Political on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Politics (from , ) is the set of activities that are associated with making decisions in groups, or other forms of power relations among individuals, such as the distribution of resources or
 The history of politics spans human history and is not limited to modern institutions of government.
The history of politics spans human history and is not limited to modern institutions of government.
 The Peace of Westphalia (1648) is considered by
The Peace of Westphalia (1648) is considered by
 The study of politics is called political science, or politology. It comprises numerous subfields, including
The study of politics is called political science, or politology. It comprises numerous subfields, including

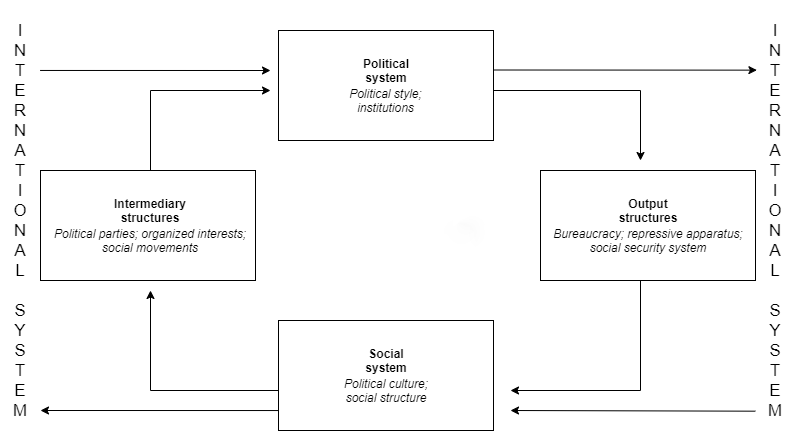 The political system defines the process for making official government decisions. It is usually compared to the legal system, economic system, cultural system, and other
The political system defines the process for making official government decisions. It is usually compared to the legal system, economic system, cultural system, and other
 Forms of government can be classified by several ways. In terms of the structure of power, there are
Forms of government can be classified by several ways. In terms of the structure of power, there are

 All the above forms of government are variations of the same basic polity, the sovereign state. The
All the above forms of government are variations of the same basic polity, the sovereign state. The
 Political culture describes how culture impacts politics. Every political system is embedded in a particular political culture.
Political culture describes how culture impacts politics. Every political system is embedded in a particular political culture.
 Equality is a state of affairs in which all people within a specific society or isolated group have the same social status, especially socioeconomic status, including protection of human rights and dignity, and equal access to certain social goods and social services. Furthermore, it may also include health equality, economic equality and other social securities. Social equality requires the absence of legally enforced social class or caste boundaries and the absence of discrimination motivated by an inalienable part of a person's identity. To this end there must be
Equality is a state of affairs in which all people within a specific society or isolated group have the same social status, especially socioeconomic status, including protection of human rights and dignity, and equal access to certain social goods and social services. Furthermore, it may also include health equality, economic equality and other social securities. Social equality requires the absence of legally enforced social class or caste boundaries and the absence of discrimination motivated by an inalienable part of a person's identity. To this end there must be
What Is Libertarian?
" ''Institute for Humane Studies''. George Mason University. For anarchist political philosopher L. Susan Brown (1993), "liberalism and anarchism are two political philosophies that are fundamentally concerned with individual freedom yet differ from one another in very distinct ways. Anarchism shares with liberalism a radical commitment to individual freedom while rejecting liberalism's competitive property relations." Brown, L. Susan. 1993. '' The Politics of Individualism: Liberalism, Liberal Feminism, and Anarchism''.
status
Status (Latin plural: ''statūs''), is a state, condition, or situation, and may refer to:
* Status (law)
** City status
** Legal status, in law
** Political status, in international law
** Small entity status, in patent law
** Status confere ...
. The branch of social science that studies politics and government is referred to as political science.
It may be used positively in the context of a "political solution" which is compromising and nonviolent, or descriptively as "the art or science of government", but also often carries a negative connotation.. The concept has been defined in various ways, and different approaches have fundamentally differing views on whether it should be used extensively or limitedly, empirically or normatively, and on whether conflict or co-operation is more essential to it.
A variety of methods are deployed in politics, which include promoting one's own political views among people, negotiation with other political subjects, making law
Law is a set of rules that are created and are enforceable by social or governmental institutions to regulate behavior,Robertson, ''Crimes against humanity'', 90. with its precise definition a matter of longstanding debate. It has been vario ...
s, and exercising internal and external force, including warfare against adversaries..... Politics is exercised on a wide range of social levels, from clans and tribes of traditional societies, through modern local government
Local government is a generic term for the lowest tiers of public administration within a particular sovereign state. This particular usage of the word government refers specifically to a level of administration that is both geographically-l ...
s, companies
A company, abbreviated as co., is a legal entity representing an association of people, whether natural, legal or a mixture of both, with a specific objective. Company members share a common purpose and unite to achieve specific, declared go ...
and institutions up to sovereign states, to the international level.
In modern nation states, people often form political parties to represent their ideas. Members of a party often agree to take the same position on many issues and agree to support the same changes to law and the same leaders. An election is usually a competition between different parties.
A political system is a framework which defines acceptable political methods within a society. The history of political thought can be traced back to early antiquity, with seminal works such as Plato's '' Republic'' and Aristotle's ''Politics
Politics (from , ) is the set of activities that are associated with making decisions in groups, or other forms of power relations among individuals, such as the distribution of resources or status. The branch of social science that stud ...
'' in the West, and Confucius's political manuscripts and Chanakya's '' Arthashastra'' in the non-Western cultures.
Etymology
The English ''politics'' has its roots in the name of Aristotle's classic work, '' Politiká'', which introduced theGreek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
term ( grc, Πολιτικά, label=none, italic=yes, lit=affairs of the cities)''.'' In the mid-15th century, Aristotle's composition would be rendered in Early Modern English
Early Modern English or Early New English (sometimes abbreviated EModE, EMnE, or ENE) is the stage of the English language from the beginning of the Tudor period to the English Interregnum and Restoration, or from the transition from Middle E ...
as ,"The book of " (Bhuler 1961/1941:154). which would become ''Politics'' in Modern English.
The singular ''politic'' first attested in English in 1430, coming from Middle French —itself taking from , a Latinization of the Greek grc, πολιτικός, label=none, italic=yes () from grc, πολίτης, label=none ( grc, polites, label=none, italic=yes, lit=citizen) and grc, πόλις, label=none ( grc, polis, label=none, italic=yes, lit=city).
Definitions
* Harold Lasswell: "who gets what, when, how" *David Easton
David Easton (June 24, 1917 – July 19, 2014) was a Canadian-born American political scientist. From 1947 to 1997, he served as a professor of political science at the University of Chicago.
At the forefront of both the behavioralist and post ...
: "the authoritative allocation of values for a society".
* Vladimir Lenin: "the most concentrated expression of economics"
* Otto von Bismarck: "the capacity of always choosing at each instant, in constantly changing situations, the least harmful, the most useful"
* Bernard Crick
Sir Bernard Rowland Crick (16 December 1929 – 19 December 2008) was a British political theorist and democratic socialist whose views can be summarised as "politics is ethics done in public". He sought to arrive at a "politics of action", as ...
: "a distinctive form of rule whereby people act together through institutionalized procedures to resolve differences"
* Adrian Leftwich: "comprises all the activities of co-operation, negotiation and conflict within and between societies"
Approaches
There are several ways in which approaching politics has been conceptualized.Extensive and limited
Adrian Leftwich has differentiated views of politics based on how extensive or limited their perception of what accounts as 'political' is. The extensive view sees politics as present across the sphere of human social relations, while the limited view restricts it to certain contexts. For example, in a more restrictive way, politics may be viewed as primarily about governance, while a feminist perspective could argue that sites which have been viewed traditionally as non-political, should indeed be viewed as political as well. This latter position is encapsulated in the slogan "'' the personal is political''," which disputes the distinction between private and public issues. Politics may also be defined by the use of power, as has been argued by Robert A. Dahl.Moralism and realism
Some perspectives on politics view it empirically as an exercise of power, while others see it as a social function with anormative
Normative generally means relating to an evaluative standard. Normativity is the phenomenon in human societies of designating some actions or outcomes as good, desirable, or permissible, and others as bad, undesirable, or impermissible. A norm in ...
basis. This distinction has been called the difference between political ''moralism'' and political ''realism''''.''. For moralists, politics is closely linked to ethics, and is at its extreme in utopian thinking. For example, according to Hannah Arendt, the view of Aristotle was that "to be political…meant that everything was decided through words and persuasion and not through violence;" while according to Bernard Crick
Sir Bernard Rowland Crick (16 December 1929 – 19 December 2008) was a British political theorist and democratic socialist whose views can be summarised as "politics is ethics done in public". He sought to arrive at a "politics of action", as ...
"politics is the way in which free societies are governed. Politics is politics and other forms of rule are something else." In contrast, for realists, represented by those such as Niccolò Machiavelli, Thomas Hobbes, and Harold Lasswell, politics is based on the use of power, irrespective of the ends being pursued.
Conflict and co-operation
Agonism argues that politics essentially comes down to conflict between conflicting interests. Political scientist Elmer Schattschneider argued that "at the root of all politics is the universal language of conflict," while forCarl Schmitt
Carl Schmitt (; 11 July 1888 – 7 April 1985) was a German jurist, political theorist, and prominent member of the Nazi Party. Schmitt wrote extensively about the effective wielding of political power. A conservative theorist, he is noted as ...
the essence of politics is the distinction of 'friend' from foe'. This is in direct contrast to the more co-operative views of politics by Aristotle and Crick. However, a more mixed view between these extremes is provided by Irish political scientist Michael Laver, who noted that:Politics is about the characteristic blend of conflict and co-operation that can be found so often in human interactions. Pure conflict is war. Pure co-operation is true love. Politics is a mixture of both.
History
 The history of politics spans human history and is not limited to modern institutions of government.
The history of politics spans human history and is not limited to modern institutions of government.
Prehistoric
Frans de Waal
Franciscus Bernardus Maria "Frans" de Waal (born October 29, 1948) is a Dutch primatologist and ethologist. He is the Charles Howard Candler Professor of Primate Behavior in the Department of Psychology at Emory University in Atlanta, Georgia, ...
argued that chimpanzees engage in politics through "social manipulation to secure and maintain influential positions." Early human forms of social organization—bands and tribes—lacked centralized political structures. These are sometimes referred to as stateless societies
A stateless society is a society that is not governed by a state. In stateless societies, there is little concentration of authority; most positions of authority that do exist are very limited in power and are generally not permanently held p ...
.
Early states
In ancient history, civilizations did not have definite boundaries as states have today, and their borders could be more accurately described as frontiers. Early dynastic Sumer, and early dynastic Egypt were the first civilizations to define their borders. Moreover, up to the 12th century, many people lived in non-state societies. These range from relatively egalitarian bands and tribes to complex and highly stratifiedchiefdom
A chiefdom is a form of hierarchical political organization in non-industrial societies usually based on kinship, and in which formal leadership is monopolized by the legitimate senior members of select families or 'houses'. These elites form a ...
s.
State formation
There are a number of different theories and hypotheses regarding early state formation that seek generalizations to explain why the state developed in some places but not others. Other scholars believe that generalizations are unhelpful and that each case of early state formation should be treated on its own. Voluntary theories contend that diverse groups of people came together to form states as a result of some shared rational interest.. The theories largely focus on the development of agriculture, and the population and organizational pressure that followed and resulted in state formation. One of the most prominent theories of early and primary state formation is the ''hydraulic hypothesis'', which contends that the state was a result of the need to build and maintain large-scale irrigation projects.Conflict theories
Conflict theories are perspectives in sociology and social psychology that emphasize a materialist interpretation of history, dialectical method of analysis, a critical stance toward existing social arrangements, and political program of revolut ...
of state formation regard conflict and dominance of some population over another population as key to the formation of states. In contrast with voluntary theories, these arguments believe that people do not voluntarily agree to create a state to maximize benefits, but that states form due to some form of oppression by one group over others. Some theories in turn argue that warfare was critical for state formation.
Ancient history
The first states of sorts were those of early dynastic Sumer and early dynastic Egypt, which arose from the Uruk period and Predynastic Egypt respectively around approximately 3000 BCE.. Early dynastic Egypt was based around the Nile River in the north-east ofAfrica
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area ...
, the kingdom's boundaries being based around the Nile and stretching to areas where oases existed. Early dynastic Sumer was located in southern Mesopotamia with its borders extending from the Persian Gulf to parts of the Euphrates and Tigris rivers.
Egyptians, Romans, and the Greeks were the first people known to have explicitly formulated a political philosophy of the state, and to have rationally analyzed political institutions. Prior to this, states were described and justified in terms of religious myths.
Several important political innovations of classical antiquity
Classical antiquity (also the classical era, classical period or classical age) is the period of cultural history between the 8th century BC and the 5th century AD centred on the Mediterranean Sea, comprising the interlocking civilizations of ...
came from the Greek city-states ('' polis'') and the Roman Republic. The Greek city-states before the 4th century granted citizenship rights to their free population; in Athens these rights were combined with a directly democratic form of government that was to have a long afterlife in political thought and history.
Modern states
 The Peace of Westphalia (1648) is considered by
The Peace of Westphalia (1648) is considered by political scientists
This is a list of notable political scientists. See the list of political theorists for those who study political theory. See also political science.
A
* Robert Abelson - Yale University psychologist and political scientist with special int ...
to be the beginning of the modern international system,.. in which external powers should avoid interfering in another country's domestic affairs.. The principle of non-interference in other countries' domestic affairs was laid out in the mid-18th century by Swiss jurist Emer de Vattel
Emer (Emmerich) de Vattel ( 25 April 171428 December 1767) was an international lawyer. He was born in Couvet in the Principality of Neuchâtel (now a canton part of Switzerland but part of Prussia at the time) in 1714 and died in 1767. He was l ...
. States became the primary institutional agents in an interstate system of relations. The Peace of Westphalia is said to have ended attempts to impose supranational authority on European states. The "Westphalian" doctrine of states as independent agents was bolstered by the rise in 19th century thought of nationalism, under which legitimate states were assumed to correspond to ''nations
A nation is a community of people formed on the basis of a combination of shared features such as language, history, ethnicity, culture and/or society. A nation is thus the collective identity of a group of people understood as defined by t ...
''—groups of people united by language and culture.
In Europe, during the 18th century, the classic non-national states were the multinational empires: the Austrian Empire, Kingdom of France, Kingdom of Hungary, the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War. ...
, the Spanish Empire, the Ottoman Empire, and the British Empire. Such empires also existed in Asia, Africa, and the Americas; in the Muslim world, immediately after the death of Muhammad
Muhammad ( ar, مُحَمَّد; 570 – 8 June 632 CE) was an Arab religious, social, and political leader and the founder of Islam. According to Islamic doctrine, he was a prophet divinely inspired to preach and confirm the mono ...
in 632, Caliphates were established, which developed into multi-ethnic trans-national empires. The multinational empire was an absolute monarchy
Absolute monarchy (or Absolutism (European history), Absolutism as a doctrine) is a form of monarchy in which the monarch rules in their own right or power. In an absolute monarchy, the king or queen is by no means limited and has absolute pow ...
ruled by a king, emperor or sultan. The population belonged to many ethnic groups, and they spoke many languages. The empire was dominated by one ethnic group, and their language was usually the language of public administration. The ruling dynasty was usually, but not always, from that group. Some of the smaller European states were not so ethnically diverse, but were also dynastic
A dynasty is a sequence of rulers from the same family,''Oxford English Dictionary'', "dynasty, ''n''." Oxford University Press (Oxford), 1897. usually in the context of a monarchical system, but sometimes also appearing in republics. A d ...
states, ruled by a royal house. A few of the smaller states survived, such as the independent principalities of Liechtenstein, Andorra, Monaco, and the republic of San Marino.
Most theories see the nation state as a 19th-century European phenomenon, facilitated by developments such as state-mandated education, mass literacy, and mass media. However, historians also note the early emergence of a relatively unified state and identity in Portugal
Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic ( pt, República Portuguesa, links=yes ), is a country whose mainland is located on the Iberian Peninsula of Southwestern Europe, and whose territory also includes the Atlantic archipelagos of ...
and the Dutch Republic. Scholars such as Steven Weber, David Woodward, Michel Foucault, and Jeremy Black have advanced the hypothesis that the nation state did not arise out of political ingenuity or an unknown undetermined source, nor was it an accident of history or political invention. Rather, the nation state is an inadvertent byproduct of 15th-century intellectual discoveries in political economy, capitalism, mercantilism, political geography, and geography combined with cartography and advances in map-making technologies.
Some nation states, such as Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
and Italy, came into existence at least partly as a result of political campaigns by nationalists
Nationalism is an idea and movement that holds that the nation should be congruent with the state. As a movement, nationalism tends to promote the interests of a particular nation (as in a group of people), Smith, Anthony. ''Nationalism: The ...
, during the 19th century. In both cases, the territory was previously divided among other states, some of them very small. Liberal ideas of free trade played a role in German unification, which was preceded by a customs union, the Zollverein
The (), or German Customs Union, was a coalition of German states formed to manage tariffs and economic policies within their territories. Organized by the 1833 treaties, it formally started on 1 January 1834. However, its foundations had b ...
. National self-determination was a key aspect of United States President Woodrow Wilson's Fourteen Points
U.S. President Woodrow Wilson
The Fourteen Points was a statement of principles for peace that was to be used for peace negotiations in order to end World War I. The principles were outlined in a January 8, 1918 speech on war aims and peace terms ...
, leading to the dissolution of the Austro-Hungarian Empire and the Ottoman Empire after the First World War, while the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War. ...
became the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
after the Russian Civil War. Decolonization
Decolonization or decolonisation is the undoing of colonialism, the latter being the process whereby imperial nations establish and dominate foreign territories, often overseas. Some scholars of decolonization focus especially on separatism, in ...
lead to the creation of new nation states in place of multinational empires in the Third World.
Globalization
Political globalization began in the 20th century through intergovernmental organizations and supranational unions. The League of Nations was founded afterWorld War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
, and after World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
it was replaced by the United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be a centre for harmoniz ...
. Various international treaties have been signed through it. Regional integration has been pursued by the African Union, ASEAN, the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been de ...
, and Mercosur
The Southern Common Market, commonly known by Spanish abbreviation Mercosur, and Portuguese Mercosul, is a South American trade bloc established by the Treaty of Asunción in 1991 and Protocol of Ouro Preto in 1994. Its full members are Arge ...
. International political institutions on the international level include the International Criminal Court, the International Monetary Fund, and the World Trade Organization.
Political science
 The study of politics is called political science, or politology. It comprises numerous subfields, including
The study of politics is called political science, or politology. It comprises numerous subfields, including comparative politics
Comparative politics is a field in political science characterized either by the use of the ''comparative method'' or other empirical methods to explore politics both within and between countries. Substantively, this can include questions relatin ...
, political economy, international relations, political philosophy, public administration, public policy, gender and politics
Gender and politics, also called gender in politics, is a field of study in political science and gender studies that aims to understand the relationship between peoples' genders and phenomena in politics. Researchers of gender and politics study ...
, and political methodology. Furthermore, political science is related to, and draws upon, the fields of economics, law
Law is a set of rules that are created and are enforceable by social or governmental institutions to regulate behavior,Robertson, ''Crimes against humanity'', 90. with its precise definition a matter of longstanding debate. It has been vario ...
, sociology, history, philosophy, geography, psychology/ psychiatry, anthropology, and neurosciences.
Comparative politics
Comparative politics is a field in political science characterized either by the use of the ''comparative method'' or other empirical methods to explore politics both within and between countries. Substantively, this can include questions relatin ...
is the science of comparison and teaching of different types of constitutions
A constitution is the aggregate of fundamental principles or established precedents that constitute the legal basis of a polity, organisation or other type of entity and commonly determine how that entity is to be governed.
When these prin ...
, political actors, legislature and associated fields. International relations deals with the interaction between nation-states as well as intergovernmental and transnational organizations. Political philosophy is more concerned with contributions of various classical and contemporary thinkers and philosophers.
Political science is methodologically diverse and appropriates many methods originating in psychology, social research
Social research is a research conducted by social scientists following a systematic plan. Social research methodologies can be classified as quantitative and qualitative.
* Quantitative designs approach social phenomena through quantifiable ...
, and cognitive neuroscience
Cognitive neuroscience is the scientific field that is concerned with the study of the biological processes and aspects that underlie cognition, with a specific focus on the neural connections in the brain which are involved in mental process ...
. Approaches include positivism, interpretivism, rational choice theory, behavioralism
Behaviouralism (or behavioralism) is an approach in political science that emerged in the 1930s in the United States. It represented a sharp break from previous approaches in emphasizing an objective, quantified approach to explain and predict pol ...
, structuralism, post-structuralism
Post-structuralism is a term for philosophical and literary forms of theory that both build upon and reject ideas established by structuralism, the intellectual project that preceded it. Though post-structuralists all present different critiques ...
, realism, institutionalism, and pluralism. Political science, as one of the social sciences, uses methods and techniques that relate to the kinds of inquiries sought: primary sources such as historical documents and official records, secondary sources such as scholarly journal articles, survey
Survey may refer to:
Statistics and human research
* Statistical survey, a method for collecting quantitative information about items in a population
* Survey (human research), including opinion polls
Spatial measurement
* Surveying, the techniq ...
research, statistical analysis, case studies, experimental research
An experiment is a procedure carried out to support or refute a hypothesis, or determine the efficacy or likelihood of something previously untried. Experiments provide insight into cause-and-effect by demonstrating what outcome occurs when a ...
, and model building.
Political system
 The political system defines the process for making official government decisions. It is usually compared to the legal system, economic system, cultural system, and other
The political system defines the process for making official government decisions. It is usually compared to the legal system, economic system, cultural system, and other social system
In sociology, a social system is the patterned network of relationships constituting a coherent whole that exist between individuals, groups, and institutions. It is the formal structure of role and status that can form in a small, stable group. A ...
s. According to David Easton
David Easton (June 24, 1917 – July 19, 2014) was a Canadian-born American political scientist. From 1947 to 1997, he served as a professor of political science at the University of Chicago.
At the forefront of both the behavioralist and post ...
, "A political system can be designated as the interactions through which values are authoritatively allocated for a society." Each political system is embedded in a society with its own political culture, and they in turn shape their societies through public policy. The interactions between different political systems are the basis for global politics
Global politics, also known as world politics, names both the discipline that studies the political and economic patterns of the world and the field that is being studied. At the centre of that field are the different processes of political globa ...
.
Forms of government
 Forms of government can be classified by several ways. In terms of the structure of power, there are
Forms of government can be classified by several ways. In terms of the structure of power, there are monarchies
A monarchy is a form of government in which a person, the monarch, is head of state for life or until abdication. The political legitimacy and authority of the monarch may vary from restricted and largely symbolic (constitutional monarchy), ...
(including constitutional monarchies) and republics (usually presidential, semi-presidential
A semi-presidential republic, is a republic in which a president exists alongside a prime minister and a cabinet, with the latter two being responsible to the legislature of the state. It differs from a parliamentary republic in that it has a ...
, or parliamentary).
The separation of powers describes the degree of horizontal integration between the legislature
A legislature is an assembly with the authority to make law
Law is a set of rules that are created and are enforceable by social or governmental institutions to regulate behavior,Robertson, ''Crimes against humanity'', 90. with its p ...
, the executive, the judiciary, and other independent institutions.
Source of power
The source of power determines the difference betweendemocracies
Democracy (From grc, δημοκρατία, dēmokratía, ''dēmos'' 'people' and ''kratos'' 'rule') is a form of government in which the people have the authority to deliberate and decide legislation (" direct democracy"), or to choose go ...
, oligarchies, and autocracies.
In a democracy, political legitimacy is based on popular sovereignty
Popular sovereignty is the principle that the authority of a state and its government are created and sustained by the consent of its people, who are the source of all political power. Popular sovereignty, being a principle, does not imply any ...
. Forms of democracy include representative democracy
Representative democracy, also known as indirect democracy, is a type of democracy where elected people represent a group of people, in contrast to direct democracy. Nearly all modern Western-style democracies function as some type of represe ...
, direct democracy, and demarchy
In governance, sortition (also known as selection by lottery, selection by lot, allotment, demarchy, stochocracy, aleatoric democracy, democratic lottery, and lottocracy) is the selection of political officials as a random sample from a larger ...
. These are separated by the way decisions are made, whether by elected Elected may refer to:
* "Elected" (song), by Alice Cooper, 1973
* ''Elected'' (EP), by Ayreon, 2008
*The Elected, an American indie rock band
See also
*Election
An election is a formal group decision-making process by which a population ...
representatives, referendums, or by citizen juries. Democracies can be either republics or constitutional monarchies.
Oligarchy is a power structure where a minority rules. These may be in the form of anocracy, aristocracy, ergatocracy, geniocracy
Geniocracy is the framework for a system of government which was first proposed by Raël (leader of the International Raëlian Movement) in 1977 and which advocates a certain minimal criterion of intelligence for political candidates and also the ...
, gerontocracy
A gerontocracy is a form of oligarchical rule in which an entity is ruled by leaders who are significantly older than most of the adult population. In many political structures, power within the ruling class accumulates with age, making the oldes ...
, kakistocracy, kleptocracy
Kleptocracy (from Ancient Greek, Greek κλέπτης ''kléptēs'', "thief", κλέπτω ''kléptō'', "I steal", and -κρατία -''kratía'' from κράτος ''krátos'', "power, rule") is a government whose Corruption, corrupt leaders ...
, meritocracy, noocracy, particracy, plutocracy
A plutocracy () or plutarchy is a society that is ruled or controlled by people of great wealth or income. The first known use of the term in English dates from 1631. Unlike most political systems, plutocracy is not rooted in any establishe ...
, stratocracy
A stratocracy (from στρατός, ''stratos'', "army" and κράτος, ''kratos'', "dominion", "power", also ''stratiocracy'') is a form of government headed by military chiefs. The branches of government are administered by military forces, ...
, technocracy
Technocracy is a form of government in which the decision-maker or makers are selected based on their expertise in a given area of responsibility, particularly with regard to scientific or technical knowledge. This system explicitly contrasts wi ...
, theocracy, or timocracy.
Autocracies are either dictatorships (including military dictatorships) or absolute monarchies
Absolute monarchy (or Absolutism as a doctrine) is a form of monarchy in which the monarch rules in their own right or power. In an absolute monarchy, the king or queen is by no means limited and has absolute power, though a limited constitut ...
.
Vertical integration
In terms of level of vertical integration, political systems can be divided into (from least to most integrated) confederations, federations, and unitary states. A federation (also known as a federal state) is a political entity characterized by aunion
Union commonly refers to:
* Trade union, an organization of workers
* Union (set theory), in mathematics, a fundamental operation on sets
Union may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment
Music
* Union (band), an American rock group
** ''Un ...
of partially self-governing provinces, states, or other regions under a central federal government ( federalism). In a federation, the self-governing status of the component states, as well as the division of power between them and the central government, is typically constitutionally entrenched and may not be altered by a unilateral decision of either party, the states or the federal political body. Federations were formed first in Switzerland, then in the United States in 1776, in Canada in 1867 and in Germany in 1871 and in 1901, Australia. Compared to a federation, a confederation has less centralized power.
State
state
State may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Literature
* ''State Magazine'', a monthly magazine published by the U.S. Department of State
* ''The State'' (newspaper), a daily newspaper in Columbia, South Carolina, United States
* ''Our S ...
has been defined by Max Weber as a political entity that has monopoly on violence
In political philosophy, a monopoly on violence or monopoly on the legal use of force is the property of a polity that is the only entity in its jurisdiction to legitimately use force, and thus the supreme authority of that area.
While the mon ...
within its territory, while the Montevideo Convention holds that states need to have a defined territory; a permanent population; a government; and a capacity to enter into international relations.
A stateless society is a society that is not governed by a state
State may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Literature
* ''State Magazine'', a monthly magazine published by the U.S. Department of State
* ''The State'' (newspaper), a daily newspaper in Columbia, South Carolina, United States
* ''Our S ...
.. In stateless societies, there is little concentration of authority; most positions of authority that do exist are very limited in power
Power most often refers to:
* Power (physics), meaning "rate of doing work"
** Engine power, the power put out by an engine
** Electric power
* Power (social and political), the ability to influence people or events
** Abusive power
Power may a ...
and are generally not permanently held positions; and social bodies that resolve disputes through predefined rules tend to be small. Stateless societies are highly variable in economic organization and cultural practices.
While stateless societies were the norm in human prehistory, few stateless societies exist today; almost the entire global population resides within the jurisdiction of a sovereign state. In some regions nominal state authorities may be very weak and wield little or no actual power. Over the course of history most stateless peoples have been integrated into the state-based societies around them.
Some political philosophies consider the state undesirable, and thus consider the formation of a stateless society a goal to be achieved. A central tenet of anarchism is the advocacy of society without states. The type of society sought for varies significantly between anarchist schools of thought, ranging from extreme individualism to complete collectivism
Collectivism may refer to:
* Bureaucratic collectivism, a theory of class society whichto describe the Soviet Union under Joseph Stalin
* Collectivist anarchism, a socialist doctrine in which the workers own and manage the production
* Collectivis ...
. In Marxism, Marx's theory of the state considers that in a post-capitalist society the state, an undesirable institution, would be unnecessary and wither away. A related concept is that of stateless communism, a phrase sometimes used to describe Marx's anticipated post-capitalist society.
Constitutions
Constitutions
A constitution is the aggregate of fundamental principles or established precedents that constitute the legal basis of a polity, organisation or other type of entity and commonly determine how that entity is to be governed.
When these prin ...
are written documents that specify and limit the powers of the different branches of government. Although a constitution is a written document, there is also an unwritten constitution. The unwritten constitution is continually being written by the legislative and judiciary branch of government; this is just one of those cases in which the nature of the circumstances determines the form of government that is most appropriate. England did set the fashion of written constitutions during the Civil War but after the Restoration abandoned them to be taken up later by the American Colonies after their emancipation
Emancipation generally means to free a person from a previous restraint or legal disability. More broadly, it is also used for efforts to procure economic and social rights, political rights or equality, often for a specifically disenfranch ...
and then France after the Revolution and the rest of Europe including the European colonies.
Constitutions often set out separation of powers, dividing the government into the executive, the legislature
A legislature is an assembly with the authority to make law
Law is a set of rules that are created and are enforceable by social or governmental institutions to regulate behavior,Robertson, ''Crimes against humanity'', 90. with its p ...
, and the judiciary (together referred to as the trias politica), in order to achieve checks and balances within the state. Additional independent branches may also be created, including civil service commission
A civil service commission is a government agency that is constituted by legislature to regulate the employment and working conditions of civil servants, oversee hiring and promotions, and promote the values of the public service. Its role is rough ...
s, election commissions, and supreme audit institutions.
Political culture
 Political culture describes how culture impacts politics. Every political system is embedded in a particular political culture.
Political culture describes how culture impacts politics. Every political system is embedded in a particular political culture. Lucian Pye
Lucian W. Pye (; October 21, 1921 – September 5, 2008) was an American political scientist, sinologist and comparative politics expert considered one of the leading China scholars in the United States. Educated at Carleton College and Yale Univ ...
's definition is that "Political culture is the set of attitudes, beliefs, and sentiments, which give order and meaning to a political process and which provide the underlying assumptions and rules that govern behavior in the political system".
Trust is a major factor in political culture, as its level determines the capacity of the state to function.. Postmaterialism is the degree to which a political culture is concerned with issues which are not of immediate physical or material concern, such as human rights and environmentalism. Religion has also an impact on political culture.
Political dysfunction
Political corruption
Political corruption is the use of powers for illegitimate private gain, conducted by government officials or their network contacts. Forms of political corruption include bribery,cronyism
Cronyism is the spoils system practice of Impartiality, partiality in awarding jobs and other advantages to friends or trusted colleagues, especially in politics and between politicians and supportive organizations. For example, cronyism occurs ...
, nepotism, and political patronage
Patronage is the support, encouragement, privilege, or financial aid that an organization or individual bestows on another. In the history of art, arts patronage refers to the support that kings, popes, and the wealthy have provided to artists su ...
. Forms of political patronage, in turn, includes clientelism, earmarking, pork barreling, slush funds, and spoils system
In politics and government, a spoils system (also known as a patronage system) is a practice in which a political party, after winning an election, gives government jobs to its supporters, friends (cronyism), and relatives (nepotism) as a reward ...
s; as well as political machines, which is a political system that operates for corrupt ends.
When corruption is embedded in political culture, this may be referred to as patrimonialism
Patrimonialism is a form of governance in which all power flows directly from the ruler. There is no distinction between the public and private domains. These regimes are autocratic or oligarchic and exclude the lower, middle and upper classes ...
or neopatrimonialism
Neopatrimonialism is a system of social hierarchy where patrons use state resources to secure the loyalty of clients in the general population. It is an informal patron–client relationship that can reach from very high up in state structures d ...
. A form of government that is built on corruption is called a ''kleptocracy
Kleptocracy (from Ancient Greek, Greek κλέπτης ''kléptēs'', "thief", κλέπτω ''kléptō'', "I steal", and -κρατία -''kratía'' from κράτος ''krátos'', "power, rule") is a government whose Corruption, corrupt leaders ...
'' ('rule of thieves').
Levels of politics
Macropolitics
Macropolitics can either describe political issues that affect an entire political system (e.g. the nation state), or refer to interactions between political systems (e.g. international relations). Global politics (or world politics) covers all aspects of politics that affect multiple political systems, in practice meaning any political phenomenon crossing national borders. This can includecities
A city is a human settlement of notable size.Goodall, B. (1987) ''The Penguin Dictionary of Human Geography''. London: Penguin.Kuper, A. and Kuper, J., eds (1996) ''The Social Science Encyclopedia''. 2nd edition. London: Routledge. It can be def ...
, nation-states, multinational corporations, non-governmental organization
A non-governmental organization (NGO) or non-governmental organisation (see American and British English spelling differences#-ise, -ize (-isation, -ization), spelling differences) is an organization that generally is formed independent from g ...
s, and/or international organization
An international organization or international organisation (see spelling differences), also known as an intergovernmental organization or an international institution, is a stable set of norms and rules meant to govern the behavior of states a ...
s. An important element is international relations: the relations between nation-states may be peaceful when they are conducted through diplomacy, or they may be violent, which is described as war
War is an intense armed conflict between states, governments, societies, or paramilitary groups such as mercenaries, insurgents, and militias. It is generally characterized by extreme violence, destruction, and mortality, using regular o ...
. States that are able to exert strong international influence are referred to as superpowers, whereas less-powerful ones may be called regional
In geography, regions, otherwise referred to as zones, lands or territories, are areas that are broadly divided by physical characteristics (physical geography), human impact characteristics (human geography), and the interaction of humanity and t ...
or middle power
In international relations, a middle power is a sovereign state that is not a great power nor a superpower, but still has large or moderate influence and international recognition.
The concept of the "middle power" dates back to the origin ...
s. The international system of power
Power most often refers to:
* Power (physics), meaning "rate of doing work"
** Engine power, the power put out by an engine
** Electric power
* Power (social and political), the ability to influence people or events
** Abusive power
Power may a ...
is called the ''world order'', which is affected by the balance of power that defines the degree of polarity in the system. Emerging powers are potentially destabilizing to it, especially if they display revanchism
Revanchism (french: revanchisme, from ''revanche'', "revenge") is the political manifestation of the will to reverse territorial losses incurred by a country, often following a war or social movement. As a term, revanchism originated in 1870s Fr ...
or irredentism
Irredentism is usually understood as a desire that one state annexes a territory of a neighboring state. This desire is motivated by ethnic reasons (because the population of the territory is ethnically similar to the population of the parent sta ...
.
Politics inside the limits of political systems, which in contemporary context correspond to national borders, are referred to as domestic politics. This includes most forms of public policy, such as social policy, economic policy, or law enforcement, which are executed by the state bureaucracy.
Mesopolitics
Mesopolitics describes the politics of intermediary structures within a political system, such as national political parties ormovements
Movement may refer to:
Common uses
* Movement (clockwork), the internal mechanism of a timepiece
* Motion, commonly referred to as movement
Arts, entertainment, and media
Literature
* "Movement" (short story), a short story by Nancy Fu ...
.
A political party is a political organization
A political organization is any organization that involves itself in the political process, including political parties, non-governmental organizations, and special interest advocacy groups. Political organizations are those engaged in poli ...
that typically seeks to attain and maintain political power within government, usually by participating in political campaigns, educational outreach, or protest actions. Parties often espouse an expressed ideology or vision, bolstered by a written platform
Platform may refer to:
Technology
* Computing platform, a framework on which applications may be run
* Platform game, a genre of video games
* Car platform, a set of components shared by several vehicle models
* Weapons platform, a system or ...
with specific goals, forming a coalition among disparate interests.
Political parties within a particular political system together form the party system, which can be either multiparty
In political science, a multi-party system is a political system in which multiple political parties across the political spectrum run for national elections, and all have the capacity to gain control of government offices, separately or in coal ...
, two-party
A two-party system is a political party system in which two major political parties consistently dominate the political landscape. At any point in time, one of the two parties typically holds a majority in the legislature and is usually referr ...
, dominant-party
A dominant-party system, or one-party dominant system, is a political occurrence in which a single political party continuously dominates election results over running opposition groups or parties. Any ruling party staying in power for more t ...
, or one-party
A government is the system or group of people governing an organized community, generally a state.
In the case of its broad associative definition, government normally consists of legislature, executive, and judiciary. Government ...
, depending on the level of pluralism. This is affected by characteristics of the political system, including its electoral system. According to Duverger's law, first-past-the-post systems are likely to lead to two-party systems, while proportional representation systems are more likely to create a multiparty system.
Micropolitics
Micropolitics describes the actions of individual actors within the political system. This is often described aspolitical participation
Citizen Participation or Public Participation in social science refers to different mechanisms for the public to express opinions—and ideally exert influence—regarding political, economic, management or other social decisions. Participato ...
. Political participation may take many forms, including:
* Activism
* Boycott
* Civil disobedience
* Demonstration
* Petition
* Picketing
* Strike action
* Tax resistance
* Voting (or its opposite, abstentionism
Abstentionism is standing for election to a deliberative assembly while refusing to take up any seats won or otherwise participate in the assembly's business. Abstentionism differs from an election boycott in that abstentionists participate in ...
)
Political values
Democracy
Democracy is a system of processing conflicts in which outcomes depend on what participants do, but no single force controls what occurs and its outcomes. The uncertainty of outcomes is inherent in democracy. Democracy makes all forces struggle repeatedly to realize their interests and devolves power from groups of people to sets of rules. Among modern political theorists, there are three contending conceptions of democracy: ''aggregative'', '' deliberative'', and '' radical''.Aggregative
The theory of ''aggregative democracy'' claims that the aim of the democratic processes is to solicit the preferences of citizens, and aggregate them together to determine what social policies the society should adopt. Therefore, proponents of this view hold that democratic participation should primarily focus on voting, where the policy with the most votes gets implemented. Different variants of aggregative democracy exist. Under ''minimalism'', democracy is a system of government in which citizens have given teams of political leaders the right to rule in periodic elections. According to this minimalist conception, citizens cannot and should not "rule" because, for example, on most issues, most of the time, they have no clear views or their views are not well-founded.Joseph Schumpeter
Joseph Alois Schumpeter (; February 8, 1883 – January 8, 1950) was an Austrian-born political economist. He served briefly as Finance Minister of German-Austria in 1919. In 1932, he emigrated to the United States to become a professor at H ...
articulated this view most famously in his book '' Capitalism, Socialism, and Democracy''. Contemporary proponents of minimalism include William H. Riker, Adam Przeworski
Adam Przeworski (; born May 5, 1940) is a Polish-American professor of political science specializing in comparative politics. He is Carroll and Milton Professor Emeritus in the Department of Politics of New York University. He is a scholar of de ...
, Richard Posner
Richard Allen Posner (; born January 11, 1939) is an American jurist and legal scholar who served as a federal appellate judge on the U.S. Court of Appeals for the Seventh Circuit from 1981 to 2017. A senior lecturer at the University of Chic ...
.
According to the theory of '' direct democracy'', on the other hand, citizens should vote directly, not through their representatives, on legislative proposals. Proponents of direct democracy offer varied reasons to support this view. Political activity can be valuable in itself, it socializes and educates citizens, and popular participation can check powerful elites. Most importantly, citizens do not rule themselves unless they directly decide laws and policies.
Governments will tend to produce laws and policies that are close to the views of the median voter—with half to their left and the other half to their right. This is not a desirable outcome as it represents the action of self-interested and somewhat unaccountable political elites competing for votes. Anthony Downs suggests that ideological political parties are necessary to act as a mediating broker between individual and governments. Downs laid out this view in his 1957 book '' An Economic Theory of Democracy''.
Robert A. Dahl argues that the fundamental democratic principle is that, when it comes to binding collective decisions, each person in a political community is entitled to have his/her interests be given equal consideration (not necessarily that all people are equally satisfied by the collective decision). He uses the term polyarchy to refer to societies in which there exists a certain set of institutions and procedures which are perceived as leading to such democracy. First and foremost among these institutions is the regular occurrence of free and open elections which are used to select representatives who then manage all or most of the public policy of the society. However, these polyarchic procedures may not create a full democracy if, for example, poverty prevents political participation. Similarly, Ronald Dworkin argues that "democracy is a substantive, not a merely procedural, ideal."
Deliberative
''Deliberative democracy'' is based on the notion that democracy is government by deliberation. Unlike aggregative democracy, deliberative democracy holds that, for a democratic decision to be legitimate, it must be preceded by authentic deliberation, not merely the aggregation of preferences that occurs in voting. ''Authentic deliberation'' is deliberation among decision-makers that is free from distortions of unequal political power, such as power a decision-maker obtained through economic wealth or the support of interest groups. If the decision-makers cannot reach consensus after authentically deliberating on a proposal, then they vote on the proposal using a form of majority rule.Radical
''Radical democracy'' is based on the idea that there are hierarchical and oppressive power relations that exist in society. Democracy's role is to make visible and challenge those relations by allowing for difference, dissent and antagonisms in decision-making processes.Equality
equal justice under law
Equal justice under law is a phrase engraved on the West Pediment, above the front entrance of the United States Supreme Court building in Washington D.C. It is also a societal ideal that has influenced the American legal system.
The phrase wa ...
, and equal opportunity
Equal opportunity is a state of fairness in which individuals are treated similarly, unhampered by artificial barriers, prejudices, or preferences, except when particular distinctions can be explicitly justified. The intent is that the important ...
regardless of, for example, sex, gender, ethnicity, age, sexual orientation, origin, caste or class, income or property, language, religion, convictions, opinions, health or disability.
Left–right spectrum
A common way of understanding politics is through theleft–right political spectrum
The left–right political spectrum is a system of classifying political positions characteristic of left-right politics, ideologies and parties with emphasis placed upon issues of social equality and social hierarchy. In addition to position ...
, which ranges from left-wing politics via centrism to right-wing politics. This classification is comparatively recent and dates from the French Revolution
The French Revolution ( ) was a period of radical political and societal change in France that began with the Estates General of 1789 and ended with the formation of the French Consulate in coup of 18 Brumaire, November 1799. Many of its ...
, when those members of the National Assembly who supported the republic, the common people and a secular society sat on the left and supporters of the monarchy
A monarchy is a government#Forms, form of government in which a person, the monarch, is head of state for life or until abdication. The legitimacy (political)#monarchy, political legitimacy and authority of the monarch may vary from restric ...
, aristocratic
Aristocracy (, ) is a form of government that places strength in the hands of a small, privileged ruling class, the aristocrats. The term derives from the el, αριστοκρατία (), meaning 'rule of the best'.
At the time of the word' ...
privilege and the Church sat on the right.
Today, the left is generally progressivist, seeking social progress
Progress is the movement towards a refined, improved, or otherwise desired state. In the context of progressivism, it refers to the proposition that advancements in technology, science, and social organization have resulted, and by extension w ...
in society. The more extreme elements of the left, named the far-left, tend to support revolutionary means for achieving this. This includes ideologies such as Communism and Marxism. The center-left
Centre-left politics lean to the left on the left–right political spectrum but are closer to the centre than other left-wing politics. Those on the centre-left believe in working within the established systems to improve social justice. The ce ...
, on the other hand, advocate for more reformist
Reformism is a political doctrine advocating the reform of an existing system or institution instead of its abolition and replacement.
Within the socialist movement, reformism is the view that gradual changes through existing institutions can ...
approaches, for example that of social democracy.
In contrast, the right is generally motivated by conservatism, which seeks to conserve what it sees as the important elements of society. The far-right goes beyond this, and often represents a reactionary turn against progress, seeking to undo it. Examples of such ideologies have included Fascism and Nazism. The center-right may be less clear-cut and more mixed in this regard, with neoconservatives
Neoconservatism is a political movement that began in the United States during the 1960s among liberal hawks who became disenchanted with the increasingly pacifist foreign policy of the Democratic Party and with the growing New Left and cou ...
supporting the spread of free markets and capitalism, and one-nation conservatives more open to social welfare programs.
According to Norberto Bobbio
Norberto Bobbio (; 18 October 1909 – 9 January 2004) was an Italian philosopher of law and political sciences and a historian of political thought. He also wrote regularly for the Turin-based daily ''La Stampa''.
Bobbio was a social libe ...
, one of the major exponents of this distinction, the left believes in attempting to eradicate social inequality—believing it to be unethical or unnatural, while the right regards most social inequality as the result of ineradicable natural inequalities, and sees attempts to enforce social equality as utopian or authoritarian..
Some ideologies, notably Christian Democracy, claim to combine left and right-wing politics; according to Geoffrey K. Roberts and Patricia Hogwood, "In terms of ideology, Christian Democracy has incorporated many of the views held by liberals, conservatives and socialists within a wider framework of moral and Christian principles." Movements which claim or formerly claimed to be above the left-right divide include Fascist Terza Posizione
Terza Posizione ( en, Third Position) was a short-lived neo-fascist political movement founded in Rome
, established_title = Founded
, established_date = 753 BC
, founder = King Romulus ( legendary)
, image_map ...
economic politics in Italy and Peronism in Argentina.
Freedom
Political freedom (also known as political liberty or autonomy) is a central concept in political thought and one of the most important features of democratic societies.Negative liberty
Negative liberty is freedom from interference by other people. Negative liberty is primarily concerned with freedom from external restraint and contrasts with positive liberty (the possession of the power and resources to fulfill one's own pote ...
has been described as freedom from oppression or coercion and unreasonable external constraints on action, often enacted through civil and political rights, while positive liberty is the absence of disabling conditions for an individual and the fulfillment of enabling conditions, e.g. economic compulsion, in a society. This capability approach to freedom requires economic, social and cultural rights in order to be realized.
Authoritarianism and libertarianism
Authoritarianism
Authoritarianism is a political system characterized by the rejection of political plurality, the use of strong central power to preserve the political ''status quo'', and reductions in the rule of law, separation of powers, and democratic voti ...
and libertarianism disagree the amount of individual freedom each person possesses in that society relative to the state. One author describes authoritarian political systems as those where "individual rights and goals are subjugated to group goals, expectations and conformities," while libertarians generally oppose the state
State may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Literature
* ''State Magazine'', a monthly magazine published by the U.S. Department of State
* ''The State'' (newspaper), a daily newspaper in Columbia, South Carolina, United States
* ''Our S ...
and hold the individual as sovereign. In their purest form, libertarians are anarchists
Anarchism is a political philosophy and movement that is skeptical of all justifications for authority and seeks to abolish the institutions it claims maintain unnecessary coercion and hierarchy, typically including, though not necessari ...
, who argue for the total abolition of the state, of political parties and of other political entities, while the purest authoritarians are, by definition, totalitarians who support state control over all aspects of society.
For instance, classical liberalism (also known as '' laissez-faire liberalism'')Adams, Ian. 2001. ''Political Ideology Today''. Manchester: Manchester University Press. p. 20. is a doctrine stressing individual freedom and limited government
In political philosophy, limited government is the concept of a government limited in power. It is a key concept in the history of liberalism.Amy Gutmann, "How Limited Is Liberal Government" in Liberalism Without Illusions: Essays on Liberal Th ...
. This includes the importance of human rationality, individual property rights
The right to property, or the right to own property (cf. ownership) is often classified as a human right for natural persons regarding their possessions. A general recognition of a right to private property is found more rarely and is typically h ...
, free markets, natural rights, the protection of civil liberties, constitutional limitation of government, and individual freedom from restraint as exemplified in the writings of John Locke, Adam Smith, David Hume, David Ricardo, Voltaire, Montesquieu and others. According to the libertarian Institute for Humane Studies
The Institute for Humane Studies (IHS) is a non-profit organization that promotes the teaching and research of classical liberalism in higher education in the United States. IHS offers funding opportunities, programs, and events for faculty and g ...
, "the libertarian, or 'classical liberal,' perspective is that individual well-being, prosperity, and social harmony are fostered by 'as much liberty as possible' and 'as little government as necessary.'"IHS. 2019.What Is Libertarian?
" ''Institute for Humane Studies''. George Mason University. For anarchist political philosopher L. Susan Brown (1993), "liberalism and anarchism are two political philosophies that are fundamentally concerned with individual freedom yet differ from one another in very distinct ways. Anarchism shares with liberalism a radical commitment to individual freedom while rejecting liberalism's competitive property relations." Brown, L. Susan. 1993. '' The Politics of Individualism: Liberalism, Liberal Feminism, and Anarchism''.
Black Rose Books
Dimitrios I. Roussopoulos (born 1936) is a Canadian political activist and publisher.
Early life
Roussopoulos studied philosophy, politics, and economics at several Montreal and London universities. He has remained institutionally independent ...
.
See also
* Political history of the world * Horseshoe theory * Index of law articles * Index of politics articles – alphabetical list of political subjects * List of politics awards * List of years in politics * Outline of law * Outline of political science – structured list of political topics, arranged by subject area *Political polarization
Political polarization (spelled ''polarisation'' in British English) is the divergence of political attitudes away from the center, towards ideological extremes.
Most discussions of polarization in political science consider polarization in the ...
* Political lists – lists of political topics
* Politics of present-day states
* List of political ideologies
In social studies, a political ideology is a certain set of Ethics, ethical Ideal (ethics), ideals, principles, doctrines, myths or symbols of a social movement, institution, Social class, class or Social group, large group that explains how s ...
References
Notes
Citations
Bibliography
* * * * * * ** * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *Further reading
* Adcock, Robert. 2014. ''Liberalism and the Emergence of American Political Science: A Transatlantic Tale''. New York: Oxford University Press. * Adcock, Robert, Mark Bevir, and Shannon Stimson (eds.). 2007. ''Modern Political Science: Anglo-American Exchanges Since 1870''. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press. * Almond, Gabriel A. 1996. "Political Science: The History of the Discipline," pp. 50–96, in Robert E. Goodin and Hans-Dieter Klingemann (eds.), ''The New Handbook of Political Science''. Oxford, UK: Oxford University Press. * * * Mount, Ferdinand, "Ruthless and Truthless" (review ofPeter Oborne
Peter Alan Oborne (; born 11 July 1957) is a British journalist and broadcaster. He is the former chief political commentator of ''The Daily Telegraph'', from which he resigned in early 2015. He is author of ''The Rise of Political Lying'', ''Th ...
, ''The Assault on Truth: Boris Johnson, Donald Trump and the Emergence of a New Moral Barbarism'', Simon and Schuster, February 2021, , 192 pp.; and Colin Kidd and Jacqueline Rose
Jacqueline Rose, FBA (born 1949 in London) is a British academic who is Professor of Humanities at the Birkbeck Institute for the Humanities.
Life and work
Jacqueline Rose is known for her work on the relationship between psychoanalysis, fem ...
, eds., ''Political Advice: Past, Present and Future'', I.B. Tauris, February 2021, , 240 pp.), '' London Review of Books'', vol. 43, no. 9 (6 May 2021), pp. 3, 5–8.
* Munck, Gerardo L., and Richard Snyder (eds.). ''Passion, Craft, and Method in Comparative Politics.'' Johns Hopkins University Press, 2007.
* Ross, Dorothy. 1991. '' The Origins of American Social Science''. New York: Cambridge University Press.
*
{{Authority control
Main topic articles