|
Confucius
Confucius (; pinyin: ; ; ), born Kong Qiu (), was a Chinese philosopher of the Spring and Autumn period who is traditionally considered the paragon of Chinese sages. Much of the shared cultural heritage of the Sinosphere originates in the philosophy and teachings of Confucius. His philosophical teachings, called Confucianism, emphasized personal and governmental morality, harmonious social relationships, righteousness, kindness, sincerity, and a ruler's responsibilities to lead by virtue. Confucius considered himself a transmitter for the values of Ancient China, earlier periods which he claimed had been abandoned in his time. He advocated for filial piety, endorsing strong family loyalty, Ancestor veneration in China, ancestor veneration, the respect of elders by their children and of husbands by their wives. Confucius recommended a robust family unit as the cornerstone for an ideal government. He championed the Silver Rule, or a negative form of the Golden Rule, advising, "Do ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Disciples Of Confucius
According to Sima Qian, Confucius said: "The disciples who received my instructions, and could themselves comprehend them, were seventy-seven individuals. They were all scholars of extraordinary ability." It was traditionally believed that Confucius had three thousand students, but that only 72 mastered what he taught. The following is a list of students who have been identified as Confucius's followers. Very little is known of most of Confucius's students, but some of them are mentioned in the ''Analects of Confucius''. Many of their biographies are recorded in the Sima Qian's ''Shiji''. The Six Arts were practiced by the 72 disciples. Disciples Yan Hui (Ziyuan) Yan Hui (顏回) was a native of the Lu. His courtesy name was Ziyuan (子淵). He was Confucius's favorite student, and was younger than Confucius by 30 years. He became Confucius's disciple when he was very young. "After I got Hui," Confucius once said, "the disciples came closer to me." Confucius once traveled to Nan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Confucianism
Confucianism, also known as Ruism or Ru classicism, is a system of thought and behavior originating in ancient China, and is variously described as a tradition, philosophy, Religious Confucianism, religion, theory of government, or way of life. Founded by Confucius in the Hundred Schools of Thought era (c. 500 BCE), Confucianism integrates philosophy, ethics, and social governance, with a core focus on virtue, Harmonious Society, social harmony, and Filial piety, familial responsibility. Confucianism emphasizes virtue through self-cultivation and communal effort. Key virtues include ''Ren (philosophy), ren'' (benevolence), ''Yi (philosophy), yi'' (righteousness), ''Li (Confucianism), li'' (propriety), ''Wisdom, zhi'' (wisdom), and ''Xin (virtue), xin'' (sincerity). These values, deeply tied to the notion of ''tian'' (heaven), present a worldview where human relationships and social order are manifestations of sacred moral principles.. While Confucianism does not emphasize an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
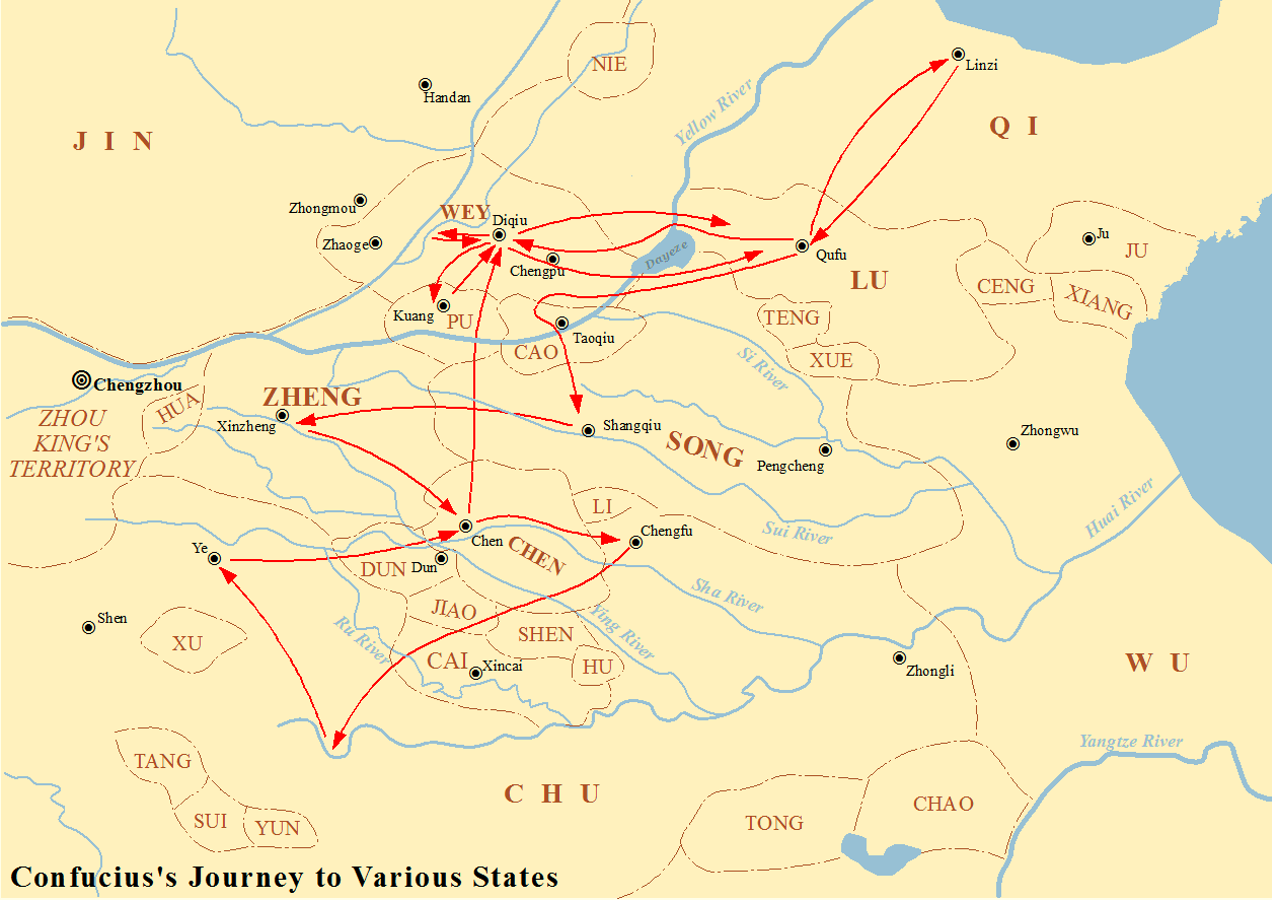
Qufu
Qufu ( ; zh, c=曲阜) is a county-level city in southwestern Shandong province, East China. It is located about south of the provincial capital Jinan and northeast of the prefectural seat at Jining. Qufu has an area of 815 square kilometers, and a total population of 653,000 inhabitants, of which, 188,000 live in urban areas. Qufu is best known as the hometown of Confucius, who is traditionally believed to have been born at nearby Mount Ni. The city contains numerous historic palaces, temples and cemeteries. The three most famous cultural sites of the city, collectively known as ''San Kong'' ( zh, labels=no , c=三孔 , l=the Three Confucian ites}, are the Temple of Confucius ( zh, s=, p=Kǒngmiào), the Cemetery of Confucius ( zh, labels=no , c=, p=Kǒnglín), and the Kong Family Mansion ( zh, labels=no , c=, p=Kǒngfǔ). Together, these three sites have been listed as a UNESCO World Heritage Site since 1994. Etymology The name Qufu literally means "crooked hill", and r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yan Hui
Yan Hui (–481 BC) was a Chinese philosopher. He was the favorite disciple of Confucius and one of the most revered figures of Confucianism. He is venerated in Confucian temples as one of the Four Sages. Names Yan Hui is also known by his courtesy name Ziyuan and as Yan Yuan, a combination of his surname and courtesy name. He is also reverently referred to as Master Yan or Yanzi. Life Yan Hui was a native of the state of Lu. His father Yan Wuyou (Yan Lu) was one of the earliest disciples of Confucius. Yan Hui was about 30 years younger than Confucius, and became a student of the Master at a young age. Yan Hui was Confucius' favorite disciple. "After I got Yan Hui," Confucius remarked, "the disciples came closer to me." We are told that once, when he found himself on the Nang hill with Yan Hui, Zilu, and Zigong, Confucius asked them to tell him their different aims, and he would choose between them. Zilu began, and when he had done, the master said, "It marks your brave ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cemetery Of Confucius
The Cemetery of Confucius () is a cemetery of the Kong clan (the descendants of Confucius) in Confucius' hometown Qufu in eastern Shandong province. Confucius himself and some of his disciples are buried there, as well as many thousands of his descendants. Since 1994, the Cemetery of Confucius has been part of the UNESCO World Heritage Site "Temple and Cemetery of Confucius and the Kong Family Mansion in Qufu". The two other components of the site are the Temple of Confucius dedicated to the memory of the statesman and philosopher and the Kong Family Mansion, where his descendants lived. The three sites are collectively known in Qufu as ''San Kong'' (), i.e. "The Three Confucian ites. History By the 2nd century AD, at least 50 of Confucius's descendants had been buried alongside him. In 1331 construction work began on the wall and gate of the cemetery. In total, the cemetery has undergone 13 renovations and extensions. Eventually, by the late 18th century, the perimeter wal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Philosophy
Chinese philosophy (Simplified Chinese characters, simplified Chinese: 中国哲学; Traditional Chinese characters, traditional Chinese: 中國哲學) refers to the philosophical traditions that originated and developed within the historical and cultural context of China. It encompasses systematic reflections on issues such as existence, knowledge, ethics, and politics. Evolving over more than two millennia, Chinese philosophy includes classical traditions such as Confucianism, Taoism, Daoism, and Buddhism, as well as modern responses to Western philosophical currents. As a cultural form of philosophy, it addresses universal philosophical concerns while also reflecting the specific historical and social conditions of China. The historical development of Chinese philosophy began during the Spring and Autumn period, Spring and Autumn and Warring States period, Warring States periods, a time known as the "Hundred Schools of Thought". Major schools such as Confucianism, Taoism, Da ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Philosopher
Chinese philosophy (simplified Chinese: 中国哲学; traditional Chinese: 中國哲學) refers to the philosophical traditions that originated and developed within the historical and cultural context of China. It encompasses systematic reflections on issues such as existence, knowledge, ethics, and politics. Evolving over more than two millennia, Chinese philosophy includes classical traditions such as Confucianism, Daoism, and Buddhism, as well as modern responses to Western philosophical currents. As a cultural form of philosophy, it addresses universal philosophical concerns while also reflecting the specific historical and social conditions of China. The historical development of Chinese philosophy began during the Spring and Autumn and Warring States periods, a time known as the " Hundred Schools of Thought". Major schools such as Confucianism, Daoism, Mohism, and Legalism emerged with distinct views on human nature, social order, and political authority. During the Han ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zengzi
Zeng Shen (505–435 BC), better known as Zengzi (Master Zeng), courtesy name Ziyu (), was a Chinese philosopher and disciple of Confucius. He later taught Zisi (Kong Ji), the grandson of Confucius, who was in turn the teacher of Mencius, thus beginning a line of transmitters of orthodox Confucian traditions. He is revered as one of the Four Sages of Confucianism. Life Zeng Shen was 46 years younger than Confucius. He was a native of South Wu City in the State of Lu, and was the son of Zeng Dian, one of the earliest disciples of Confucius. When he was sixteen, he was sent by his father to study under Confucius. Confucians later considered him to be his second most senior student, after Yan Hui. Duanmu Ci said of him, "There is no subject which he has not studied. His appearance is respectful. His virtue is solid. His words command credence. Before great men he draws himself up in the pride of self-respect. His eyebrows are those of longevity." He was noted for his filial pi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Filial Piety
Filial piety is the virtue of exhibiting love and respect for one's parents, elders, and ancestors, particularly within the context of Confucian ethics, Confucian, Chinese Buddhism, Chinese Buddhist ethics, Buddhist, and Daoism, Daoist ethics. The Confucian ''Classic of Filial Piety'', thought to be written around the late Warring States-Qin dynasty, Qin-Han dynasty, Han period, has historically been the authoritative source on the Confucian tenet of filial piety. The book—a purported dialogue between Confucius and his student Zengzi—is about how to set up a good society using the principle of filial piety. Filial piety is central to Confucian role ethics. In more general terms, filial piety means to be good to one's parents; to take care of one's parents; to engage in good conduct, not just towards parents but also outside the home so as to bring a good name to one's parents and ancestors; to show love, respect, and support; to display courtesy; to ensure male heirs; to uph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spring And Autumn Period
The Spring and Autumn period () was a period in History of China, Chinese history corresponding roughly to the first half of the Eastern Zhou (256 BCE), characterized by the gradual erosion of royal power as local lords nominally subject to the Zhou exercised increasing political autonomy. The period's name derives from the ''Spring and Autumn Annals'', a chronicle of the state of Lu between 722 and 481 BCE, which tradition associates with Confucius (551–479 BCE). During this period, local polities negotiated their own alliances, waged wars against one another, up to defying the king's court in Luoyang, Luoyi. The gradual Partition of Jin, one of the most powerful states, is generally considered to mark the end of the Spring and Autumn period and the beginning of the Warring States period. The periodization dates to the late Western Han (). Background In 771 BCE, a Quanrong invasion in coalition with the states of Zeng (state), Zeng and Shen (state), Shen— ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neo-Confucianism
Neo-Confucianism (, often shortened to ''lǐxué'' 理學, literally "School of Principle") is a moral, ethical, and metaphysical Chinese philosophy influenced by Confucianism, which originated with Han Yu (768–824) and Li Ao (772–841) in the Tang dynasty, and became prominent during the Song and Ming dynasties under the formulations of Zhu Xi (1130–1200). After the Mongol conquest of China in the thirteenth century, Chinese scholars and officials restored and preserved neo-Confucianism as a way to safeguard the cultural heritage of China. Neo-Confucianism could have been an attempt to create a more rationalist and secular form of Confucianism by rejecting mystical elements of Taoism and Buddhism that had influenced Confucianism during and after the Han dynasty. Although the neo-Confucianists were critical of Taoism and Buddhism, the two did have an influence on the philosophy, and the neo-Confucianists borrowed terms and concepts. However, unlike the Buddhists and Tao ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hundred Schools Of Thought
The Hundred Schools of Thought () were philosophies and schools that flourished during the late Spring and Autumn period and Warring States period (221 BC). The term was not used to describe these different philosophies until Confucianism, Mohism, and Legalism were created. The era in which they flourished was one of turbulence in China, fraught with chaos and mass militarization, but where Chinese philosophy was developed and patronized by competing bureaucracies. This phenomenon has been called the Contention of a Hundred Schools of Thought. The philosophies that emerged during this period have profoundly influenced East Asian culture and societies. The intellectual landscape of this era was characterized by itinerant scholars, who were often employed by various state rulers as advisers on the way of government, war, and diplomacy. Often, members and traditions of the same school had little in common other than the same influential figure that their beliefs were based on. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |