Yehoshua Heschel on Chumash''. Translated by Avraham Peretz Friedman, pages 184–88. Southfield, Michigan: Targum Press/Feldheim Publishers, 2004.
*Thomas Hobbes. ''Leviathan (Hobbes book), Leviathan'', s:Leviathan/The Third Part#Chapter XL: Of the Rights of the Kingdom of God.2C in Abraham.2C Moses.2C the High Priests.2C and the Kings of Judah, 3:40; s:Leviathan/The Fourth Part#Chapter XLV: Of Demonology and Other Relics of the Religion of the Gentiles, 4:45. England, 1651. Reprint edited by C. B. Macpherson, pages 503–04, 675–76. Harmondsworth, England: Penguin Classics, 1982.
*Edward Taylor. "18. Meditation. Heb. 13.10. Wee Have an Altar." In ''Preliminary Meditations: First Series''. Cambridge, Massachusetts: Early 18th Century. In Harold Bloom. ''American Religious Poems'', 21–22. New York: Library of America, 2006.
*Avraham Yehoshua Heschel. ''Commentaries on the Torah''. Kraków, Cracow, Poland, mid 17th century. Compiled as ''Chanukat HaTorah''. Edited by Chanoch Henoch Erzohn. Piotrków Trybunalski, Piotrkow, Poland, 1900. In Avraham Yehoshua Heschel. ''Chanukas HaTorah: Mystical Insights of Rav Avraham Yehoshua Heschel on Chumash''. Translated by Avraham Peretz Friedman, pages 184–88. Southfield, Michigan: Targum Press/Feldheim Publishers, 2004.
*Thomas Hobbes. ''Leviathan (Hobbes book), Leviathan'', s:Leviathan/The Third Part#Chapter XL: Of the Rights of the Kingdom of God.2C in Abraham.2C Moses.2C the High Priests.2C and the Kings of Judah, 3:40; s:Leviathan/The Fourth Part#Chapter XLV: Of Demonology and Other Relics of the Religion of the Gentiles, 4:45. England, 1651. Reprint edited by C. B. Macpherson, pages 503–04, 675–76. Harmondsworth, England: Penguin Classics, 1982.
*Edward Taylor. "18. Meditation. Heb. 13.10. Wee Have an Altar." In ''Preliminary Meditations: First Series''. Cambridge, Massachusetts: Early 18th Century. In Harold Bloom. ''American Religious Poems'', 21–22. New York: Library of America, 2006.
 *Chaim ibn Attar. ''Ohr ha-Chaim''. Venice, 1742. In Chayim ben Attar. ''Or Hachayim: Commentary on the Torah''. Translated by Eliyahu Munk, volume 2, pages 753–88. Brooklyn: Lambda Publishers, 1999.
*Yaakov Culi and Yitzchak Magriso. ''Me'am Lo'ez''. Istanbul, Constantinople, 1746. In Jacob Culi and Yitzchak Magriso. ''The Torah Anthology: Me'am Lo'ez''. Translated by Aryeh Kaplan, volume 9, pages 3–140. Jerusalem: Moznaim Publishing, 1990.
*Nachman of Breslov. ''Teachings''. Bratslav, Ukraine, before 1811. In ''Rebbe Nachman's Torah: Breslov Insights into the Weekly Torah Reading: Exodus-Leviticus''. Compiled by Chaim Kramer; edited by Y. Hall, pages 213–22. Jerusalem: Breslov Research Institute, 2011.
*Samson Raphael Hirsch. ''The Pentateuch: Exodus''. Translated by Isaac Levy, volume 2, pages 427–509. Gateshead: Judaica Press, 2nd edition 1999. Originally published as ''Der Pentateuch uebersetzt und erklaert''. Frankfurt, 1867–1878.
*M.D William Brown. ''The Tabernacle and Its Priests and Services: Described and Considered in Relation to Christ and the Church, With Numerous Illustrations''. Edinburgh 1871. Reprinted Peabody, Massachusetts: Hendrickson Publishers, 1996.
*Chaim ibn Attar. ''Ohr ha-Chaim''. Venice, 1742. In Chayim ben Attar. ''Or Hachayim: Commentary on the Torah''. Translated by Eliyahu Munk, volume 2, pages 753–88. Brooklyn: Lambda Publishers, 1999.
*Yaakov Culi and Yitzchak Magriso. ''Me'am Lo'ez''. Istanbul, Constantinople, 1746. In Jacob Culi and Yitzchak Magriso. ''The Torah Anthology: Me'am Lo'ez''. Translated by Aryeh Kaplan, volume 9, pages 3–140. Jerusalem: Moznaim Publishing, 1990.
*Nachman of Breslov. ''Teachings''. Bratslav, Ukraine, before 1811. In ''Rebbe Nachman's Torah: Breslov Insights into the Weekly Torah Reading: Exodus-Leviticus''. Compiled by Chaim Kramer; edited by Y. Hall, pages 213–22. Jerusalem: Breslov Research Institute, 2011.
*Samson Raphael Hirsch. ''The Pentateuch: Exodus''. Translated by Isaac Levy, volume 2, pages 427–509. Gateshead: Judaica Press, 2nd edition 1999. Originally published as ''Der Pentateuch uebersetzt und erklaert''. Frankfurt, 1867–1878.
*M.D William Brown. ''The Tabernacle and Its Priests and Services: Described and Considered in Relation to Christ and the Church, With Numerous Illustrations''. Edinburgh 1871. Reprinted Peabody, Massachusetts: Hendrickson Publishers, 1996.
 *Samuel David Luzzatto (Shadal). ''Commentary on the Torah.'' Padua, 1871. In, e.g., Samuel David Luzzatto. ''Torah Commentary''. Translated and annotated by Eliyahu Munk, volume 3, pages 848–57. New York: Lambda Publishers, 2012.
*Archibald R.S. Kennedy
*Samuel David Luzzatto (Shadal). ''Commentary on the Torah.'' Padua, 1871. In, e.g., Samuel David Luzzatto. ''Torah Commentary''. Translated and annotated by Eliyahu Munk, volume 3, pages 848–57. New York: Lambda Publishers, 2012.
*Archibald R.S. Kennedy
"Tabernacle."
In ''Hastings' Dictionary of the Bible, Dictionary of the Bible''. Edited by James Hastings, John A. Selbie, John C. Lambert, and Shailer Mathews, volume 4, pages 653–68. Edinburgh, 1898–1904. Reprinted, e.g., Harrington, Delaware: Delmarva Publications, 2014.
*Yehudah Aryeh Leib Alter. ''Sefat Emet''. Góra Kalwaria (Ger), Poland, before 1906. Excerpted in ''The Language of Truth: The Torah Commentary of Sefat Emet''. Translated and interpreted by Arthur Green, pages 117–22. Philadelphia: Jewish Publication Society, 1998. Reprinted 2012.
 *Hermann Cohen. ''Religion of Reason: Out of the Sources of Judaism''. Translated with an introduction by Simon Kaplan; introductory essays by Leo Strauss, page 80. New York: Ungar, 1972. Reprinted Atlanta: Scholars Press, 1995. Originally published as ''Religion der Vernunft aus den Quellen des Judentums''. Leipzig: Gustav Fock, 1919.
*Alexander Alan Steinbach. ''Sabbath Queen: Fifty-four Bible Talks to the Young Based on Each Portion of the Pentateuch'', pages 57–60. New York: Behrman's Jewish Book House, 1936.
*Benno Jacob. ''The Second Book of the Bible: Exodus''. London, 1940. Translated by Walter Jacob, pages 758–809. Hoboken, New Jersey: Ktav, 1992.
*Julian Morgenstern
*Hermann Cohen. ''Religion of Reason: Out of the Sources of Judaism''. Translated with an introduction by Simon Kaplan; introductory essays by Leo Strauss, page 80. New York: Ungar, 1972. Reprinted Atlanta: Scholars Press, 1995. Originally published as ''Religion der Vernunft aus den Quellen des Judentums''. Leipzig: Gustav Fock, 1919.
*Alexander Alan Steinbach. ''Sabbath Queen: Fifty-four Bible Talks to the Young Based on Each Portion of the Pentateuch'', pages 57–60. New York: Behrman's Jewish Book House, 1936.
*Benno Jacob. ''The Second Book of the Bible: Exodus''. London, 1940. Translated by Walter Jacob, pages 758–809. Hoboken, New Jersey: Ktav, 1992.
*Julian Morgenstern
"The Ark, the Ephod, and the ‘Tent of Meeting.’"
''Hebrew Union College Annual'', volume 17 (1942–43): pages 153–266.
 *Frank Moore Cross. "The Tabernacle." ''Near Eastern Archaeology (journal), Biblical Archaeologist'', volume 10 (1947): pages 45–68.
*Umberto Cassuto. ''A Commentary on the Book of Exodus''. Jerusalem, 1951. Translated by Israel Abrahams, pages 317–68. Jerusalem: The Magnes Press, Hebrew University of Jerusalem, The Hebrew University, 1967.
*D.W. Gooding. ''The Account of the Tabernacle: Translation and Textual Problems of the Greek Exodus''. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1959. Reprinted 2009.
*Menachem Haran. "The Complex of Ritual Acts Performed inside the Tabernacle," ''Scripta Hierosolymitana'', volume 8 (1961): pages 272–302.
*R. E. Clements. ''God and Temple''. Oxford and Philadelphia: Fortress, 1965.
*Menachem Haran
*Frank Moore Cross. "The Tabernacle." ''Near Eastern Archaeology (journal), Biblical Archaeologist'', volume 10 (1947): pages 45–68.
*Umberto Cassuto. ''A Commentary on the Book of Exodus''. Jerusalem, 1951. Translated by Israel Abrahams, pages 317–68. Jerusalem: The Magnes Press, Hebrew University of Jerusalem, The Hebrew University, 1967.
*D.W. Gooding. ''The Account of the Tabernacle: Translation and Textual Problems of the Greek Exodus''. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1959. Reprinted 2009.
*Menachem Haran. "The Complex of Ritual Acts Performed inside the Tabernacle," ''Scripta Hierosolymitana'', volume 8 (1961): pages 272–302.
*R. E. Clements. ''God and Temple''. Oxford and Philadelphia: Fortress, 1965.
*Menachem Haran
"The Priestly Image of the Tabernacle."
''Hebrew Union College Annual'', volume 36 (1965): pages 191–226.
*Baruch A. Levine
"The Descriptive Tabernacle Texts of the Pentateuch."
''Journal of the American Oriental Society'', volume 85 (number 3) (July–September 1965): pages 307–18.
 *Gerhard von Rad. "The Tent and the Ark." In ''The Problem of the Hexateuch and Other Essays'', pages 103–24. New York: McGraw-Hill Book Company, 1966.
*Carol Meyers, Carol L. Meyers. ''The Tabernacle Menorah''. Missoula, Montana: Society of Biblical Literature, Scholars Press, 1976.
*Elie Munk. ''The Call of the Torah: An Anthology of Interpretation and Commentary on the Five Books of Moses''. Translated by E.S. Mazer, volume 2, pages 362–91. Brooklyn: Mesorah Publications, 1995. Originally published as ''La Voix de la Thora''. Paris: Fondation Samuel et Odette Levy, 1981.
*Marc A. Gellman. "A Tent of Dolphin Skins." In ''Gates to the New City: A Treasury of Modern Jewish Tales''. Edited by Howard Schwartz, pages 173–74. New York: Avon, 1983. Reissue edition Northvale, New Jersey: Jason Aronson, 1991.
*Victor (Avigdor) Hurowitz
*Gerhard von Rad. "The Tent and the Ark." In ''The Problem of the Hexateuch and Other Essays'', pages 103–24. New York: McGraw-Hill Book Company, 1966.
*Carol Meyers, Carol L. Meyers. ''The Tabernacle Menorah''. Missoula, Montana: Society of Biblical Literature, Scholars Press, 1976.
*Elie Munk. ''The Call of the Torah: An Anthology of Interpretation and Commentary on the Five Books of Moses''. Translated by E.S. Mazer, volume 2, pages 362–91. Brooklyn: Mesorah Publications, 1995. Originally published as ''La Voix de la Thora''. Paris: Fondation Samuel et Odette Levy, 1981.
*Marc A. Gellman. "A Tent of Dolphin Skins." In ''Gates to the New City: A Treasury of Modern Jewish Tales''. Edited by Howard Schwartz, pages 173–74. New York: Avon, 1983. Reissue edition Northvale, New Jersey: Jason Aronson, 1991.
*Victor (Avigdor) Hurowitz
"The Priestly Account of Building the Tabernacle."
''Journal of the American Oriental Society'', volume 105 (number 1) (January–March 1985): pages 21–30.
*Nahum M. Sarna. ''Exploring Exodus: The Origins of Biblical Israel'', pages 190–215. 1986. Reprinted New York: Schocken Books, 1996.
*Richard Elliott Friedman. "A Brilliant Mistake" and "The Sacred Tent." In ''Who Wrote the Bible?'' pages 161–87. New York: Summit Books, 1987.
*Pinchas Hacohen Peli, Pinchas H. Peli. ''Torah Today: A Renewed Encounter with Scripture'', pages 81–84. Washington, D.C.: B'nai B'rith Books, 1987.
*Gabriel Josipovici. "Building the Tabernacle." In ''The Book of God: A Response to the Bible'', pages 90–107. New Haven: Yale University Press, 1988.
*Jon D. Levenson. "Cosmos and Microcosm." In ''Creation and the Persistence of Evil: The Jewish Drama of Divine Omnipotence'', pages 78–99. San Francisco: Harper & Row, 1988.
*Craig R. Koester. ''Dwelling of God: The Tabernacle in the Old Testament, Intertestamental Jewish Literature, and the New Testament''. Catholic Biblical Association of America, 1989.
*Mark S. Smith. ''The Early History of God: Yahweh and the Other Deities in Ancient Israel'', pages 10, 101. New York: HarperSanFrancisco, 1990. (; ).
*Harvey J. Fields. ''A Torah Commentary for Our Times: Volume II: Exodus and Leviticus'', pages 61–68. New York: UAHC Press, 1991.
*Nahum M. Sarna. ''The JPS Torah Commentary: Exodus: The Traditional Hebrew Text with the New JPS Translation'', pages 155–75. Philadelphia: Jewish Publication Society, 1991.
*Richard Elliott Friedman. "Tabernacle." in ''Anchor Bible Series, Anchor Bible Dictionary''. Edited by David Noel Freedman, volume 6, pages 292–300. New York: Doubleday, 1992.
*Nechama Leibowitz, Nehama Leibowitz. ''New Studies in Shemot (Exodus)'', volume 2, pages 459–507. Jerusalem: Haomanim Press, 1993. Reprinted as ''New Studies in the Weekly Parasha''. Lambda Publishers, 2010.
*Walter Brueggemann. "The Book of Exodus." In ''Interpreter's Bible series, The New Interpreter's Bible''. Edited by Leander E. Keck, volume 1, pages 884–902. Nashville: Abingdon Press, 1994.
*Judith S. Antonelli. "The Tabernacle." In ''In the Image of God: A Feminist Commentary on the Torah'', pages 203–12. Northvale, New Jersey: Jason Aronson, 1995.
*Victor Avigdor Hurowitz
"The Form and Fate of the Tabernacle: Reflections on a Recent Proposal."
''The Jewish Quarterly Review'', volume 86 (number 1/2) (July–October 1995): pages 127–51.
 *Ellen Frankel. "Terumah: The Image of God." In ''The Five Books of Miriam: A Woman's Commentary on the Torah'', pages 130–32. New York: G. P. Putnam's Sons, 1996.
*Gunther Plaut, W. Gunther Plaut. ''The Haftarah Commentary'', pages 187–94. New York: UAHC Press, 1996.
*Sorel Goldberg Loeb and Barbara Binder Kadden. ''Teaching Torah: A Treasury of Insights and Activities'', pages 128–33. Denver: A.R.E. Publishing, 1997.
*Susan Freeman. ''Teaching Jewish Virtues: Sacred Sources and Arts Activities'', pages 165–78. Springfield Township, Union County, New Jersey, Springfield, New Jersey: A.R.E. Publishing, 1999. ().
*Stephanie Dalley. “Hebrew tahaš, Akkadian duhšu, Faience and Beadwork.” ''Journal of Semitic Studies'', volume 45 (numer 1) 2000: pages 1–19.
*''Exodus to Deuteronomy: A Feminist Companion to the Bible (Second Series)''. Edited by Athalya Brenner, page 34, 38. Sheffield: Sheffield Academic Press, 2000.
*Daniel E. Fleming. [Stable URL: https://www.jstor.org/stable/1585490 “Mari’s Large Public Tent and the Priestly Tent Sanctuary.”] ''Vetus Testamentum'', volume 50 (number 4) (October 2000): pages 484–98.
*Sharon L. Sobel. "Community as Sacred Space." In ''The Women's Torah Commentary: New Insights from Women Rabbis on the 54 Weekly Torah Portions''. Edited by Elyse Goldstein, pages 154–59. Woodstock, Vermont: Jewish Lights Publishing, 2000.
*Martin R. Hauge. ''The Descent from the Mountain: Narrative Patterns in Exodus 19–40''. Sheffield: Journal for the Study of the Old Testament Press, 2001.
*Avivah Gottlieb Zornberg. ''The Particulars of Rapture: Reflections on Exodus'', pages 315–50. New York: Doubleday, 2001.
*Lainie Blum Cogan and Judy Weiss. ''Teaching Haftarah: Background, Insights, and Strategies'', pages 127–37. Denver: A.R.E. Publishing, 2002.
*Michael Fishbane. ''The JPS Bible Commentary: Haftarot'', pages 120–23. Philadelphia: Jewish Publication Society, 2002.
*Alan Lew. ''This Is Real and You Are Completely Unprepared: The Days of Awe as a Journey of Transformation'', pages 53–55. Boston: Little, Brown and Company, 2003.
*Robert Alter. ''The Five Books of Moses: A Translation with Commentary'', pages 460–71. New York: W.W. Norton & Co., 2004.
*Stephen G. Rosenberg
*Ellen Frankel. "Terumah: The Image of God." In ''The Five Books of Miriam: A Woman's Commentary on the Torah'', pages 130–32. New York: G. P. Putnam's Sons, 1996.
*Gunther Plaut, W. Gunther Plaut. ''The Haftarah Commentary'', pages 187–94. New York: UAHC Press, 1996.
*Sorel Goldberg Loeb and Barbara Binder Kadden. ''Teaching Torah: A Treasury of Insights and Activities'', pages 128–33. Denver: A.R.E. Publishing, 1997.
*Susan Freeman. ''Teaching Jewish Virtues: Sacred Sources and Arts Activities'', pages 165–78. Springfield Township, Union County, New Jersey, Springfield, New Jersey: A.R.E. Publishing, 1999. ().
*Stephanie Dalley. “Hebrew tahaš, Akkadian duhšu, Faience and Beadwork.” ''Journal of Semitic Studies'', volume 45 (numer 1) 2000: pages 1–19.
*''Exodus to Deuteronomy: A Feminist Companion to the Bible (Second Series)''. Edited by Athalya Brenner, page 34, 38. Sheffield: Sheffield Academic Press, 2000.
*Daniel E. Fleming. [Stable URL: https://www.jstor.org/stable/1585490 “Mari’s Large Public Tent and the Priestly Tent Sanctuary.”] ''Vetus Testamentum'', volume 50 (number 4) (October 2000): pages 484–98.
*Sharon L. Sobel. "Community as Sacred Space." In ''The Women's Torah Commentary: New Insights from Women Rabbis on the 54 Weekly Torah Portions''. Edited by Elyse Goldstein, pages 154–59. Woodstock, Vermont: Jewish Lights Publishing, 2000.
*Martin R. Hauge. ''The Descent from the Mountain: Narrative Patterns in Exodus 19–40''. Sheffield: Journal for the Study of the Old Testament Press, 2001.
*Avivah Gottlieb Zornberg. ''The Particulars of Rapture: Reflections on Exodus'', pages 315–50. New York: Doubleday, 2001.
*Lainie Blum Cogan and Judy Weiss. ''Teaching Haftarah: Background, Insights, and Strategies'', pages 127–37. Denver: A.R.E. Publishing, 2002.
*Michael Fishbane. ''The JPS Bible Commentary: Haftarot'', pages 120–23. Philadelphia: Jewish Publication Society, 2002.
*Alan Lew. ''This Is Real and You Are Completely Unprepared: The Days of Awe as a Journey of Transformation'', pages 53–55. Boston: Little, Brown and Company, 2003.
*Robert Alter. ''The Five Books of Moses: A Translation with Commentary'', pages 460–71. New York: W.W. Norton & Co., 2004.
*Stephen G. Rosenberg
"The Jewish Temple at Elephantine."
''Near Eastern Archaeology (journal), Near Eastern Archaeology'', volume 67 (number 1) (March 2004): pages 4–13.
*Jeffrey H. Tigay. "Exodus." In ''The Jewish Study Bible''. Edited by Adele Berlin and Marc Zvi Brettler, pages 163–71. New York: Oxford University Press, 2004.
*''Professors on the Parashah: Studies on the Weekly Torah Reading'' Edited by Leib Moscovitz, pages 135–41. Jerusalem: Urim Publications, 2005.
*W. Gunther Plaut. ''The Torah: A Modern Commentary: Revised Edition''. Revised edition edited by David E. Stern, David E.S. Stern, pages 543–60. New York: Union for Reform Judaism, 2006.
*William H.C. Propp. ''Exodus 19–40'', volume 2A, pages 310–428, 495–528. New York: Anchor Bible, 2006.
*Suzanne A. Brody. "Tabernacle Kit #40." In ''Dancing in the White Spaces: The Yearly Torah Cycle and More Poems'', page 81. Shelbyville, Kentucky: Wasteland Press, 2007.
 *James Kugel, James L. Kugel. ''How To Read the Bible: A Guide to Scripture, Then and Now'', pages 285, 288–89, 486, 524. New York: Free Press, 2007.
*Kenton L. Sparks
*James Kugel, James L. Kugel. ''How To Read the Bible: A Guide to Scripture, Then and Now'', pages 285, 288–89, 486, 524. New York: Free Press, 2007.
*Kenton L. Sparks
“‘Enūma Elish’ and Priestly Mimesis: Elite Emulation in Nascent Judaism.”
''Journal of Biblical Literature'', volume 126 (2007): 637–42. (“Priestly Mimesis in the Tabernacle Narrative (Exodus 25–40)”).
''The Mishkan: The Tabernacle: Its Structure, Its Vessels, and the Kohen’s Vestments''
Brooklyn: Artscroll, 2008. (multimedia representation).
*''The Torah: A Women's Commentary''. Edited by Tamara Cohn Eskenazi and Andrea Weiss (rabbi), Andrea L. Weiss, pages 451–72. New York: Union for Reform Judaism, URJ Press, 2008.
*Thomas B. Dozeman. ''Commentary on Exodus'', pages 569–632. Grand Rapids, Michigan: William B. Eerdmans Publishing Company, 2009.
*Mark George. "Building an Inclusive Social Space: Parashat Terumah (Exodus 25:1–27:19)." In ''Torah Queeries: Weekly Commentaries on the Hebrew Bible''. Edited by Gregg Drinkwater, Joshua Lesser, and David Shneer; foreword by Judith Plaskow, pages 102–05. New York: New York University Press, 2009.
*Reuven Hammer. ''Entering Torah: Prefaces to the Weekly Torah Portion'', pages 113–17. New York: Gefen Publishing House, 2009.
*Rebecca G.S. Idestrom
“Echoes of the Book of Exodus in Ezekiel.”
''Journal for the Study of the Old Testament'', volume 33 (number 4) (June 2009): pages 489–510. (Motifs from Exodus found in Ezekiel, including the call narrative, divine encounters, captivity, signs, plagues, judgment, redemption, tabernacle/temple, are considered.).
*Bruce Wells. "Exodus." In ''Zondervan Illustrated Bible Backgrounds Commentary''. Edited by John H. Walton, volume 1, pages 247–53. Grand Rapids, Michigan: Zondervan, 2009.
* Carol Meyers. "Exodus." In ''The New Oxford Annotated Bible: New Revised Standard Version With The Apocrypha: An Ecumenical Study Bible''. Edited by Michael D. Coogan
Michael D. Coogan is lecturer on Hebrew Bible/Old Testament at Harvard Divinity School, Director of Publications for the Harvard Semitic Museum, editor-in-chief of Oxford Biblical Studies Online, and professor emeritus of religious studies at Stone ...
, Marc Z. Brettler, Carol A. Newsom, and Pheme Perkins Pheme Perkins (born 1945 in Louisville, Kentucky) is a Professor of Theology at Boston College, where she has been teaching since 1972. She is a nationally recognized expert on the Greco-Roman cultural setting of early Christianity, as well as the P ...
, pages 117–22. New York: Oxford University Press, Revised 4th Edition 2010.
*Jonathan Sacks. ''Covenant & Conversation: A Weekly Reading of the Jewish Bible: Exodus: The Book of Redemption'', pages 187–215. Jerusalem: Maggid Books, 2010.
*Avrohom Biderman
''The Mishkan: The Tabernacle: Its Structure and its Sacred Vessels''
Brooklyn: Artscroll, 2011.
*James W. Watts
"Aaron and the Golden Calf in the Rhetoric of the Pentateuch."
''Journal of Biblical Literature'', volume 130 (number 3) (fall 2011): pages 417–30.
 *Shmuel Herzfeld. "Learning To Give." In ''Fifty-Four Pick Up: Fifteen-Minute Inspirational Torah Lessons'', pages 112–16. Jerusalem: Gefen Publishing House, 2012.
*''Torah MiEtzion: New Readings in Tanach: Shemot''. Edited by Ezra Bick and Yaakov Beasley, pages 339–75. Jerusalem: Maggid Books, 2012.
*Michael B. Hundley. ''Gods in Dwellings: Temples and Divine Presence in the Ancient Near East''. Atlanta: Society of Biblical Literature, 2013.
*Dov Linzer. "Just the People of the Book, Really?" ''The Jerusalem Report'', volume 24 (number 22) (February 10, 2014): page 48.
*Jonathan Sacks. ''Lessons in Leadership: A Weekly Reading of the Jewish Bible'', pages 93–97. New Milford, Connecticut: Maggid Books, 2015.
*Raanan Eichler
*Shmuel Herzfeld. "Learning To Give." In ''Fifty-Four Pick Up: Fifteen-Minute Inspirational Torah Lessons'', pages 112–16. Jerusalem: Gefen Publishing House, 2012.
*''Torah MiEtzion: New Readings in Tanach: Shemot''. Edited by Ezra Bick and Yaakov Beasley, pages 339–75. Jerusalem: Maggid Books, 2012.
*Michael B. Hundley. ''Gods in Dwellings: Temples and Divine Presence in the Ancient Near East''. Atlanta: Society of Biblical Literature, 2013.
*Dov Linzer. "Just the People of the Book, Really?" ''The Jerusalem Report'', volume 24 (number 22) (February 10, 2014): page 48.
*Jonathan Sacks. ''Lessons in Leadership: A Weekly Reading of the Jewish Bible'', pages 93–97. New Milford, Connecticut: Maggid Books, 2015.
*Raanan Eichler
"The Poles of the Ark: On the Ins and Outs of a Textual Contradiction."
''Journal of Biblical Literature'', volume 135, number 4 (Winter 2016): pages 733–41.
*Nathan Mastnjak
“Hebrew taḥaš and the West Semitic Tent Tradition.”
''Vetus Testamentum'', volume 66 (November 2016): pages 1–9.
*Jonathan Sacks. ''Essays on Ethics: A Weekly Reading of the Jewish Bible'', pages 117–22. New Milford, Connecticut: Maggid Books, 2016.
*Kenneth Seeskin. ''Thinking about the Torah: A Philosopher Reads the Bible'', pages 85–100. Philadelphia: The Jewish Publication Society, 2016.
*Shai Held. ''The Heart of Torah, Volume 1: Essays on the Weekly Torah Portion: Genesis and Exodus'', pages 184–93. Philadelphia: Jewish Publication Society, 2017.
*Steven Levy and Sarah Levy. ''The JPS Rashi Discussion Torah Commentary'', pages 59–61. Philadelphia: Jewish Publication Society, 2017.
External links

Texts
Masoretic text and 1917 JPS translationHear the parashah chantedAcacia Wood
Commentaries
Academy for Jewish Religion, CaliforniaAcademy for Jewish Religion, New YorkAkhlah: The Jewish Children’s Learning NetworkAleph Beta AcademyAmerican Jewish University—Ziegler School of Rabbinic StudiesAscent of SafedBar-Ilan UniversityChabad.orgThe Desert Tabernacleeparsha.comG-dcastJewish Theological SeminaryMiriam AflaloMyJewishLearning.comOhr SameachOzTorah, Torah from AustraliaOz Ve Shalom—Netivot ShalomPardes from JerusalemProfessor James L. KugelProfessor Michael CarasikRabbi Dov LinzerRabbi Eli MallonRabbi Jonathan SacksRabbiShimon.comRabbi Shmuel HerzfeldReconstructionist JudaismShiur.comTeach613.org, Torah Education at Cherry HillTheTorah.comTorah from DixieTorah.orgTorahVort.comUnion for Reform JudaismUnited Synagogue of Conservative JudaismYeshivat Chovevei TorahYeshiva University
{{Weekly Torah Portions
Weekly Torah readings in Adar
Weekly Torah readings from Exodus
 Terumah, Terumoh, Terimuh, or Trumah (—
Terumah, Terumoh, Terimuh, or Trumah (—

 The Priestly story of the Tabernacle in echoes the Priestly story of creation in . As the creation story unfolds in seven days, the instructions about the Tabernacle unfold in seven speeches. In both creation and Tabernacle accounts, the text notes the completion of the task. In both creation and Tabernacle, the work done is seen to be good. In both creation and Tabernacle, when the work is finished, God takes an action in acknowledgement. In both creation and Tabernacle, when the work is finished, a blessing is invoked. And in both creation and Tabernacle, God declares something "holy."
Jeffrey Tigay notedJeffrey H. Tigay, "Exodus," in Adele Berlin and Marc Brettler, editors, ''Jewish Study Bible: 2nd Edition'', page 157. that the lampstand held seven candles, Aaron wore seven sacral vestments, the account of the building of the Tabernacle alludes to the creation account, and the Tabernacle was completed on New Year's Day. And Carol Meyers noted that and list seven kinds of substances—metals, yarn, skins, wood, oil, spices, and gemstones—signifying the totality of supplies.Carol Meyers, "Exodus," in
The Priestly story of the Tabernacle in echoes the Priestly story of creation in . As the creation story unfolds in seven days, the instructions about the Tabernacle unfold in seven speeches. In both creation and Tabernacle accounts, the text notes the completion of the task. In both creation and Tabernacle, the work done is seen to be good. In both creation and Tabernacle, when the work is finished, God takes an action in acknowledgement. In both creation and Tabernacle, when the work is finished, a blessing is invoked. And in both creation and Tabernacle, God declares something "holy."
Jeffrey Tigay notedJeffrey H. Tigay, "Exodus," in Adele Berlin and Marc Brettler, editors, ''Jewish Study Bible: 2nd Edition'', page 157. that the lampstand held seven candles, Aaron wore seven sacral vestments, the account of the building of the Tabernacle alludes to the creation account, and the Tabernacle was completed on New Year's Day. And Carol Meyers noted that and list seven kinds of substances—metals, yarn, skins, wood, oil, spices, and gemstones—signifying the totality of supplies.Carol Meyers, "Exodus," in  The Tabernacle also exhibited similarities with Mount Sinai. Both Mount Sinai and the Tabernacle had three separate areas with increasing levels of exclusivity—one for the people generally, one for the anointed class, and one for only the single representative of the people; the tablets of the law a cloud; and God's presence. And God spoke to Moses at both Mount Sinai and the Tabernacle. But in contrast to Mount Sinai, with the Tabernacle God's presence was constant; God's presence was in their midst, no longer distant; and God's presence was no longer rooted to a fixed place.
God's request for "willing" gifts in is echoed in the accounts of gifts given "willingly" in
The Tabernacle also exhibited similarities with Mount Sinai. Both Mount Sinai and the Tabernacle had three separate areas with increasing levels of exclusivity—one for the people generally, one for the anointed class, and one for only the single representative of the people; the tablets of the law a cloud; and God's presence. And God spoke to Moses at both Mount Sinai and the Tabernacle. But in contrast to Mount Sinai, with the Tabernacle God's presence was constant; God's presence was in their midst, no longer distant; and God's presence was no longer rooted to a fixed place.
God's request for "willing" gifts in is echoed in the accounts of gifts given "willingly" in 

 Rabbi Elai said in the name of Rabbi
Rabbi Elai said in the name of Rabbi  A Midrash taught that everything God created in heaven has a replica on earth. And the Midrash taught that many things in the Tabernacle reflected things in heaven. Thus reports that there are cherubim in heaven, saying, "O Lord of hosts, the God of Israel, Who sits between the cherubim." While below on earth, directs the Israelites to fashion two cherubim of gold to spread their wings to cover the Ark. Of heaven,
A Midrash taught that everything God created in heaven has a replica on earth. And the Midrash taught that many things in the Tabernacle reflected things in heaven. Thus reports that there are cherubim in heaven, saying, "O Lord of hosts, the God of Israel, Who sits between the cherubim." While below on earth, directs the Israelites to fashion two cherubim of gold to spread their wings to cover the Ark. Of heaven,  Rabbi Simeon son of Rabbi Ishmael interpreted the term "the Tabernacle of the testimony" in to mean that the Tabernacle was God's testimony to the whole world that God had forgiven Israel for having made the
Rabbi Simeon son of Rabbi Ishmael interpreted the term "the Tabernacle of the testimony" in to mean that the Tabernacle was God's testimony to the whole world that God had forgiven Israel for having made the  A Midrash told that when God told Moses to make a tabernacle for God (in ), Moses questioned how God could command Moses make a tabernacle for God, if God's Glory fills heaven and earth. And Moses saw prophetically that
A Midrash told that when God told Moses to make a tabernacle for God (in ), Moses questioned how God could command Moses make a tabernacle for God, if God's Glory fills heaven and earth. And Moses saw prophetically that  Once when Rabbi
Once when Rabbi  Noting that says, "You shall overlay it with pure gold, within and without," Rava interpreted that any scholar whose inside is not like the outside is no scholar. (A scholar thus should have the same golden character inside and out.)
The Mishnah described how on
Noting that says, "You shall overlay it with pure gold, within and without," Rava interpreted that any scholar whose inside is not like the outside is no scholar. (A scholar thus should have the same golden character inside and out.)
The Mishnah described how on  Rabbi
Rabbi  Rabbi Johanan and Rabbi Eleazar differed on how the Cherubim stood. One said that they faced each other, and the other said they faced inward (toward the door). The Gemara asked how one could reconcile the view that they faced each other with , which says, "And their faces were inward." The Gemara explained that they faced each other (in a sign of affection, symbolizing the relationship between God and the people) when Israel obeyed God's will of God; they faced inward (away from each other, symbolizing God's unrequited love for Israel) when Israel did not obey God's will. The Gemara asked how one could reconcile the view that they faced inward with , which says, "With their faces one to another." The Gemara explained that they were slightly turned sideways (partly facing each other and partly facing inward). As it was taught in a Baraita,
Rabbi Johanan and Rabbi Eleazar differed on how the Cherubim stood. One said that they faced each other, and the other said they faced inward (toward the door). The Gemara asked how one could reconcile the view that they faced each other with , which says, "And their faces were inward." The Gemara explained that they faced each other (in a sign of affection, symbolizing the relationship between God and the people) when Israel obeyed God's will of God; they faced inward (away from each other, symbolizing God's unrequited love for Israel) when Israel did not obey God's will. The Gemara asked how one could reconcile the view that they faced inward with , which says, "With their faces one to another." The Gemara explained that they were slightly turned sideways (partly facing each other and partly facing inward). As it was taught in a Baraita,  Rabbi Meir and Rabbi Judah differed over what the "testimony" was that God directed Moses to place in the Ark in . Rabbi Meir taught that the Ark contained the stone tablets and a Torah scroll. Rabbi Judah, however, taught that the Ark contained only the stone tablets, with the Torah scroll placed outside. Reading , Rabbi Meir noted that the Ark was 2½ cubits long, and as a standard cubit equals 6 handbreadths, the Ark was thus 15 handbreadths long. Rabbi Meir calculated that the tablets were 6 handbreadths long, 6 wide, and 3 thick, and were placed next to each other in the Ark. Thus the tablets accounted for 12 handbreadths, leaving 3 handbreadths unaccounted for. Rabbi Meir subtracted 1 handbreadth for the two sides of the Ark (½ handbreadth for each side), leaving 2 handbreadths for the Torah scroll. Rabbi Meir deduced that a scroll was in the Ark from the words of , "There was nothing in the Ark save the two tablets of stone that Moses put there." As the words "nothing" and "save" create a limitation followed by a limitation, Rabbi Meir followed the rule of Scriptural construction that a limitation on a limitation implies the opposite—here the presence of something not mentioned—the Torah scroll. Rabbi Judah, however, taught that the cubit of the Ark equaled only 5 handbreadths, meaning that the Ark was 12½ handbreadths long. The tablets (each 6 handbreadths wide) were deposited next to each other in the Ark, accounting for 12 handbreadths. There was thus left half a handbreadth, for which the two sides of the Ark accounted. Accounting next for width of the Ark, Rabbi Judah calculated that the tablets took up 6 handbreadths and the sides of the Ark accounted for ½ handbreadth, leaving 1 handbreadth. There Rabbi Judah taught were deposited the silver columns mentioned in Song of Songs ,, "King Solomon made himself a palanquin of the wood of Lebanon, he made the pillars thereof of silver." At the side of the Ark was placed the coffer that the
Rabbi Meir and Rabbi Judah differed over what the "testimony" was that God directed Moses to place in the Ark in . Rabbi Meir taught that the Ark contained the stone tablets and a Torah scroll. Rabbi Judah, however, taught that the Ark contained only the stone tablets, with the Torah scroll placed outside. Reading , Rabbi Meir noted that the Ark was 2½ cubits long, and as a standard cubit equals 6 handbreadths, the Ark was thus 15 handbreadths long. Rabbi Meir calculated that the tablets were 6 handbreadths long, 6 wide, and 3 thick, and were placed next to each other in the Ark. Thus the tablets accounted for 12 handbreadths, leaving 3 handbreadths unaccounted for. Rabbi Meir subtracted 1 handbreadth for the two sides of the Ark (½ handbreadth for each side), leaving 2 handbreadths for the Torah scroll. Rabbi Meir deduced that a scroll was in the Ark from the words of , "There was nothing in the Ark save the two tablets of stone that Moses put there." As the words "nothing" and "save" create a limitation followed by a limitation, Rabbi Meir followed the rule of Scriptural construction that a limitation on a limitation implies the opposite—here the presence of something not mentioned—the Torah scroll. Rabbi Judah, however, taught that the cubit of the Ark equaled only 5 handbreadths, meaning that the Ark was 12½ handbreadths long. The tablets (each 6 handbreadths wide) were deposited next to each other in the Ark, accounting for 12 handbreadths. There was thus left half a handbreadth, for which the two sides of the Ark accounted. Accounting next for width of the Ark, Rabbi Judah calculated that the tablets took up 6 handbreadths and the sides of the Ark accounted for ½ handbreadth, leaving 1 handbreadth. There Rabbi Judah taught were deposited the silver columns mentioned in Song of Songs ,, "King Solomon made himself a palanquin of the wood of Lebanon, he made the pillars thereof of silver." At the side of the Ark was placed the coffer that the  Rabbi Hanina noted that for all the vessels that Moses made, the Torah gave the measurements of their length, breadth, and height (in for the altar, for the table, and for the incense altar). But for the Ark-cover, gave its length and breadth, but not its height. Rabbi Hanina taught that one can deduce the Ark-cover's height from the smallest of the vessel features, the border of the table, concerning which says, "And you shall make for it a border of a handbreadth round about." Just as the height of the table's border was a handbreadth, so was it also for the Ark-cover.
Rabbi Hanina noted that for all the vessels that Moses made, the Torah gave the measurements of their length, breadth, and height (in for the altar, for the table, and for the incense altar). But for the Ark-cover, gave its length and breadth, but not its height. Rabbi Hanina taught that one can deduce the Ark-cover's height from the smallest of the vessel features, the border of the table, concerning which says, "And you shall make for it a border of a handbreadth round about." Just as the height of the table's border was a handbreadth, so was it also for the Ark-cover.  The Mishnah taught that the absence of one of the seven branches of the menorah mandated in invalidated the others and the absence of one of the seven lamps of the menorah invalidated the others. The Gemara explained that this is so because uses the expression "shall be" in this connection. Similarly, the Tosefta taught that invalidity of any of the cups, knops, or flowers of the menorah described in invalidated the others.
The Mishnah taught that the absence of one of the seven branches of the menorah mandated in invalidated the others and the absence of one of the seven lamps of the menorah invalidated the others. The Gemara explained that this is so because uses the expression "shall be" in this connection. Similarly, the Tosefta taught that invalidity of any of the cups, knops, or flowers of the menorah described in invalidated the others.
 Rabbi Abin compared the instruction of to a handsome king who instructed a servant to fashion a bust exactly like him. The servant exclaimed that he could not possibly make a likeness exactly like the king. But the king replied that the servant would paint it with his materials, but the king would appear in his own glory. Thus, when in God told Moses "see that you make them after their pattern," Moses complained that he was not God that he should be able to make one exactly like the pattern. God replied that Moses should follow the pattern of blue, purple, and scarlet that he saw above. The "acacia-wood, standing up" of would reflect the Seraphim who stand above, and Rabbi Hiyya bar Abba said that the gold clasps of would reflect the glittering stars in heaven. Thus God told Moses that if he would make below a replica of that which was above, God would cause God's Shechinah to dwell among the people.
Rabbi Abin compared the instruction of to a handsome king who instructed a servant to fashion a bust exactly like him. The servant exclaimed that he could not possibly make a likeness exactly like the king. But the king replied that the servant would paint it with his materials, but the king would appear in his own glory. Thus, when in God told Moses "see that you make them after their pattern," Moses complained that he was not God that he should be able to make one exactly like the pattern. God replied that Moses should follow the pattern of blue, purple, and scarlet that he saw above. The "acacia-wood, standing up" of would reflect the Seraphim who stand above, and Rabbi Hiyya bar Abba said that the gold clasps of would reflect the glittering stars in heaven. Thus God told Moses that if he would make below a replica of that which was above, God would cause God's Shechinah to dwell among the people.

 In , Moses foretold that "A prophet will the Lord your God raise up for you . . . ''like me''," and Rabbi Johanan thus taught that prophets would have to be, like Moses, strong, wealthy, wise, and meek. Strong, for says of Moses, "he spread the tent over the tabernacle," and a Master taught that Moses himself spread it, and reports, "Ten cubits shall be the length of a board." Similarly, the strength of Moses can be derived from , in which Moses reports, "And I took the two tablets, and cast them out of my two hands, and broke them," and it was taught that the tablets were six handbreadths in length, six in breadth, and three in thickness. Wealthy, as reports God's instruction to Moses, "Carve yourself two tablets of stone," and the Rabbis interpreted the verse to teach that the chips would belong to Moses. Wise, for Abba Arika, Rav and Samuel both said that 50 gates of understanding were created in the world, and all but one were given to Moses, for said of Moses, "You have made him a little lower than God." Meek, for reports, "Now the man Moses was very meek."
Rabbi Samuel ben Nahman used the description of the side (, ''zela'') of the tabernacle in to help interpret the creation of woman. Rabbi Jeremiah ben Leazar taught that when God created Adam, God created him a hermaphrodite—two bodies, male and female, joined together—for says, "male and female created He them . . . and called their name Adam." Rabbi Samuel ben Nahman taught that when God created Adam, God created Adam double-faced. Then God split Adam and made Adam of two backs, one back on this side and one back on the other side. An objection was raised that says, "And He took one of his ribs" (implying that God created Eve separately from Adam). Rabbi Samuel ben Nahman replied that the word read as "rib"—, ''mi-zalotav''—actually means one of Adam's sides, just as one reads in , "And for the second side (, ''zela'') of the tabernacle."
In , Moses foretold that "A prophet will the Lord your God raise up for you . . . ''like me''," and Rabbi Johanan thus taught that prophets would have to be, like Moses, strong, wealthy, wise, and meek. Strong, for says of Moses, "he spread the tent over the tabernacle," and a Master taught that Moses himself spread it, and reports, "Ten cubits shall be the length of a board." Similarly, the strength of Moses can be derived from , in which Moses reports, "And I took the two tablets, and cast them out of my two hands, and broke them," and it was taught that the tablets were six handbreadths in length, six in breadth, and three in thickness. Wealthy, as reports God's instruction to Moses, "Carve yourself two tablets of stone," and the Rabbis interpreted the verse to teach that the chips would belong to Moses. Wise, for Abba Arika, Rav and Samuel both said that 50 gates of understanding were created in the world, and all but one were given to Moses, for said of Moses, "You have made him a little lower than God." Meek, for reports, "Now the man Moses was very meek."
Rabbi Samuel ben Nahman used the description of the side (, ''zela'') of the tabernacle in to help interpret the creation of woman. Rabbi Jeremiah ben Leazar taught that when God created Adam, God created him a hermaphrodite—two bodies, male and female, joined together—for says, "male and female created He them . . . and called their name Adam." Rabbi Samuel ben Nahman taught that when God created Adam, God created Adam double-faced. Then God split Adam and made Adam of two backs, one back on this side and one back on the other side. An objection was raised that says, "And He took one of his ribs" (implying that God created Eve separately from Adam). Rabbi Samuel ben Nahman replied that the word read as "rib"—, ''mi-zalotav''—actually means one of Adam's sides, just as one reads in , "And for the second side (, ''zela'') of the tabernacle."
 Rabbi Levi read , regarding "the middle bar in the midst of the boards, which shall pass through from end to end," calculated that the beam must have been 32 cubits in length, and asked where the Israelites would find such a beam in the desert. Rabbi Levi deduced that the Israelites had stored up the cedar to construct the Tabernacle since the days of Jacob. Thus reports, "And every man, with whom ''was found'' acacia-wood," not "with whom ''would be found'' acacia-wood." Rabbi Levi taught that the Israelites cut the trees down in Magdala of the Dyers near Tiberias and brought them with them to Ancient Egypt, Egypt, and no knot or crack was found in them.
The Mishnah described two veils that separated the Holy Place from the Most Holy Place in the Second Temple, but Rabbi Jose said that there was only a single veil, as described in in connection with the Tabernacle.
Rabbi Levi read , regarding "the middle bar in the midst of the boards, which shall pass through from end to end," calculated that the beam must have been 32 cubits in length, and asked where the Israelites would find such a beam in the desert. Rabbi Levi deduced that the Israelites had stored up the cedar to construct the Tabernacle since the days of Jacob. Thus reports, "And every man, with whom ''was found'' acacia-wood," not "with whom ''would be found'' acacia-wood." Rabbi Levi taught that the Israelites cut the trees down in Magdala of the Dyers near Tiberias and brought them with them to Ancient Egypt, Egypt, and no knot or crack was found in them.
The Mishnah described two veils that separated the Holy Place from the Most Holy Place in the Second Temple, but Rabbi Jose said that there was only a single veil, as described in in connection with the Tabernacle.

 A Midrash taught that the altar was overlaid with copper (, ''nechosheit''), as instructs, to atone for the Israelites' brazen forehead (, ''meitzach ha-nechosheit''), as says, "Your neck is an iron sinew, and your forehead brazen (, ''nechushah'')."
Rabbi Jose noted that even though reported that the Tabernacle's courtyard was just 100 cubits by 50 cubits (about 150 feet by 75 feet), a little space held a lot, as implied that the space miraculously held the entire Israelite people.
A Midrash taught that the length of the courtyard reported in at 100 cubits added to the length of the Tabernacle—30 cubits—to total 130 cubits. And the Midrash taught that this number was alluded to when (as reports) the prince of the Tribe of Simeon brought an offering of "one silver dish, the weight of which was 130 shekels." The Midrash taught that the dish was in allusion to the court that encompassed the Tabernacle as the sea encompasses the world.
The Gemara, however, cited Abaye's as the plain meaning of the words, "The length of the court shall be 100 cubits, and the breadth 50 everywhere," in . Abaye taught that the Israelites erected the Tabernacle 50 cubits from the entrance to the courtyard, so that there might be a space of 50 cubits in front of the Tabernacle and a space of 20 cubits on every other side of the Tabernacle.
A Midrash taught that God considers studying the sanctuary's structure as equivalent to rebuilding it.
A Midrash taught that the altar was overlaid with copper (, ''nechosheit''), as instructs, to atone for the Israelites' brazen forehead (, ''meitzach ha-nechosheit''), as says, "Your neck is an iron sinew, and your forehead brazen (, ''nechushah'')."
Rabbi Jose noted that even though reported that the Tabernacle's courtyard was just 100 cubits by 50 cubits (about 150 feet by 75 feet), a little space held a lot, as implied that the space miraculously held the entire Israelite people.
A Midrash taught that the length of the courtyard reported in at 100 cubits added to the length of the Tabernacle—30 cubits—to total 130 cubits. And the Midrash taught that this number was alluded to when (as reports) the prince of the Tribe of Simeon brought an offering of "one silver dish, the weight of which was 130 shekels." The Midrash taught that the dish was in allusion to the court that encompassed the Tabernacle as the sea encompasses the world.
The Gemara, however, cited Abaye's as the plain meaning of the words, "The length of the court shall be 100 cubits, and the breadth 50 everywhere," in . Abaye taught that the Israelites erected the Tabernacle 50 cubits from the entrance to the courtyard, so that there might be a space of 50 cubits in front of the Tabernacle and a space of 20 cubits on every other side of the Tabernacle.
A Midrash taught that God considers studying the sanctuary's structure as equivalent to rebuilding it.


 Umberto Cassuto argued that the purpose of the Tabernacle (literally, "Dwelling") in was to serve as a tangible symbol of God's presence among the Israelites, who were about to journey away from Mount Sinai, the site of the theophany where they had witnessed the revelation of God. As long as they were encamped at Sinai, they were conscious of God's nearness, but once they set out on their journey, the link would seem broken without the symbol in their midst.
Terence E. Fretheim, Terence Fretheim argued that represent a climax in both Israel's and God's journeys, signaling a change in God's presence with Israel: (1) God's occasional appearance on the mountain or at the traveling tent (in ) became the ongoing presence of God with Israel; (2) God's distance from the people changed from the remote mountaintop to the center of the camp; and (3) God's dwelling was no longer a fixed place but portable, on the move with God's people.
Robert Alter reported the strong scholarly consensus that is the work of the Priestly source (P), reflecting P's special fascination with the details of cultic paraphernalia. Alter argued that the Biblical editors chose to introduce this block of material when Moses had disappeared into the cloud on the mountaintop to offer a reassuring antithesis to the people's fearful distance from the fiery Divine presence and the closeness of Moses to God. The architectural plan for the Tabernacle promised that God would come down from above to dwell among God's people within the Tabernacle's secure sanctum. As well, the Divinely-endorsed donations contrast with the transgressive donations that enable the Golden Calf in .
Meyers argued that although a modest tent shrine, perhaps reflected in the term "tent of meeting" (, ''ohel moed'') in , would have been possible, the elaborate and costly structure of likely in part reflected the actual Jerusalem Temple. Like Mount Sinai (in ) and the Jerusalem Temple, the Tabernacle had three zones of sanctity. Thus unlike religious edifices today, which are places for people to enter and worship, the Tabernacle was like temples and shrines in the ancient world, which were considered earthly residences for deities (see ), off-limits for most humans—costly, well-furnished structures befitting their divine occupants.
Tigay reported that scholars debate whether the Tabernacle actually existed. Some believe that describes some form of the First Temple in Jerusalem, historically retrojected into the period of the wanderings to give it legitimacy. Others note parallels to aspects of the Tabernacle's architecture in second millennium Egypt and Mari, Syria, and among Arabs, Arab tribes, and suggest that (at least in broad strokes) the Tabernacle reflected a recollection of a sanctuary that may have antedated the Israelites' settlement in Canaan.
Umberto Cassuto argued that the purpose of the Tabernacle (literally, "Dwelling") in was to serve as a tangible symbol of God's presence among the Israelites, who were about to journey away from Mount Sinai, the site of the theophany where they had witnessed the revelation of God. As long as they were encamped at Sinai, they were conscious of God's nearness, but once they set out on their journey, the link would seem broken without the symbol in their midst.
Terence E. Fretheim, Terence Fretheim argued that represent a climax in both Israel's and God's journeys, signaling a change in God's presence with Israel: (1) God's occasional appearance on the mountain or at the traveling tent (in ) became the ongoing presence of God with Israel; (2) God's distance from the people changed from the remote mountaintop to the center of the camp; and (3) God's dwelling was no longer a fixed place but portable, on the move with God's people.
Robert Alter reported the strong scholarly consensus that is the work of the Priestly source (P), reflecting P's special fascination with the details of cultic paraphernalia. Alter argued that the Biblical editors chose to introduce this block of material when Moses had disappeared into the cloud on the mountaintop to offer a reassuring antithesis to the people's fearful distance from the fiery Divine presence and the closeness of Moses to God. The architectural plan for the Tabernacle promised that God would come down from above to dwell among God's people within the Tabernacle's secure sanctum. As well, the Divinely-endorsed donations contrast with the transgressive donations that enable the Golden Calf in .
Meyers argued that although a modest tent shrine, perhaps reflected in the term "tent of meeting" (, ''ohel moed'') in , would have been possible, the elaborate and costly structure of likely in part reflected the actual Jerusalem Temple. Like Mount Sinai (in ) and the Jerusalem Temple, the Tabernacle had three zones of sanctity. Thus unlike religious edifices today, which are places for people to enter and worship, the Tabernacle was like temples and shrines in the ancient world, which were considered earthly residences for deities (see ), off-limits for most humans—costly, well-furnished structures befitting their divine occupants.
Tigay reported that scholars debate whether the Tabernacle actually existed. Some believe that describes some form of the First Temple in Jerusalem, historically retrojected into the period of the wanderings to give it legitimacy. Others note parallels to aspects of the Tabernacle's architecture in second millennium Egypt and Mari, Syria, and among Arabs, Arab tribes, and suggest that (at least in broad strokes) the Tabernacle reflected a recollection of a sanctuary that may have antedated the Israelites' settlement in Canaan.
 Baruch Spinoza asserted that a perusal of Scripture shows that all God's revelations to the prophets were made through words or appearances, or a combination of the two, and these words and appearances were either real, when external to the mind of the prophet who heard or saw them, or imaginary, when the imagination of the prophet was in a state that led the prophet distinctly to suppose that the prophet heard or saw them. Spinoza read , where God says, "And there I will meet with you and I will commune with you from the mercy seat that is between the Cherubim," to report that God revealed to Moses the laws that God wished to transmit to the Israelites with a real voice. Spinoza argued that God must necessarily have employed some sort of real voice, for Moses found God ready to commune with him at any time. And Spinoza argued that this, where God proclaimed the law, was the only instance of a real voice.
Baruch Spinoza asserted that a perusal of Scripture shows that all God's revelations to the prophets were made through words or appearances, or a combination of the two, and these words and appearances were either real, when external to the mind of the prophet who heard or saw them, or imaginary, when the imagination of the prophet was in a state that led the prophet distinctly to suppose that the prophet heard or saw them. Spinoza read , where God says, "And there I will meet with you and I will commune with you from the mercy seat that is between the Cherubim," to report that God revealed to Moses the laws that God wished to transmit to the Israelites with a real voice. Spinoza argued that God must necessarily have employed some sort of real voice, for Moses found God ready to commune with him at any time. And Spinoza argued that this, where God proclaimed the law, was the only instance of a real voice.
 In the Weekly Maqam, Sephardi Jews each week base the songs of the services on the content of that week's parashah. For Parashat Terumah, Sephardi Jews apply Maqam Hoseni, the maqam that expresses beauty, as it is the parashah where the beauty of the Tabernacle and its utensils are elaborated.
In the Weekly Maqam, Sephardi Jews each week base the songs of the services on the content of that week's parashah. For Parashat Terumah, Sephardi Jews apply Maqam Hoseni, the maqam that expresses beauty, as it is the parashah where the beauty of the Tabernacle and its utensils are elaborated.

 Solomon began to build the Temple in the 480th year after the Israelites came out of Egypt, in the fourth year of his reign, in the month Iyar, Ziv. The Temple measured 60 cubits long, 20 cubits wide, and 30 cubits high, and had a portico 20 cubits long and 10 cubits deep. Its windows were broad within and narrow without. Along the Temple's wall all around were side-structures and side-chambers, with the lowest story of the side-structure 5 cubits broad, the middle 6 cubits broad, and the third story 7 cubits broad, and recesses ringed the outside wall. The Temple was built from stone made ready at the quarry, and no hammer, ax, or other iron tool was heard at the building site. The door for the lowest story of side-chambers was on the right side of the Temple, and winding stairs went into the middle story and out into the third. So Solomon built the Temple and finished it with planks of cedar over beams, with all the Temple resting on cedar timbers.
Solomon began to build the Temple in the 480th year after the Israelites came out of Egypt, in the fourth year of his reign, in the month Iyar, Ziv. The Temple measured 60 cubits long, 20 cubits wide, and 30 cubits high, and had a portico 20 cubits long and 10 cubits deep. Its windows were broad within and narrow without. Along the Temple's wall all around were side-structures and side-chambers, with the lowest story of the side-structure 5 cubits broad, the middle 6 cubits broad, and the third story 7 cubits broad, and recesses ringed the outside wall. The Temple was built from stone made ready at the quarry, and no hammer, ax, or other iron tool was heard at the building site. The door for the lowest story of side-chambers was on the right side of the Temple, and winding stairs went into the middle story and out into the third. So Solomon built the Temple and finished it with planks of cedar over beams, with all the Temple resting on cedar timbers.
 And the word of the Lord came to Solomon, saying: "As for this house that you are building, if you will walk in My statutes, and execute My ordinances, and keep all My commandments, then I will establish My word with you that I spoke to David your father and I will dwell therein among the children of Israel, and will not forsake My people Israel."
And the word of the Lord came to Solomon, saying: "As for this house that you are building, if you will walk in My statutes, and execute My ordinances, and keep all My commandments, then I will establish My word with you that I spoke to David your father and I will dwell therein among the children of Israel, and will not forsake My people Israel."
 *Midrash Tanhuma Terumah. 5th–10th centuries. In, e.g., ''The Metsudah Midrash Tanchuma: Shemos II.'' Translated and annotated by Avrohom Davis; edited by Yaakov Y.H. Pupko, volume 4 (Shemos volume 2), pages 101–44. Monsey, New York: Eastern Book Press, 2004.
*Babylonian
*Midrash Tanhuma Terumah. 5th–10th centuries. In, e.g., ''The Metsudah Midrash Tanchuma: Shemos II.'' Translated and annotated by Avrohom Davis; edited by Yaakov Y.H. Pupko, volume 4 (Shemos volume 2), pages 101–44. Monsey, New York: Eastern Book Press, 2004.
*Babylonian  *Rashi. ''Commentary''
*Rashi. ''Commentary'' *Maimonides. ''The Guide for the Perplexed'', part 1, chapters s:The Guide for the Perplexed (Friedlander)/Part I#CHAPTER III, 3, s:The Guide for the Perplexed (Friedlander)/Part I#CHAPTER VI, 6, s:The Guide for the Perplexed (Friedlander)/Part I#CHAPTER XXXVIII, 38; part 2, chapters s:Page:Guideforperplexed.djvu/284, 30, s:Page:Guideforperplexed.djvu/313, 45; part 3, chapter s:Page:Guideforperplexed.djvu/426, 45. Cairo, Egypt, 1190. In, e.g., Moses Maimonides. ''The Guide for the Perplexed''. Translated by Michael Friedländer, pages 16, 19, 53, 216, 245, 356. New York: Dover Publications, 1956.
*Hezekiah ben Manoah. ''Hizkuni''. France, circa 1240. In, e.g., Chizkiyahu ben Manoach. ''Chizkuni: Torah Commentary''. Translated and annotated by Eliyahu Munk, volume 2, pages 575–94. Jerusalem: Ktav Publishers, 2013.
*Nahmanides, Nachmanides. ''Commentary on the Torah''. Jerusalem, circa 1270. In, e.g., ''Ramban (Nachmanides): Commentary on the Torah.'' Translated by Charles B. Chavel, volume 2, pages 434–70. New York: Shilo Publishing House, 1973.
*Maimonides. ''The Guide for the Perplexed'', part 1, chapters s:The Guide for the Perplexed (Friedlander)/Part I#CHAPTER III, 3, s:The Guide for the Perplexed (Friedlander)/Part I#CHAPTER VI, 6, s:The Guide for the Perplexed (Friedlander)/Part I#CHAPTER XXXVIII, 38; part 2, chapters s:Page:Guideforperplexed.djvu/284, 30, s:Page:Guideforperplexed.djvu/313, 45; part 3, chapter s:Page:Guideforperplexed.djvu/426, 45. Cairo, Egypt, 1190. In, e.g., Moses Maimonides. ''The Guide for the Perplexed''. Translated by Michael Friedländer, pages 16, 19, 53, 216, 245, 356. New York: Dover Publications, 1956.
*Hezekiah ben Manoah. ''Hizkuni''. France, circa 1240. In, e.g., Chizkiyahu ben Manoach. ''Chizkuni: Torah Commentary''. Translated and annotated by Eliyahu Munk, volume 2, pages 575–94. Jerusalem: Ktav Publishers, 2013.
*Nahmanides, Nachmanides. ''Commentary on the Torah''. Jerusalem, circa 1270. In, e.g., ''Ramban (Nachmanides): Commentary on the Torah.'' Translated by Charles B. Chavel, volume 2, pages 434–70. New York: Shilo Publishing House, 1973.
 *Zohar 1:31a, 74a, 130a, 217a, 224a; 2:14b, 55a, 63a, 76a, 89b, 126a–43a, 154b, 157b, 159a, 162b, 169a, 171a, 176a, 195a, 221a, 233b, 235b, 241a; 3:4b, 126a, 192a. Spain, late 13th Century. In, e.g., ''The Zohar''. Translated by Harry Sperling and Maurice Simon. 5 volumes. London: Soncino Press, 1934.
*Bahya ben Asher. ''Commentary on the Torah''. Spain, early 14th century. In, e.g., ''Midrash Rabbeinu Bachya: Torah Commentary by Rabbi Bachya ben Asher''. Translated and annotated by Eliyahu Munk, volume 4, pages 1217–75. Jerusalem: Lambda Publishers, 2003.
*Jacob ben Asher (Baal Ha-Turim). ''Commentary on the Torah''. Early 14th century. In, e.g., ''Baal Haturim Chumash: Shemos/Exodus''. Translated by Eliyahu Touger; edited and annotated by Avie Gold, volume 2, pages 813–43. Brooklyn: Mesorah Publications, 2000.
*Isaac ben Moses Arama. ''Akedat Yizhak (The Binding of Isaac)''. Late 15th century. In, e.g., Yitzchak Arama. ''Akeydat Yitzchak: Commentary of Rabbi Yitzchak Arama on the Torah''. Translated and condensed by Eliyahu Munk, volume 1, pages 458–71. New York, Lambda Publishers, 2001.
*Zohar 1:31a, 74a, 130a, 217a, 224a; 2:14b, 55a, 63a, 76a, 89b, 126a–43a, 154b, 157b, 159a, 162b, 169a, 171a, 176a, 195a, 221a, 233b, 235b, 241a; 3:4b, 126a, 192a. Spain, late 13th Century. In, e.g., ''The Zohar''. Translated by Harry Sperling and Maurice Simon. 5 volumes. London: Soncino Press, 1934.
*Bahya ben Asher. ''Commentary on the Torah''. Spain, early 14th century. In, e.g., ''Midrash Rabbeinu Bachya: Torah Commentary by Rabbi Bachya ben Asher''. Translated and annotated by Eliyahu Munk, volume 4, pages 1217–75. Jerusalem: Lambda Publishers, 2003.
*Jacob ben Asher (Baal Ha-Turim). ''Commentary on the Torah''. Early 14th century. In, e.g., ''Baal Haturim Chumash: Shemos/Exodus''. Translated by Eliyahu Touger; edited and annotated by Avie Gold, volume 2, pages 813–43. Brooklyn: Mesorah Publications, 2000.
*Isaac ben Moses Arama. ''Akedat Yizhak (The Binding of Isaac)''. Late 15th century. In, e.g., Yitzchak Arama. ''Akeydat Yitzchak: Commentary of Rabbi Yitzchak Arama on the Torah''. Translated and condensed by Eliyahu Munk, volume 1, pages 458–71. New York, Lambda Publishers, 2001.
 *Avraham Yehoshua Heschel. ''Commentaries on the Torah''. Kraków, Cracow, Poland, mid 17th century. Compiled as ''Chanukat HaTorah''. Edited by Chanoch Henoch Erzohn. Piotrków Trybunalski, Piotrkow, Poland, 1900. In Avraham Yehoshua Heschel. ''Chanukas HaTorah: Mystical Insights of Rav Avraham Yehoshua Heschel on Chumash''. Translated by Avraham Peretz Friedman, pages 184–88. Southfield, Michigan: Targum Press/Feldheim Publishers, 2004.
*Thomas Hobbes. ''Leviathan (Hobbes book), Leviathan'', s:Leviathan/The Third Part#Chapter XL: Of the Rights of the Kingdom of God.2C in Abraham.2C Moses.2C the High Priests.2C and the Kings of Judah, 3:40; s:Leviathan/The Fourth Part#Chapter XLV: Of Demonology and Other Relics of the Religion of the Gentiles, 4:45. England, 1651. Reprint edited by C. B. Macpherson, pages 503–04, 675–76. Harmondsworth, England: Penguin Classics, 1982.
*Edward Taylor. "18. Meditation. Heb. 13.10. Wee Have an Altar." In ''Preliminary Meditations: First Series''. Cambridge, Massachusetts: Early 18th Century. In Harold Bloom. ''American Religious Poems'', 21–22. New York: Library of America, 2006.
*Avraham Yehoshua Heschel. ''Commentaries on the Torah''. Kraków, Cracow, Poland, mid 17th century. Compiled as ''Chanukat HaTorah''. Edited by Chanoch Henoch Erzohn. Piotrków Trybunalski, Piotrkow, Poland, 1900. In Avraham Yehoshua Heschel. ''Chanukas HaTorah: Mystical Insights of Rav Avraham Yehoshua Heschel on Chumash''. Translated by Avraham Peretz Friedman, pages 184–88. Southfield, Michigan: Targum Press/Feldheim Publishers, 2004.
*Thomas Hobbes. ''Leviathan (Hobbes book), Leviathan'', s:Leviathan/The Third Part#Chapter XL: Of the Rights of the Kingdom of God.2C in Abraham.2C Moses.2C the High Priests.2C and the Kings of Judah, 3:40; s:Leviathan/The Fourth Part#Chapter XLV: Of Demonology and Other Relics of the Religion of the Gentiles, 4:45. England, 1651. Reprint edited by C. B. Macpherson, pages 503–04, 675–76. Harmondsworth, England: Penguin Classics, 1982.
*Edward Taylor. "18. Meditation. Heb. 13.10. Wee Have an Altar." In ''Preliminary Meditations: First Series''. Cambridge, Massachusetts: Early 18th Century. In Harold Bloom. ''American Religious Poems'', 21–22. New York: Library of America, 2006.
 *Chaim ibn Attar. ''Ohr ha-Chaim''. Venice, 1742. In Chayim ben Attar. ''Or Hachayim: Commentary on the Torah''. Translated by Eliyahu Munk, volume 2, pages 753–88. Brooklyn: Lambda Publishers, 1999.
*Yaakov Culi and Yitzchak Magriso. ''Me'am Lo'ez''. Istanbul, Constantinople, 1746. In Jacob Culi and Yitzchak Magriso. ''The Torah Anthology: Me'am Lo'ez''. Translated by Aryeh Kaplan, volume 9, pages 3–140. Jerusalem: Moznaim Publishing, 1990.
*Nachman of Breslov. ''Teachings''. Bratslav, Ukraine, before 1811. In ''Rebbe Nachman's Torah: Breslov Insights into the Weekly Torah Reading: Exodus-Leviticus''. Compiled by Chaim Kramer; edited by Y. Hall, pages 213–22. Jerusalem: Breslov Research Institute, 2011.
*Samson Raphael Hirsch. ''The Pentateuch: Exodus''. Translated by Isaac Levy, volume 2, pages 427–509. Gateshead: Judaica Press, 2nd edition 1999. Originally published as ''Der Pentateuch uebersetzt und erklaert''. Frankfurt, 1867–1878.
*M.D William Brown. ''The Tabernacle and Its Priests and Services: Described and Considered in Relation to Christ and the Church, With Numerous Illustrations''. Edinburgh 1871. Reprinted Peabody, Massachusetts: Hendrickson Publishers, 1996.
*Chaim ibn Attar. ''Ohr ha-Chaim''. Venice, 1742. In Chayim ben Attar. ''Or Hachayim: Commentary on the Torah''. Translated by Eliyahu Munk, volume 2, pages 753–88. Brooklyn: Lambda Publishers, 1999.
*Yaakov Culi and Yitzchak Magriso. ''Me'am Lo'ez''. Istanbul, Constantinople, 1746. In Jacob Culi and Yitzchak Magriso. ''The Torah Anthology: Me'am Lo'ez''. Translated by Aryeh Kaplan, volume 9, pages 3–140. Jerusalem: Moznaim Publishing, 1990.
*Nachman of Breslov. ''Teachings''. Bratslav, Ukraine, before 1811. In ''Rebbe Nachman's Torah: Breslov Insights into the Weekly Torah Reading: Exodus-Leviticus''. Compiled by Chaim Kramer; edited by Y. Hall, pages 213–22. Jerusalem: Breslov Research Institute, 2011.
*Samson Raphael Hirsch. ''The Pentateuch: Exodus''. Translated by Isaac Levy, volume 2, pages 427–509. Gateshead: Judaica Press, 2nd edition 1999. Originally published as ''Der Pentateuch uebersetzt und erklaert''. Frankfurt, 1867–1878.
*M.D William Brown. ''The Tabernacle and Its Priests and Services: Described and Considered in Relation to Christ and the Church, With Numerous Illustrations''. Edinburgh 1871. Reprinted Peabody, Massachusetts: Hendrickson Publishers, 1996.
 *Samuel David Luzzatto (Shadal). ''Commentary on the Torah.'' Padua, 1871. In, e.g., Samuel David Luzzatto. ''Torah Commentary''. Translated and annotated by Eliyahu Munk, volume 3, pages 848–57. New York: Lambda Publishers, 2012.
*Archibald R.S. Kennedy
*Samuel David Luzzatto (Shadal). ''Commentary on the Torah.'' Padua, 1871. In, e.g., Samuel David Luzzatto. ''Torah Commentary''. Translated and annotated by Eliyahu Munk, volume 3, pages 848–57. New York: Lambda Publishers, 2012.
*Archibald R.S. Kennedy *Hermann Cohen. ''Religion of Reason: Out of the Sources of Judaism''. Translated with an introduction by Simon Kaplan; introductory essays by Leo Strauss, page 80. New York: Ungar, 1972. Reprinted Atlanta: Scholars Press, 1995. Originally published as ''Religion der Vernunft aus den Quellen des Judentums''. Leipzig: Gustav Fock, 1919.
*Alexander Alan Steinbach. ''Sabbath Queen: Fifty-four Bible Talks to the Young Based on Each Portion of the Pentateuch'', pages 57–60. New York: Behrman's Jewish Book House, 1936.
*Benno Jacob. ''The Second Book of the Bible: Exodus''. London, 1940. Translated by Walter Jacob, pages 758–809. Hoboken, New Jersey: Ktav, 1992.
*Julian Morgenstern
*Hermann Cohen. ''Religion of Reason: Out of the Sources of Judaism''. Translated with an introduction by Simon Kaplan; introductory essays by Leo Strauss, page 80. New York: Ungar, 1972. Reprinted Atlanta: Scholars Press, 1995. Originally published as ''Religion der Vernunft aus den Quellen des Judentums''. Leipzig: Gustav Fock, 1919.
*Alexander Alan Steinbach. ''Sabbath Queen: Fifty-four Bible Talks to the Young Based on Each Portion of the Pentateuch'', pages 57–60. New York: Behrman's Jewish Book House, 1936.
*Benno Jacob. ''The Second Book of the Bible: Exodus''. London, 1940. Translated by Walter Jacob, pages 758–809. Hoboken, New Jersey: Ktav, 1992.
*Julian Morgenstern *Frank Moore Cross. "The Tabernacle." ''Near Eastern Archaeology (journal), Biblical Archaeologist'', volume 10 (1947): pages 45–68.
*Umberto Cassuto. ''A Commentary on the Book of Exodus''. Jerusalem, 1951. Translated by Israel Abrahams, pages 317–68. Jerusalem: The Magnes Press, Hebrew University of Jerusalem, The Hebrew University, 1967.
*D.W. Gooding. ''The Account of the Tabernacle: Translation and Textual Problems of the Greek Exodus''. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1959. Reprinted 2009.
*Menachem Haran. "The Complex of Ritual Acts Performed inside the Tabernacle," ''Scripta Hierosolymitana'', volume 8 (1961): pages 272–302.
*R. E. Clements. ''God and Temple''. Oxford and Philadelphia: Fortress, 1965.
*Menachem Haran
*Frank Moore Cross. "The Tabernacle." ''Near Eastern Archaeology (journal), Biblical Archaeologist'', volume 10 (1947): pages 45–68.
*Umberto Cassuto. ''A Commentary on the Book of Exodus''. Jerusalem, 1951. Translated by Israel Abrahams, pages 317–68. Jerusalem: The Magnes Press, Hebrew University of Jerusalem, The Hebrew University, 1967.
*D.W. Gooding. ''The Account of the Tabernacle: Translation and Textual Problems of the Greek Exodus''. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1959. Reprinted 2009.
*Menachem Haran. "The Complex of Ritual Acts Performed inside the Tabernacle," ''Scripta Hierosolymitana'', volume 8 (1961): pages 272–302.
*R. E. Clements. ''God and Temple''. Oxford and Philadelphia: Fortress, 1965.
*Menachem Haran *Gerhard von Rad. "The Tent and the Ark." In ''The Problem of the Hexateuch and Other Essays'', pages 103–24. New York: McGraw-Hill Book Company, 1966.
*Carol Meyers, Carol L. Meyers. ''The Tabernacle Menorah''. Missoula, Montana: Society of Biblical Literature, Scholars Press, 1976.
*Elie Munk. ''The Call of the Torah: An Anthology of Interpretation and Commentary on the Five Books of Moses''. Translated by E.S. Mazer, volume 2, pages 362–91. Brooklyn: Mesorah Publications, 1995. Originally published as ''La Voix de la Thora''. Paris: Fondation Samuel et Odette Levy, 1981.
*Marc A. Gellman. "A Tent of Dolphin Skins." In ''Gates to the New City: A Treasury of Modern Jewish Tales''. Edited by Howard Schwartz, pages 173–74. New York: Avon, 1983. Reissue edition Northvale, New Jersey: Jason Aronson, 1991.
*Victor (Avigdor) Hurowitz
*Gerhard von Rad. "The Tent and the Ark." In ''The Problem of the Hexateuch and Other Essays'', pages 103–24. New York: McGraw-Hill Book Company, 1966.
*Carol Meyers, Carol L. Meyers. ''The Tabernacle Menorah''. Missoula, Montana: Society of Biblical Literature, Scholars Press, 1976.
*Elie Munk. ''The Call of the Torah: An Anthology of Interpretation and Commentary on the Five Books of Moses''. Translated by E.S. Mazer, volume 2, pages 362–91. Brooklyn: Mesorah Publications, 1995. Originally published as ''La Voix de la Thora''. Paris: Fondation Samuel et Odette Levy, 1981.
*Marc A. Gellman. "A Tent of Dolphin Skins." In ''Gates to the New City: A Treasury of Modern Jewish Tales''. Edited by Howard Schwartz, pages 173–74. New York: Avon, 1983. Reissue edition Northvale, New Jersey: Jason Aronson, 1991.
*Victor (Avigdor) Hurowitz *Ellen Frankel. "Terumah: The Image of God." In ''The Five Books of Miriam: A Woman's Commentary on the Torah'', pages 130–32. New York: G. P. Putnam's Sons, 1996.
*Gunther Plaut, W. Gunther Plaut. ''The Haftarah Commentary'', pages 187–94. New York: UAHC Press, 1996.
*Sorel Goldberg Loeb and Barbara Binder Kadden. ''Teaching Torah: A Treasury of Insights and Activities'', pages 128–33. Denver: A.R.E. Publishing, 1997.
*Susan Freeman. ''Teaching Jewish Virtues: Sacred Sources and Arts Activities'', pages 165–78. Springfield Township, Union County, New Jersey, Springfield, New Jersey: A.R.E. Publishing, 1999. ().
*Stephanie Dalley. “Hebrew tahaš, Akkadian duhšu, Faience and Beadwork.” ''Journal of Semitic Studies'', volume 45 (numer 1) 2000: pages 1–19.
*''Exodus to Deuteronomy: A Feminist Companion to the Bible (Second Series)''. Edited by Athalya Brenner, page 34, 38. Sheffield: Sheffield Academic Press, 2000.
*Daniel E. Fleming. [Stable URL: https://www.jstor.org/stable/1585490 “Mari’s Large Public Tent and the Priestly Tent Sanctuary.”] ''Vetus Testamentum'', volume 50 (number 4) (October 2000): pages 484–98.
*Sharon L. Sobel. "Community as Sacred Space." In ''The Women's Torah Commentary: New Insights from Women Rabbis on the 54 Weekly Torah Portions''. Edited by Elyse Goldstein, pages 154–59. Woodstock, Vermont: Jewish Lights Publishing, 2000.
*Martin R. Hauge. ''The Descent from the Mountain: Narrative Patterns in Exodus 19–40''. Sheffield: Journal for the Study of the Old Testament Press, 2001.
*Avivah Gottlieb Zornberg. ''The Particulars of Rapture: Reflections on Exodus'', pages 315–50. New York: Doubleday, 2001.
*Lainie Blum Cogan and Judy Weiss. ''Teaching Haftarah: Background, Insights, and Strategies'', pages 127–37. Denver: A.R.E. Publishing, 2002.
*Michael Fishbane. ''The JPS Bible Commentary: Haftarot'', pages 120–23. Philadelphia: Jewish Publication Society, 2002.
*Alan Lew. ''This Is Real and You Are Completely Unprepared: The Days of Awe as a Journey of Transformation'', pages 53–55. Boston: Little, Brown and Company, 2003.
*Robert Alter. ''The Five Books of Moses: A Translation with Commentary'', pages 460–71. New York: W.W. Norton & Co., 2004.
*Stephen G. Rosenberg
*Ellen Frankel. "Terumah: The Image of God." In ''The Five Books of Miriam: A Woman's Commentary on the Torah'', pages 130–32. New York: G. P. Putnam's Sons, 1996.
*Gunther Plaut, W. Gunther Plaut. ''The Haftarah Commentary'', pages 187–94. New York: UAHC Press, 1996.
*Sorel Goldberg Loeb and Barbara Binder Kadden. ''Teaching Torah: A Treasury of Insights and Activities'', pages 128–33. Denver: A.R.E. Publishing, 1997.
*Susan Freeman. ''Teaching Jewish Virtues: Sacred Sources and Arts Activities'', pages 165–78. Springfield Township, Union County, New Jersey, Springfield, New Jersey: A.R.E. Publishing, 1999. ().
*Stephanie Dalley. “Hebrew tahaš, Akkadian duhšu, Faience and Beadwork.” ''Journal of Semitic Studies'', volume 45 (numer 1) 2000: pages 1–19.
*''Exodus to Deuteronomy: A Feminist Companion to the Bible (Second Series)''. Edited by Athalya Brenner, page 34, 38. Sheffield: Sheffield Academic Press, 2000.
*Daniel E. Fleming. [Stable URL: https://www.jstor.org/stable/1585490 “Mari’s Large Public Tent and the Priestly Tent Sanctuary.”] ''Vetus Testamentum'', volume 50 (number 4) (October 2000): pages 484–98.
*Sharon L. Sobel. "Community as Sacred Space." In ''The Women's Torah Commentary: New Insights from Women Rabbis on the 54 Weekly Torah Portions''. Edited by Elyse Goldstein, pages 154–59. Woodstock, Vermont: Jewish Lights Publishing, 2000.
*Martin R. Hauge. ''The Descent from the Mountain: Narrative Patterns in Exodus 19–40''. Sheffield: Journal for the Study of the Old Testament Press, 2001.
*Avivah Gottlieb Zornberg. ''The Particulars of Rapture: Reflections on Exodus'', pages 315–50. New York: Doubleday, 2001.
*Lainie Blum Cogan and Judy Weiss. ''Teaching Haftarah: Background, Insights, and Strategies'', pages 127–37. Denver: A.R.E. Publishing, 2002.
*Michael Fishbane. ''The JPS Bible Commentary: Haftarot'', pages 120–23. Philadelphia: Jewish Publication Society, 2002.
*Alan Lew. ''This Is Real and You Are Completely Unprepared: The Days of Awe as a Journey of Transformation'', pages 53–55. Boston: Little, Brown and Company, 2003.
*Robert Alter. ''The Five Books of Moses: A Translation with Commentary'', pages 460–71. New York: W.W. Norton & Co., 2004.
*Stephen G. Rosenberg *James Kugel, James L. Kugel. ''How To Read the Bible: A Guide to Scripture, Then and Now'', pages 285, 288–89, 486, 524. New York: Free Press, 2007.
*Kenton L. Sparks
*James Kugel, James L. Kugel. ''How To Read the Bible: A Guide to Scripture, Then and Now'', pages 285, 288–89, 486, 524. New York: Free Press, 2007.
*Kenton L. Sparks *Shmuel Herzfeld. "Learning To Give." In ''Fifty-Four Pick Up: Fifteen-Minute Inspirational Torah Lessons'', pages 112–16. Jerusalem: Gefen Publishing House, 2012.
*''Torah MiEtzion: New Readings in Tanach: Shemot''. Edited by Ezra Bick and Yaakov Beasley, pages 339–75. Jerusalem: Maggid Books, 2012.
*Michael B. Hundley. ''Gods in Dwellings: Temples and Divine Presence in the Ancient Near East''. Atlanta: Society of Biblical Literature, 2013.
*Dov Linzer. "Just the People of the Book, Really?" ''The Jerusalem Report'', volume 24 (number 22) (February 10, 2014): page 48.
*Jonathan Sacks. ''Lessons in Leadership: A Weekly Reading of the Jewish Bible'', pages 93–97. New Milford, Connecticut: Maggid Books, 2015.
*Raanan Eichler
*Shmuel Herzfeld. "Learning To Give." In ''Fifty-Four Pick Up: Fifteen-Minute Inspirational Torah Lessons'', pages 112–16. Jerusalem: Gefen Publishing House, 2012.
*''Torah MiEtzion: New Readings in Tanach: Shemot''. Edited by Ezra Bick and Yaakov Beasley, pages 339–75. Jerusalem: Maggid Books, 2012.
*Michael B. Hundley. ''Gods in Dwellings: Temples and Divine Presence in the Ancient Near East''. Atlanta: Society of Biblical Literature, 2013.
*Dov Linzer. "Just the People of the Book, Really?" ''The Jerusalem Report'', volume 24 (number 22) (February 10, 2014): page 48.
*Jonathan Sacks. ''Lessons in Leadership: A Weekly Reading of the Jewish Bible'', pages 93–97. New Milford, Connecticut: Maggid Books, 2015.
*Raanan Eichler